Final
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
B
Which of the following statements about radicals and radical reactions is not true?
A) Most radicals are unstable.
B) A radical contains an atom that has an octet of electrons
C) Half-headed arrows are used to show the movement of lone electrons.
D) A radical is formed by homolysis of a covalent bond.
A
Which of the following statements about carbon radicals is not true?
A) Carbon radicals are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.
B) A carbon radical is sp2 hybridized.
C) The geometry of a carbon radical is trigonal planar.
D) The unhybridized p orbital in a carbon radical contains the unpaired electron
D
Which of the following statements about radicals is true?
A) Cleavage of a stronger bond forms the more stable radical.
B) The stability of a radical increases as the number of alkyl groups bonded to the
radical carbon decreases.
C) The higher the bond dissociation energy for a C-H bond, the more stable the
resulting carbon radical.
D) Less stable radicals generally do not rearrange to more stable radicals.
C
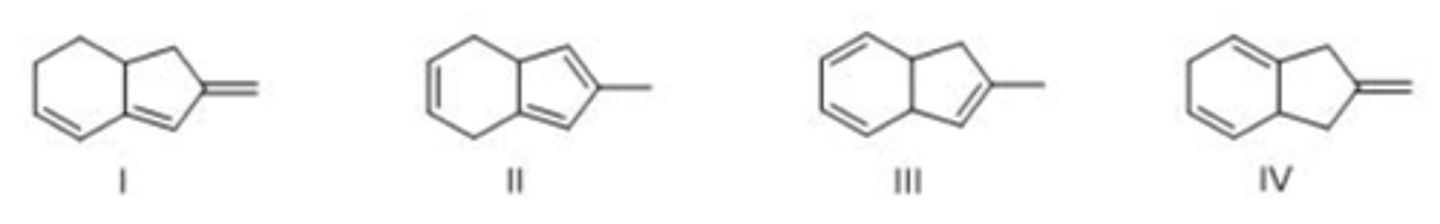
Which of the following compounds contain primary (1°) radical carbons?
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only II and IV
D
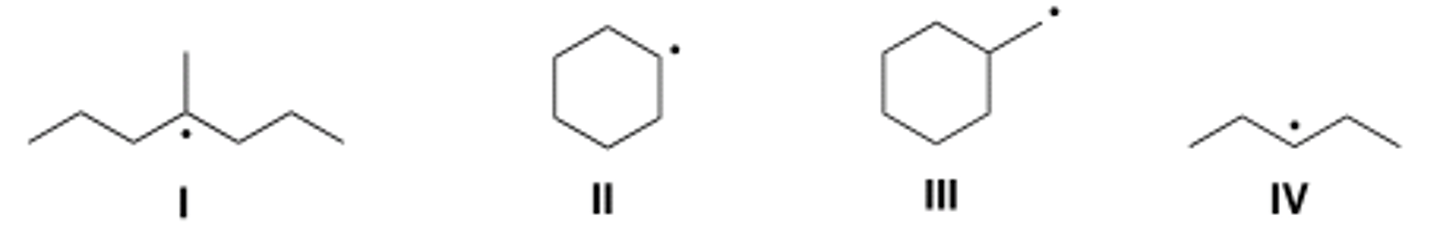
Which of the following compounds contain secondary (2°) radical carbons?
