Cell Vocab
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
cytology
the study of cells
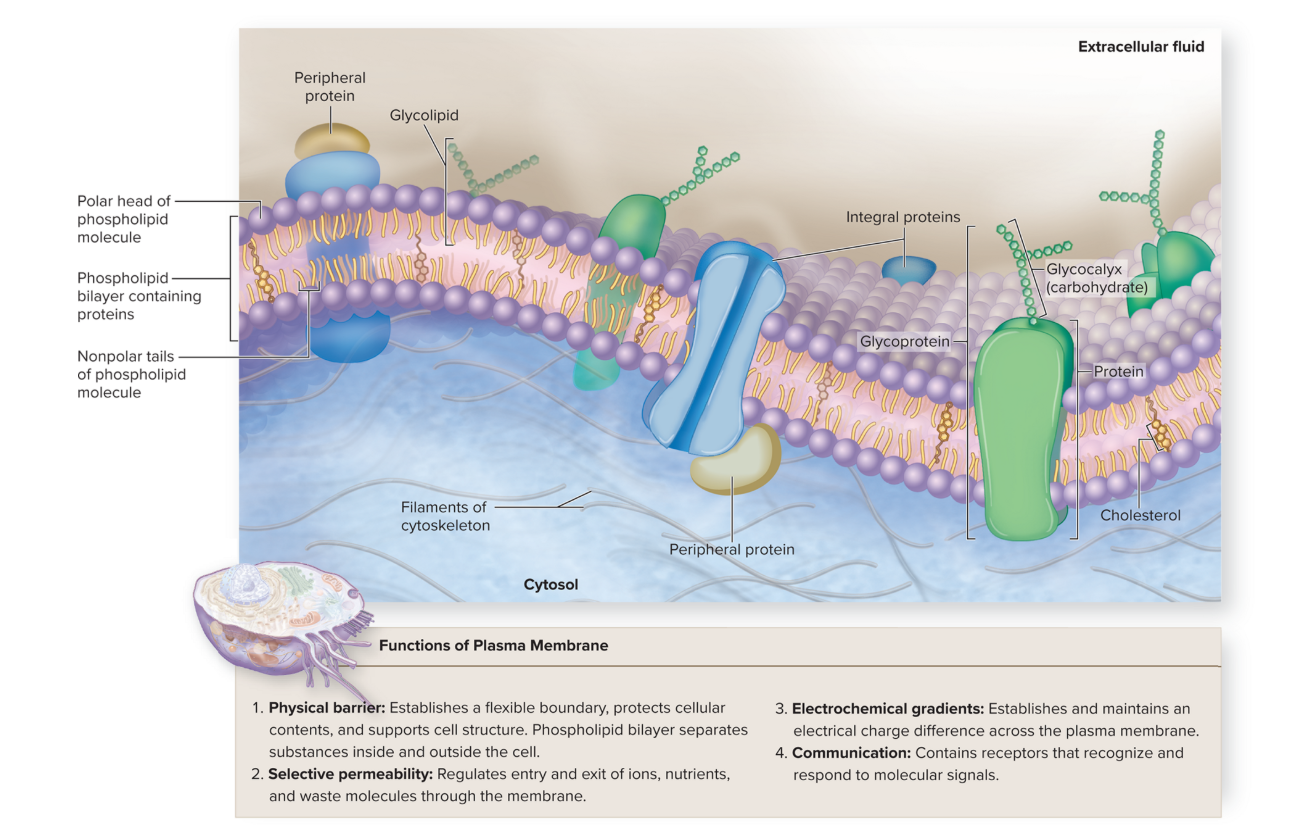
plasma membrane
composed of a phospholipid “bilayer”
→ containing proteins
