Unit 3 VCE Biology: AOS 1
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
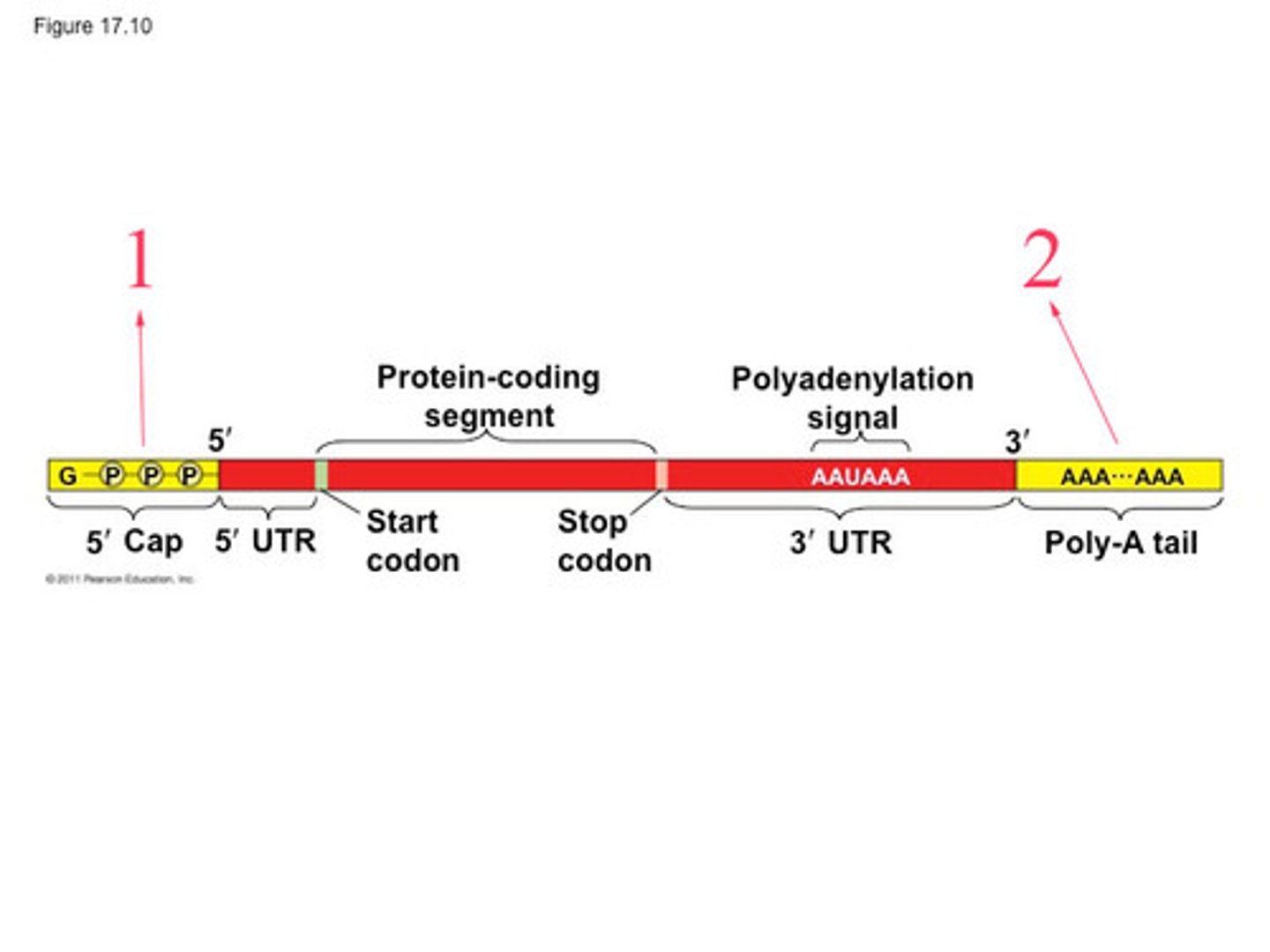
3' poly-A tail
A chain of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of pre-mRNA during RNA processing. It makes the RNA molecule more stable and prevents its degradation.
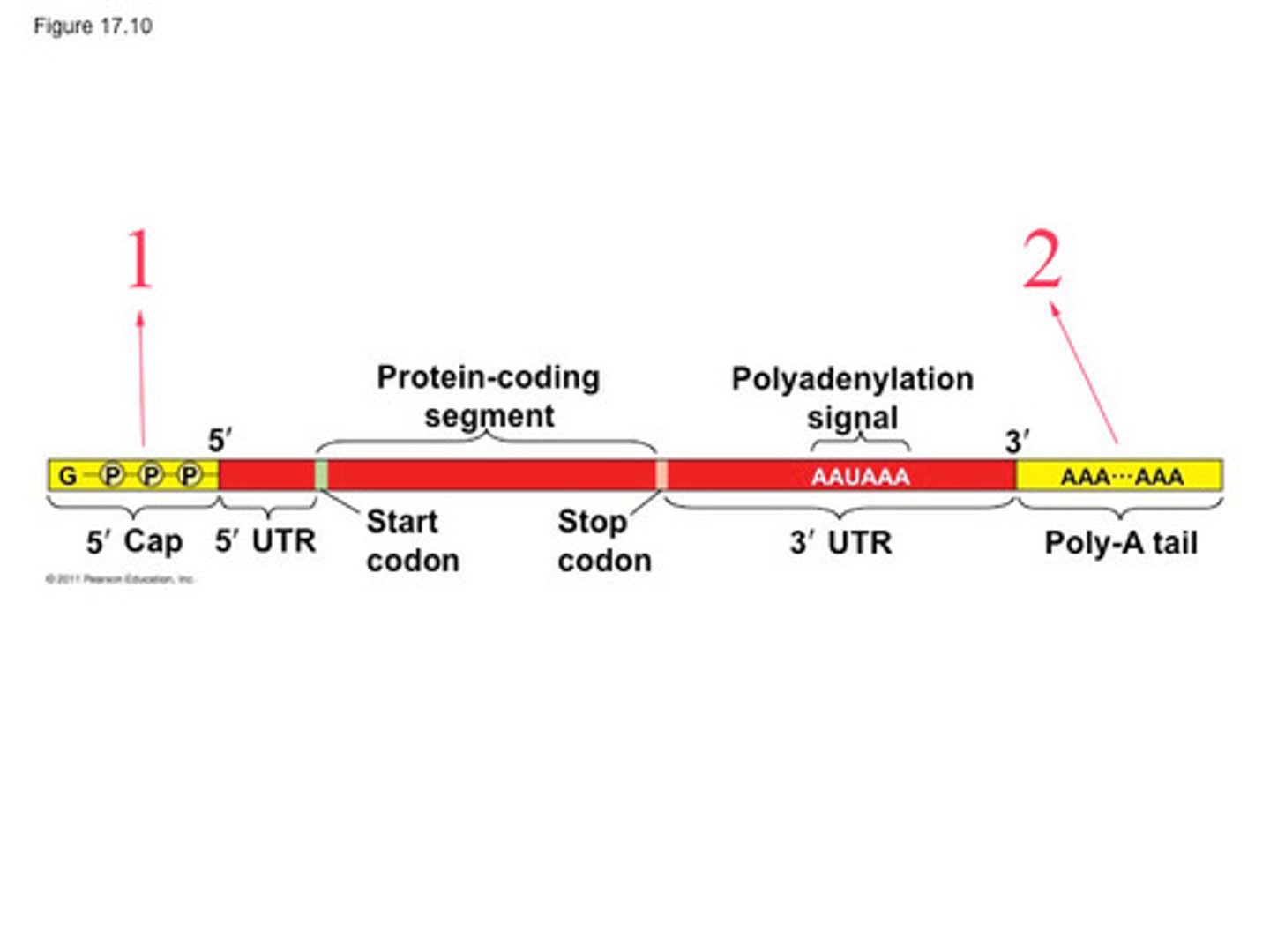
5' methyl-G cap
A molecule added to the 5' end of pre-mRNA during RNA processing. It makes the RNA molecule more stable and prevents its degradation. It also helps the ribosome attach to the mRNA.
Accurate
How close a measurement is to the true value.
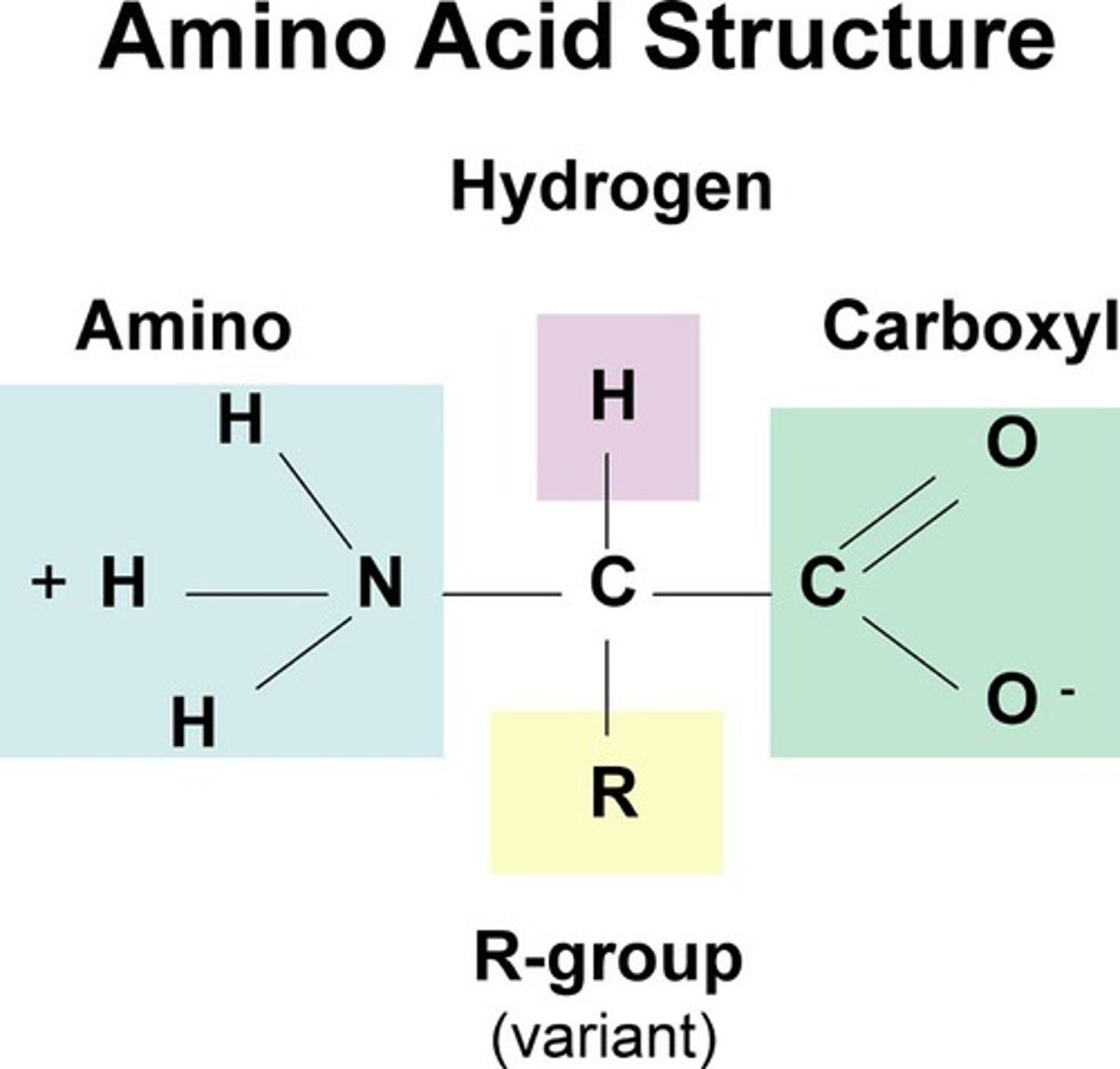
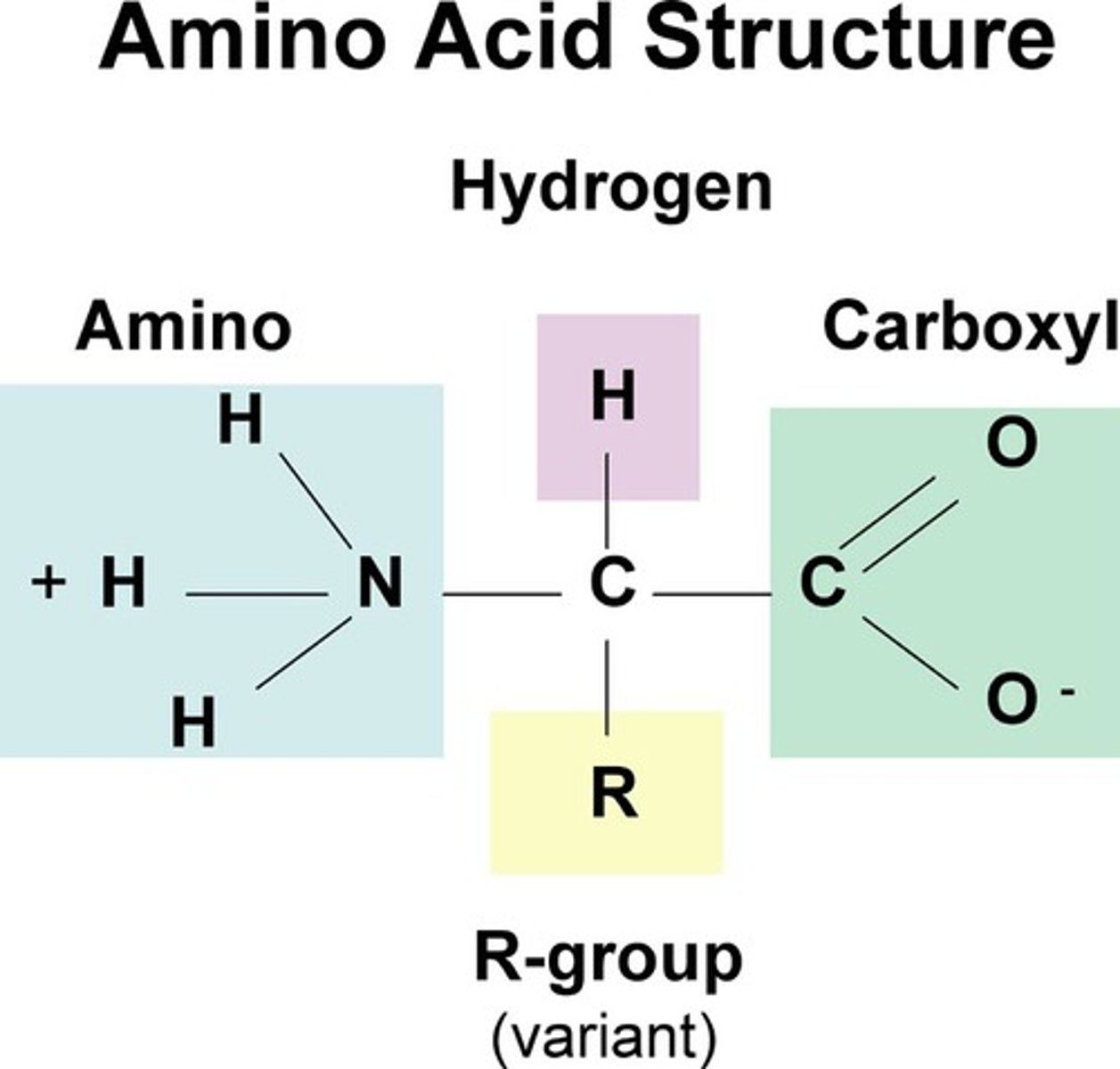
Amino group
The functional group on amino acid molecules that is made up of one nitrogen and two hydrogens (NH2)
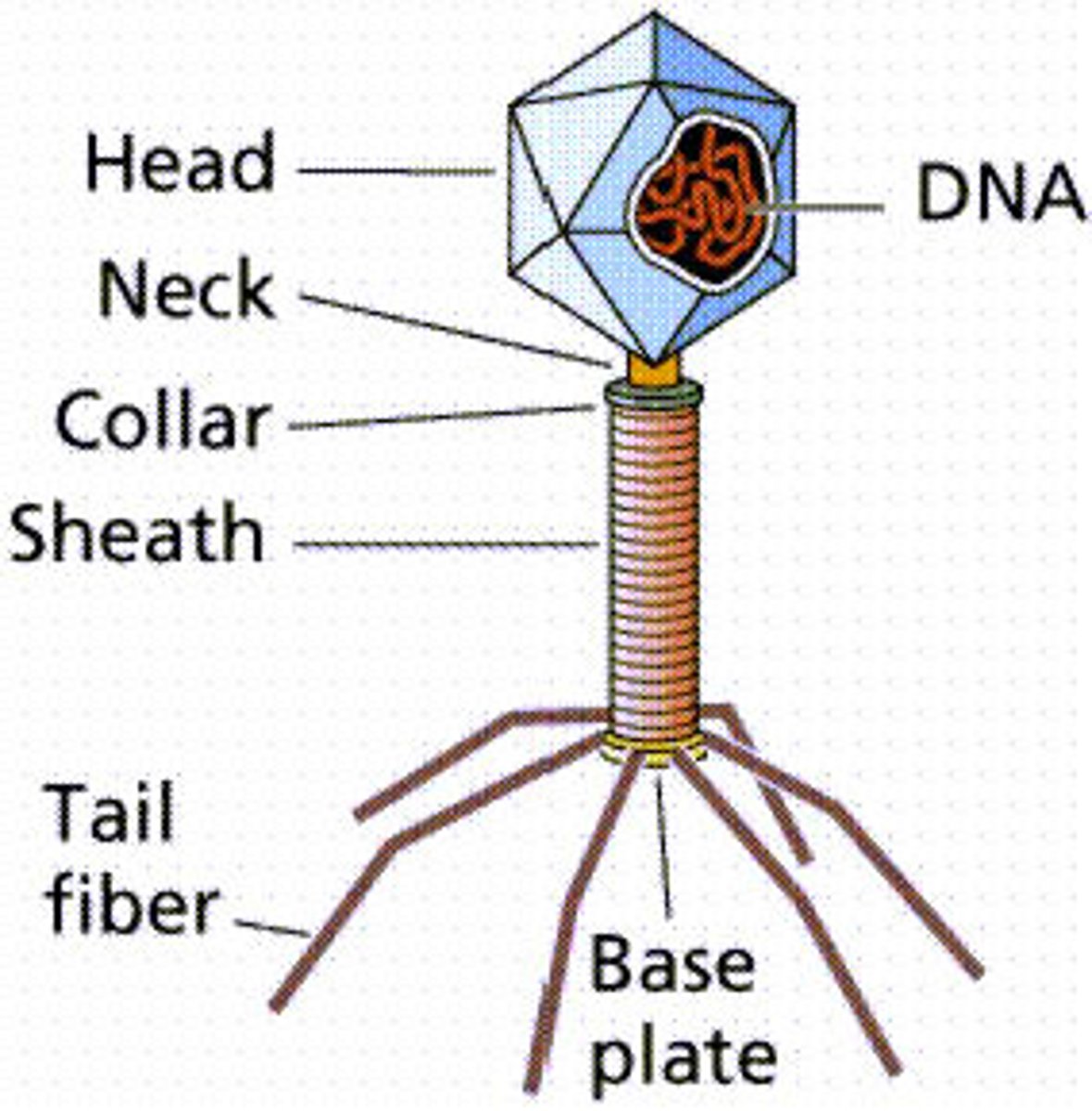
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria.