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only II and IV
A
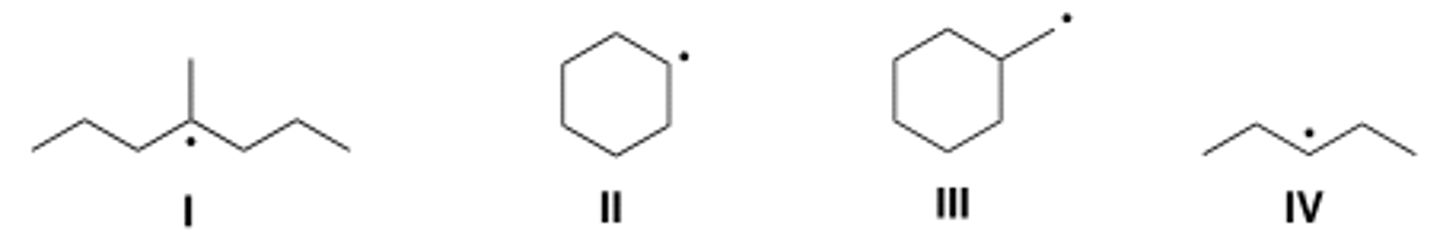
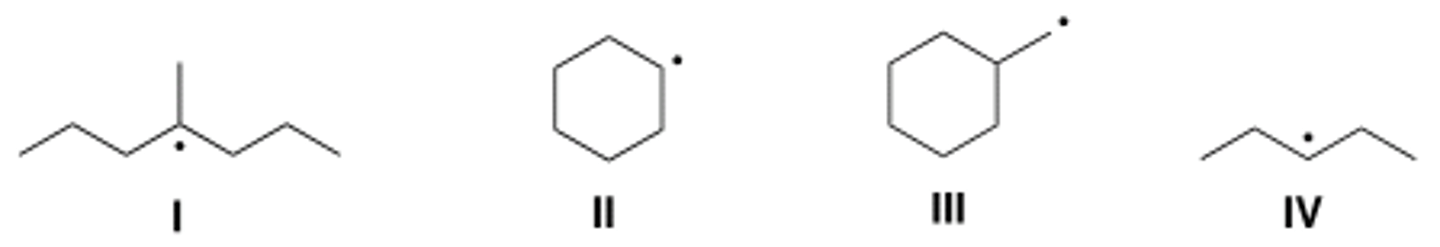
Which of the following compounds contain tertiary (3°) radical carbons?
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only II and IV
B
Which of the following is a radical scavenger?
A) O3
B) O2
C) Vitamin C
D) CO2
C
How many monochlorination products can be formed (constitutional isomers only) from
the reaction of (CH3)2CHCH2CH3 with Cl2 and hv?
A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5

A
How many monochlorination products can be formed (constitutional isomers only) from
the reaction of CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 with Cl2 and hv?
A) 3 B) 4 C) 5 D) 6

B
How many monochlorination products can be formed from the reaction of (CH3)3CH
with Cl2 and hv?
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4

D
Which of the following statements about radical reactions is not true?
A) Light or heat provides the energy needed for homolytic bond cleavage to form
radicals.
B) Breaking the weak O-O bond of peroxides initiates radical reactions.
C) The diradical O2 removes radicals from a reaction mixture.
D) Radicals rearrange.
B
Which step is the rate-determining step in the mechanism of radical halogenation?
A) Initiation
B) Propagation
C) Termination
D) Initiation and Propagation
A
Which of the following statements about the propagation steps in the chlorination of
ethane is true?
A) Radical chlorination consists of two propagation steps.
B) The energy diagram for the propagation steps has three energy barriers.
C) The first of the propagation steps is rate-determining because its transition state is
at lower energy.
D) The second of the propagation steps is rate-determining because its transition state
is at higher energy.
C
Which of the following statements about chlorination and bromination is true?
A) Bromination is unselective, yielding a mixture of products.
B) Chlorination is often selective, yielding one major product.
C) Chlorination is faster than bromination.
D) Bromination is faster than chlorination.
D
Which of the following statements about bromination is true?
A) The rate-determining step in bromination is exothermic.
B) Both radicals are formed.
C) A mixture of products results.
D) A single radical halogenation product predominates.
D
Which of the following statements about chlorination is true?
A) The rate-determining step in chlorination is endothermic.
B) The transition state resembles the product.
C) The more stable radical is formed faster.
D) A mixture of products results.
B
What is the product in the following sequence of reactions?
