Metal Mediated Synthesis
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What is a Cross-Coupling reaction?
A nucleophilic substitution at an sp2 hybridised carbon by using a transition metal mediated catalyst.
Catalytic Ni, Fe or Co can also be used as well as Pd.
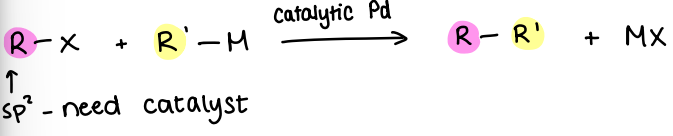
How does a bromopyridine react with nBuLi?
Can react at -78oC to remove R-X.
Can react at -40oC to form a disubstituted pyridine.
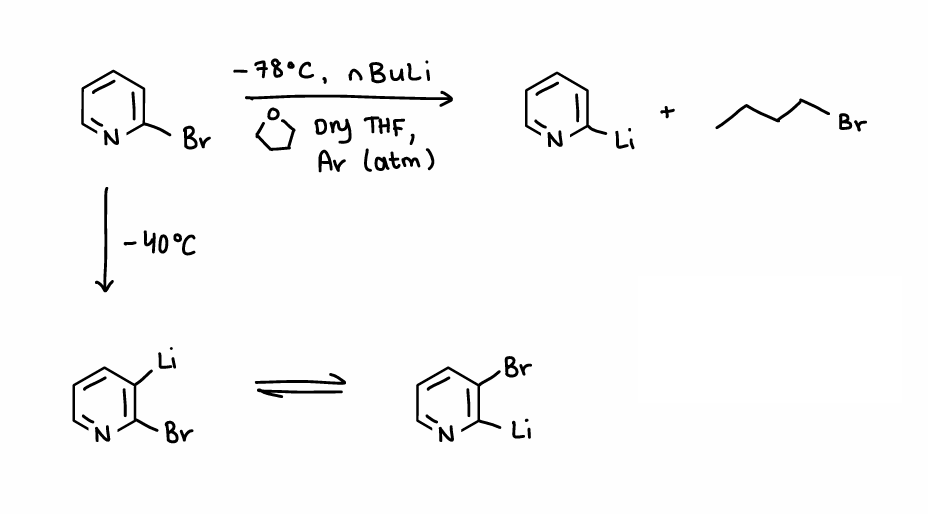
What is the halogen dance reaction?
When Li and Br are both bonded to a ring, they can swap positions.
How does an alkyne react with nBuLi?
Releases n-butane gas.

How are Grignard reagents formed?
Reaction of R-X with Mg.
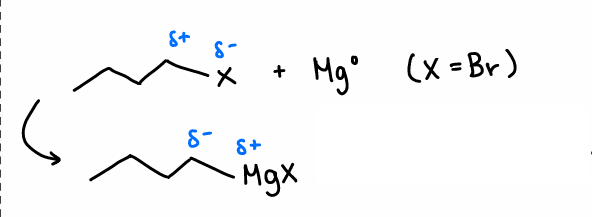
How do you add RX to an active catalyst?
Via oxidative addition.
The Pd(0) is oxidised to Pd(II)
The valence electron count is increased from 14 to 16, and the coordination number increases from 2 to 4.
Why are organo-chlorides not favoured reagents in cross-coupling?
The C-X bond strength decreases as group 17 descends, therefore Cl and F reagents have stronger C-X bonds.
The strength of the bond determines whether or not the oxidative addition step is the RDS, a stronger bond means a slower reaction.
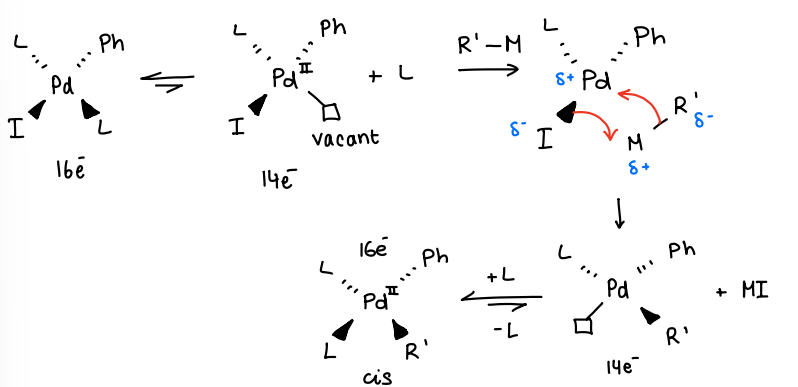
How does transmetallation occur?
The active catalyst loses a ligand, forming a vacant site.
The transmetallating agent (R’-M) reacts with the Pd centre, forming a Pd-R’ bond and losing a M-I byproduct.
The loss of MI leaves another vacant site, the ligand then coordinates to give the product.
There is no change in OS between intermediates.
The MI is a stable metal salt.
How is R-R lost from the active catalyst?
Via reductive elimination, the Pd(II) is reduced to Pd(0). The R-X is lost.
The valence electron count is reduced from 16 to 14.