→ fluid mosaic model
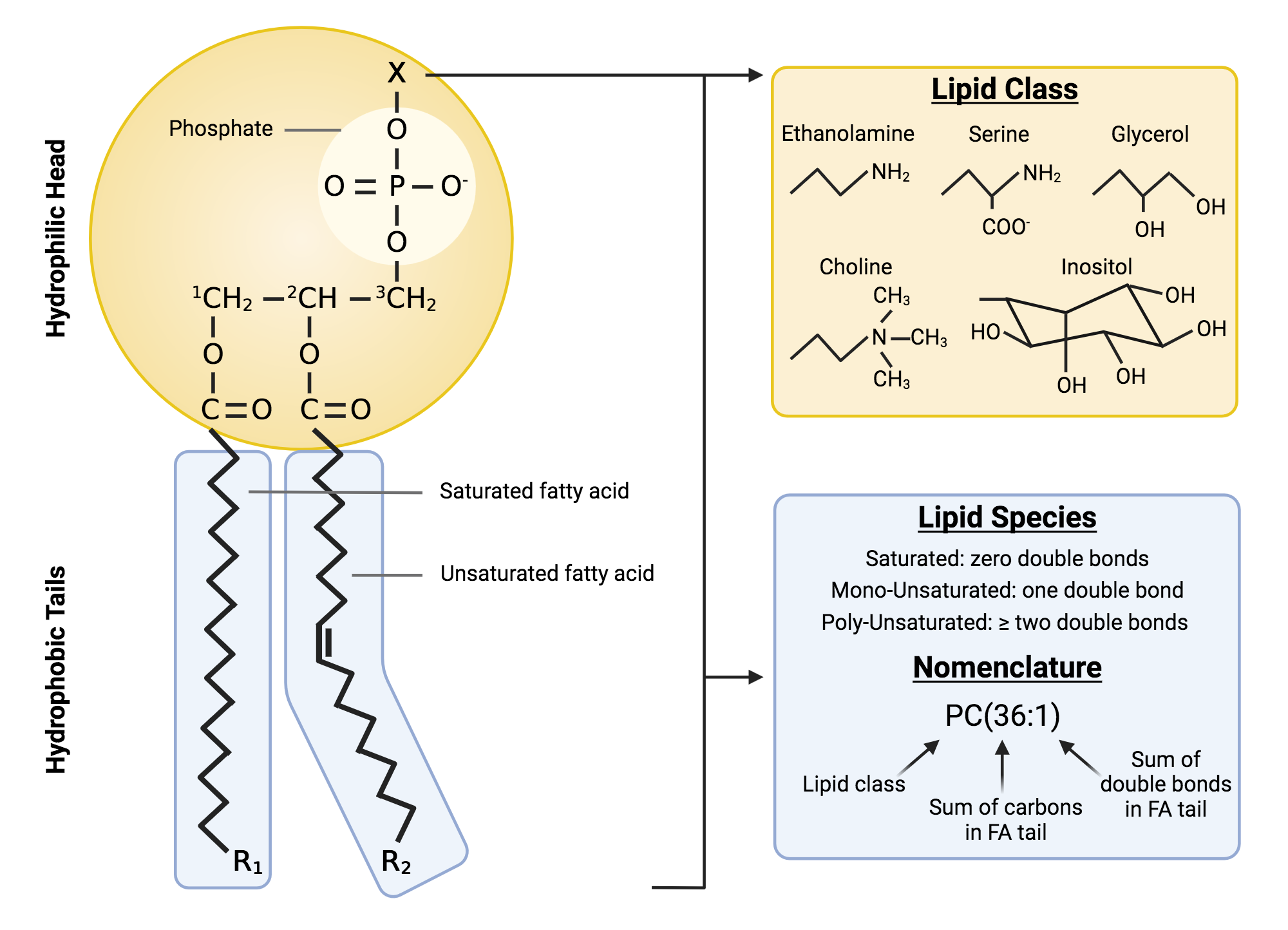
phospholipids
essential lipid molecules that form the structural foundation of cell membranes, consisting of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails.