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
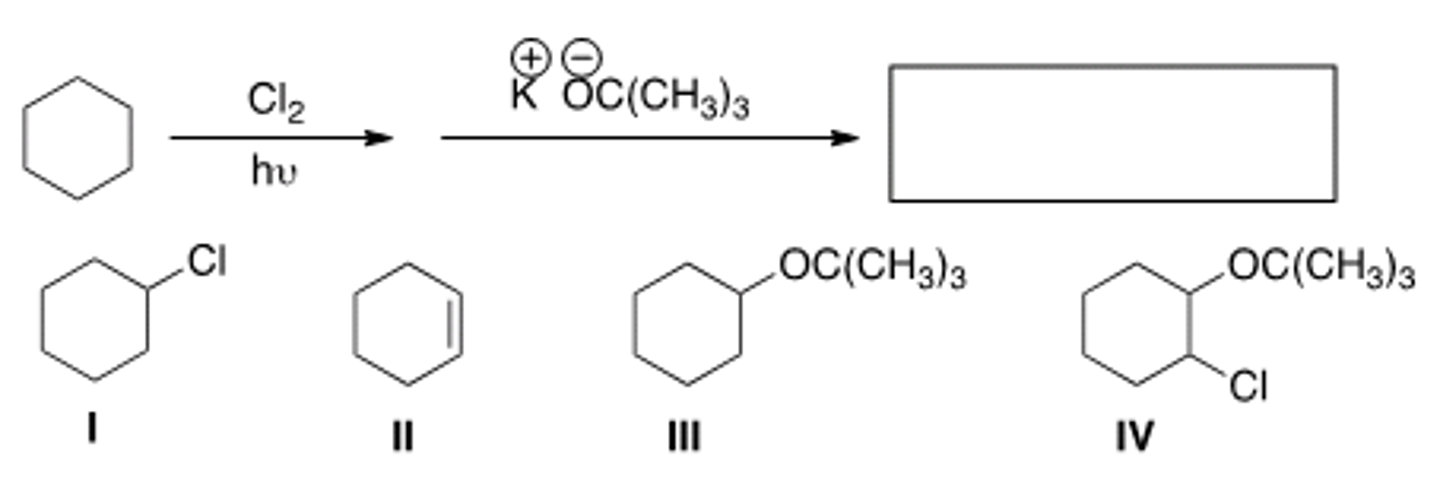
A
What is the product in the following sequence of reactions?
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
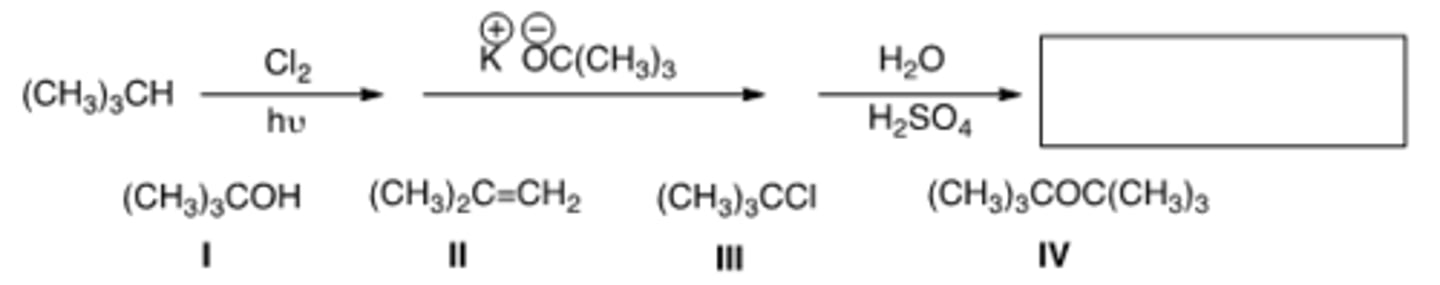
D
Which of the following statements about the stereochemistry of halogenation reactions
is true?
A) An achiral starting material always gives an achiral product only.
B) An achiral starting material always gives a racemic product only.
C) The configuration at a stereogenic center of a product must change even if a
reaction does not occur at a stereogenic center.
D) An achiral starting material always gives either an achiral or a racemic product.
B
How many monochlorination products (constitutional isomers and stereoisomers) are
formed from the reaction of butane with Cl2 and hn?
A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5
C
How many monochlorination products (constitutional isomers and stereoisomers) are
formed from the reaction of pentane with Cl2 and hv?