The coordination number lowering from 4 to 2.

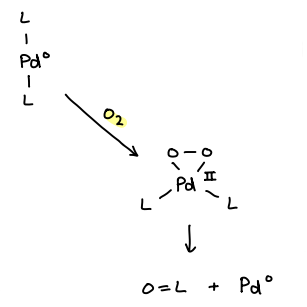
What affect does trace air have on the [L2Pd] catalyst?
The O2 adds onto the Pd, oxidising it to Pd(II) and forming a 16 electron species.
This can further break down, reforming Pd(0).
How does a precatalyst become a catalyst?
The Pd must be in the 0 O.S. and have a vacant coordination site for ligands to bind.
Must reduce a stable starting material to form the catalyst.
The catalyst may still require displacement of a neutral ligand to form a vacant site.
What is a precatalyst?
The precatalyst is not in an active form itself, but requires an activation step to form the active catalyst.
What is the ‘active catalyst’ in most C-C cross couplings?
Thought to be [L2Pd], where L is typically a phosphine ligand and Pd is in the 0 O.S..
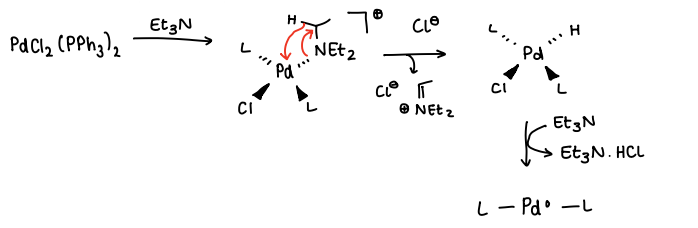
How do you reduce a precatalyst using a base?
The base (e.g. Et3N) is added to the stable starting material.
A ligand is replaced by the base.
A H on the base is added onto the Pd, the base is then lost (Beta-hydride elimination).
The base attacks a Cl ligand and the H ligand, removing it and forming HCl.
The catalyst Pd(0) is formed.
How do you reduce a precatalyst using organometallics?
The organometallic (e.g. RMgX) is added to the stable SM. 2 molecules of RMgX are required per SM.
The R group substitutes with the Cl ligands on the SM.
The two R groups are then eliminated, removing a R-R molecule.
The catalyst Pd(0) is formed.
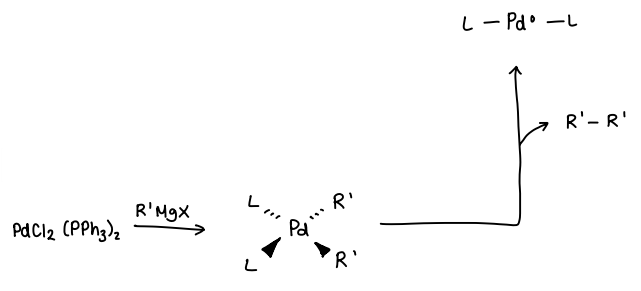
What determines which part of the catalyst activation is slowest?
Kinetics:
Bond strengths.
Nucleophilicity of organometallic reagents.
Lattice energy of metal salts.
Rate of cis-trans isomerism.
Nature of the ligands.
Unwanted side reactions.
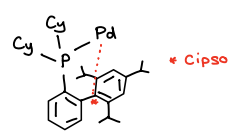
When is XPhos used as a ligand and why?
XPhos (PCy3) must be used for catalysts when R-X contains a Cl.
The C-Cl bond is too strong, XPhos activates the C-Cl bond allowing the catalyst to react with it.
There is a Cipso-Pd interaction that activates the C-Cl bond.
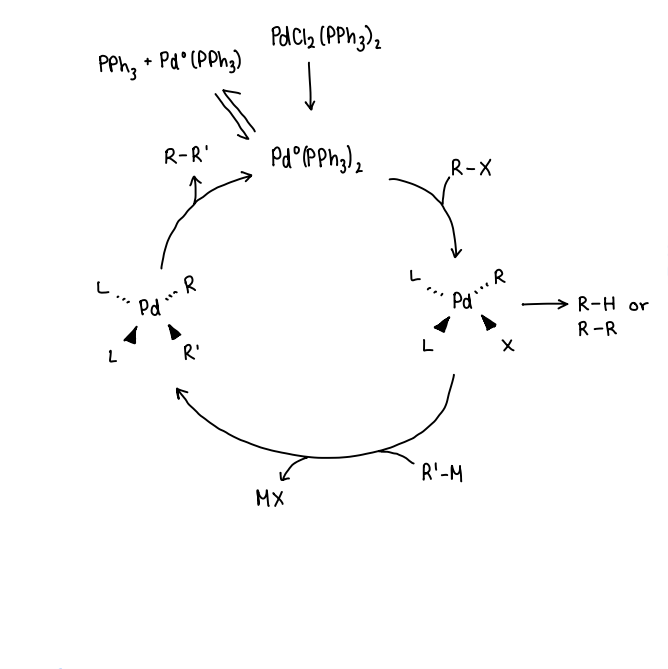
What occurs in a general catalytic cycle for Pd catalysed C-C couplings?