Bioethical issue
An ethical dilemma pertaining to biology that typically involves a decision- making process between two or more choices or options for action.
CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9)
An endonuclease that creates a blunt end cut at a site specified by guide RNA (gRNA).
CRISPR-Cas9
A complex formed between gRNA and Cas9 which can cut a target sequence of DNA. Bacteria use this complex for protection from viruses and scientists have modified it to edit genomes.
Electroporation
A method that involves delivering an electric shock to bacterial membranes to increase their membrane permeability and increase the likelihood of bacterial transformation.
Ethidium bromide
A fluorescent dye that binds to DNA fragments in a gel and allows them to be easily visualised under ultraviolet light.
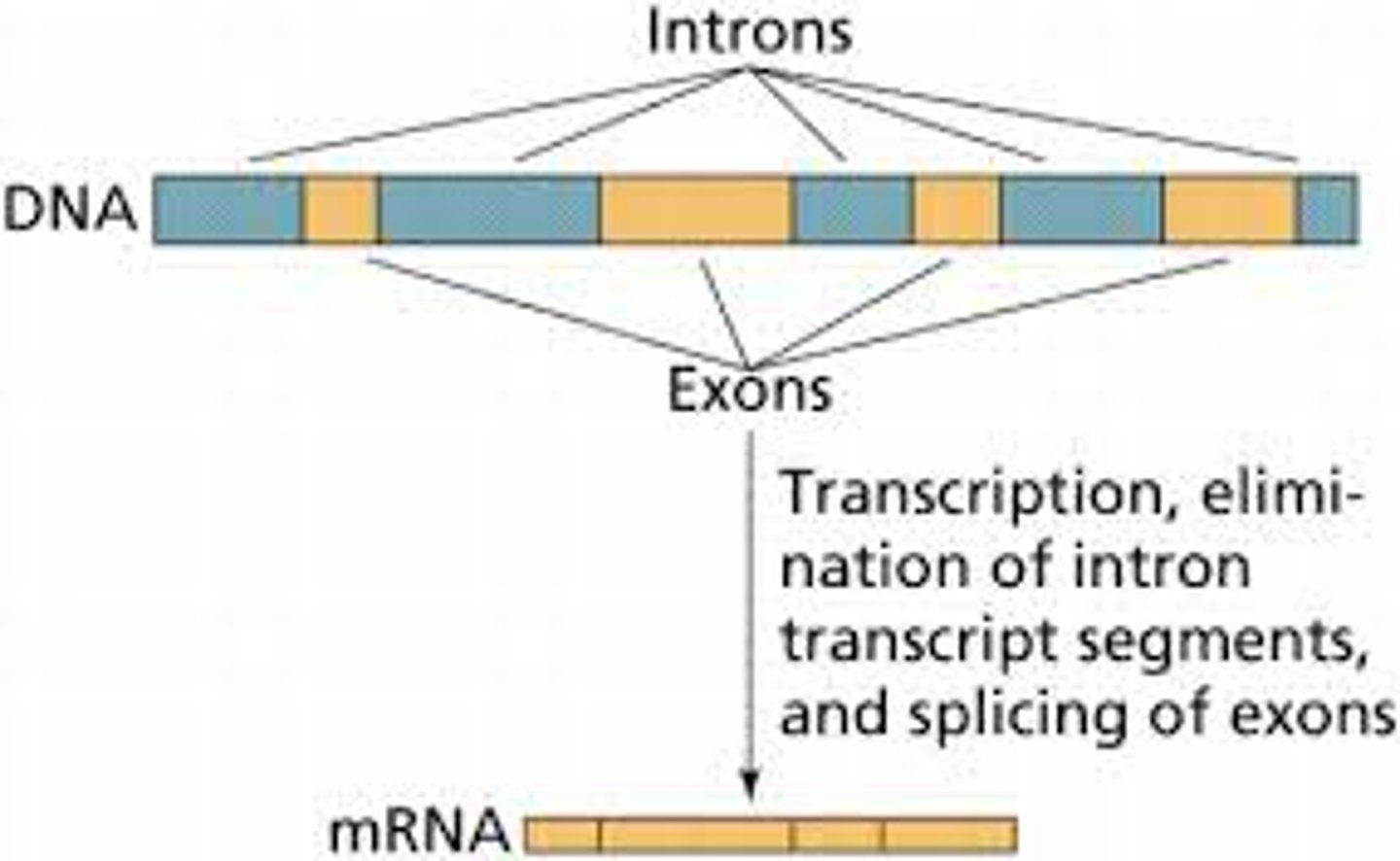
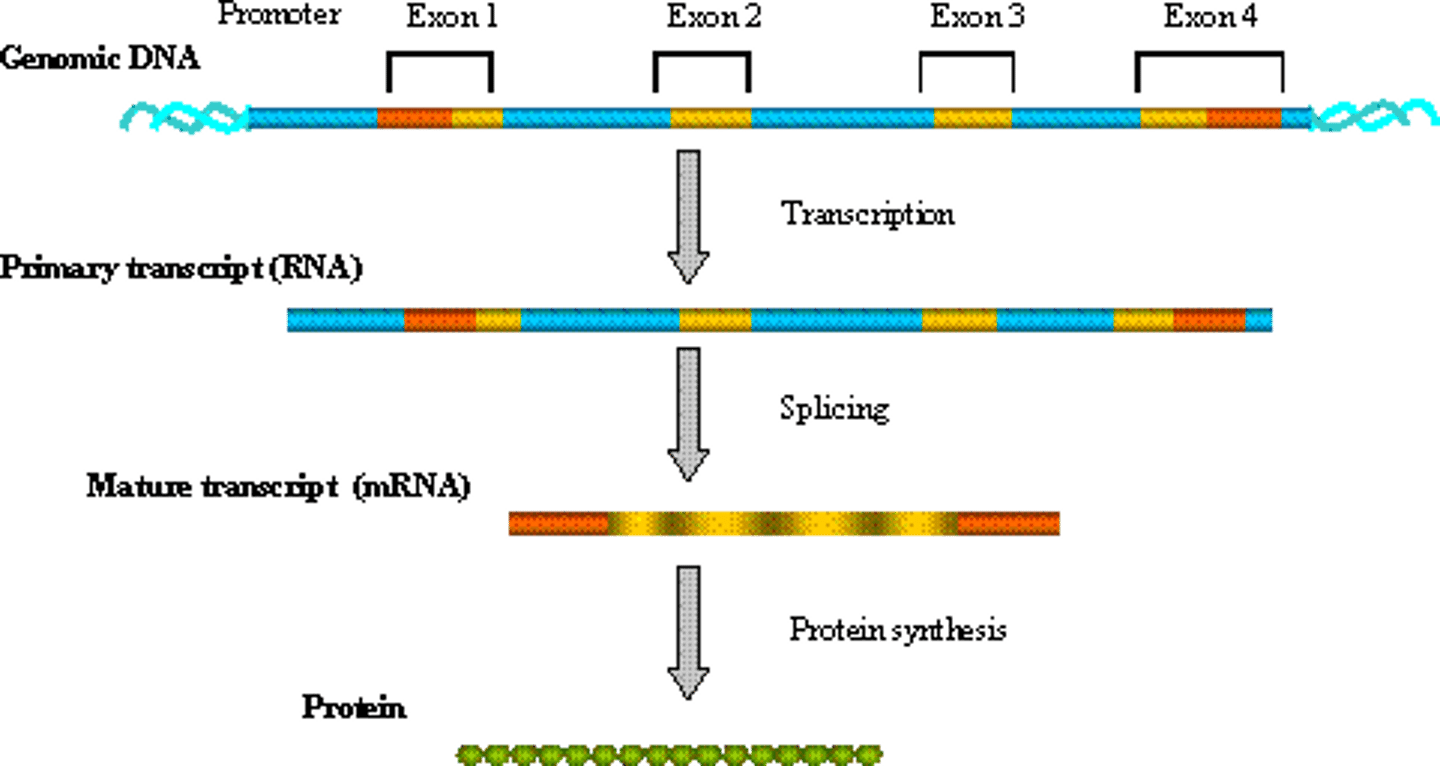
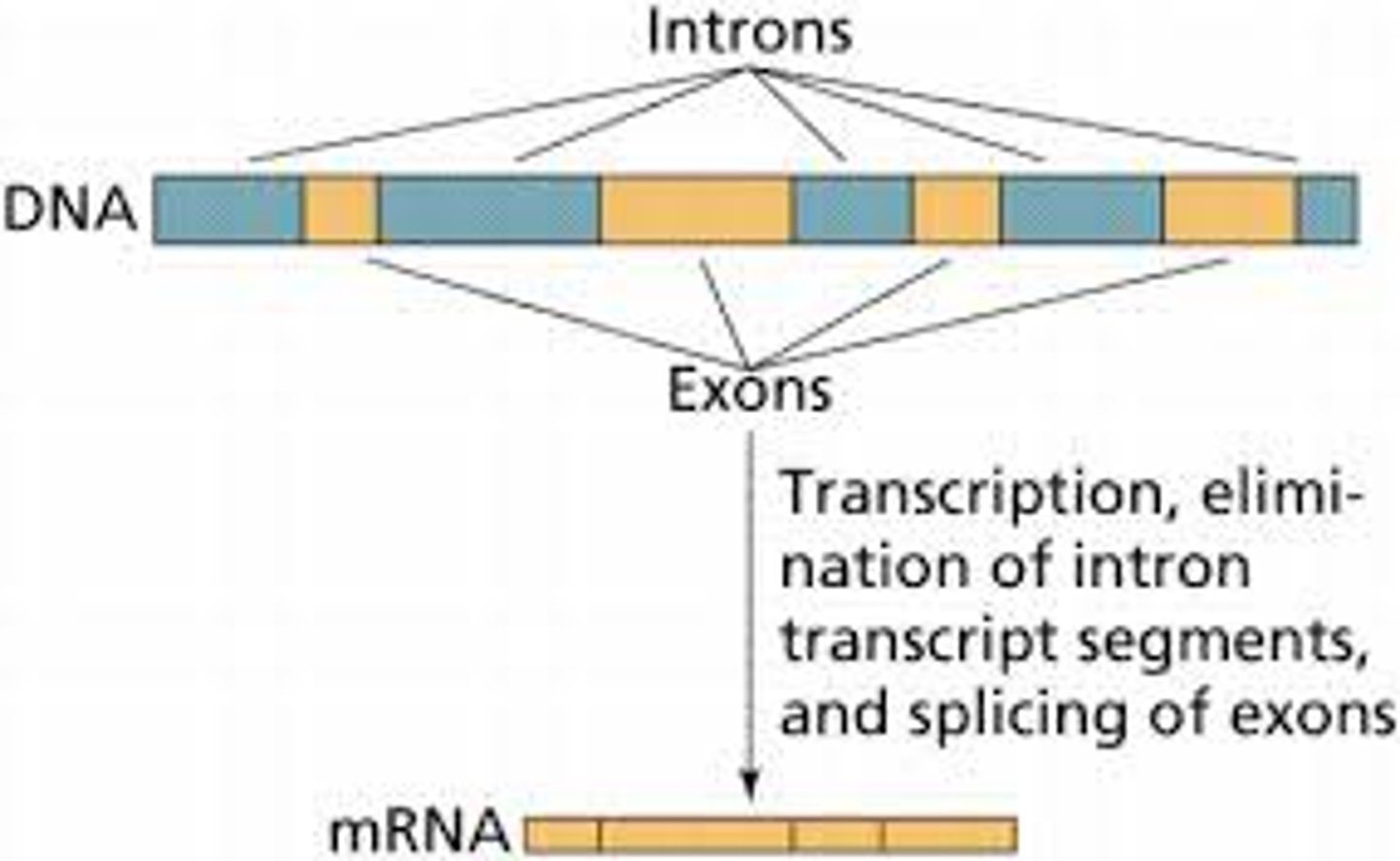
Exons
Regions of DNA that code for proteins and are not spliced out during RNA processing
Gene regulation
Any mechanism that acts to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (DNA or RNA) in the cell.
Gene therapy
Repairing genetic mutations by replacing a defective gene with a healthy one.
Genetic engineering
The process of using biotechnology to alter the genome of an organism, typically with the goal of conferring some desirable trait.
Genetic modification
The manipulation of an organism's genetic material using biotechnology.
Justice
An ethical concept that encourages fair consideration of competing claims, and ensures that there is no unfair burden on a particular group from an action.
Kilobase (kb)
A unit of measurement that corresponds to one thousand nucleotides. May also be written as kbp.
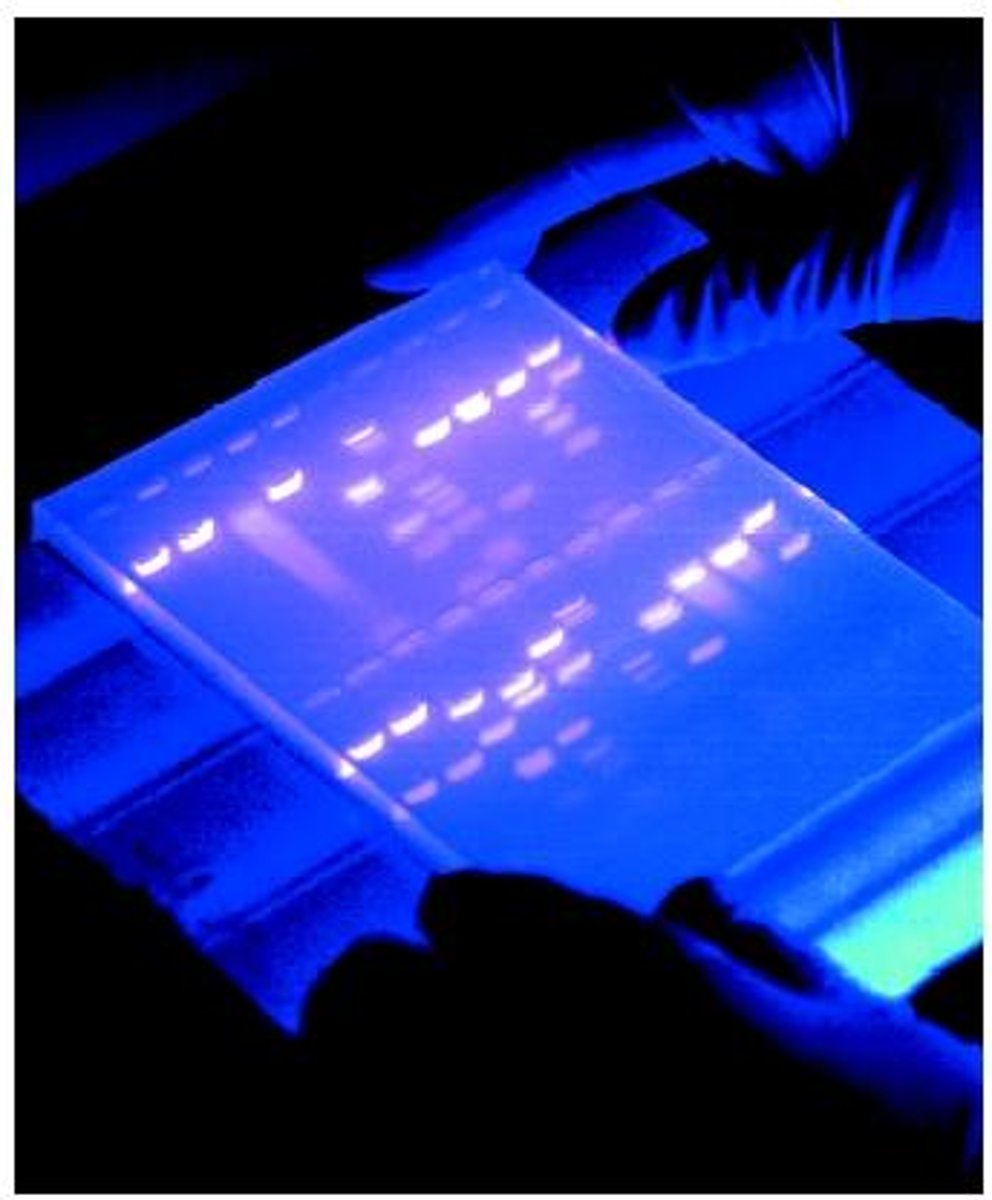
Lane
The column of the gel corresponding to each sample of DNA.
Ligase
An enzyme that joins molecules, including DNA or RNA, together by catalysing the formation of phosphodiester bonds.
Activator protein
A protein coded for by a regulatory gene that increases gene expression.
Agarose gel
A sponge-like gel used in gel electrophoresis that contains pores for DNA fragments to move through

Aim
The objective of an investigation or experiment. Always starts with "To..."
