Chemistry Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
Energy
the capacity to do work
2
New cards
Work
is movement against force (w= fxd)
3
New cards
Heat
is energy that flows from a hotter to colder object
4
New cards
motion at the molecular level
heat
5
New cards
Temperature
determines that direction of heat flow and is a measure of the average speed of that motion
6
New cards
activation energy
the energy that is needed to start a reaction
7
New cards
isomer
each of two or more compounds with the same formula but a different arrangement of atoms in the molecule and different properties
8
New cards
First law of Thermodynamics
the energy of the universe is instant, or, energy can neither be created nor destroyed; but it can be converted from one form to another
9
New cards
Potential energy
is energy due to position or composition
10
New cards
kinetic energy
energy due to movement
11
New cards
Second Law of thermodynamics
the entropy (chaos) of the universe is increasing
12
New cards
Per capita
accounting for an individual or each person
13
New cards
Countries ranked by co2 emissions
1. china
2. US
3. India
4. Russian Federation
5. Japan
6. Germany
2. US
3. India
4. Russian Federation
5. Japan
6. Germany
14
New cards
Bond energy
the amount of energy that must be absorbed to break a chemical bond
15
New cards
Bond formation
release of energy via exothermic reaction
16
New cards
Bond breaking
energy is absorbed by bonds via endothermic reaction
17
New cards
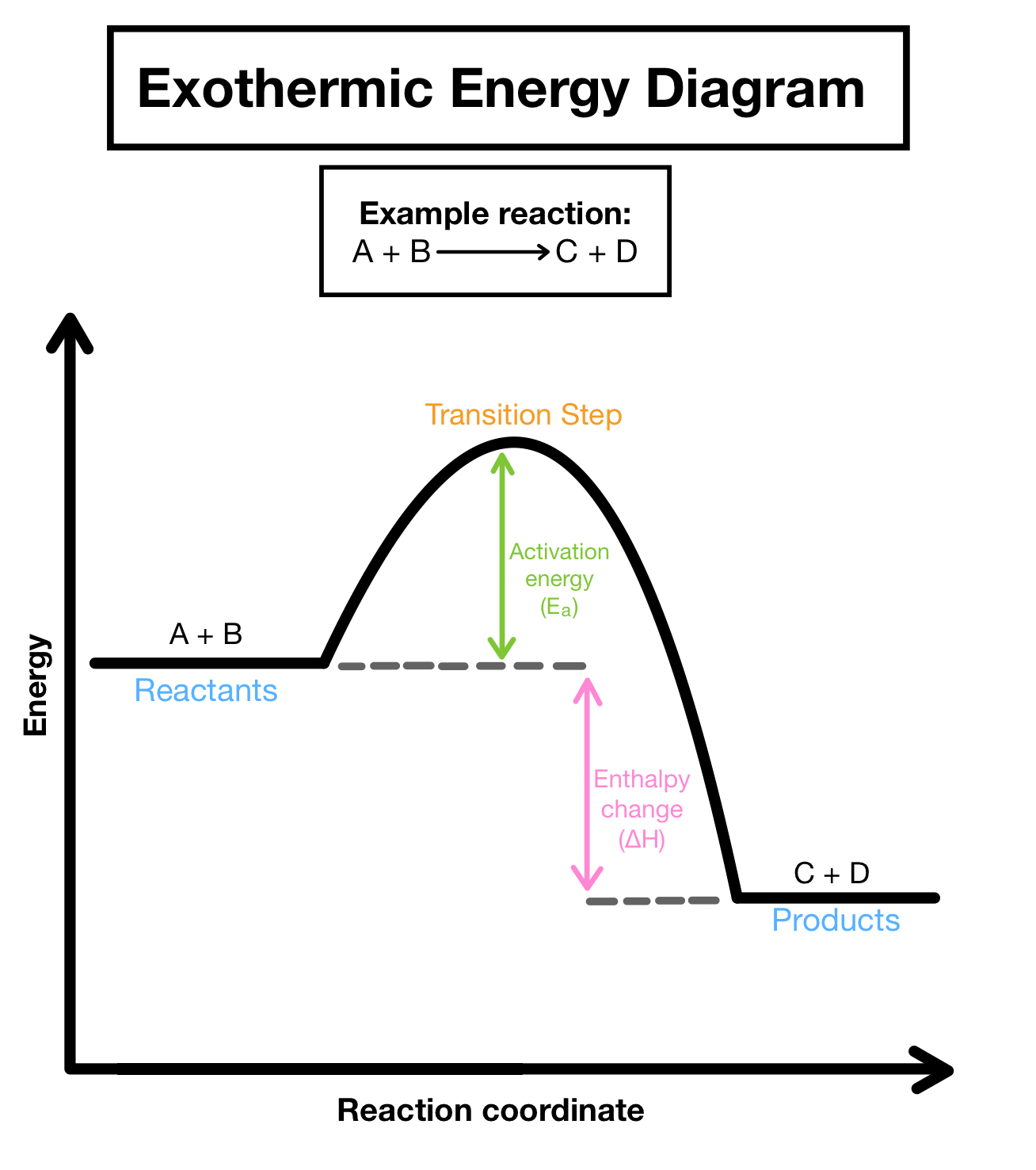
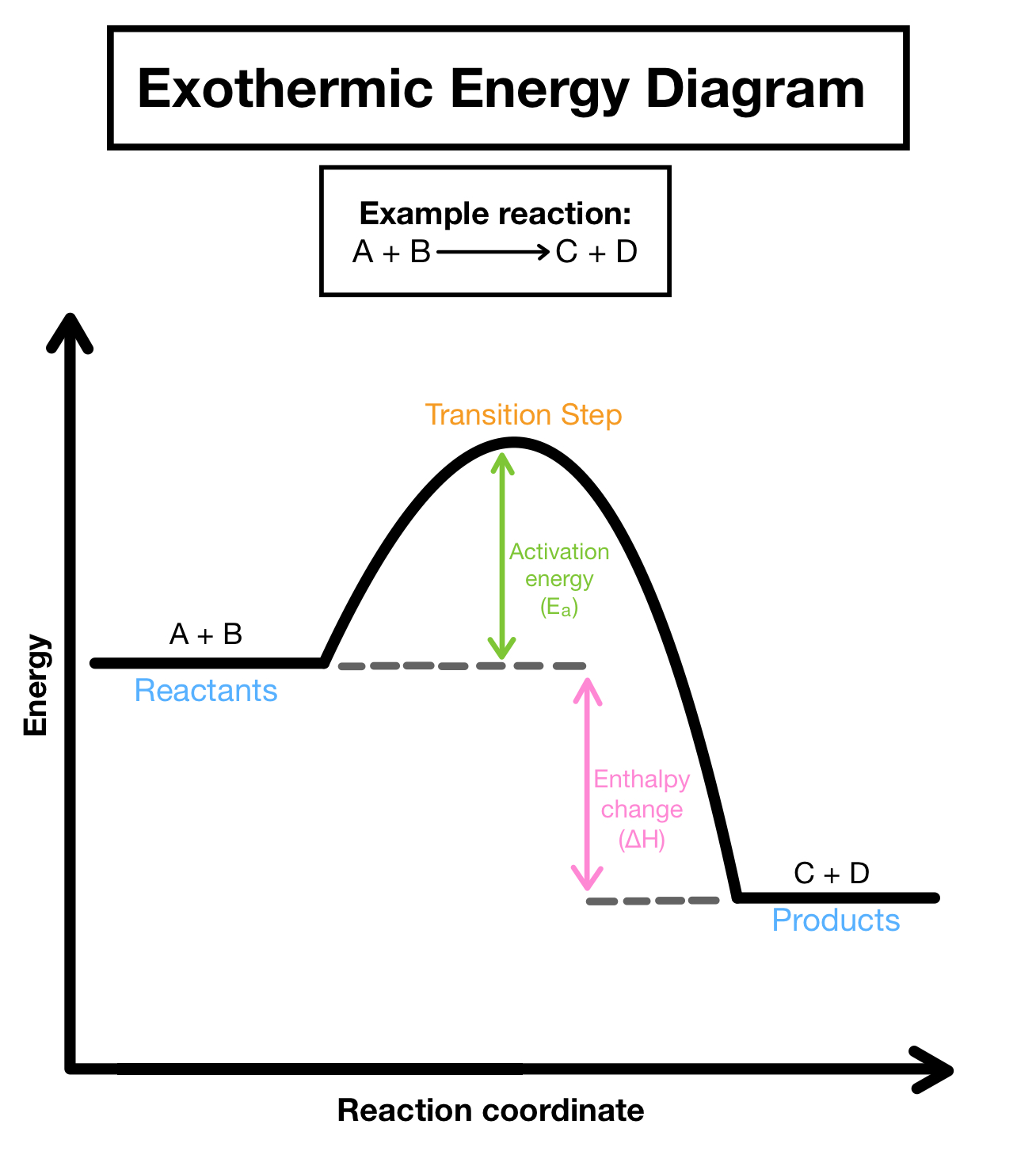
Exothermic reactions
energy is released during the course of a chemical reaction
18
New cards
Properties of an exothermic reaction
- Heat/energy is released
- net energy change is negative
- reactants have more potential energy than products
- net energy change is negative
- reactants have more potential energy than products
19
New cards
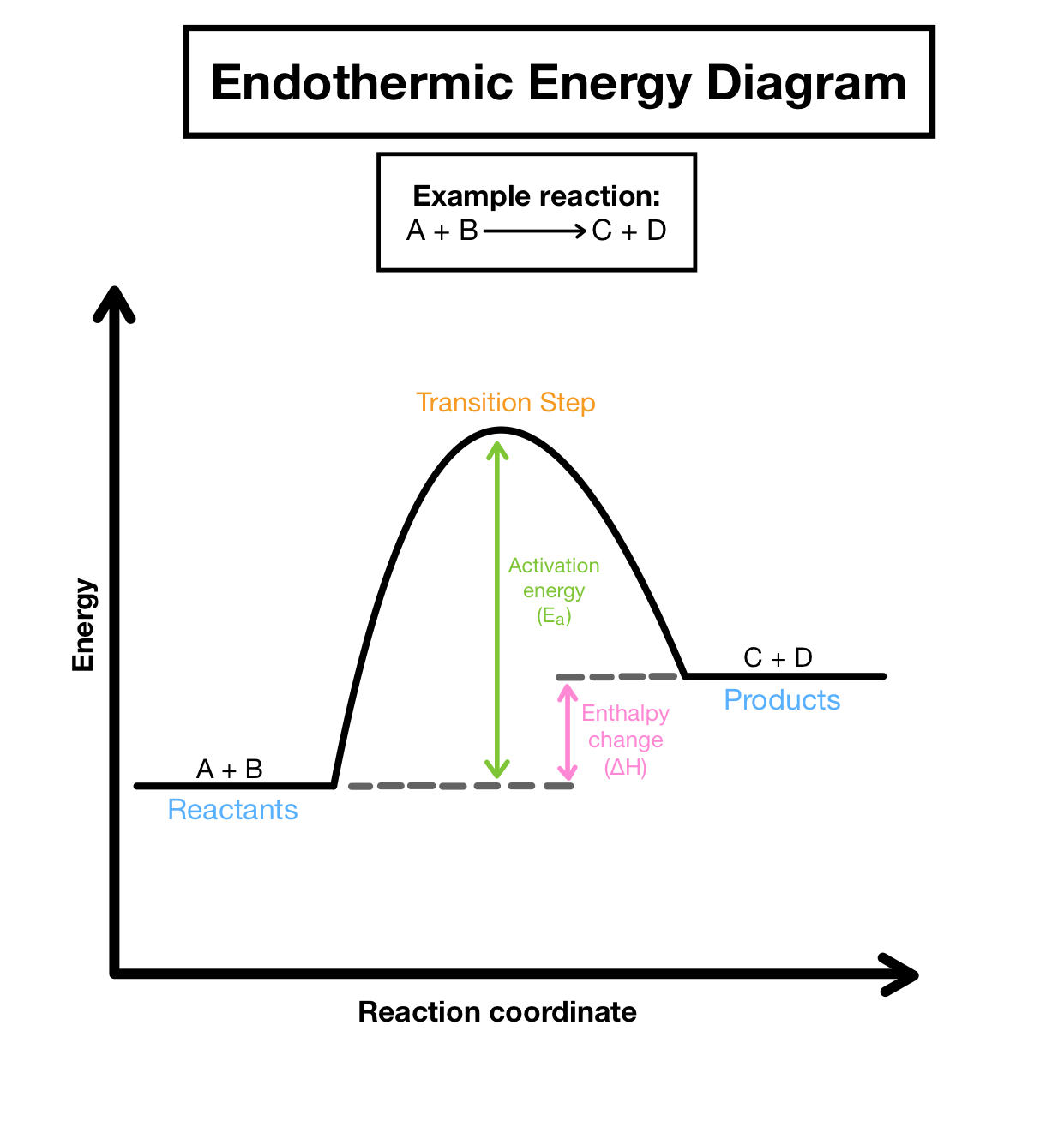
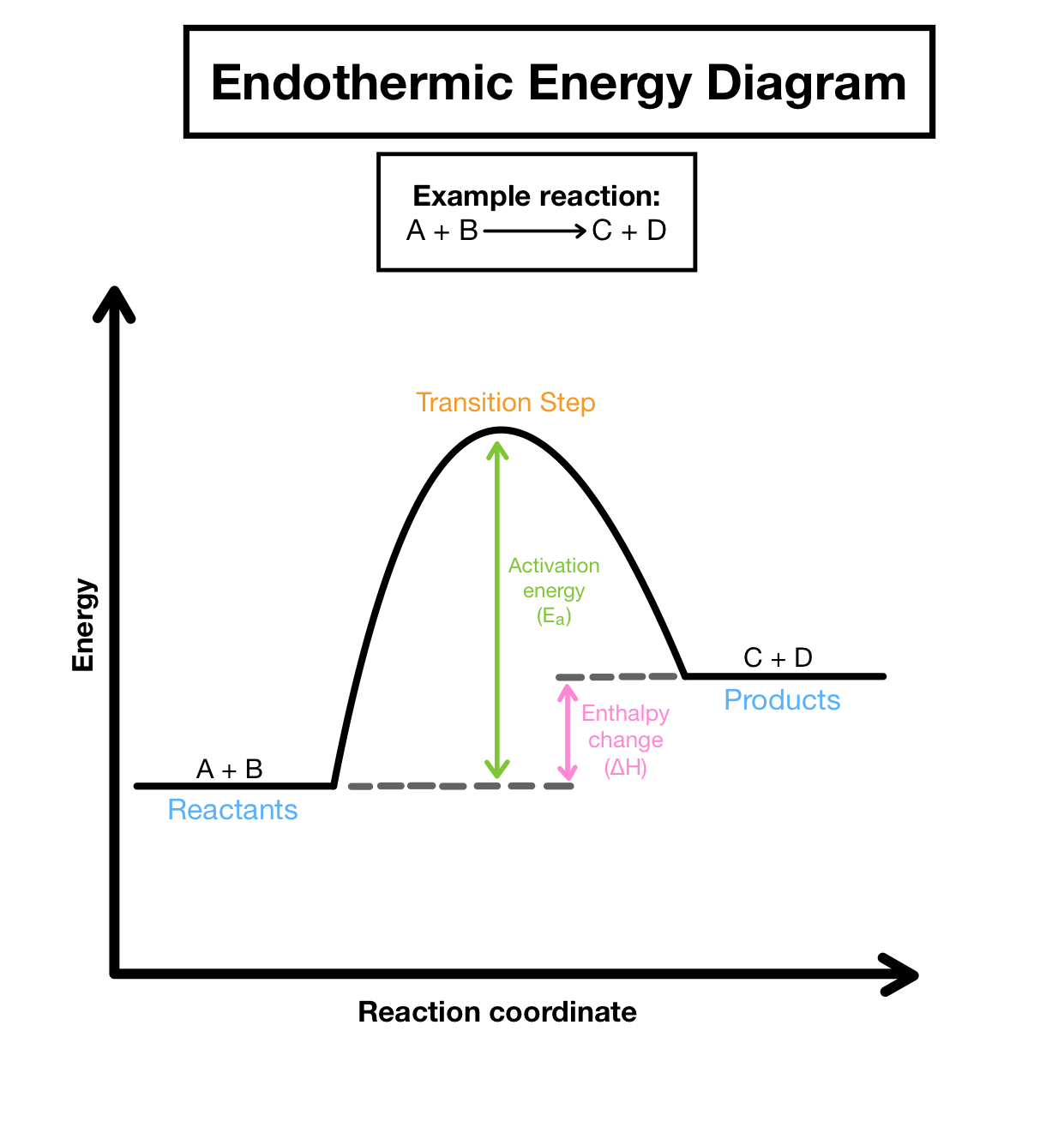
Endothermic reactions
energy is absorbed during the course of a chemical reaction
20
New cards
Properties of an endothermic reaction
- heat/ energy is absorbed
