(B4) Exam questions: Cell transport mechanisms
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from all available exam papers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Identify the name of the cellular structure that transports mucin through the cell. (1)
A mitochondria
B nucleus
C ribosomes
D vesicles
D vesicles
Name the process by which mucin leaves the goblet cell. (1)
exocytosis
Describe the function of the cilia on the ciliated epithelial cells. (2)
(Cilia) {beat/wave/waft/sweep/move} (1)
(to move) the mucus {up /out of} airways/into throat/coughed or sneezed out (1)
to remove {harmful/ named example} substances (1)
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of cell surface membranes.
State two features of the fluid mosaic model. (2)
phospholipid bilayer (1)
with proteins embedded (1)
State two roles of cholesterol in cell surface membranes. (2)
mechanical stability/membrane support/strengthens (1)
regulates membrane fluidity/increases rigidity (1)
prevents loss of ions/named ions/ electrolytes (1)
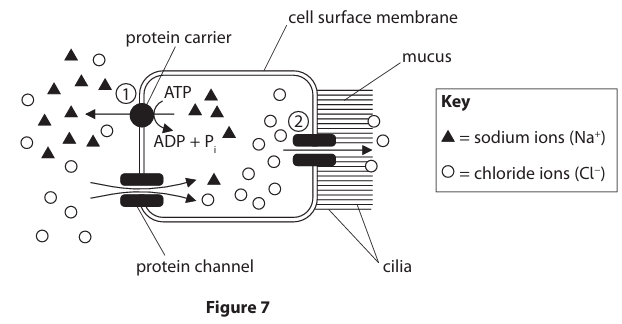
Figure 7 shows how sodium ions and chloride ions move into and out of the ciliated epithelial cells lining the bronchi of the lungs. Name the process by which sodium ions leave the ciliated epithelial cell at point 1 in Figure 7. (1)
A active transport
B exocytosis
C facilitated diffusion
D osmosis
A active transport
Explain how the chloride ions leave the ciliated epithelial cell at point 2. You may use information in Figure 7 to support your answer. (4)
facilitated (1)
diffusion (1)
down a concentration gradient/from high to low concentration (1)
through a (protein) {channel/carrier/transmembrane protein/chloride gate/Cl- gate} (1)
no {ATP/energy} involved/passive(1)
Name the process by which water moves across the cell surface membrane of a ciliated epithelial cell. (1)
osmosis
The walls of a glomerulus in a kidney nephron consist of squamous epithelial cells. Explain how the SA/V ratio of these cells helps them to filter blood efficiently. (2)
{large/high/more} (SA/V / SA/) (1)
(so) short {pathway/ distance} (1)
(so) {faster/greater/more efficient} diffusion (1)
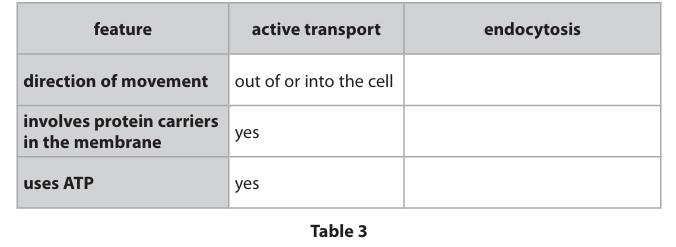
Complete Table 3 to show the differences and similarities between active transport and endocytosis. Active transport has been completed for you. (3)