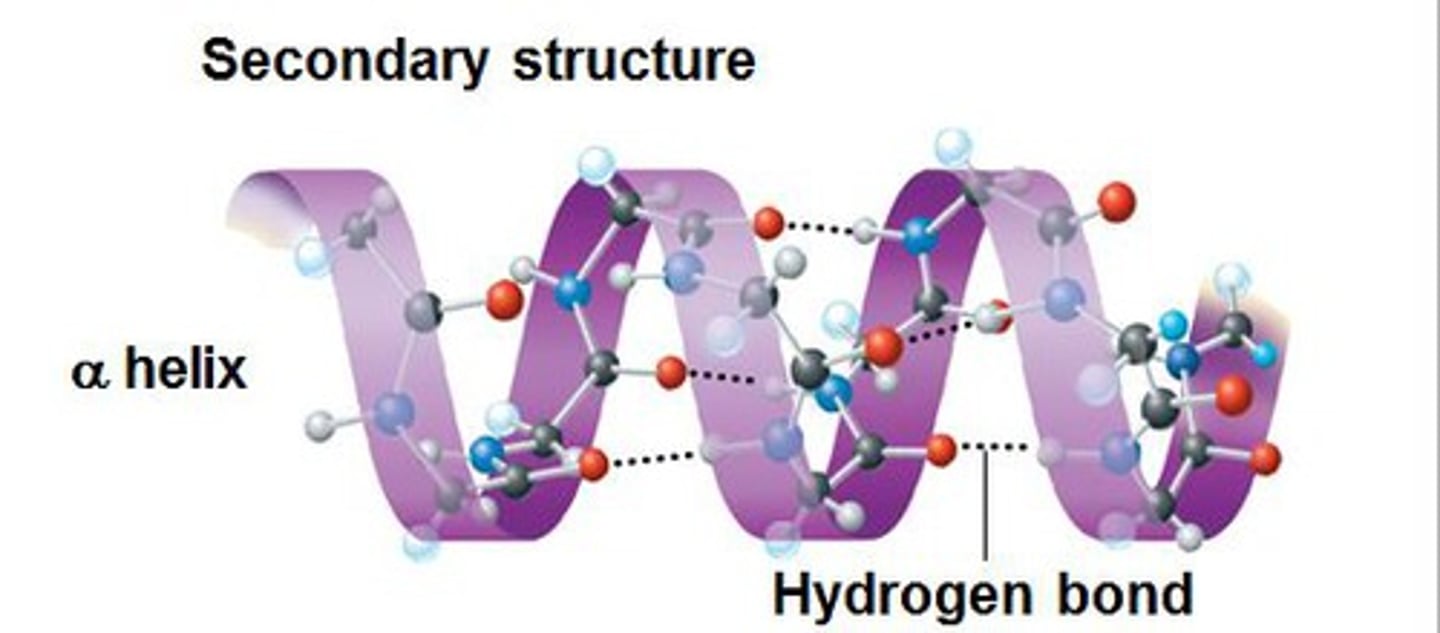
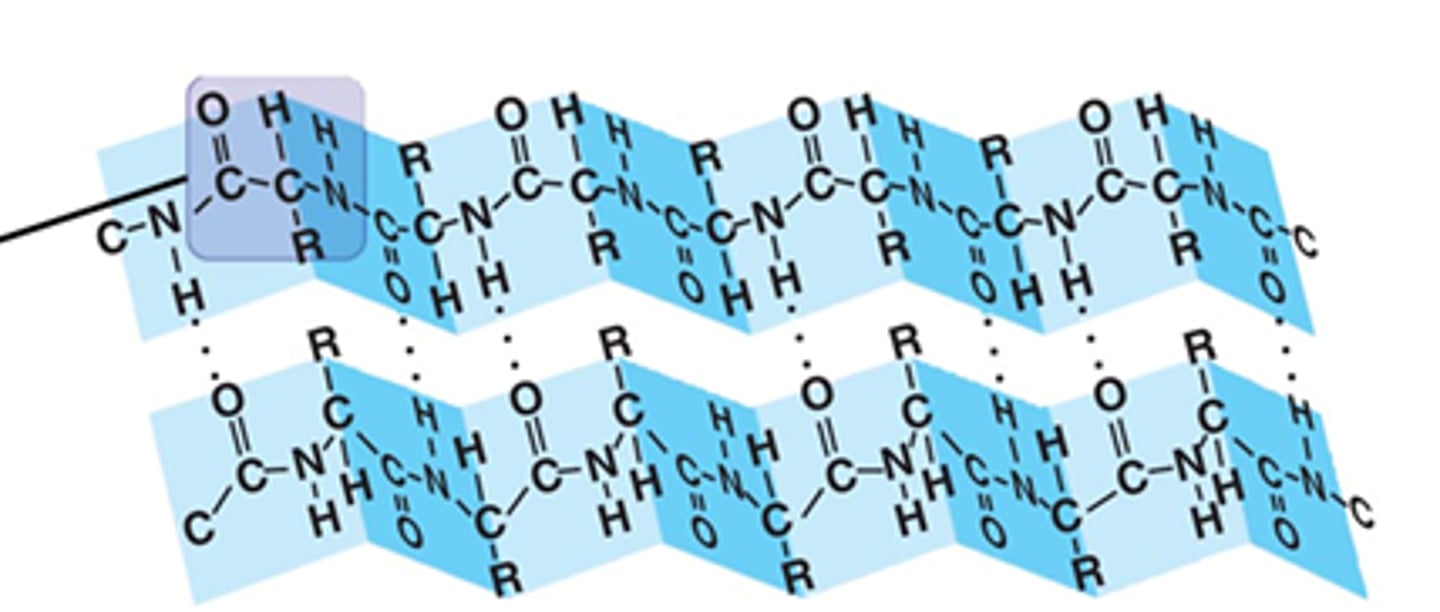
Alpha helix
An organised coiled secondary structure of proteins
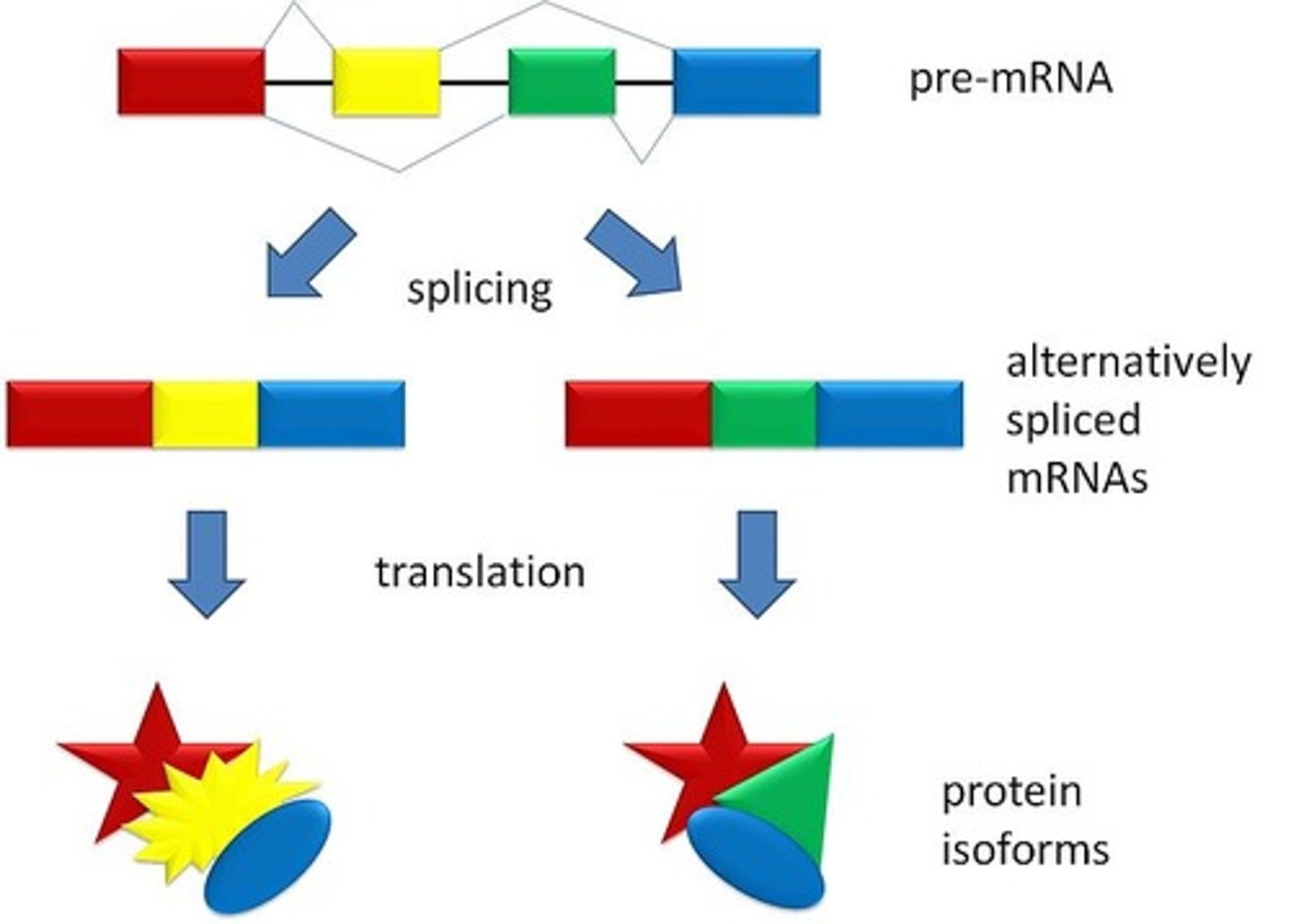
Alternative splicing
The process where different exons may
be spliced, resulting in a single gene producing multiple
different mRNA strands.
Anneal
The joining of two molecules, for example two complementary DNA strands during the cooling phase of PCR.
Antibiotic
Medications used to kill bacteria or slow their growth.
Antibiotic resistance gene
Gene which confers antibiotic
resistance.
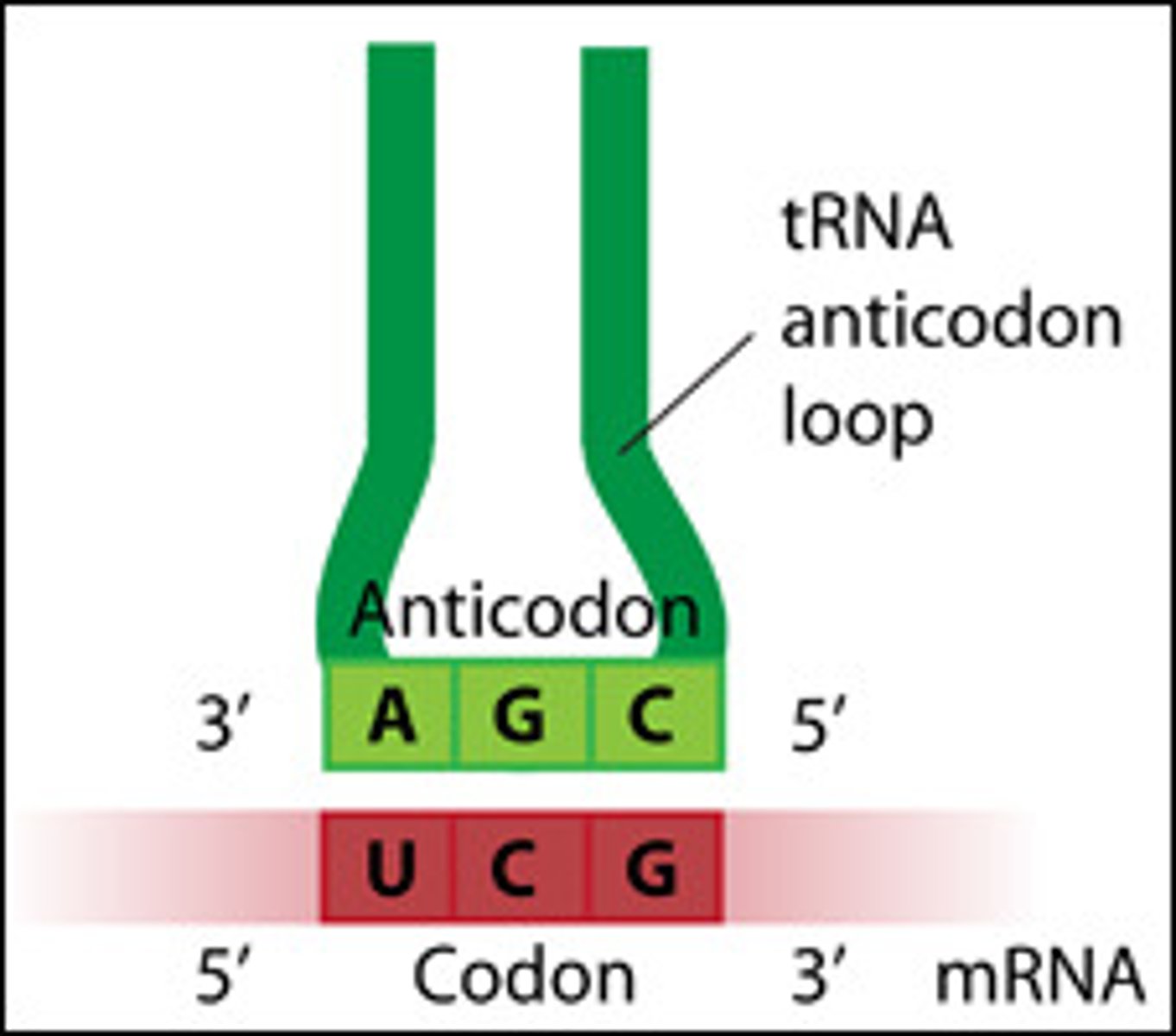
Anticodon
Sequence of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that recognises a specific sequence of three nucleotides (codon) on an mRNA strand.
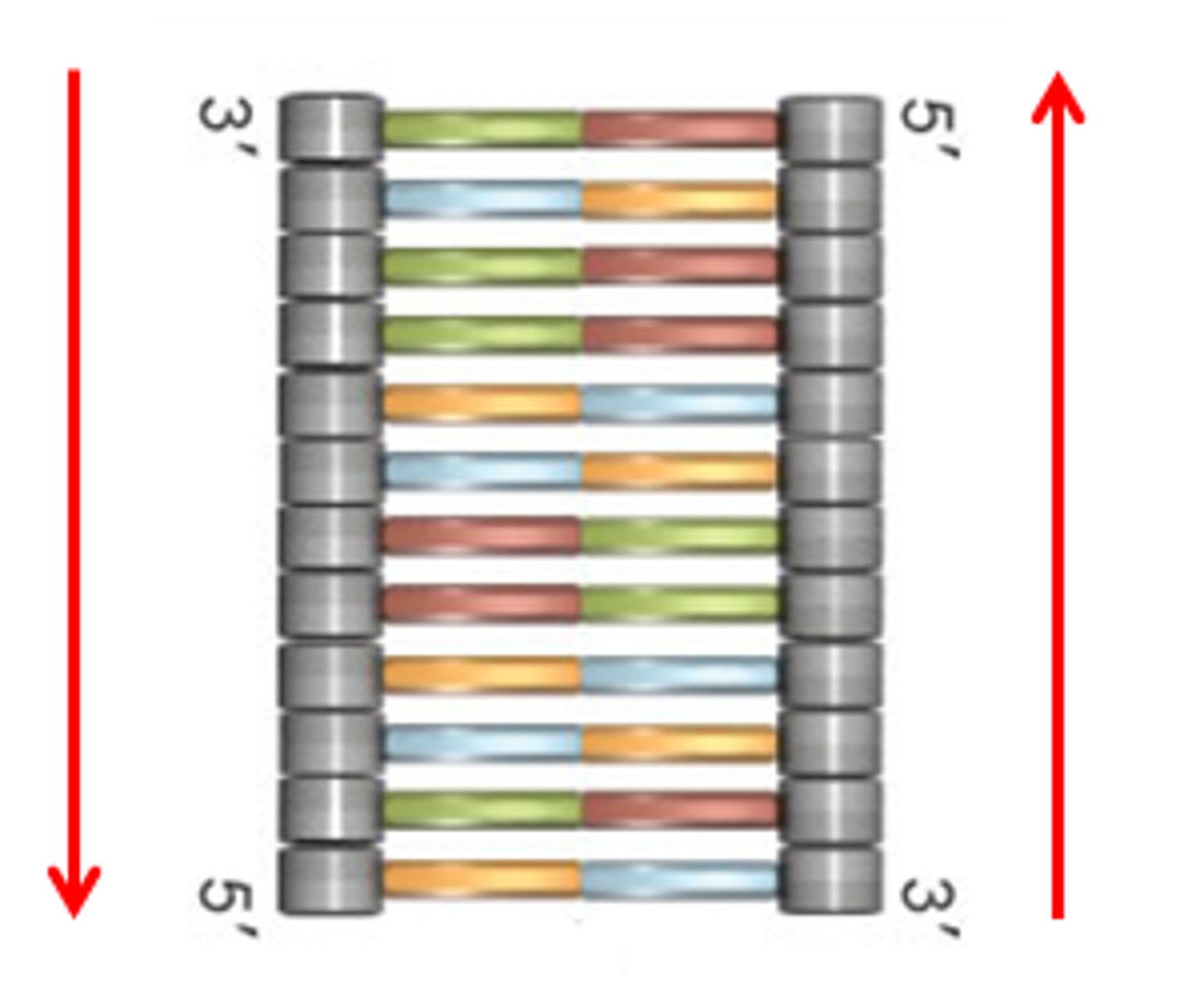
Antiparallel
A characteristic of DNA strands describing
how each strand runs in an opposite direction to the other. One strand runs in a 3' → 5' direction and the other runs in a 5' → 3' direction.
Applied ethics
The application of ethical theories to real- life moral problems and contexts
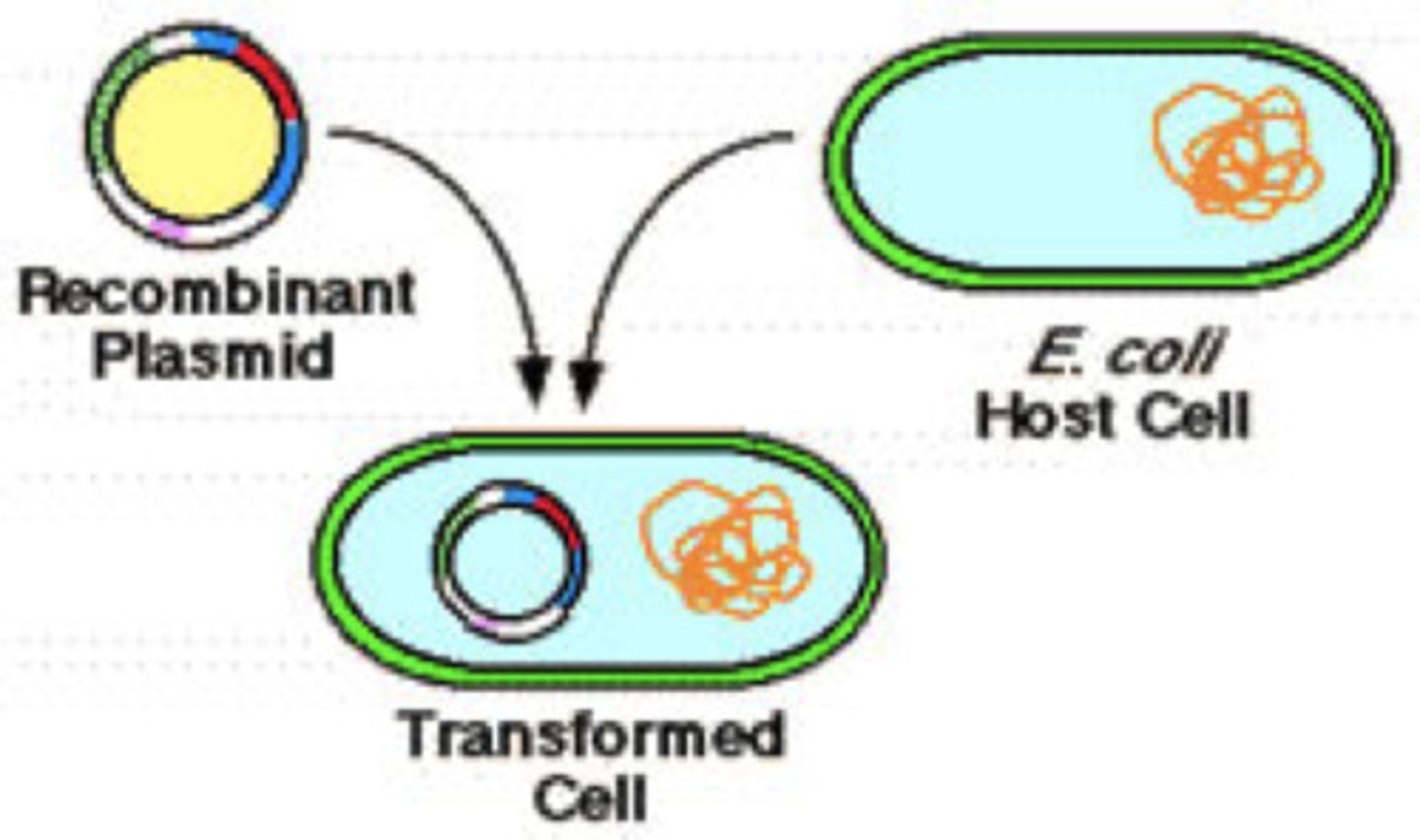
Bacterial transformation
The process by which bacteria take up foreign DNA from their environment. Scientists use this process to introduce recombinant plasmids into bacteria.