The precatalyst is reduced to form the active catalyst.
R-X is added, oxidative addition occurs to form a 4 coordinate Pd complex.
Side reactions may occur when oxidative addition is fast, forming R-H or R-R.
Transmetallation occurs, R’-M is added and reacts with the Pd complex, forming a metal salt (MX). This forms a Pd complex with the R and R’ ligands.
Reductive elimination occurs, removing the R-R’ product.
The active catalyst can undergo ligand dissociation to form a Pd(PPh3) complex, which can also act as the active catalyst.
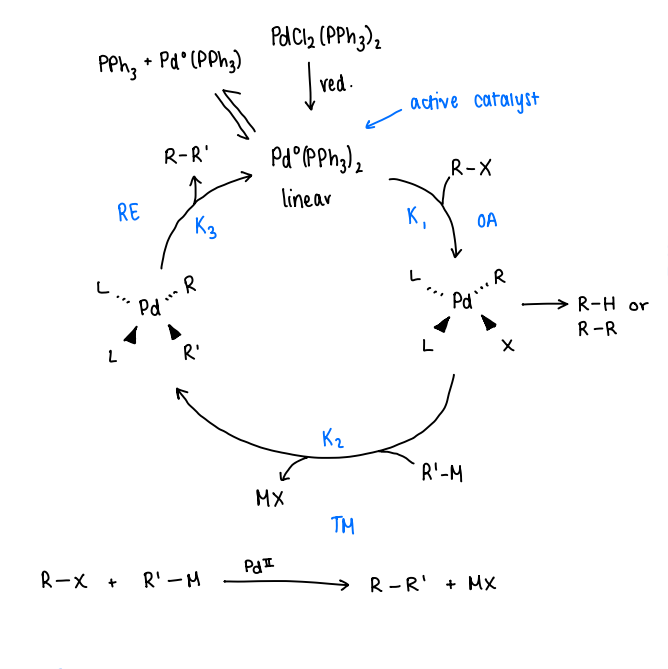
During the Pd catalysed C-C coupling, when is oxidative addition fast?
When X= Br, I, OTf or OTs: K1 is fast.
When X= Cl, F: K2 is slow, therefore a special phosphine (that is electron rich or sterically hindered) must be used.
What effect does Pd agglomeration have on the catalytic cycle?
The agglomerate Pd reacts with the R-X similarly to the normal Pd catalyst, forming the R’-R product.
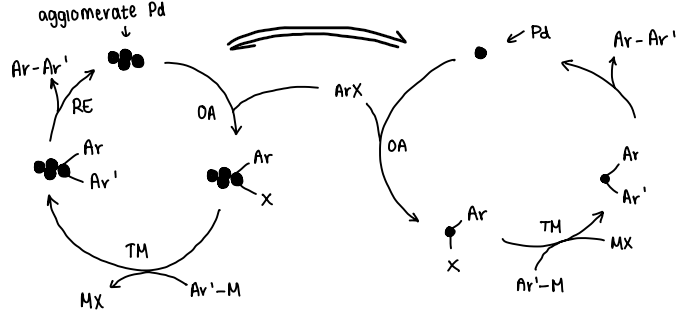
What are Pd black particles?
Inactive agglomerated Pd particles that lead to catalyst deactivation.
How do you remove Pd black?
Can react with:
R-SH: leading to breakdown of 8000ppm Pd particles to 100ppm particles.
Zn, EDTA: leads to breakdown of 100 ppm Pd particles to 5 ppm.
What is Kumada cross-coupling?
An Ar-X reacts with a Grignard reagent in the presence of a catalyst (Pd, Ni, Fe) to form a new C-C bond.
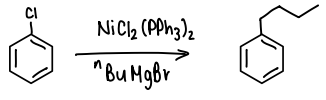
What is a problem with Kumada coupling?
The Grignard reagent required has low functional group compatability, it is likely to act as a nucleophile and attack sensitive FGs, such as ketones and esters.
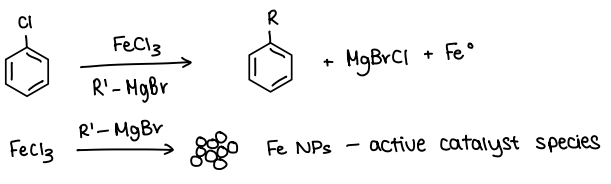
How is Fe used as a catalyst for Kumada CC?
FeCl3 is used as the precatalyst.
The R-MgBr reagent reacts with the precatalyst and forms Fe nanoparticles. These act as the active catalyst.
How can Pd/Fe nanoparticles be useful as catalysts?
They are magnetic.
Helps with recovery of catalyst (use a magnet to remove).
What is the original Negishi CC?
Negishi proposed that less electropositive metals (Al or Zr) can be used as transmetallating reagents rather than Mg or Li.
The Schwartz reagent (Cp2ZrHCl) is added to an alkyne in the presence of dry THF, forming an alkene.
R-X is then added, Pd or Ni catalyst is used.
