Lecture 5: Hypertension
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Arteriovenous Fistula
Direct connection between an artery & a vein (bypassing capillaries)
In the brain, congenital AV Malformations (AVM) may lead to fatal intracerebral hemorrhage
In other locations, if the shunting of blood large enough → may lead to high output cardiac failure
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Developmental disorder of large & medium muscular arteries manifest as segmental irregular thickening of vessel walls that result in stenosis, alternating with segments of thinned media “string of beads” appearance on angiography
Frequently involved arteries: Renal, followed by Carotids
In renal arteries → stenosis results in renovascular hypertension
Developmental Saccular (“Berry") Aneurysms
Of cerebral vessels
Vascular outpouchings arising at branching points in the Circle of Willis that may cause fatal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Frank-Starling “law”
↑ End diastolic pressure (reflecting the initial passive ventricular stretch) then ↑ peak systolic pressure developed during the ensuing beat resulting in greater volume of blood ejected
The greater the volume of blood entering the heart during diastole, the greater the stroke pressure generated & thus volume of blood ejected during systole
In a normal patient, the heart will pump OUT whatever blood it receives
The more you fill the ventricle (the higher the end diastolic fill pressure) the harder the heart will pump it all out (higher systolic pressure)
Higher blood volume results in a higher cardiac output
What are the 2 major mechanisms that increase blood pressure?
Increased blood Volume and Peripheral Resistance
Peripheral Resistance is determined
State of vasoconstriction or vasodilation of the Arterioles
Cardiac Output =
Heart rate x stroke volume (L/minute)
Blood Pressure =
Cardiac output x peripheral resistance
What is the principal mechanism by which blood volume is controlled?
Net Sodium retention/excretion
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system (RAAS)
Principal regulator of Na excretion/retention
Renin is released by the juxtaglomerular cells in the Afferent Arterioles of the Glomerulus when they sense low blood pressure
Renin converts Liver produced Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin I
Lung Endothelial cells with Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) converts Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor & also causes the Adrenal to secrete Aldosterone