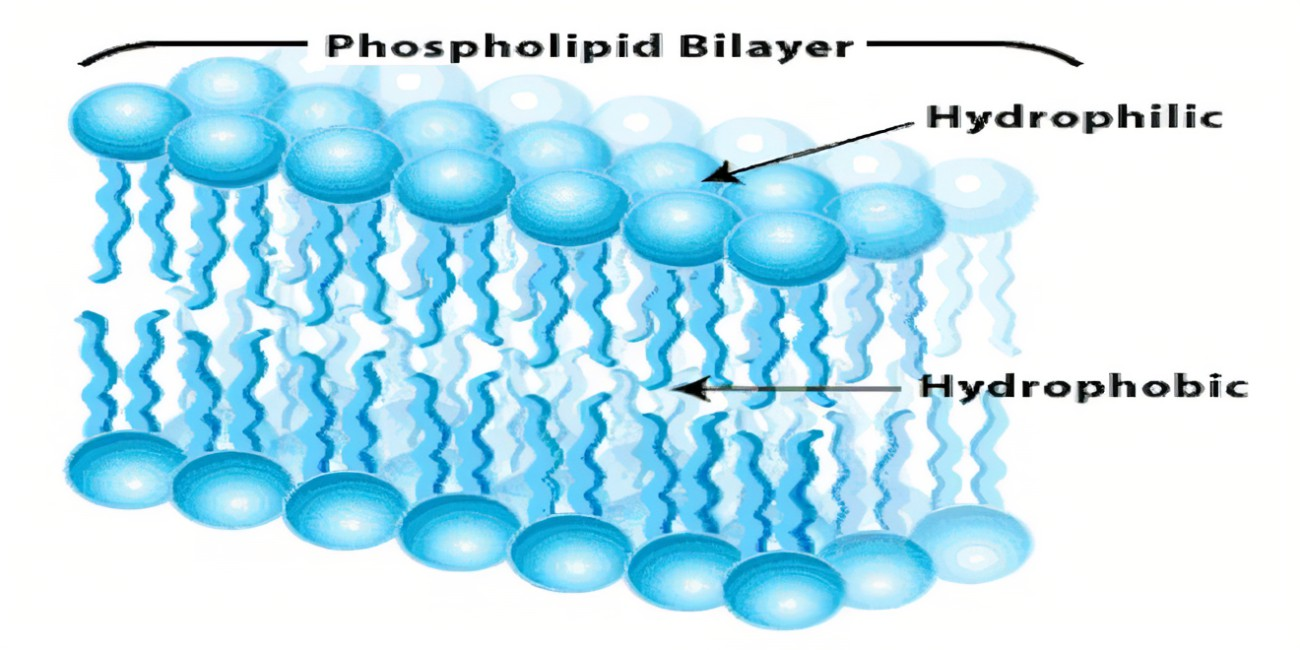
hydrophilic
opposite of hydrophobic
water loving!!
substance/molecule that has a strong affinity for water
can dissolve in or mix with water
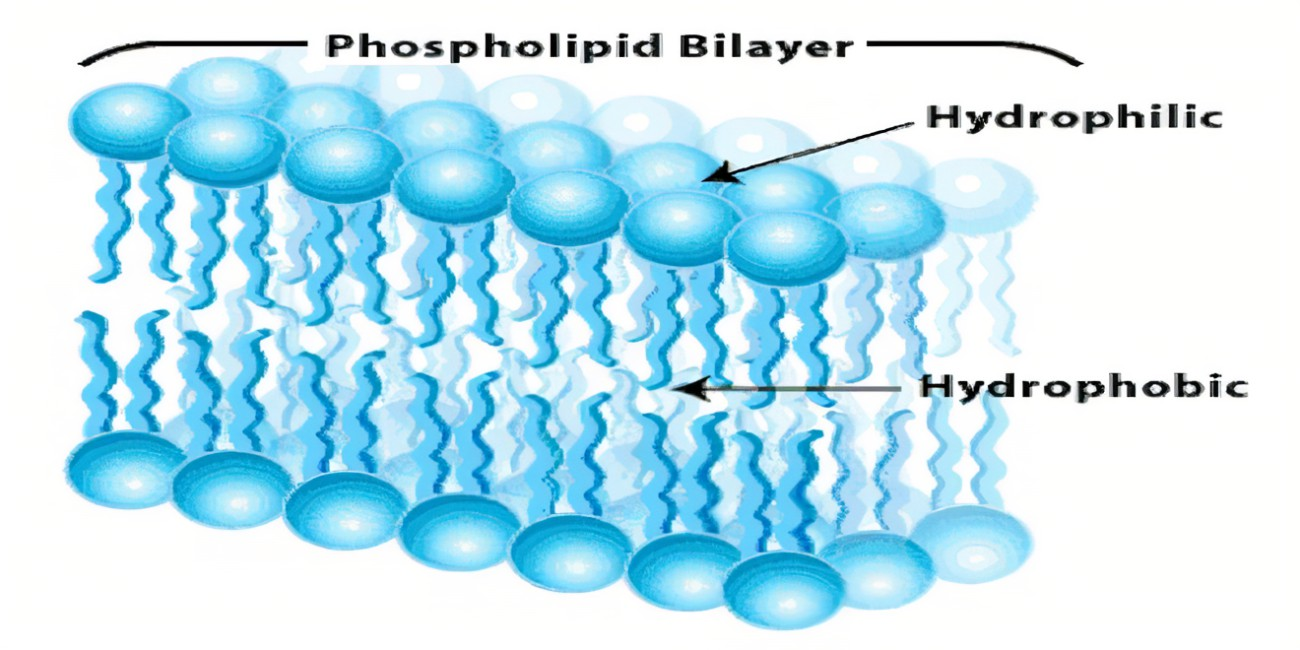
hydrophobic
substances or molecules that repel water and do not mix with it
oils!!! → formation of cell membrane
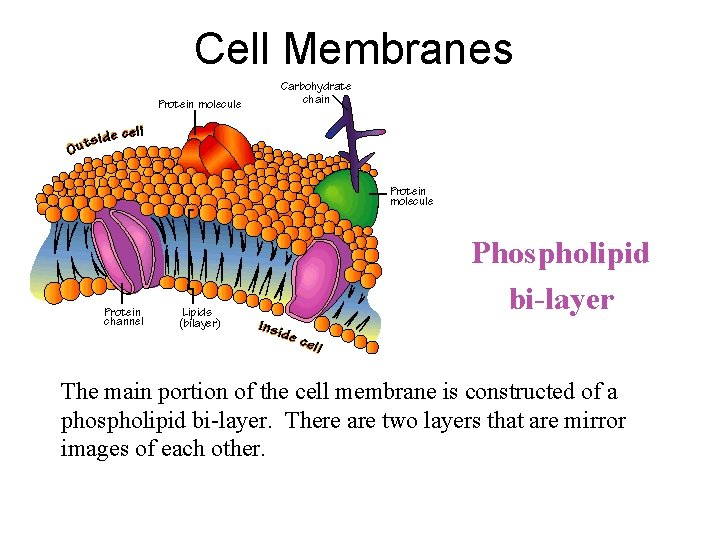
fluid mosaic