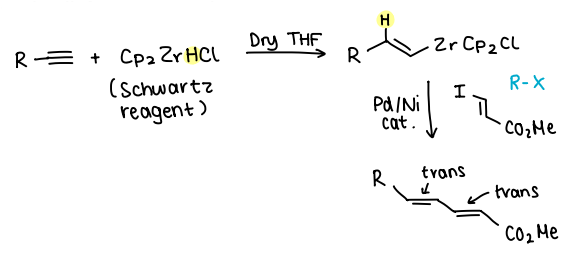
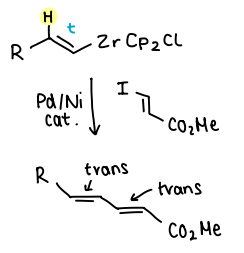
What effect does the catalyst choice (Pd or Ni) have on the products of Negishi CC?
If the R-X added contains a double bond:
Using a Ni catalyst yields 95% trans-trans and 5% trans-cis.
Using Pd yields over 99% trans-trans.
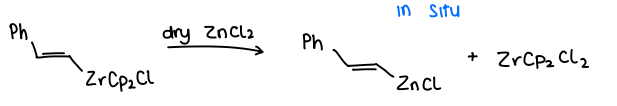
How does the addition of ZnCl2 affect Negishi CC?
The addition of ZnCl2 increases the reactivity of the transmetallating agent in situ.
The ZnCl2 reacts with the organometallic RZrCp2Cl to produce an alkenylzinc species (RZnCl).
This then reacts with the R=X.
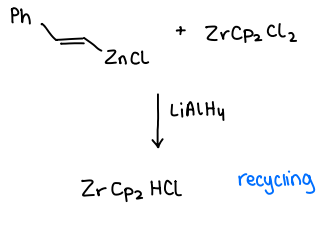
How do you recycle the Schwartz reagent in Negishi CC?
Using LiAlH4 after modifying with ZnCl2.
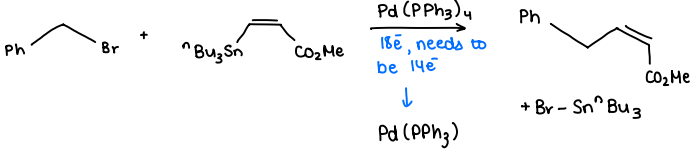
What is Stille CC?
An R-X compound is reacted with a R’-SnBu3 compound in the presence of a Pd(0) catalyst, forming the R-R’ and X-SnBu3 products.
What are the advantages of Stille coupling?
Has near complete FG tolerance.
The organostannanes and organohalides are air and moisture stable.
What is a problem with Stille CC?
The R-SnBu3 reagent is toxic.
How does the ‘fluoride effect’ increase the speed of Stille CC?
The fluoride ions activate the organotin reagent, forming a tin-fluoride species (which is more reactive).
CuI can also be used, forming a R-Cu intermediate which allows more efficient exchange of R onto the Pd catalyst.

What is Suzuki-Miyaura CC?
An Ar-X compound and an ArB(OH)2 compound are reacted in the presence of a Pd catalyst, a base, 2M Na2CO3, and in a 1:1 THF/H2O mixture.
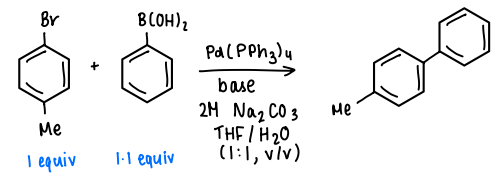
How does Suzuki-Miyaura CC occur?
The Ar-X reagent bonds to the Pd catalyst via oxidative addition.
The Pd complex undergoes ligand exchange with a OH- (from the base), forming the Pd-OH and losing a halide.
This goes on to react with the boronic acid, forming the Pd(Ar)2 complex.
The product is lost via reductive elimination.
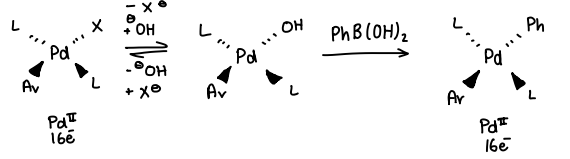
What mechanistic effect does the formation of a Pd-OH species have in Suzuki-Miyaura CC?
The formation of the Pd-OH allows efficient reaction of the catalyst with Ph-B(OH)2, forming a Pd-Ph bond and a B(OH)3 compound.

What effect does [OH] have on Suzuki-Miyaura CC?
Increasing [OH] increases rate until the point at which OH inhibits the reductive elimination step.
If [OH-] becomes too high, the reductive elimination step is inhibited as stable anionic Pd-OH- complexes are formed, which have a high electron denisty.
The reduction of Pd becomes harder, therefore reductive elimination is inhibited.
![<p>Increasing [OH] increases rate until the point at which OH inhibits the reductive elimination step.</p><ul><li><p>If [OH-] becomes too high, the reductive elimination step is inhibited as stable anionic Pd-OH- complexes are formed, which have a high electron denisty.</p></li><li><p>The reduction of Pd becomes harder, therefore reductive elimination is inhibited.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e6a9879c-4a6b-43d8-b99b-a88d6b0a5c03.png)
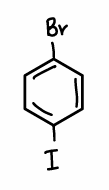
What is the chemoselectivity when bromine and iodine are both on the phenyl ring?