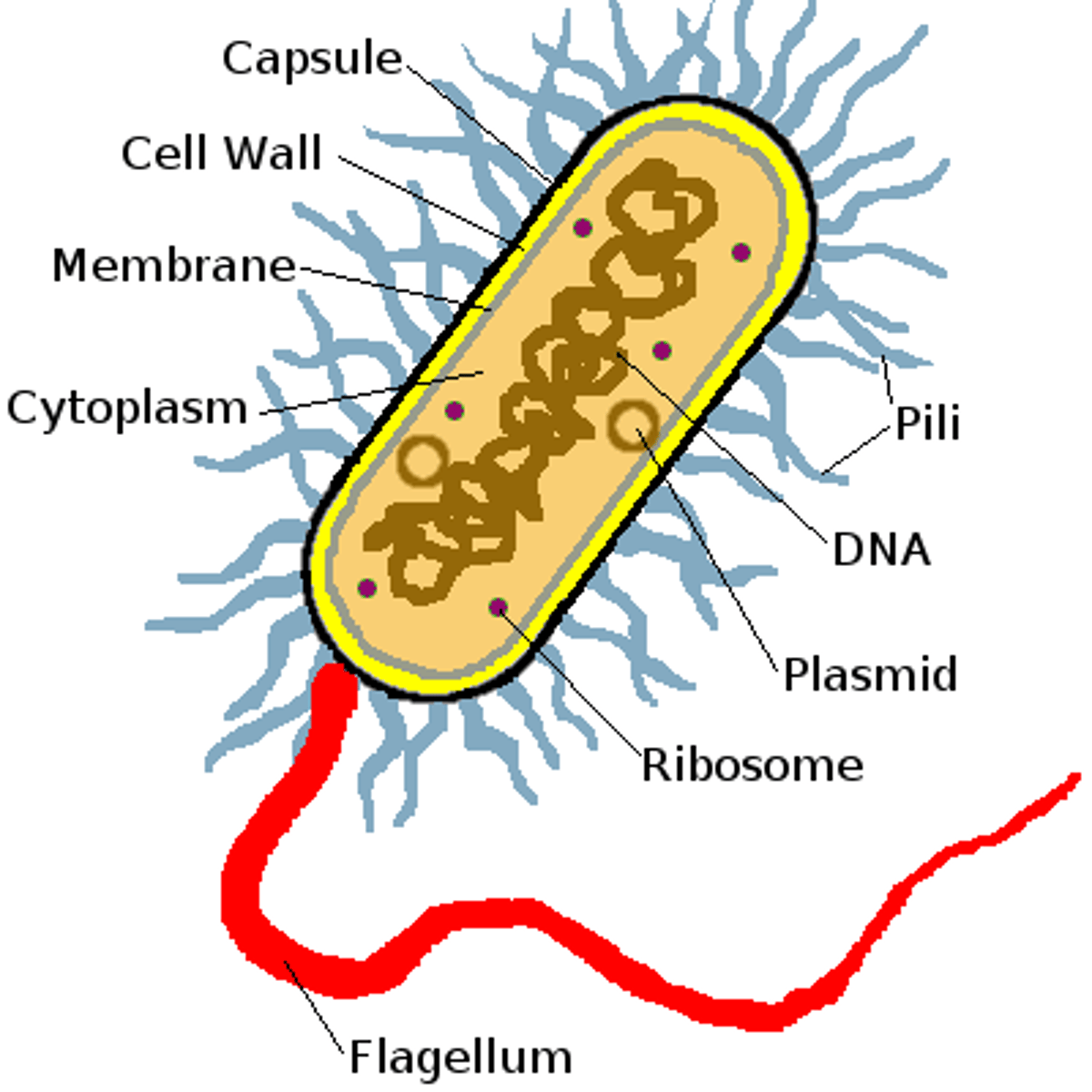
Bacterium (pl. bacteria)
A single-celled prokaryotic, microscopic organism that frequently grows in clusters. It can live symbiotically with other organisms and/or act as pathogens.
Band
A line seen in the gel after running gel electrophoresis that corresponds to a collection of DNA fragments of a specific size.
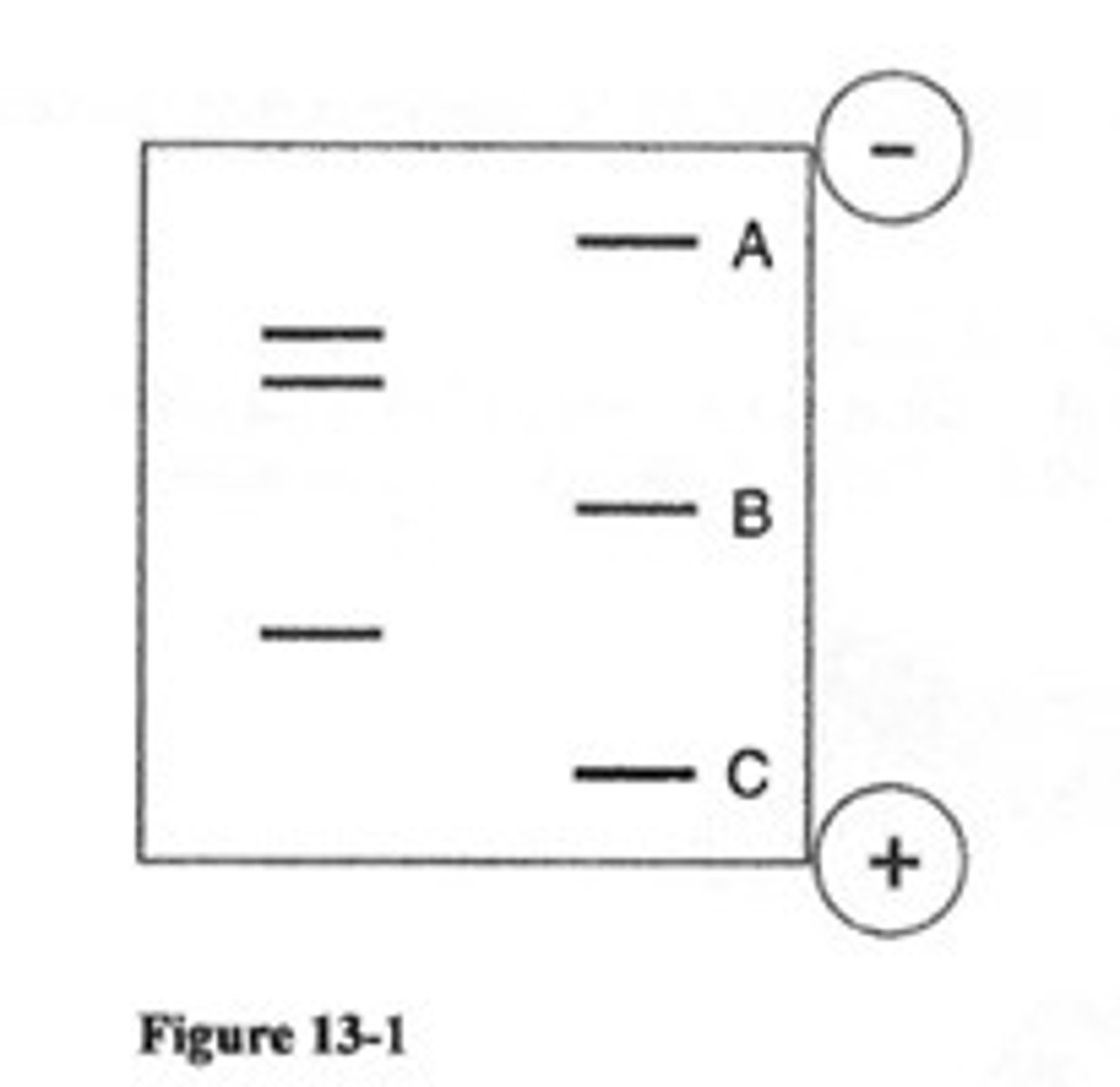
Base pair (bp)
A unit of measurement that corresponds to one nucleotide.
Benificence
An ethical concept that seeks to maximise benefits when taking a particular position or course of action.
Beta-pleated sheet
An organised folded secondary structure of proteins
Bioethical approach
A decision-making framework that helps guide ethical behaviour.
Bioethics
The study of ethics related to issues that arise in biology and medicine.
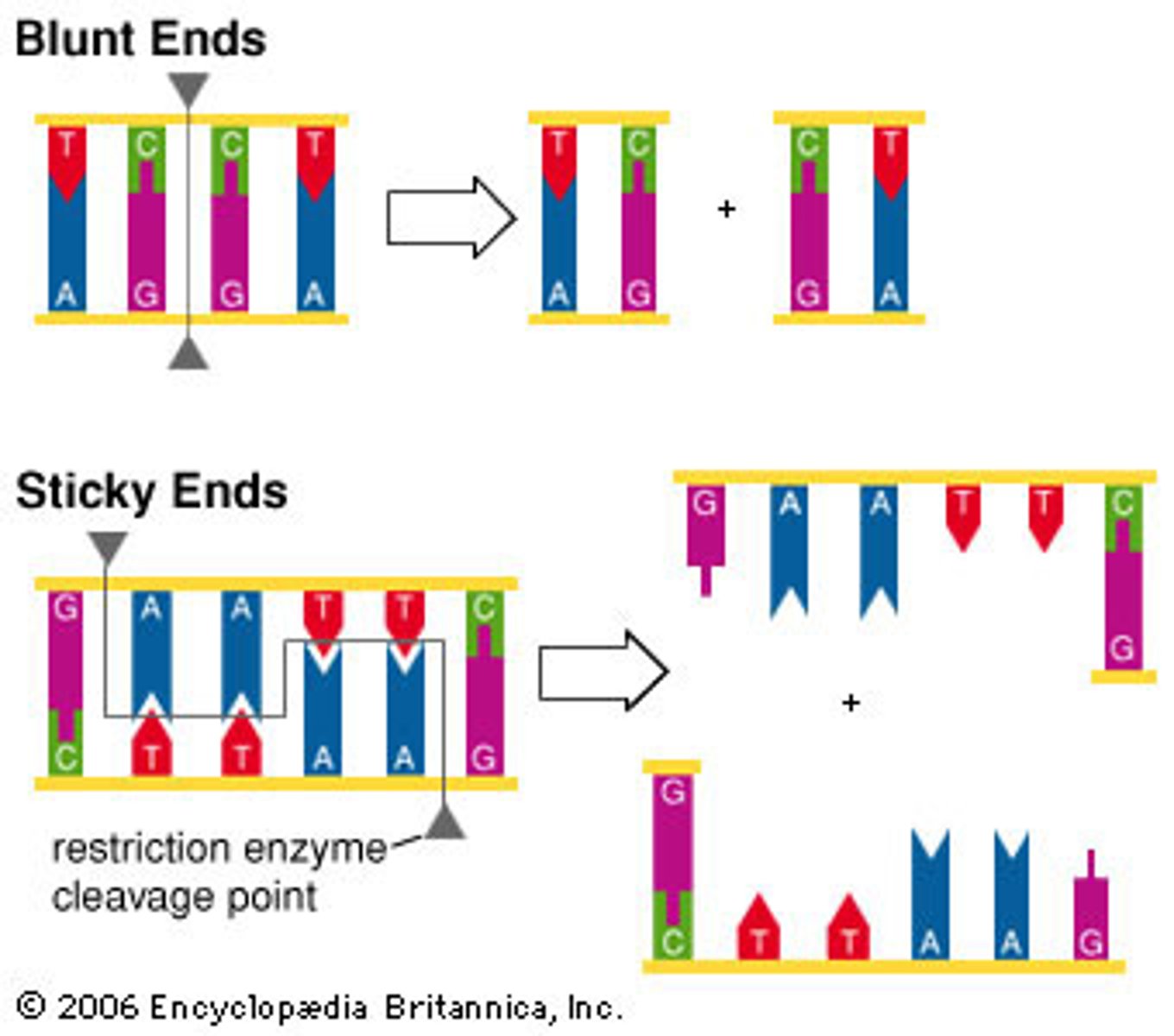
Blunt end
The result of a straight cut across the double-stranded DNA by an endonuclease resulting in no overhanging nucleotides.
Buffer
An ion-rich solution that carries electrical current through an agarose gel.
Carboxyl group
The functional group on amino acid molecules that contains a hydroxyl group (OH) and an oxygen double-bonded to a carbon atom.
Cisgenic organisms
A genetically modified organism that contains foreign genetic material from a sexually compatible donor organism, typically from the same species.
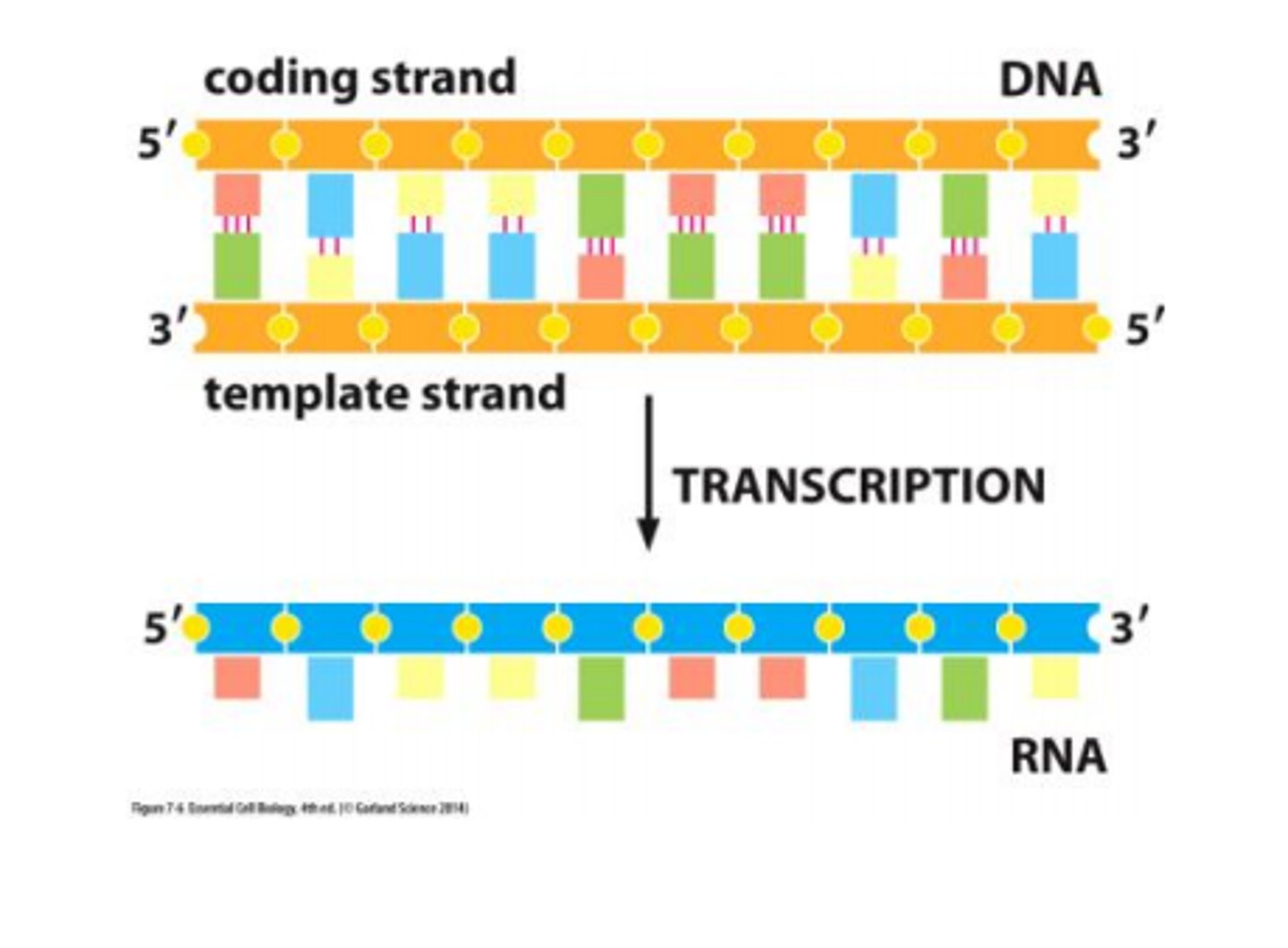
Coding strand
The strand of DNA not transcribed by RNA polymerase, contains an identical sequence to the mRNA strand produced (except thymine is replaced with uracil in mRNA).