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid lipid bilayer with embedded proteins
phospholipids forming a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads facing outwards and hydrophobic tails facing inwards.
Proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins, and cholesterol are part of this diverse "mosaic".
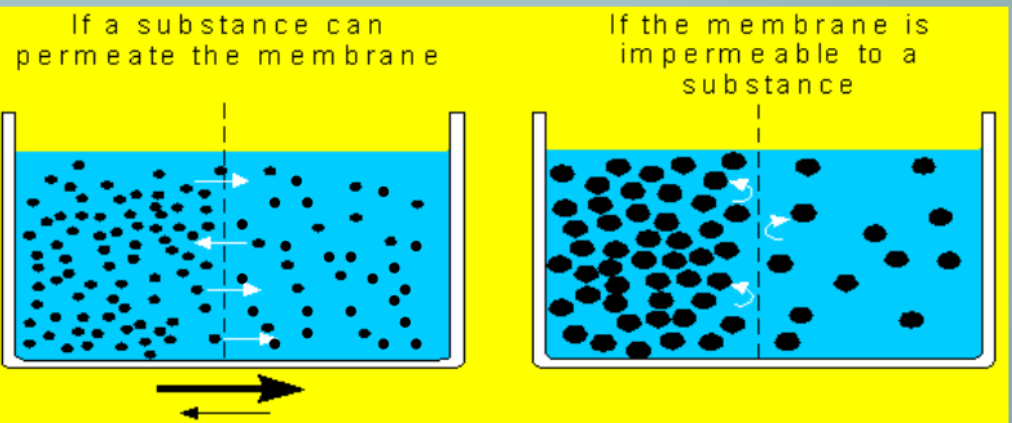
selectively permeable
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable
some things pass easily (small or uncharged) and others cannot pass through (large or charged molecules)
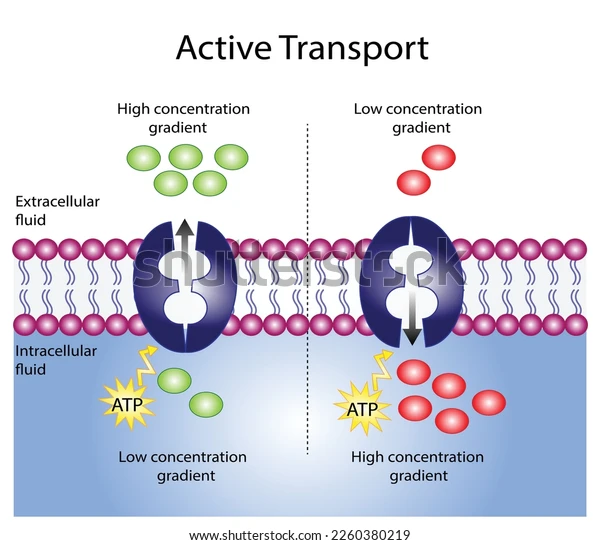
active transport
uses cell energy (ATP)
can move molecules against gradient
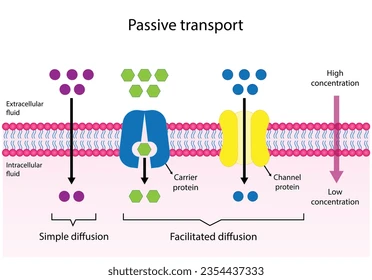
passive diffusion
does not require cell energy
moves from high to low concentration
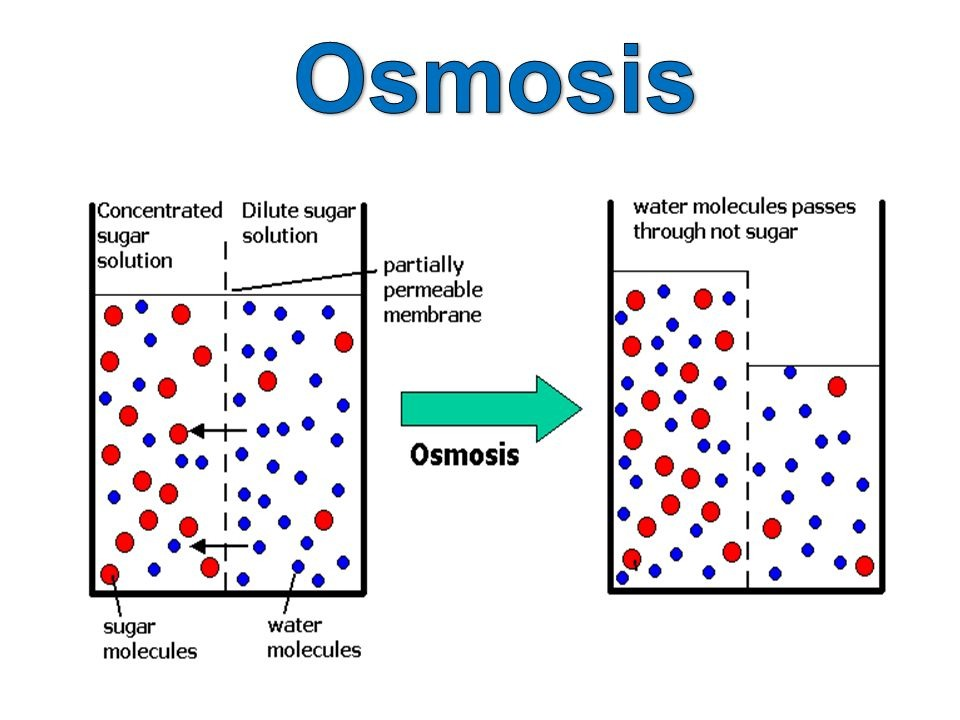
osmosis
movement of H2O from high to low H2O concentration