The C-I bond is selectively broken as this is the weaker C-X bond compared to C-Br.
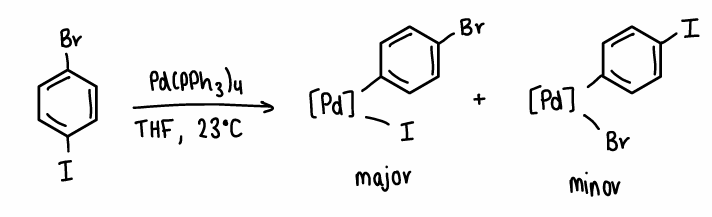
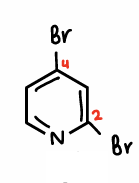
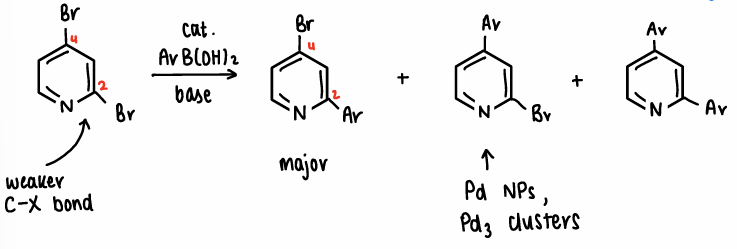
What is the chemoselectivity when there are 2 halogens on a N-substituted ring?
The C-Br located next to the N atom is weaker than the other C-Br, therefore this bond is selectively attacked, forming the major product.
In some situations, if Pd nanoparticles or Pd3 clusters are used the minor product can be formed.
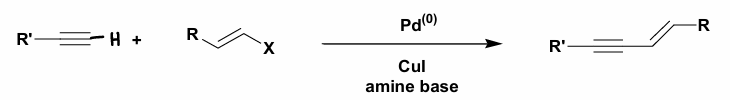
What is Sonogashira cross-coupling?
The reaction of an R-M with a R’-X in the presence of a Pd catalyst and amine base.
CuI can be added to aid Pd activation and affects the reactivity of the acetylene hydrogen.
The R’-H is usually an alkyne.
The organometallic reagent is produced in situ.
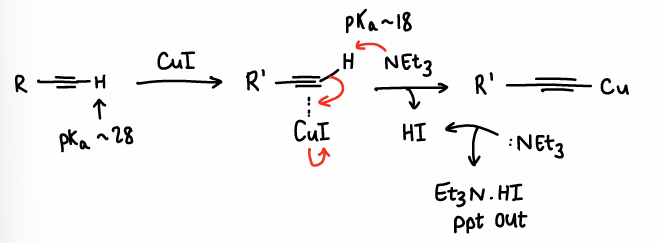
How does CuI aid Pd activation is Sonogashira CC?
The CuI reacts with the alkyne double bond, forming a C-Cu bond and removing HI.
What is the Heck reaction?
An R-X is reacted with an alkene/alkyne in the presence of a Pd catalyst and a base, forming a R=R.
B-hydride elimination occurs.
R-X must not contain and alkyl-aryl group as this would lead to unwanted byproducts
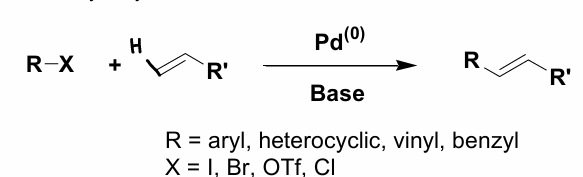
How do you make CCs more atom efficient?
Reactions where neither component is pre-activated are most atom efficient.
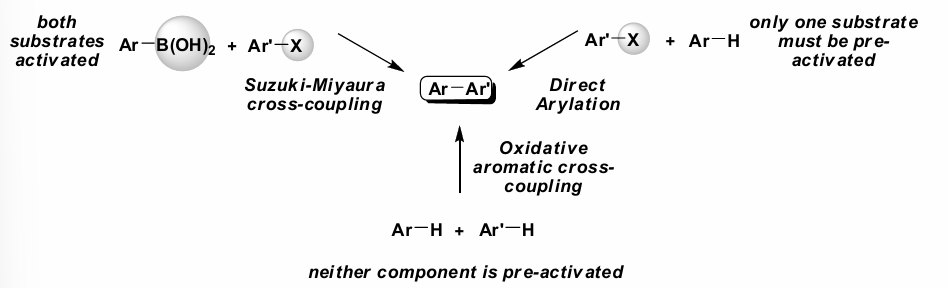
What is ‘direct arylation’?
An Ar-H reacts with an Ar-X in one step to form an Ar-Ar product.
This involves only one substrate being pre-activated.
The Ar-H is activated using a Pd catalyst, CuI and DMF, Cs2CO3 at 140oC.