vfdsgs
Substances may enter or leave cells by active transport and passive transport mechanisms. Compare how substances move into and out of cells by both active and passive transport mechanisms. You may include diagrams to support your answer. (6)

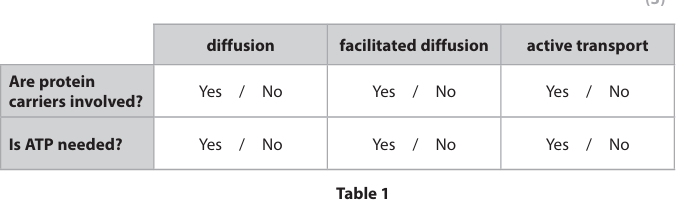
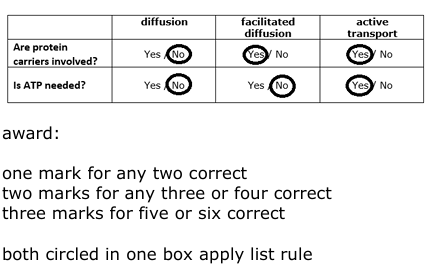
Table 1 compares some facts about diffusion, facilitated diffusion and active transport. Complete Table 1 by circling Yes or No in each box. (3)
Which diagram correctly shows the fluid mosaic model? (1)
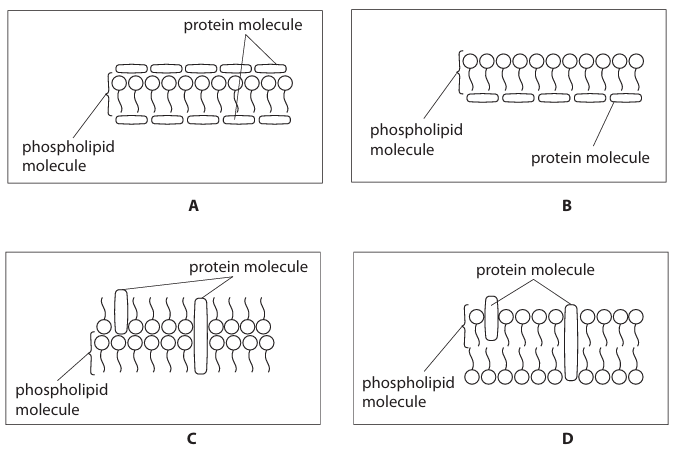
D
Identify processes X and Y in Figure 2b. (2)#
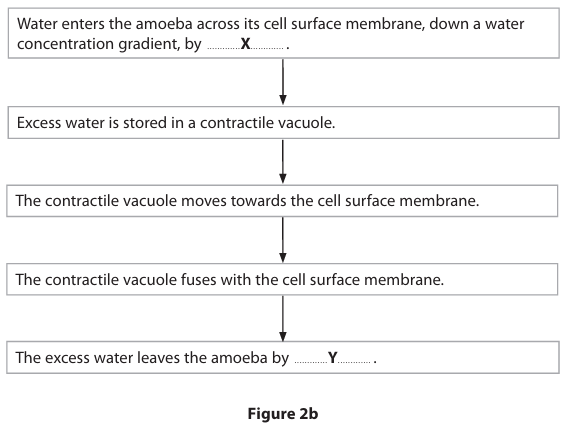
X = osmosis/diffusion/facilitated diffusion
Y = exocytosis/active transport
Which statement explains why the amoeba needs many mitochondria? (1)
A For anaerobic respiration.
B For entry of water into the cell.
C For movement of the contractile vacuole.
D For diffusion of oxygen into the cell.
C
In the lungs, phagocytic white blood cells engulf bacteria. (a) Which process do these white blood cells use to ingest bacteria? (1)
A Diffusion.
B Endocytosis.
C Exocytosis.
D Osmosis.
B Endocytosis.
Phagocytic cells contain many mitochondria. Explain why. (3)
(mitochondria) {produce/provide/supply} ATP (1)
• by (aerobic) respiration (1)
• because (phagocytosis/engulfing/ingesting/ endocytosis) {is active/needs energy}(1)
Eukaryotic cells have a cell surface membrane that prevents large molecules passing through it. Explain how large molecules move into or out of cells by bulk transport. You may include annotated diagrams in your answer. (6)

Which letter, A, B, C or D, represents a phospholipid molecule in Figure 2? (1)
A
B
C
D
B
Which letter, A, B, C or D, represents a carrier protein? (1)
A
B
C
D
C
three marks
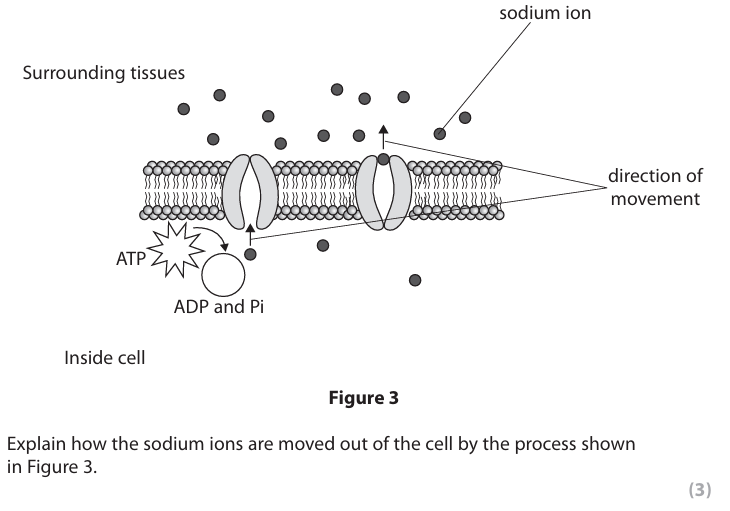
active transport (1)
• (movement is) {against/up} concentration gradient/from low to high concentration (1)
• uses ATP/energy (1)
• uses (protein) {channel/pump/carrier} (1)
Figure 4a shows a small cell in the body. Figure 4b shows a large cell in the body. The surface area : volume ratio (SA / V) of each cell is different.Describe how the SA / V of the small cell differs from the SA / V of the large cell. (1)
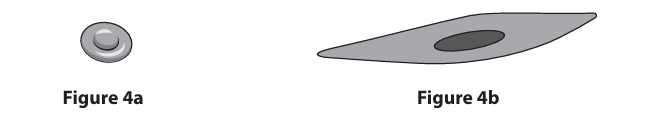
the SA/V of the small cell is bigger than the SA/V of the large cell