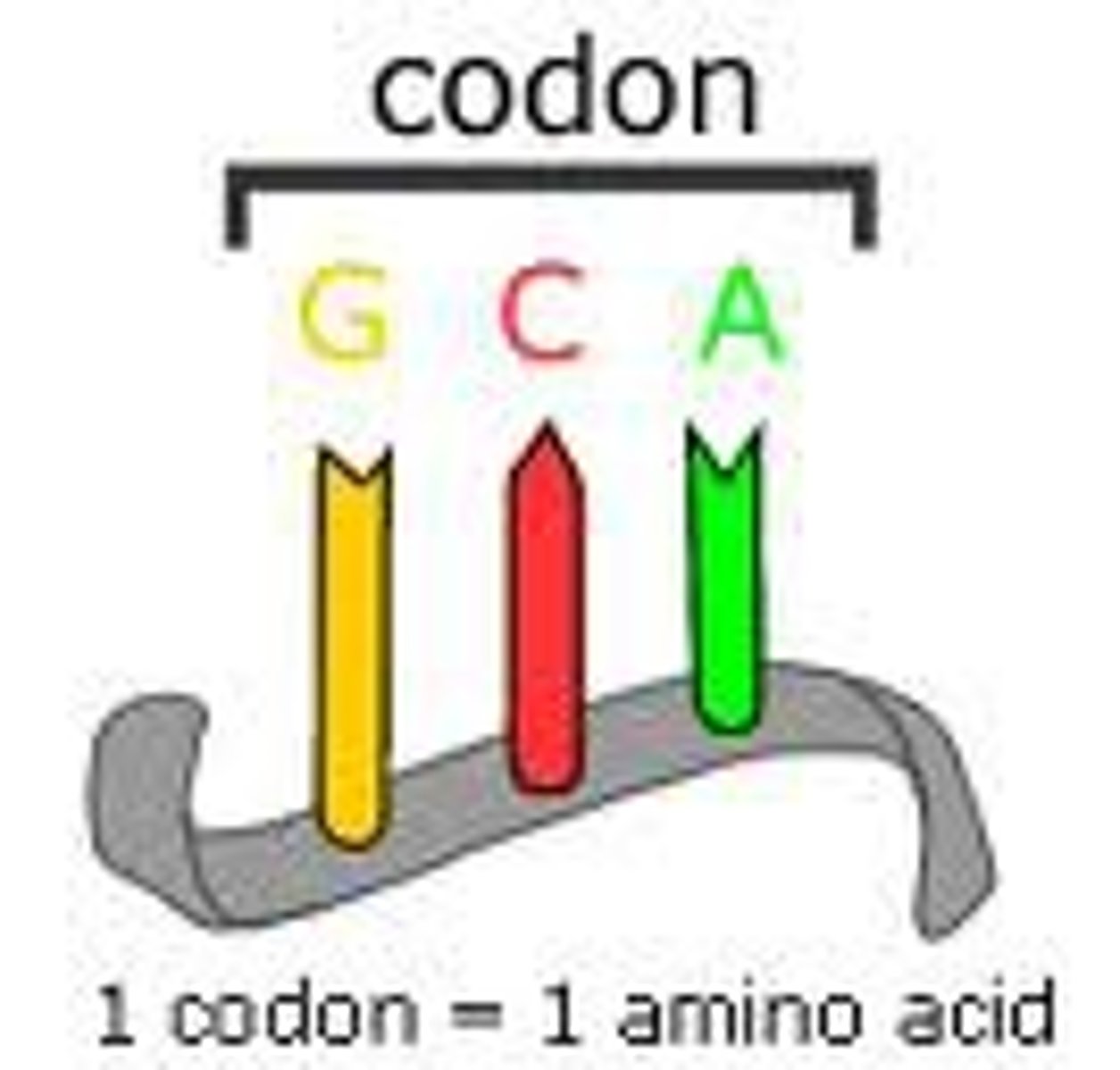
Codon
The sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA coding for one amino acid.
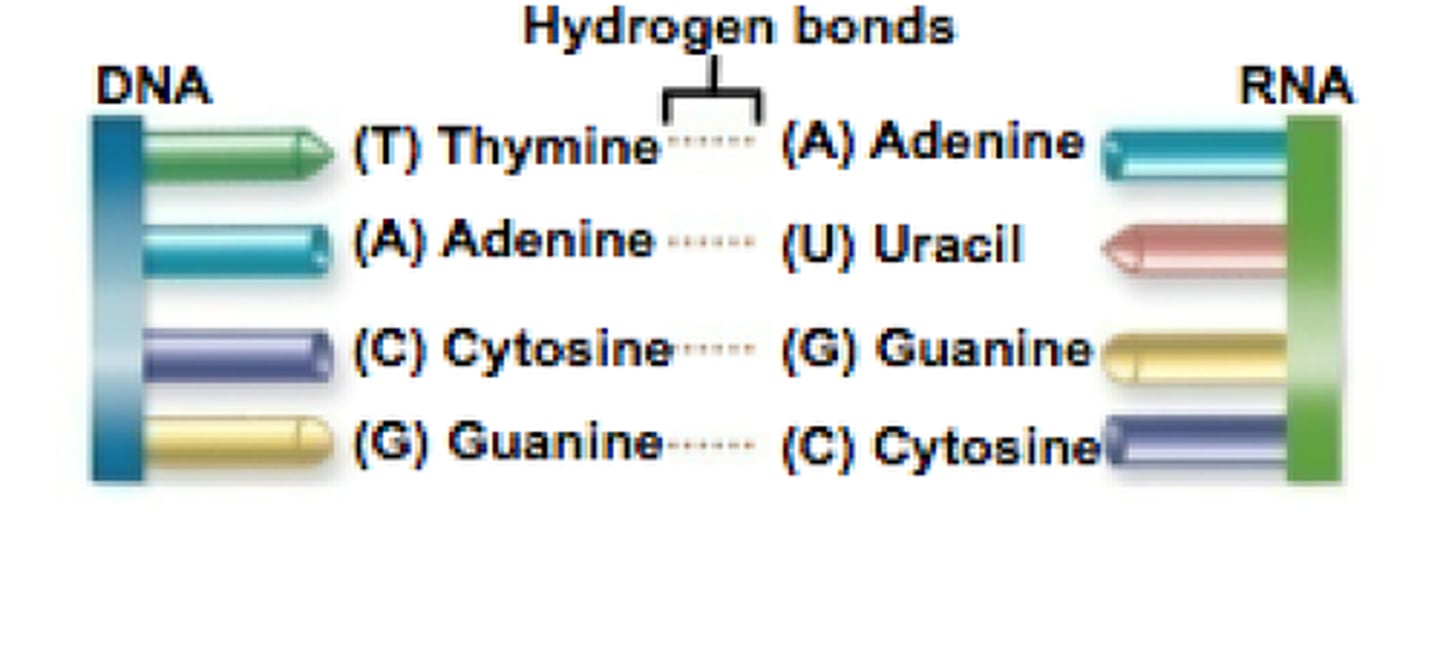
Complementary base pairing
Describes which nucleotides can form hydrogen bonds with each other. C pairs with G, A pairs with T (or U in RNA).
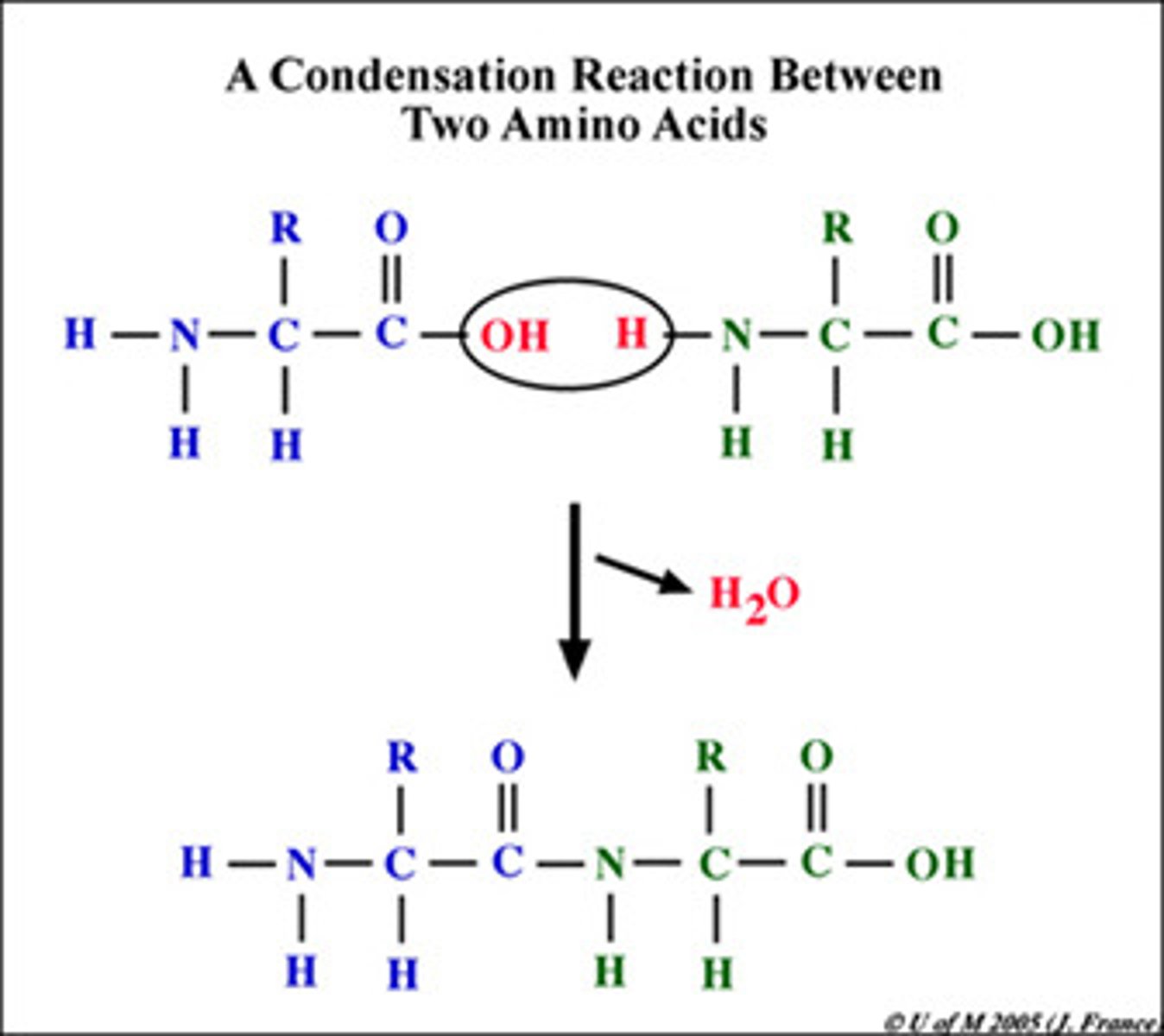
Condensation reaction
A reaction where two monomers join to form a larger molecule, producing water as a by-product.
Conformational change
A change in the three-dimensional shape of macromolecules such as proteins.
Consequences-based approach
An approach to bioethics that aims to maximise positive outcomes while minimising negative outcomes.
CRISPR
Short, clustered repeats of DNA found in prokaryotes which protects them against viral invasion
Degenerate
A property of the genetic code which means that a single amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon.
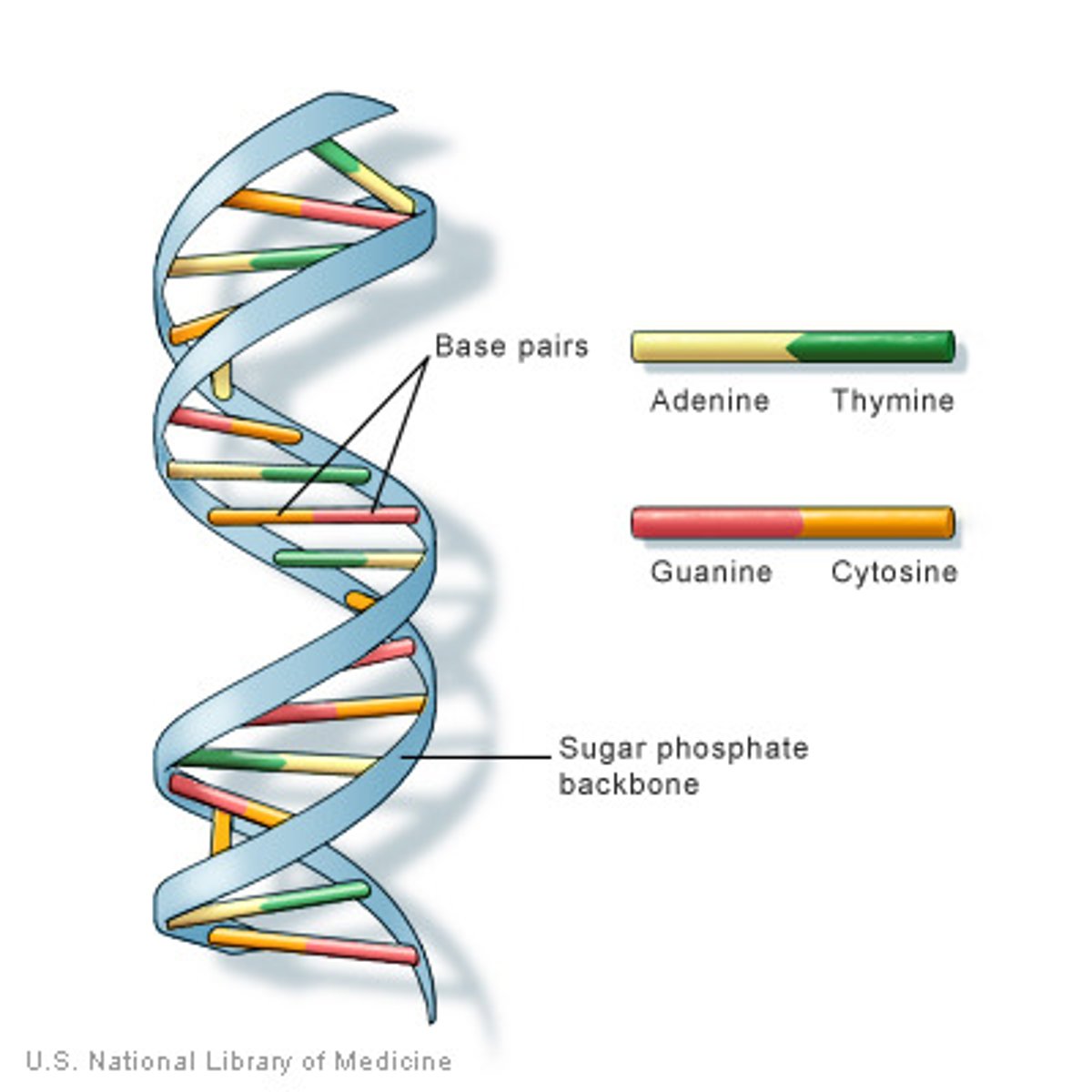
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A double-stranded nucleic acid chain made up of nucleotides. DNA carries the instructions for proteins which are required for cell and organism survival.
DNA profiling
The process of identification on the basis of an individual's genetic information.
Duty/rule-based approach
An approach to bioethics that promotes the responsibility of the agent above all else, and places importance on the duty of each individual.
Electrode
Conductors of electricity that are attached to both ends of a gel allowing an electrical current to pass through it.
Endonuclease
An enzyme that breaks the phosphodiester bond between two nucleotides in a polynucleotide chain.
Ethics
A field of knowledge that helps individuals exercise moral judgment and determine what is right and wrong.
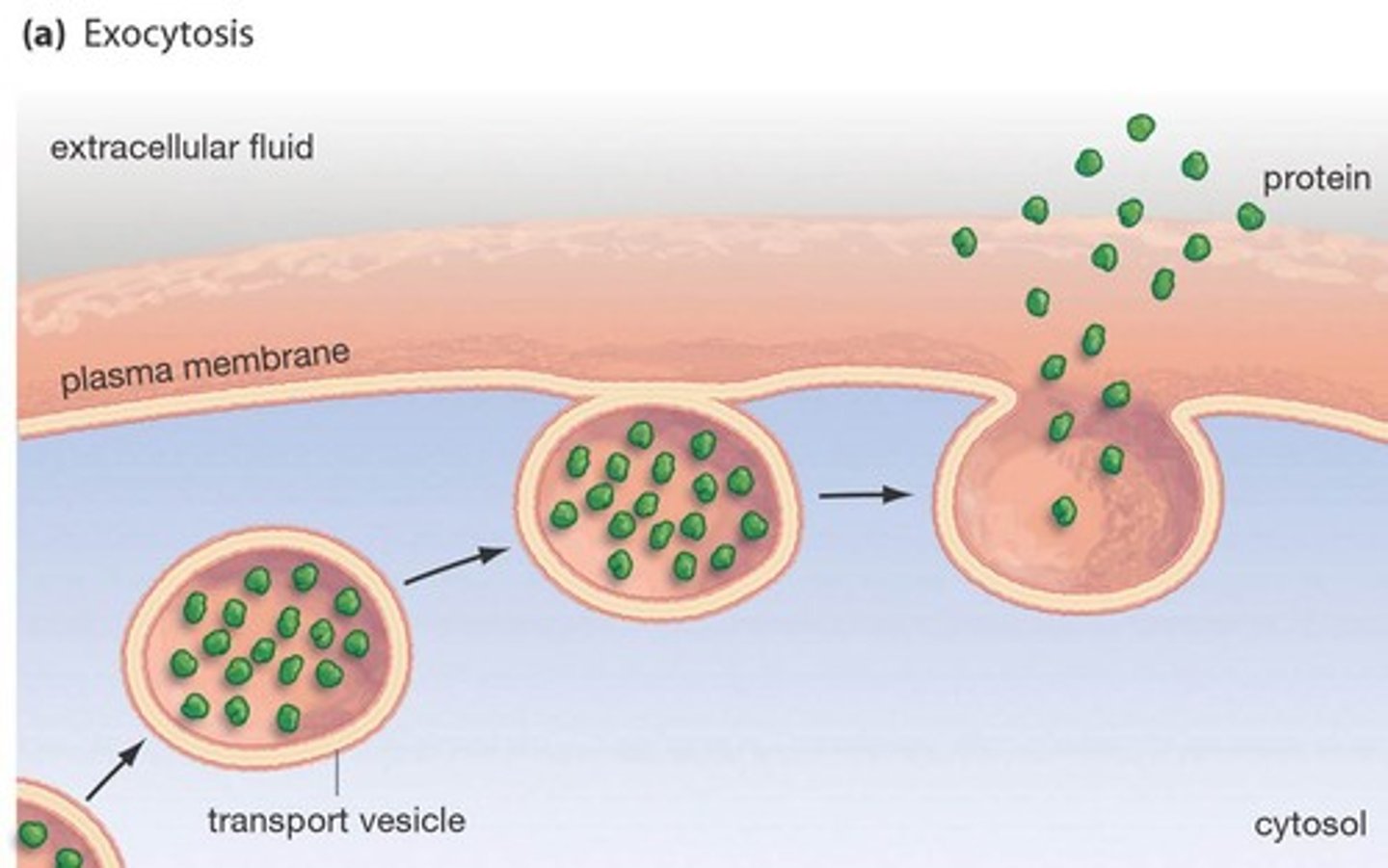
Exocytosis
A type of bulk transport that moves large substances out of a cell.