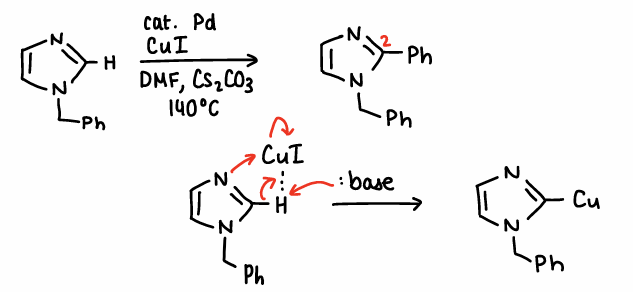
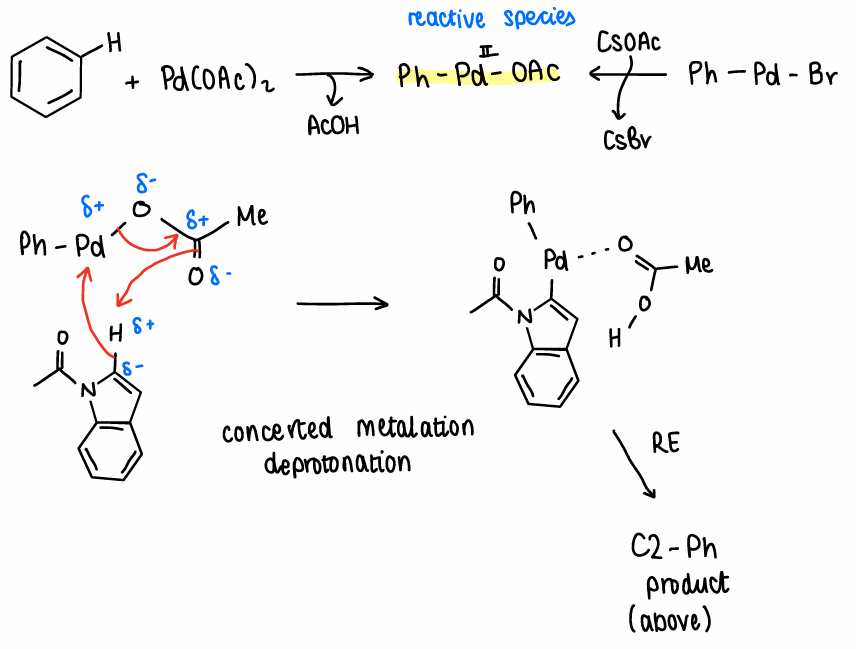
What is Oxidative Aromatic Cross-Coupling and how do you make it selective?
The reaction of Ar-H and Ar’-H in which neither component is pre-activated. They are reacted in the presence of a Pd(II) catalyst and an oxidant.
If the oxidant is AgOAc, the Ar adds onto the C2 position. If the oxidant is Cu(OAc)2 the Ar adds onto the C3.
How does Oxidative Aromatic CC occur?
The Pd(OAc)2 catalyst reacts with the Ar-H to form the reactive species PhPdOAc and removes a molecule of AcOH.
The reactive species reacts with the Ar-H bond via concerted metalation deprotonation.
Reductive elimination occurs to form the product.
What is a Buchwald-Hartwig amination?
Ar-X reacts with R-NH2 in the presence of a Pd catalyst, PtBu3 and a base (NaOtBu).
The [R-NH]- Na+ acts like a R-M species.
![<p>Ar-X reacts with R-NH<sub>2</sub> in the presence of a Pd catalyst, P<sup>t</sup>Bu<sub>3</sub> and a base (NaO<sup>t</sup>Bu).</p><ul><li><p>The [R-NH]<sup>-</sup> Na<sup>+</sup> acts like a R-M species.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/390732ec-9992-41c5-95c1-a9edb1cfa830.png)
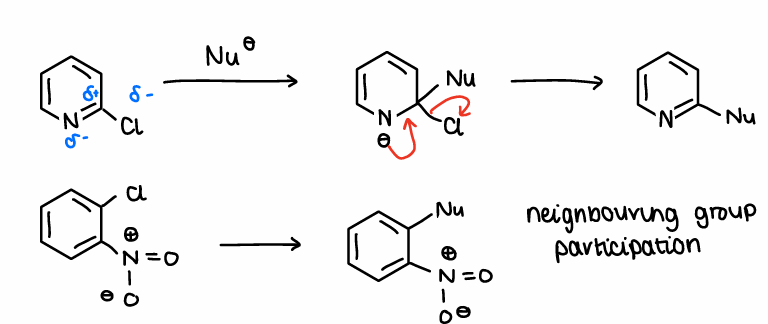
Is there a need for a metal catalyst in SNAr reactions?
Not necessary as in many cases NGP or partial charges allow the reaction to occur without catalysts.
What is the mechanism for alkene metathesis?
A Ru complex loses a ligand, forming a 14 electron adduct.
An alkene is added, which coordinates to the Ru centre.
Heat is added, allowing a [2+2] cycloaddition to form a metallocycle intermediate.