- net energy change is positive
- products have more potential energy than reactants
- net energy change is positive
- products have more potential energy than reactants
21
New cards
Uncatalyzed reaction
requires a higher activation energy
22
New cards
catalyzed reaction
requires lower activation energy
23
New cards
Chemical equation for the combustion of hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbon + O2 = CO2 = H2O
EX: CH4 + 2O2 = CO2 +2H2O + energy
EX: CH4 + 2O2 = CO2 +2H2O + energy
24
New cards
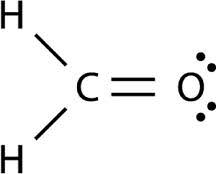
Trigonal Planar
120
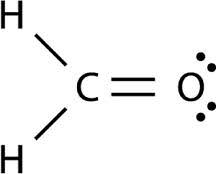
25
New cards
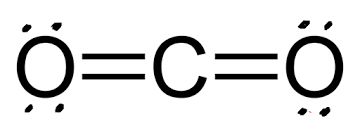
Linear
180
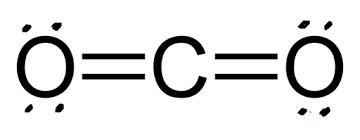
26
New cards
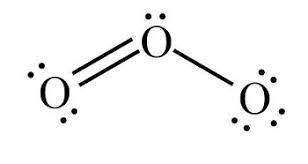
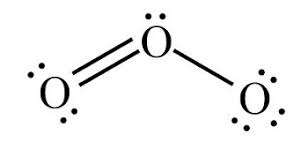
Bent
104.5
27
New cards
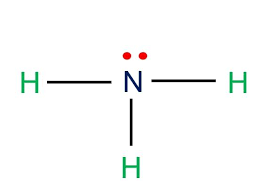
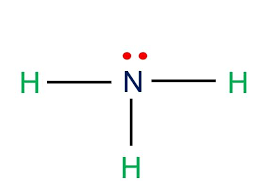
Trigonal pyramidal
107
28
New cards
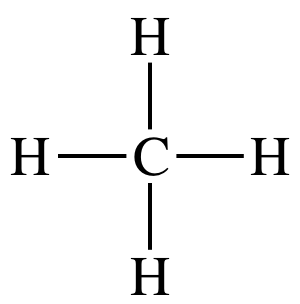
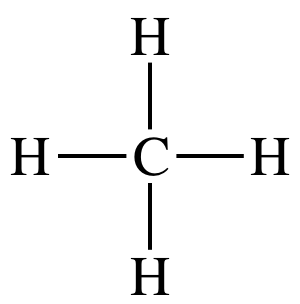
Tetrahedral
109.5
29
New cards