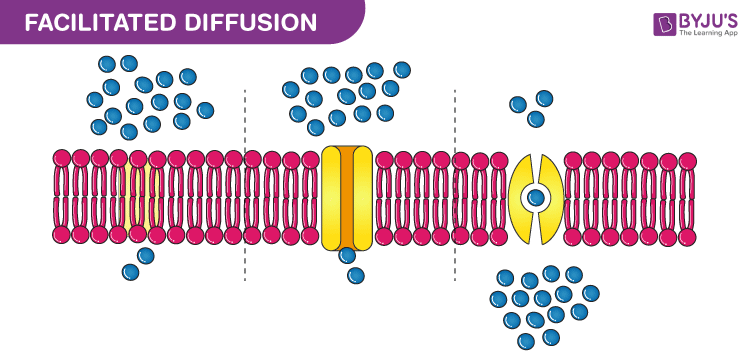
facilitated diffusion
specific molecules attach to proteins and then they can diffuse through a membrane
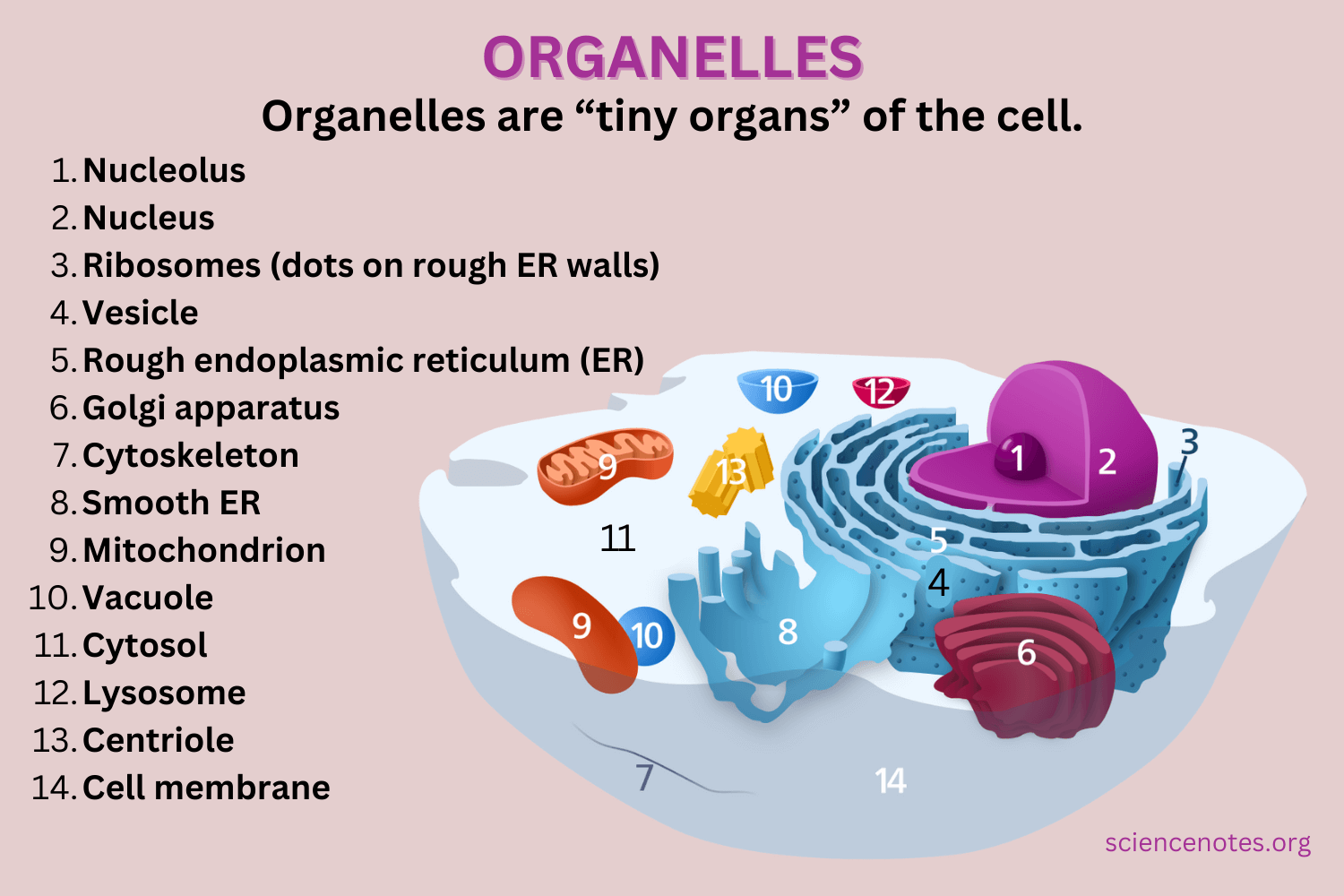
organelle
specialized subunit within a cell that performs a specific function
chromatin
the material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria (i.e., eukaryotes) are composed.
protein, RNA, and DNA.