An alkene is then lost, forming the 2 new alkenes.
![<ul><li><p>A Ru complex loses a ligand, forming a 14 electron adduct.</p></li><li><p>An alkene is added, which coordinates to the Ru centre.</p></li><li><p>Heat is added, allowing a [2+2] cycloaddition to form a metallocycle intermediate.</p></li><li><p>An alkene is then lost, forming the 2 new alkenes.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/787d24f9-01d8-4574-be0c-805597c052d6.png)
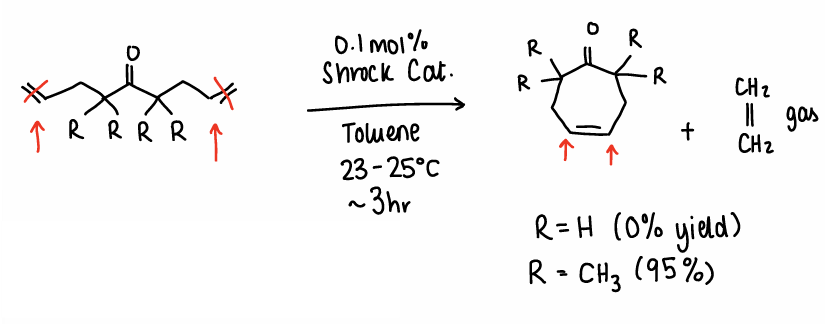
How does Ring-closing metathesis occur using Schrock catalyst and what affects the yield?
Two ends of a ketone diene molecule react with one another in the presence of a Schrock catalyst. Toluene is used as a solvent at 23-25oC and the reaction takes 3 hours.
Ethene gas is released.
When R=H, there is a 0% yield.
When R=CH3, there is a 95% yield.
What is the Thorpe-Ingold effect?
Steric constraints increase cyclisation.
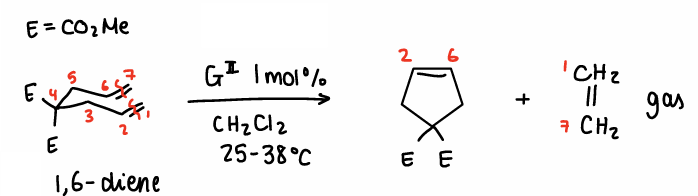
How does Ring-closing metathesis occur using Grubbs 2nd Gen catalyst?
A 1,6-diene reacts with itself in the presence of 1 mol% of Grubbs II in the presence of CH2Cl2 at 25-38oC.
Ethene gas forms and bubbles out.
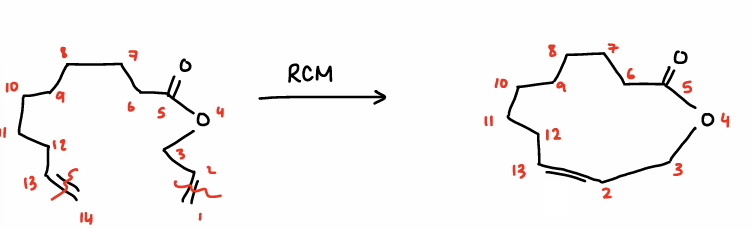
What is macrocyclisation?
A long chain diene reacts with itself via RCM to form a large ring molecule,
Forms a 1:2 mixture of E:Z
What factors can affect the macrocyclisation reaction?
Reactant concentration- typically 0.001-0.005 moldm-3.
Remote substituents (substituents away from reaction site)- OR substituents can increase reaction rates and may change stereoselectivity, whereas OH can inhibit and poison the catalyst.
Interaction that increase rigidity of the substrate- reduces entropic cost of cyclisation.
What is cross metathesis?
A reaction in which two alkene react with one another to form a new alkene.
Grubbs I or II can be used, however this changes the ratio of E:Z formed.
The reaction can be selective or non-selective, the use of the G II catalyst allows equilibration to the thermodynamically stable E isomer.
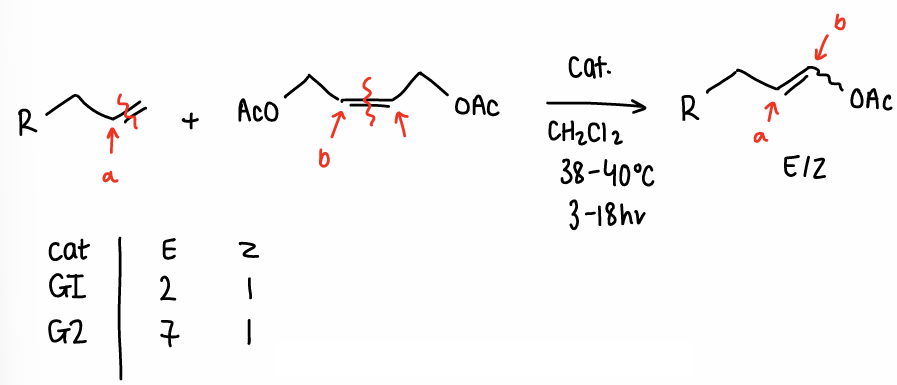
How do you prevent homodimerisation in cross-metathesis and why?