Aldosterone acts on the kidney to ↑ urinary Sodium reabsorption
→ Increase water reabsorption
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
↑ urinary Na & water excretion; Vasodilate
Triggered by volume overload of the heart
Name the 3 inherited syndromes that cause ↑ Na retention and may cause inherited hypertension?
“Channelopathies” with abnormal Na transport (Gitelman, Bartter, and Liddle)
→ Inherited hypertension
Hypertension Definitions

Why is hypertension bad?
High blood pressure damages arteries Initiated by Endothelial injury
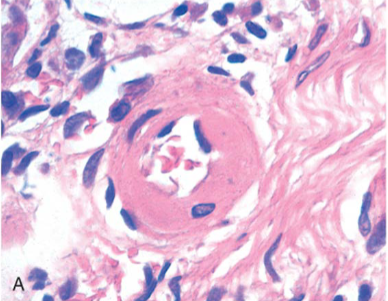
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis seen in “benign” hypertension or diabetes
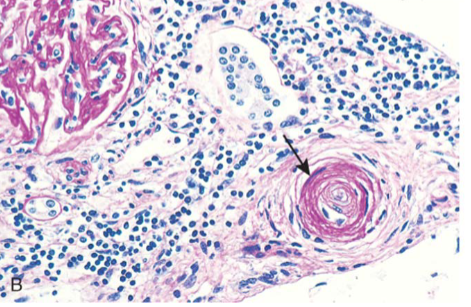
Kidney with Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis in malignant hypertension
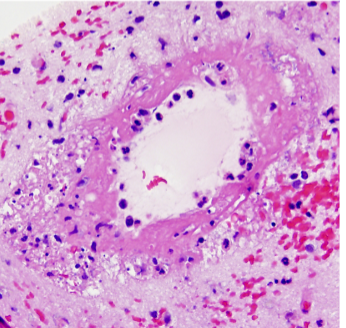
Fibrinoid necrosis in the brain in
malignant hypertension
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis
Homogeneous pink “hyaline” thickening of arteriolar wall due to deposition of extravasated proteins & extracellular matrix proteins elaborated by the medial smooth muscle cells
Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis
Occurs in malignant HTN; exhibits concentric laminated “onion skinning” thickening of walls due to reduplicated layers of basement membrane
Also in Hypertensive Crisis (Malignant Hypertension) there may be vessel wall necrosis with fibrinoid deposits (“Fibrinoid necrosis/necrotizing arteriolitis”)
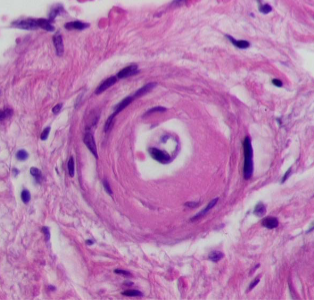
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis
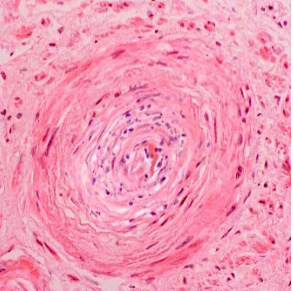
Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis
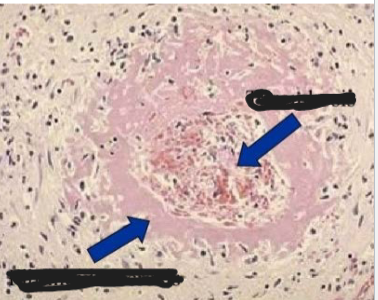
Fibrinoid necrosis
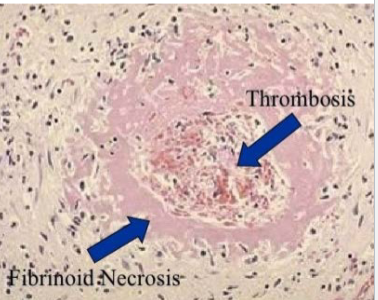
What are the 2 most common complications of hypertension?
Cardiac disease (CAD and CHF) and Stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic)
Hypertension increases the risk of:
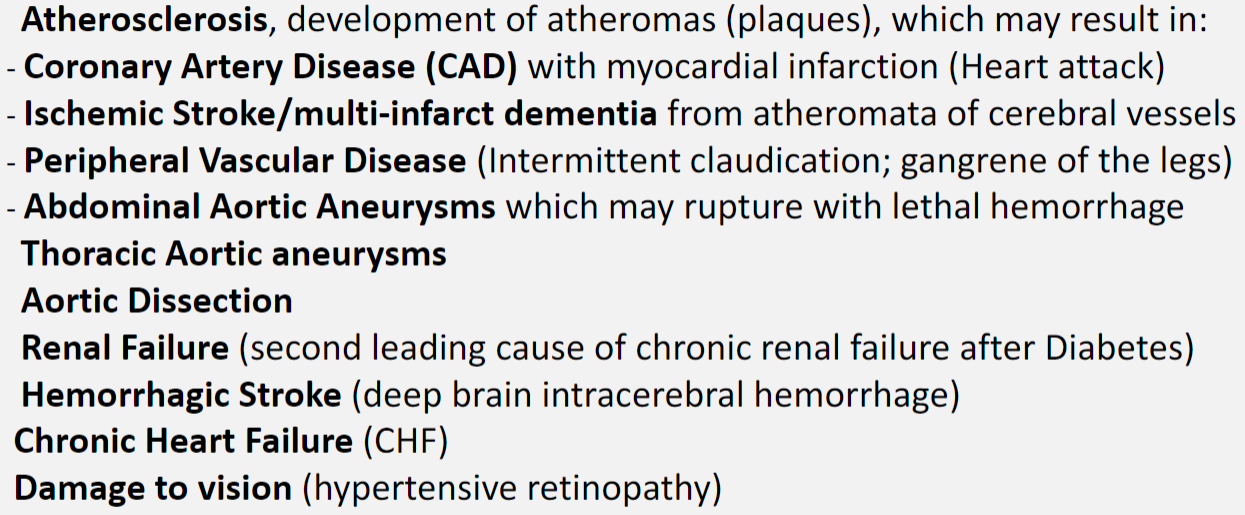
“Essential” or “Primary” Hypertension
Idiopathic
Multi-factorial
Secondary Hypertension
Specific causes are usually related to kidney disease with inappropriate activation of the RAAS, and less often mostly to adrenal abnormalities producing excess aldosterone
Rare cases are genetic due to mutations
Diagnosis of Hypertension
Measurements of blood pressure have been taken on at least three separate occasions, or by out-of-office measurements