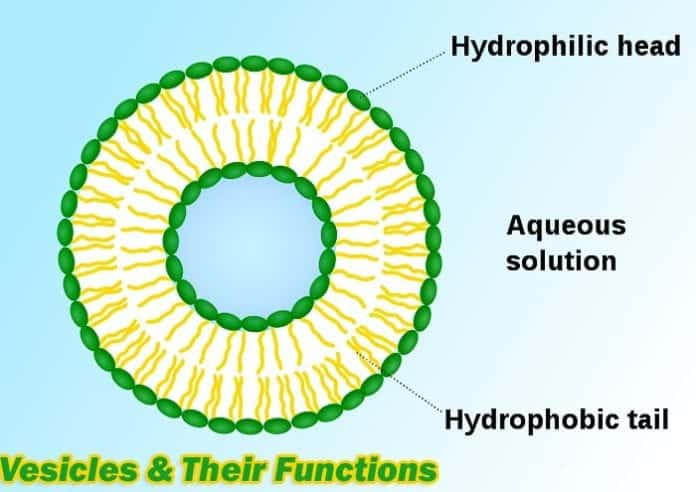
vesicles
small fluid-filled bladder, sac, cyst, or vacuole within the body
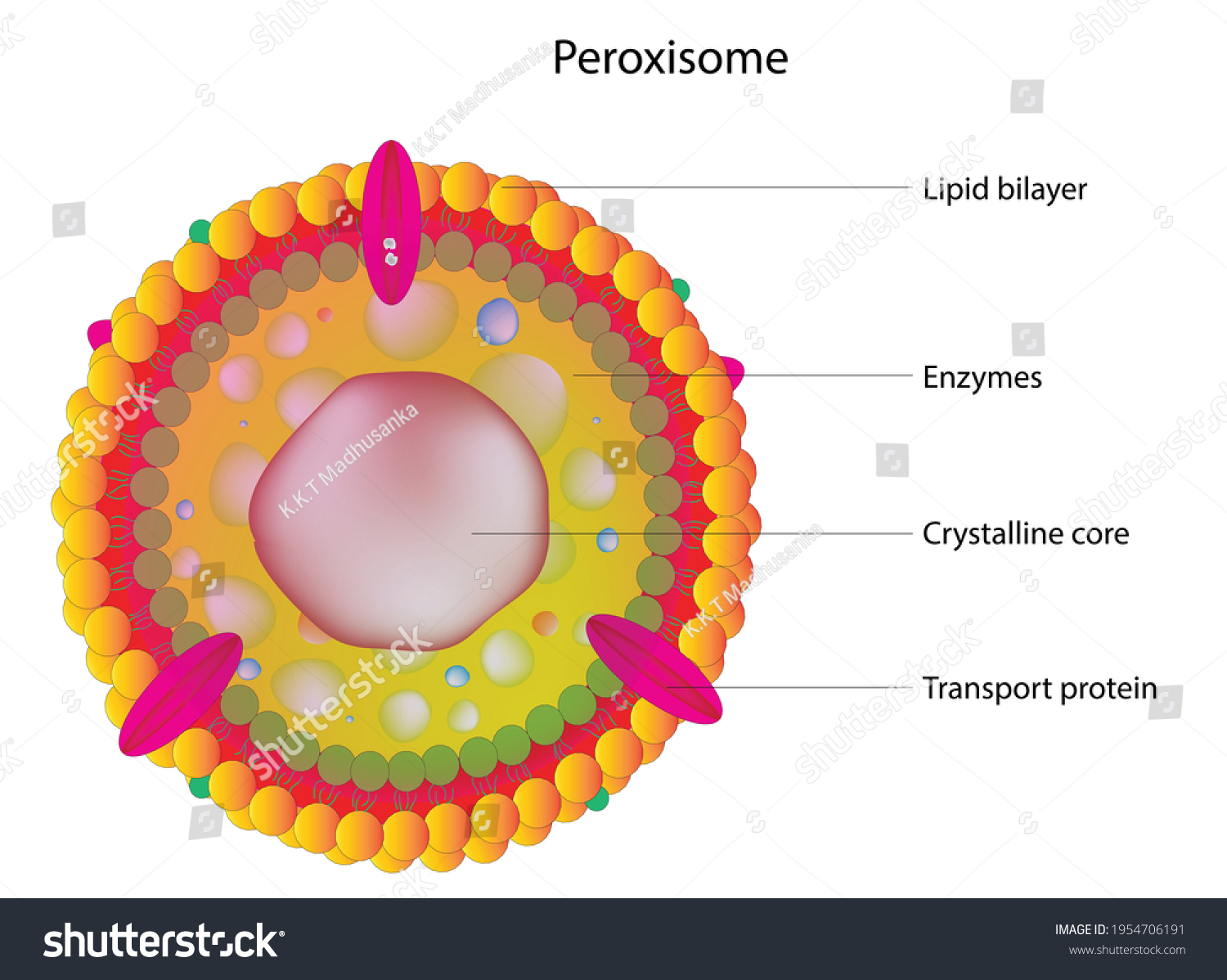
peroxisomes
membrane bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells
lipid metabolism
conversion of reactive oxygen species
ATP
molecule that supplies energy directly to a cell
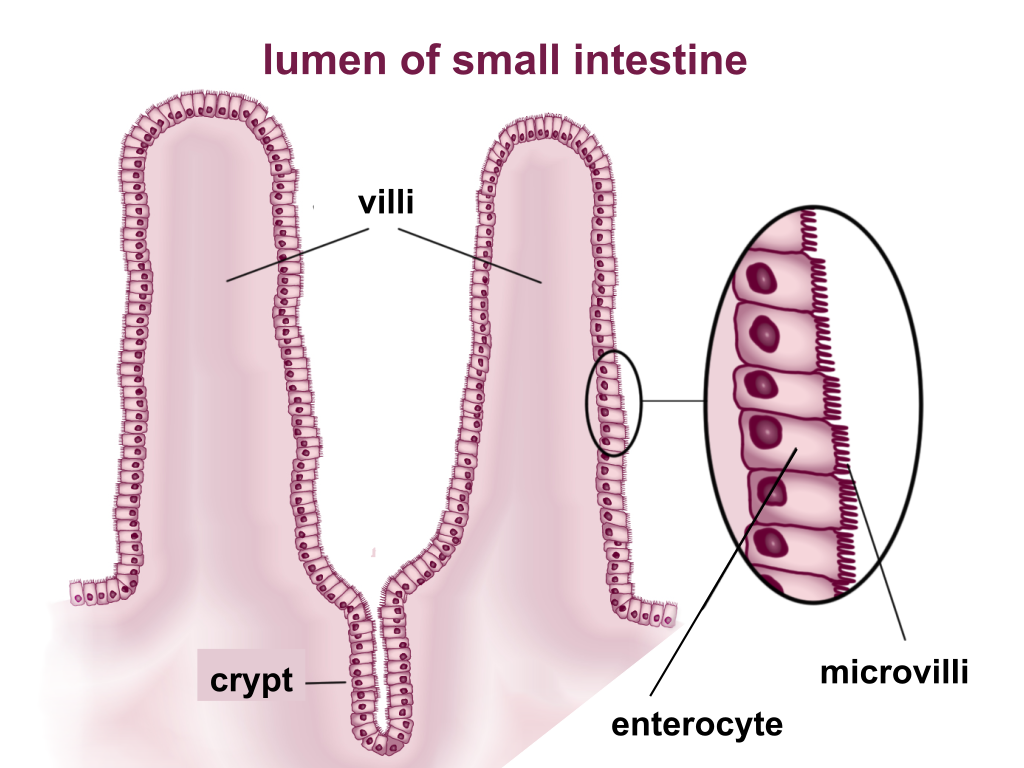