Forward primer
A DNA primer that binds to the 3' end of the template strand and reads the DNA in the same direction as RNA polymerase.
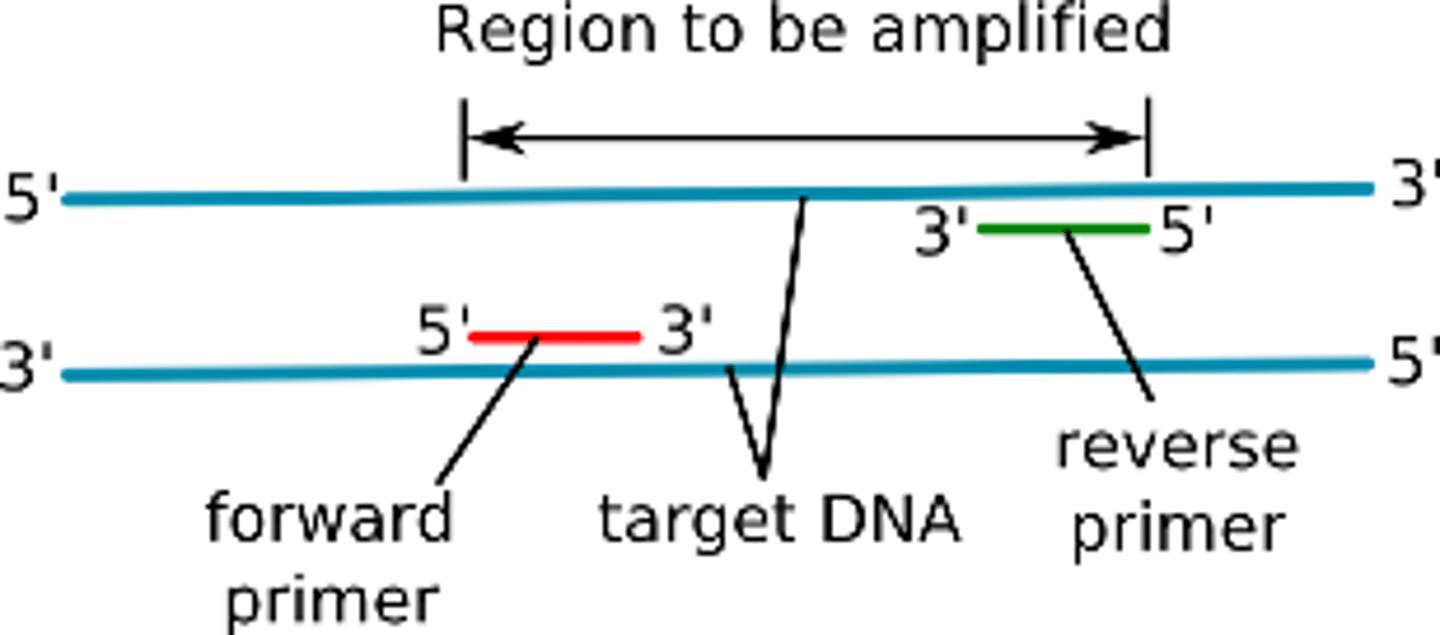
Gel electrophoresis
A technique that separates DNA fragments based on their molecular size.
Gene
A section of DNA that carries the code to make a specific protein or RNA product.
Gene expression
The process of reading the information stored within a gene to create a functional product, typically a protein.
Gene knock-in
A technique in gene editing where scientists substitute or add nucleotides in a gene.
Gene knockout
A technique in gene editing where scientists prevent the expression of a target gene to understand its function in an organism.
Gene of interest
A gene scientists want to be expressed in recombinant bacteria. This gene often encodes a protein we wish to produce in commercial quantities. Also known as the desired gene.
Genetic code
The set of rules by which information is encoded in genetic material.
Genetically modified organism (GMO)
Aan organism with genetic material that has been altered using genetic engineering technology.
Genome
The complete set of DNA housed within an organism.
Golgi apparatus
An organelle made of flattened sacs of membrane involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins. Also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex.
Guide RNA (gRNA)
RNA which has a specific sequence determined by CRISPR to guide Cas9 to a specific site.
Heat shock
A method that involves rapidly increasing and decreasing the temperature to increase membrane permeability in order to enhance the likelihood of bacterial transformation.
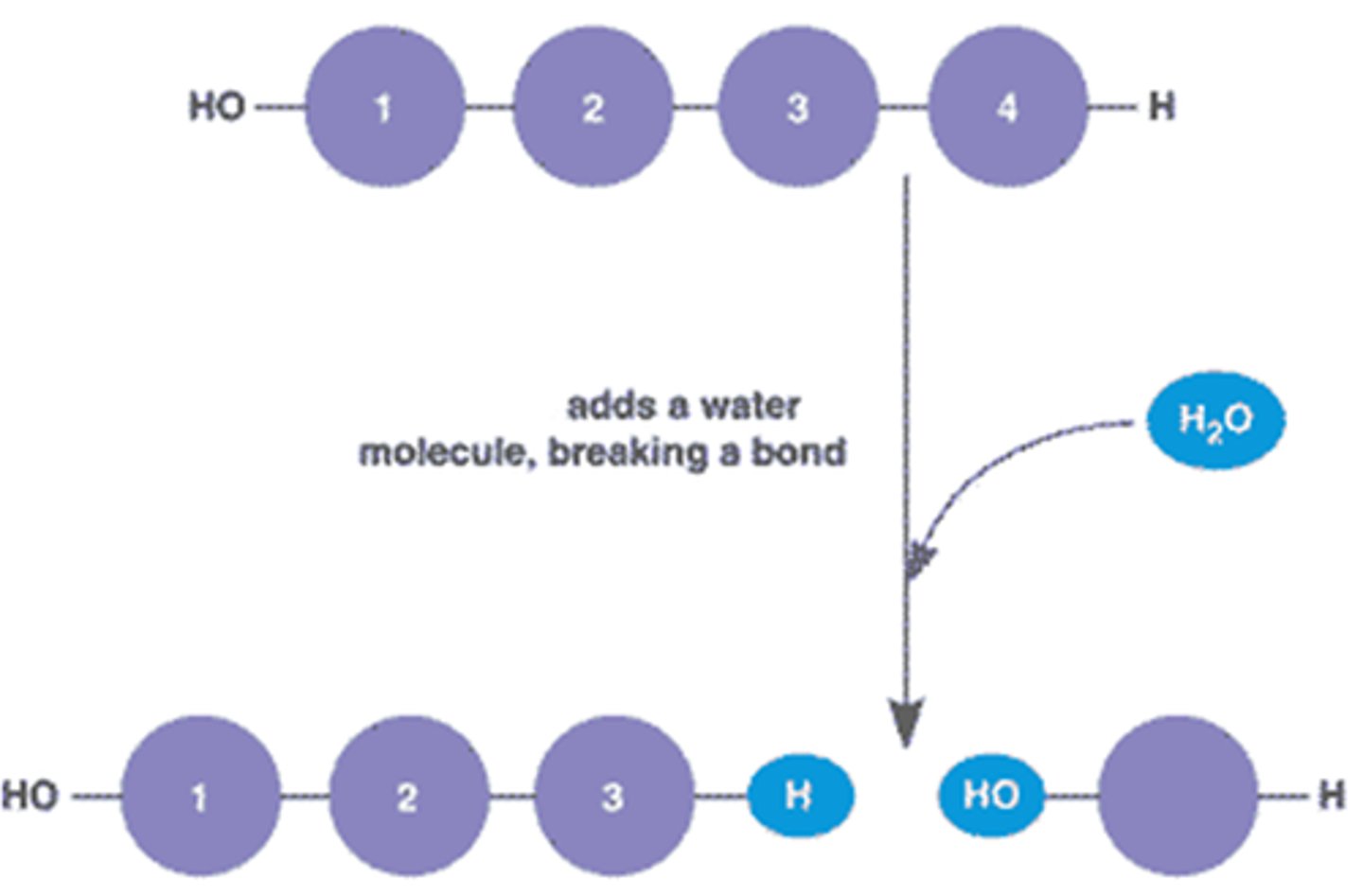
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction in which water is used to break down the chemical bonds of a substance.
Insulin
A hormone secreted by the pancreas to control blood glucose levels.
Integrity
An ethical concept that encourages a full commitment to knowledge and understanding as well as the honest reporting of all sources of information and results.
Introns
Non-coding regions of DNA that do not code for proteins. They are spliced out during RNA processing.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
RNA molecules that are produced during transcription and carry genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes.
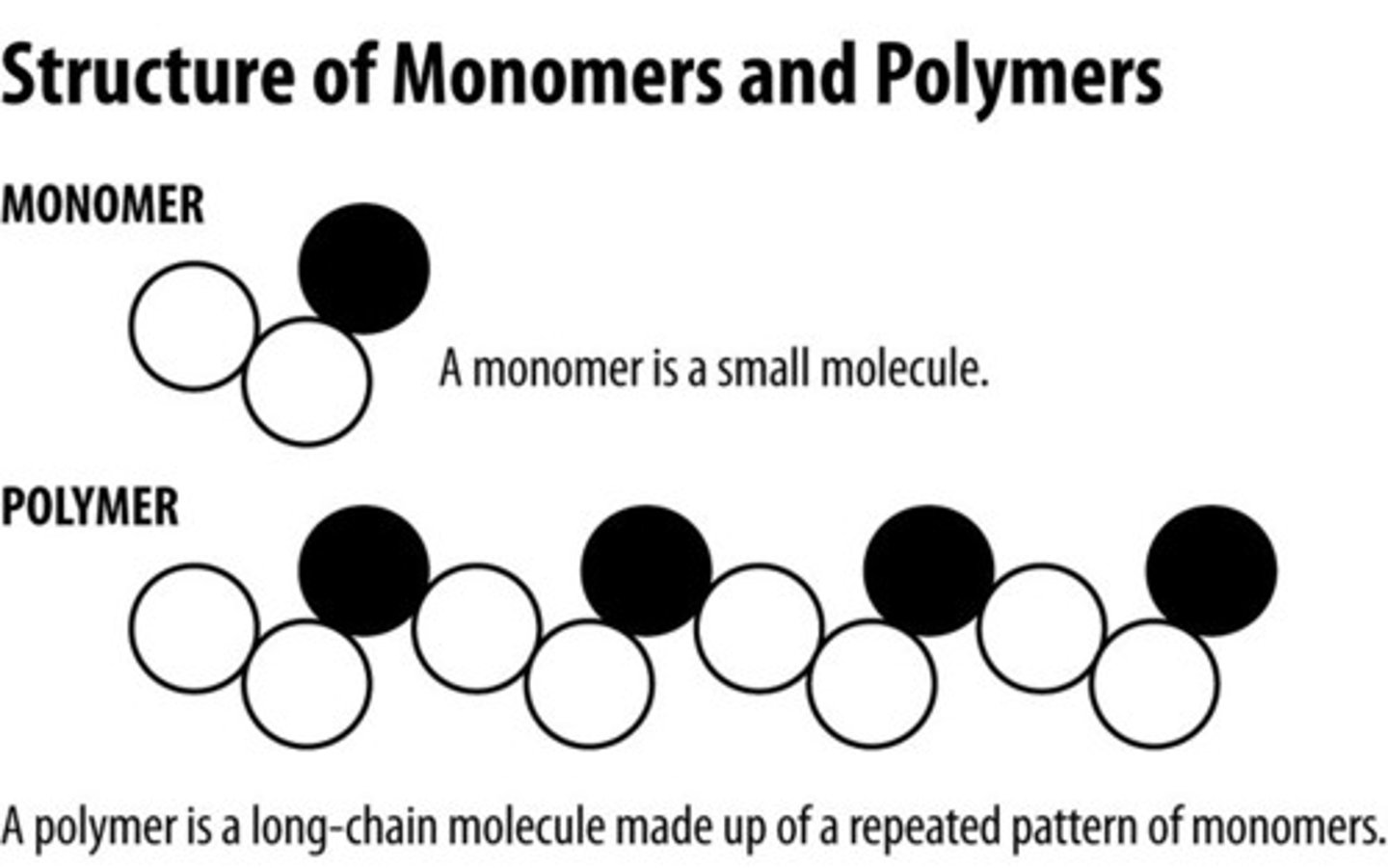
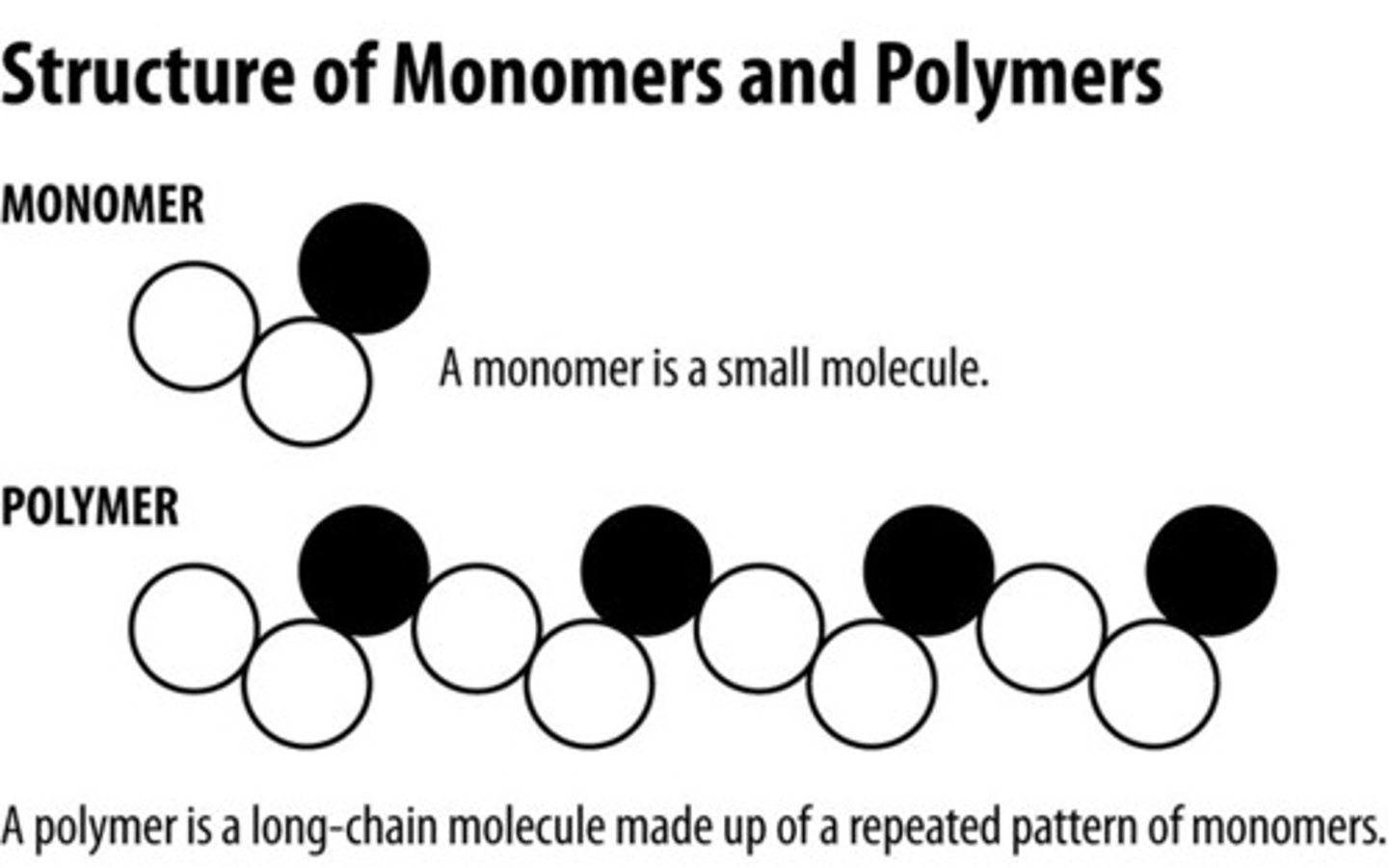
Monomer
A molecule that is the smallest building block of a polymer.
Non-malificence
An ethical concept that discourages causing harm - or when harm is unavoidable, ensuring that the harm is not disproportionate to the benefits from any position or course of action.
Nucleic acid
The class of macromolecule that includes DNA and RNA. All nucleic acids are polymers made out of nucleotide monomers.
Nucleotide
The monomer subunit of nucleic acids. Made up of a nitrogen-containing base, a five-carbon sugar molecule (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), and a phosphate group.
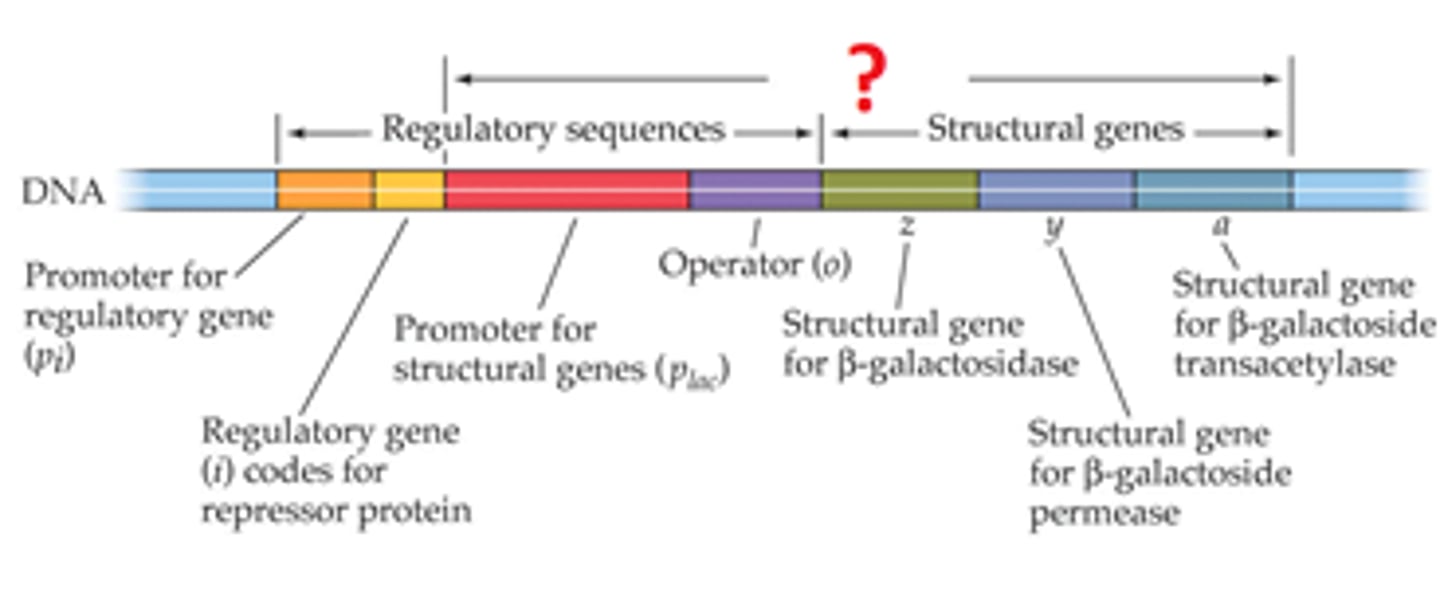
Operator
A short region of DNA that interacts with repressor proteins to alter the transcription of an operon.