the largest percentage of energy from the sun comes to the earth is this form
Infrared radiation
30
New cards
Greenhouse gases
gases capable of absorbing and emitting IR radiation thereby warming the atmosphere
31
New cards
Example of Greenhouse gases
- water vapor
- methane
- carbon dioxide
- nitrous oxide
- ozone
- chlorofluorocarbons
- methane
- carbon dioxide
- nitrous oxide
- ozone
- chlorofluorocarbons
32
New cards
Greenhouse effect
Atmospheric gases trap and return a major portion of this heat radiating from the earth through this natural and necessary process. Without this process the Earth would freeze over and be uninhabitable. As the number of atmospheric GHGs increases this process is accelerated causing the Earth's surface temperatures to rise.
33
New cards
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases
man made activities that rely on processes that put more carbon atoms into the atmosphere rather than those that remove them; ex: cutting down rainforests, combustion
34
New cards
Classification of Greenhouse Gasses
- 3 or more atoms
- the molecular geometry
- ability to bend and stretch with exposure to the infrared radiation ( without breaking apart )
- the molecular geometry
- ability to bend and stretch with exposure to the infrared radiation ( without breaking apart )
35
New cards
Ionic compound
metal bonded with nonmetal
36
New cards
Polyatomic ions
two or more atoms covalently bonded together that have an overall positive or negative charge
37
New cards
Dynamic system
natural additional and removal mechanisms
38
New cards
What process adds carbon to the atmosphere?
Respiration
39
New cards
What process removes carbon from the atmosphere?
photosynthesis
40
New cards
Isotopes
atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in number of neutrons, therefore they have different atomic masses
41
New cards
Average atomic mass
(mass of isotope)(decimal of %) + (mass of isotope)(decimal of %) = Avg. atomic mass
answer should be very similar to atomic weight
answer should be very similar to atomic weight
42
New cards
Avg. Atomic mass example
Cl35 and Cl37
(35)(.7587) + (37) (.242) = 35.51
(35)(.7587) + (37) (.242) = 35.51