microvilli
microscopic, finger like projections found on surface of certain cells
→ epithelial cells
increasing the surface area for absorption and secretion
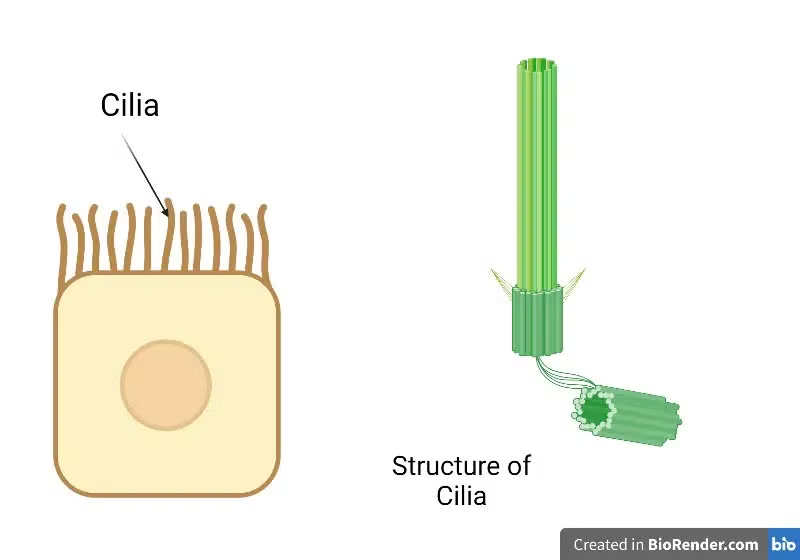
cilia
small, hairlike structures found on the surface of eukaryotic cells
locomotion, can be involved in moving fluids across the cell surface
motile + nonmotile