Operon
A cluster of linked genes that all share a common promoter and operator and are transcribed at the same time.
Origin of replication (ori)
A sequence found in prokaryotes that signals the start site of DNA replication.
Overhanging nucleotides
Unbonded nucleotides on the ends of the DNA strand resulting from a staggered cut.
Peptide bond
The chemical bond linking two amino acids.
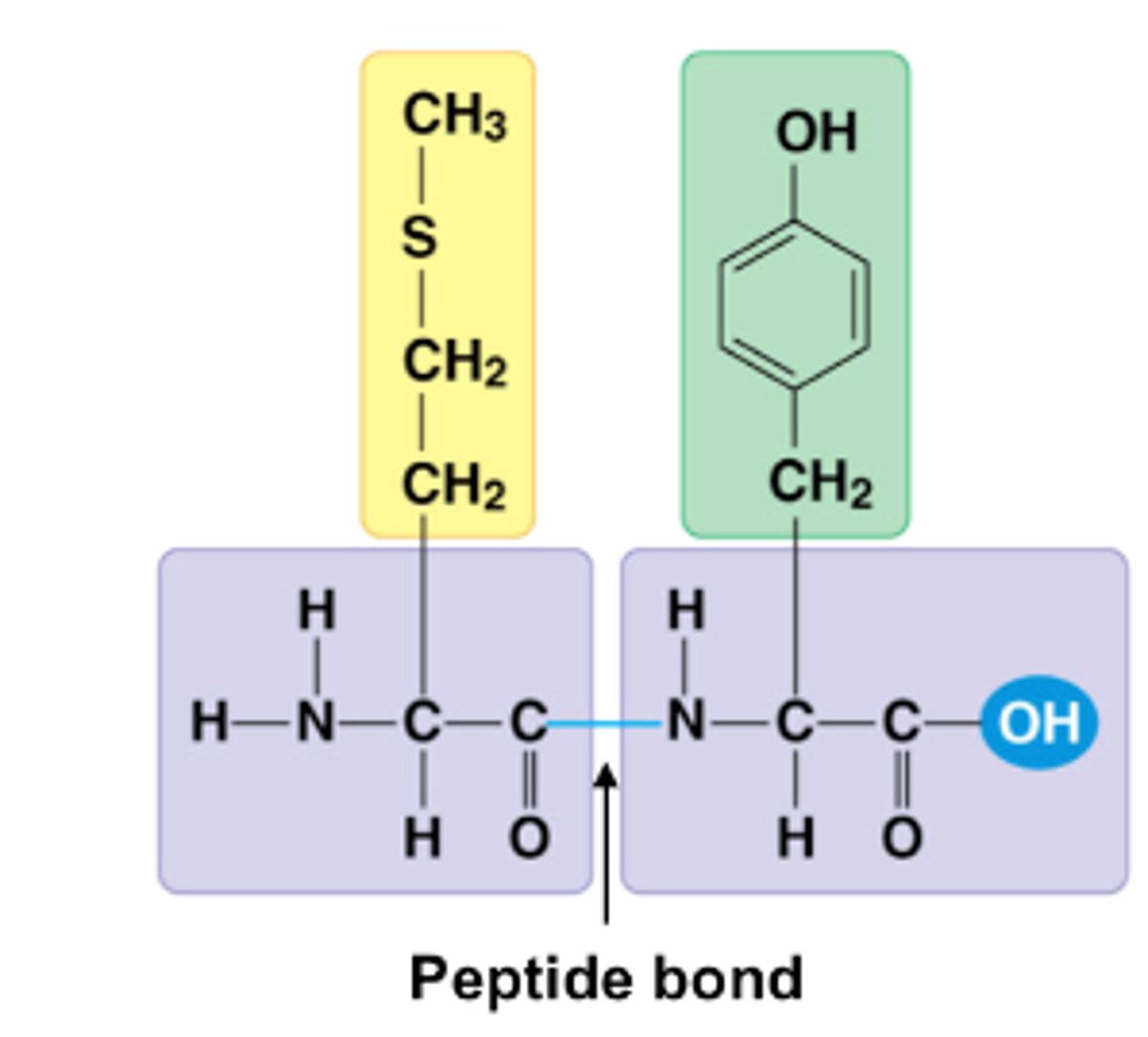
Phosphodieseter bond
A strong covalent bond linking a five-carbon sugar to a phosphate group.
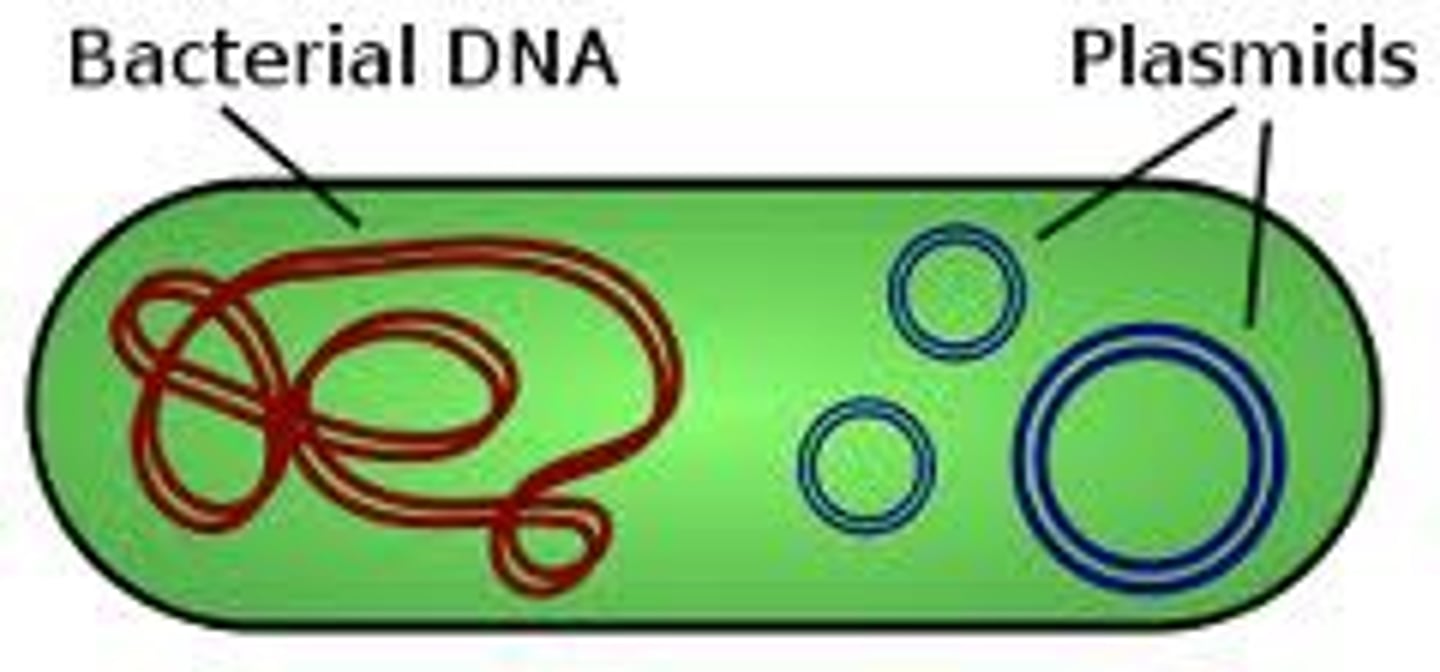
Plasmid
A small, circular loop of DNA separate from the chromosome, typically found in bacteria.
Polymer
A large molecule that is made up of small, repeated monomer subunits
Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesises a polymer from monomers, such as forming a DNA strand from nucleic acids.
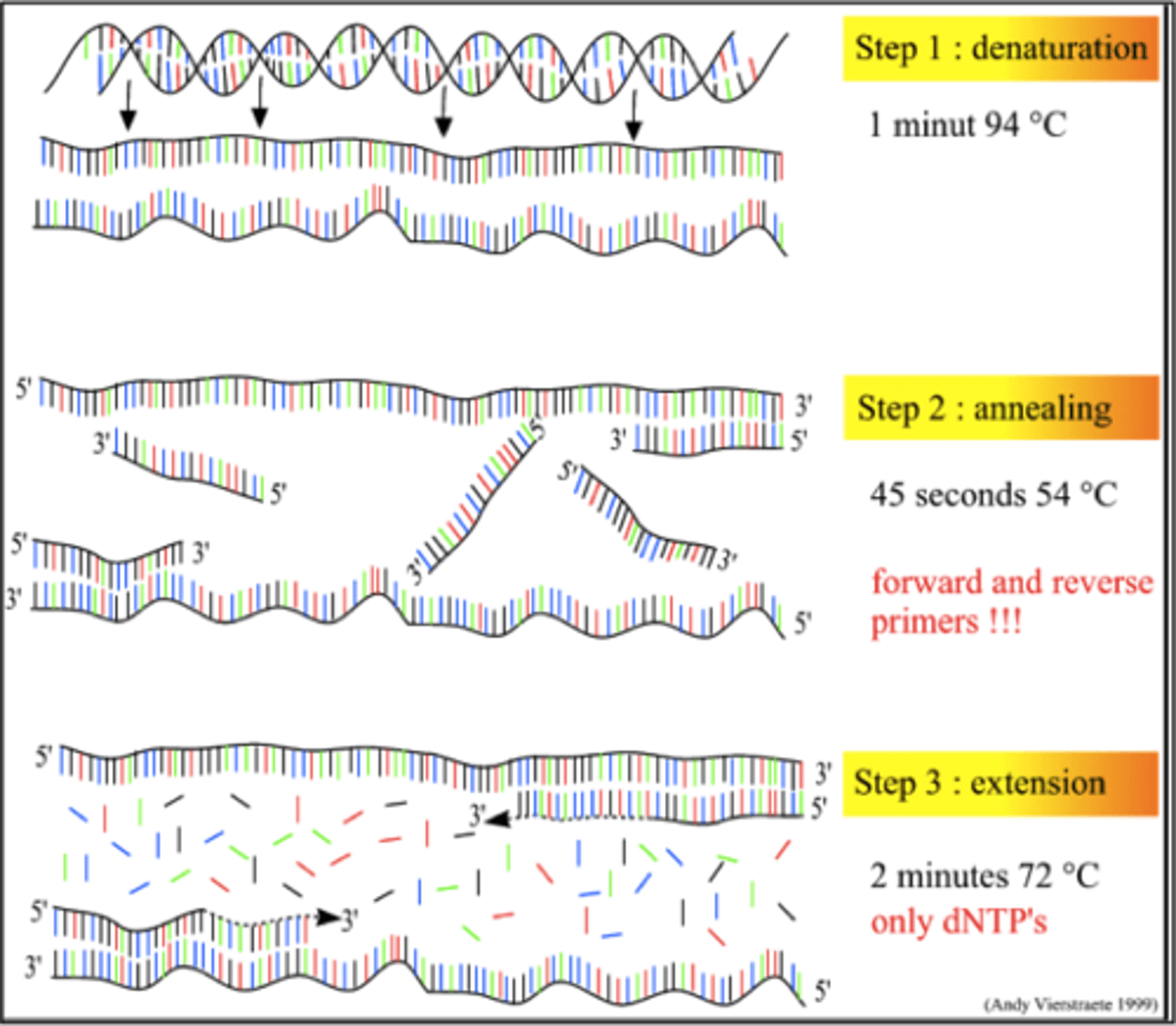
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A laboratory technique used to produce many identical copies of DNA from a small initial sample.
Polypeptide
A long chain of amino acids. Proteins can be made of one or many polypeptides.
Precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA)
the immediate product of transcription of a DNA sequence. Requires modifications before it can undergo translation.