Having steric bulk in one alkene can help favour the cross-metathesis over the homodimerisation.
Using a protecting group can help increase bulk and prevent homodimerisation.
Homodimerisation causes a lower yield.
What is a Pauson-Khand reaction?
A formal [2+2] cycloaddition of an alkyne, alkene and CO. This can occur catalytically (intramolecularly) or stoichiometrically (intermolecularly).
![<p>A formal [2+2] cycloaddition of an alkyne, alkene and CO. This can occur catalytically (intramolecularly) or stoichiometrically (intermolecularly).</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1258b918-6fee-466f-9a53-1ba05bce3dec.png)
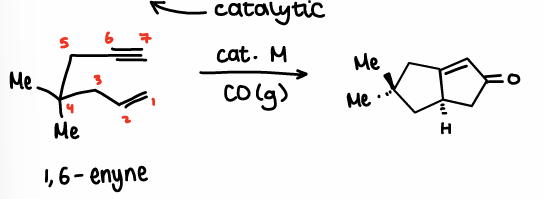
What is Intramolecular PK?
Requires Co2(CO)8, THF and rt-60oC temp.
The enyne reacts with itself to form the product.
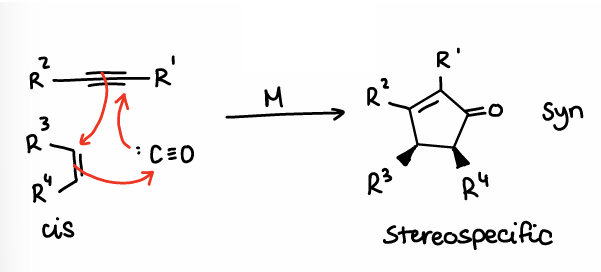
What is intermolecular PK?
Occurs via the reaction of an alkene and an alkyne from separate molecules in the presence of CO and a metal (usually Co2(CO)8).
This is a stereospecific reaction.
Requires THF and rt-60oC
What are the limitations of intermolecular PK?
Co2(CO)8 is toxic and difficult to handle- complexes can be affected by air and water as Co-H species can form.
Intermolecular reactions are more difficult and side reactions can occur,
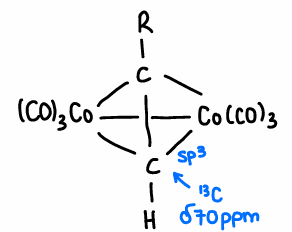
What is the Co2(CO)8 intermediate formed in PK?
Binds to the alkyne.
Forms an sp3 hybridised carbon.
How do substituents effect intermolecular PK reactions?
Monosubstituted terminal acetylenes will give products where the substituent is in the alpha-position of the enone. Regiochemistry is dominated by steric effects.
For disubstituted acetylenes, EDG tend to prefer the alpha-position, whereas EWG tend to prefer the beta position. Regiochemistry is dominated by electronic effects.
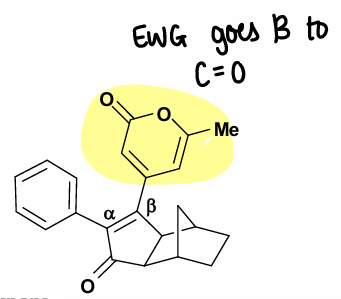
How are DMSO and TMANO used in PK reactions?
They can displace the CO ligand in the formation of the inital alkynyl-cobalt(0) complex.
Can also assist in alkene insertion (CO loss may be neccessary).
What is a con of classical cross couplings?
They require substrate activation.
Aggregation of Pd can be a problem, therefore choice of ligand is important.
What is a con of C-H bond activation reactions?
They are often better than classical cross couplings, but often require additives (such as special ligands, base, etc.)
What is a con of cross-metathesis?
Selectivity can be an issue (such as homodimerisation vs. cross-dimerisation).
High catalyst loadings are often required, and the choice of catalyst is important.
What conditions are used for metathesis?
Mild conditions (ambient temp).
Which CC reactions require inert conditions, dry solvents and rt?
Kumada
Negishi
Stille
Sonogashira
Which CC reactions require a base?
Suzuki
Direct Arylation
Sonogashira (dry NEt3)
Heat reactions to 60oC in THF or CH3CN.
What FGs do Grignard/organolithium reagents react with?
They will react with aldehydes, ketones, esters and deprotonate acidic groups.
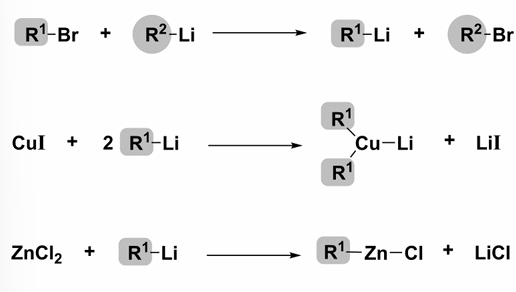
How does organolithium reagents react with R-Br, CuI and ZnCl2?
Reactions often require inert conditions and require dry solvents.