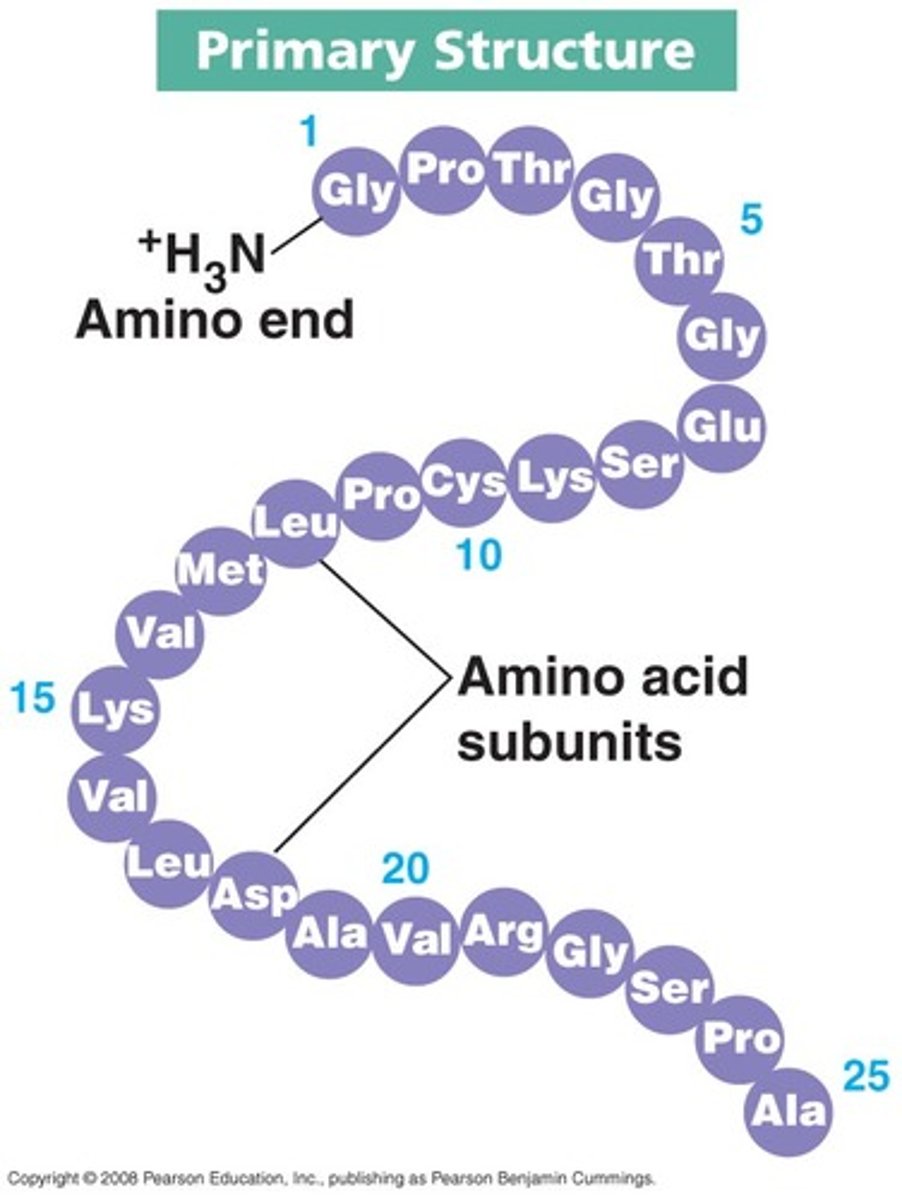
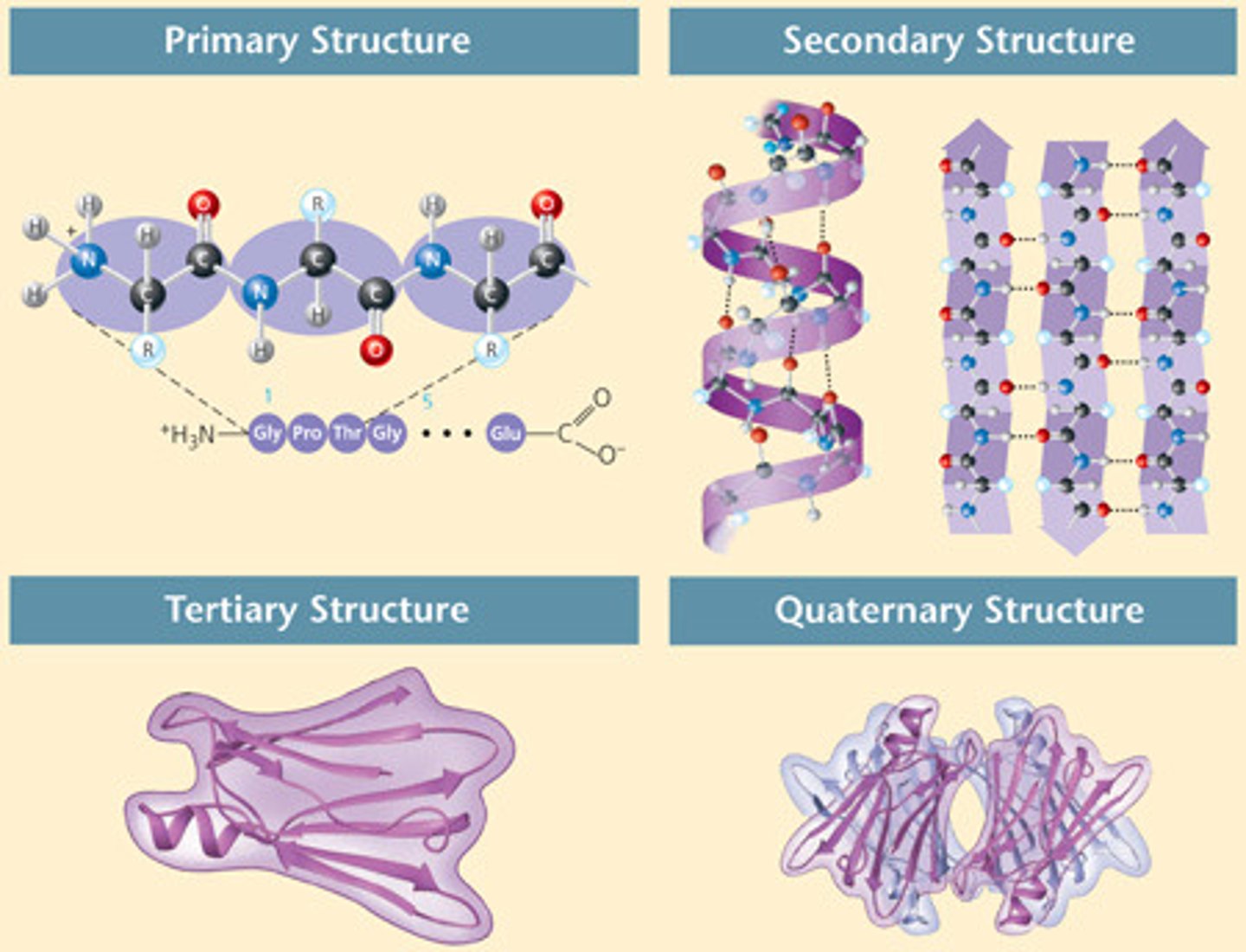
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure, which refers to the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
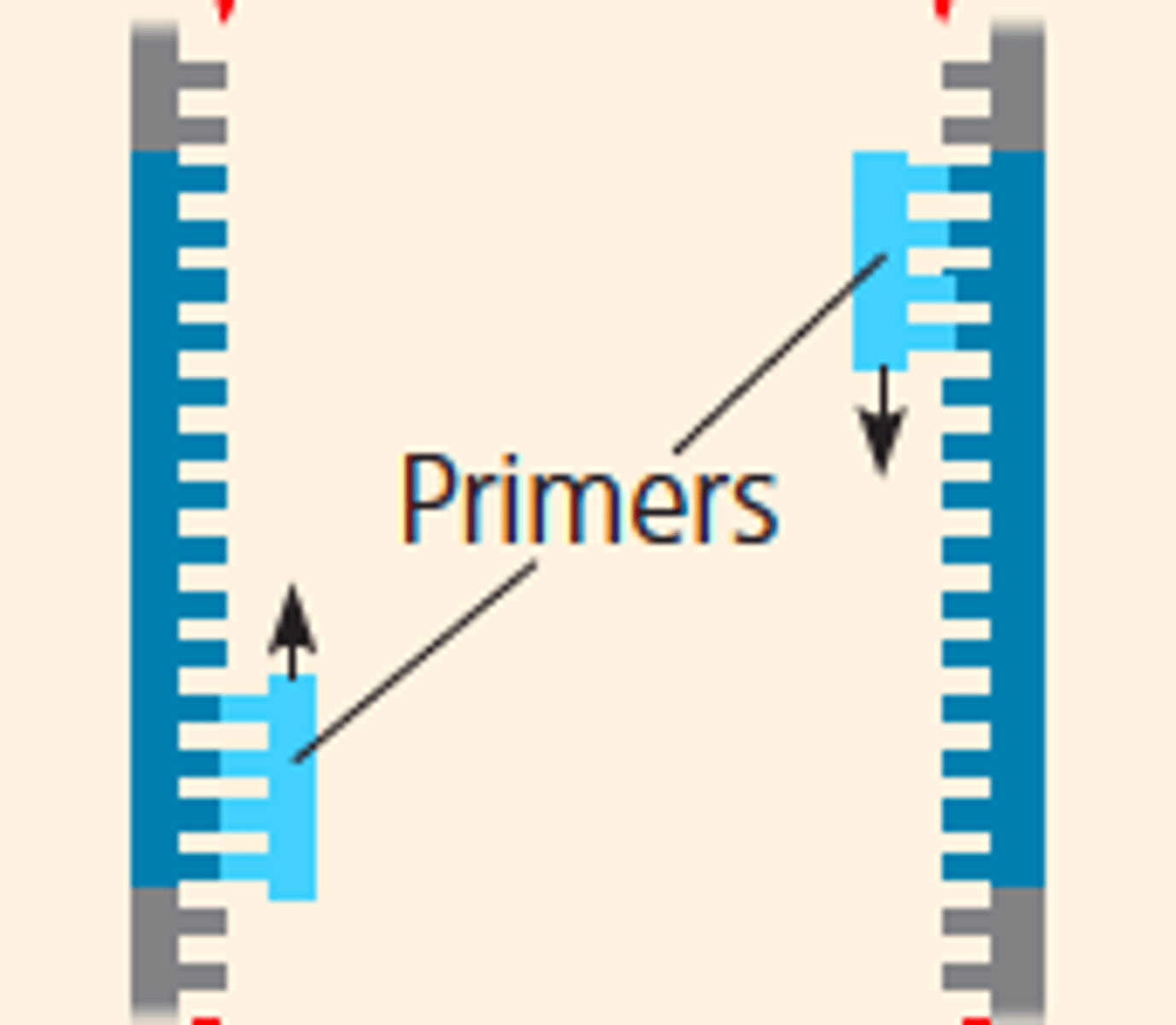
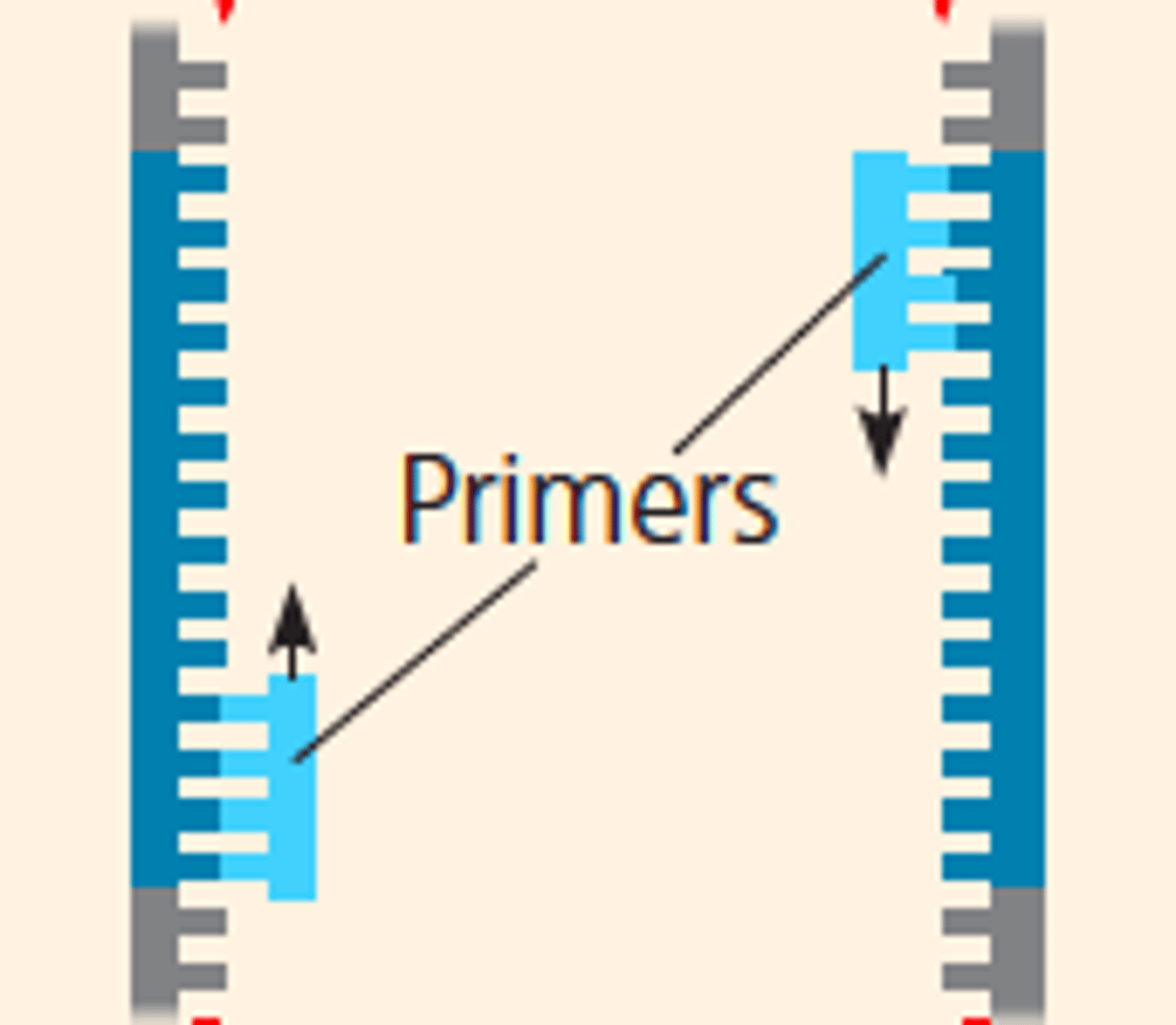
Primer
A short, single strand of nucleic acids that acts as a starting point for polymerase enzymes to attach.
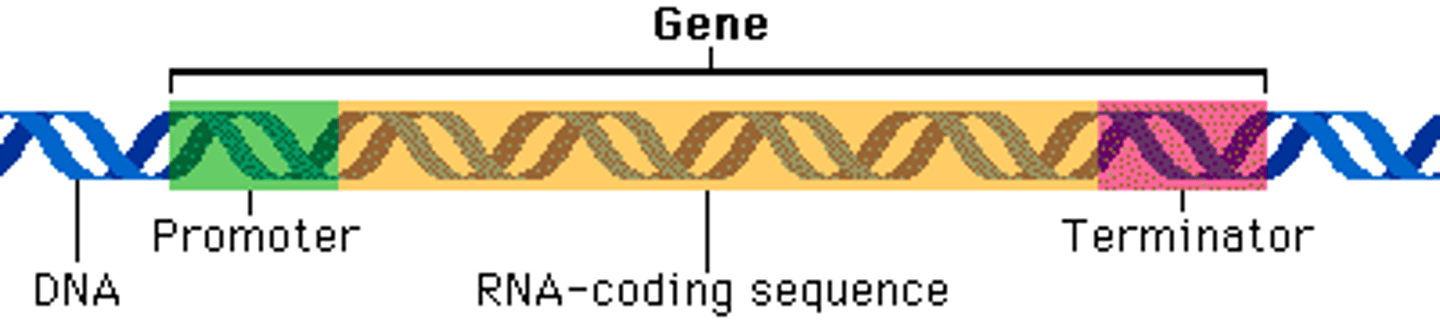
Promoter
The sequence of DNA to which RNA polymerase binds.
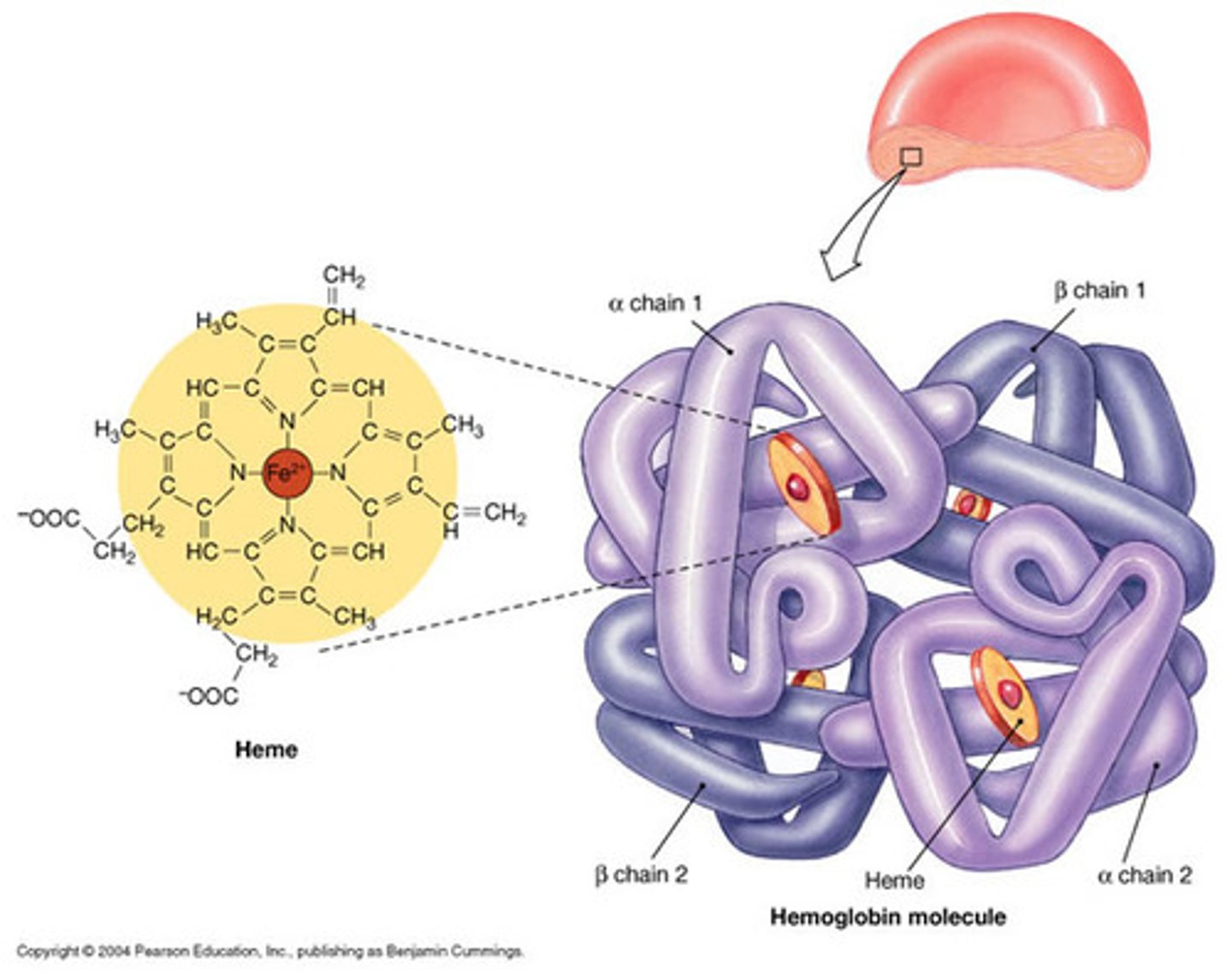
Prosthetic group
A non-protein group bound to a protein. For example, a vitamin or ion.
Protein
A biomacromolecule made of amino acid chains folded into a 3D shape.
Proteome
All the proteins that are expressed by a cell or organism at a given time.
Protospacer
A short sequence of DNA extracted from a bacteriophage by Cas1 and Cas2, which has yet to be incorporated into the CRISPR gene.
Protospacer Adjacent Motif (PAM)
A sequence of two-six nucleotides that is found immediately next to the DNA targeted by Cas9.
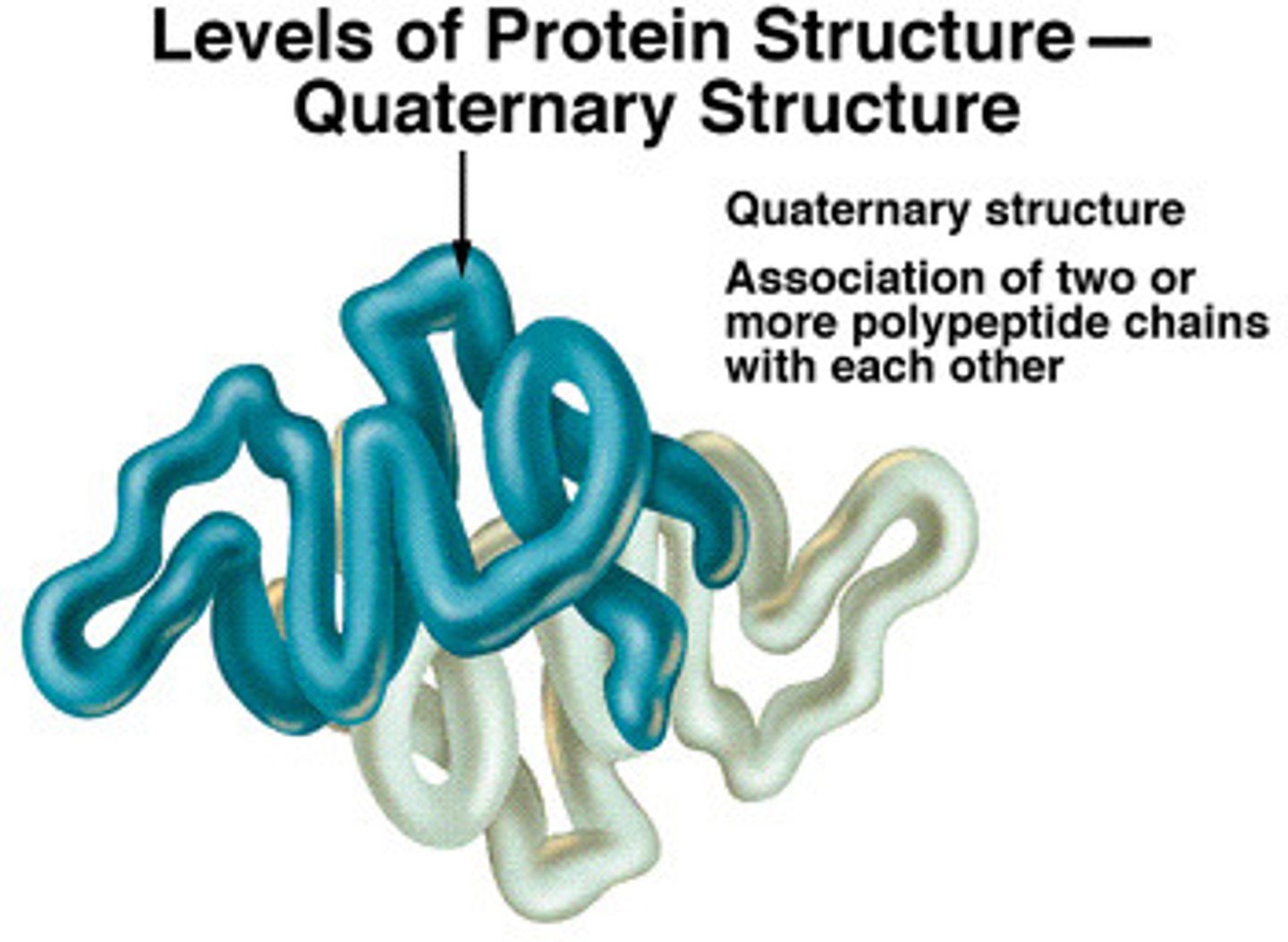
Quarternary structure
The level of protein structure where multiple polypeptide chains bond together, or other non-protein groups are added to form a fully functional protein.