A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5
C
Rank the following radicals in order of increasing stability, putting the least stable first.
A) III < I < II
B) I < II < III
C) III < II < I
D) I < III < II
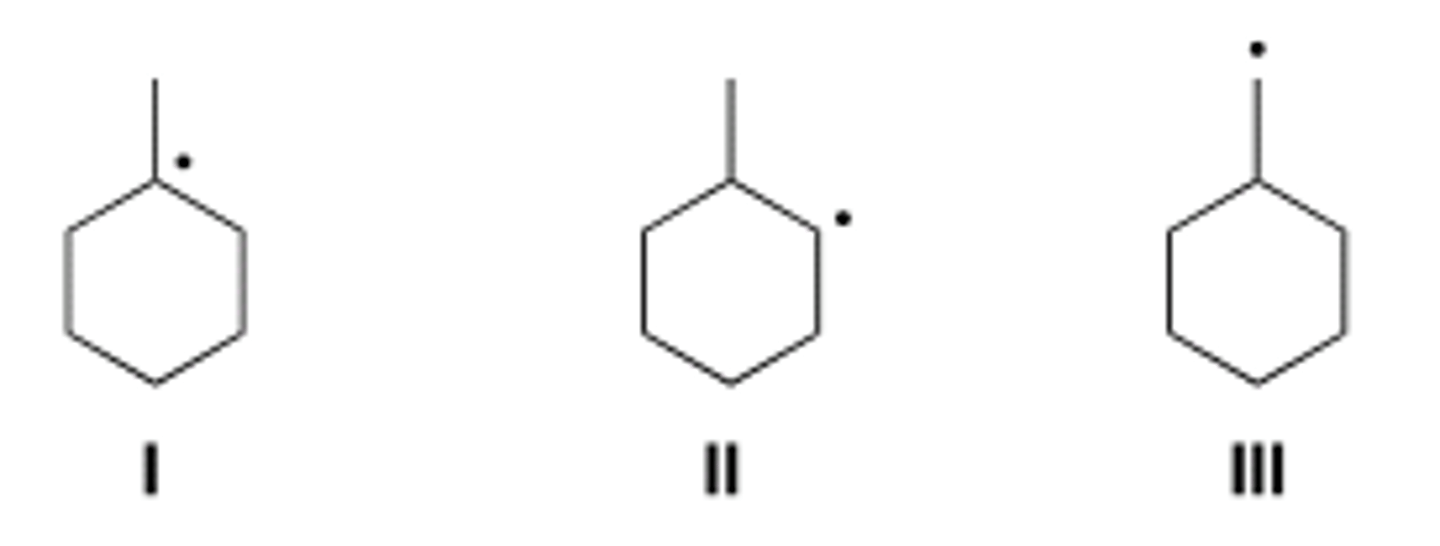
A
Rank the following radicals in order of decreasing stability, putting the most stable first.
A) II > IV > III > I
B) III > II > IV > I
C) IV > III > II > I
D) IV > III > I > II
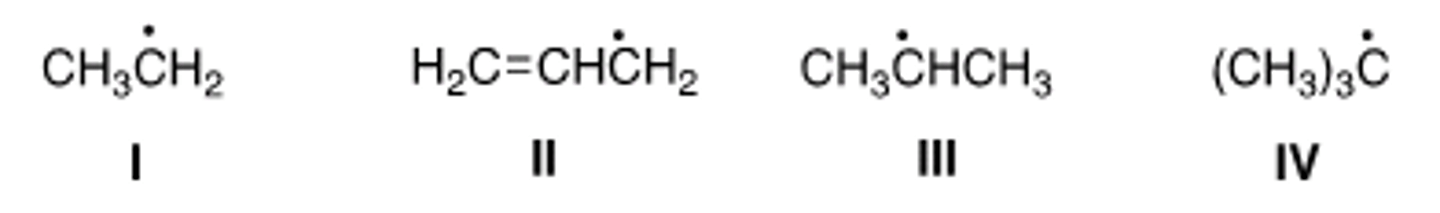
D
What is the product of the following reaction?
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
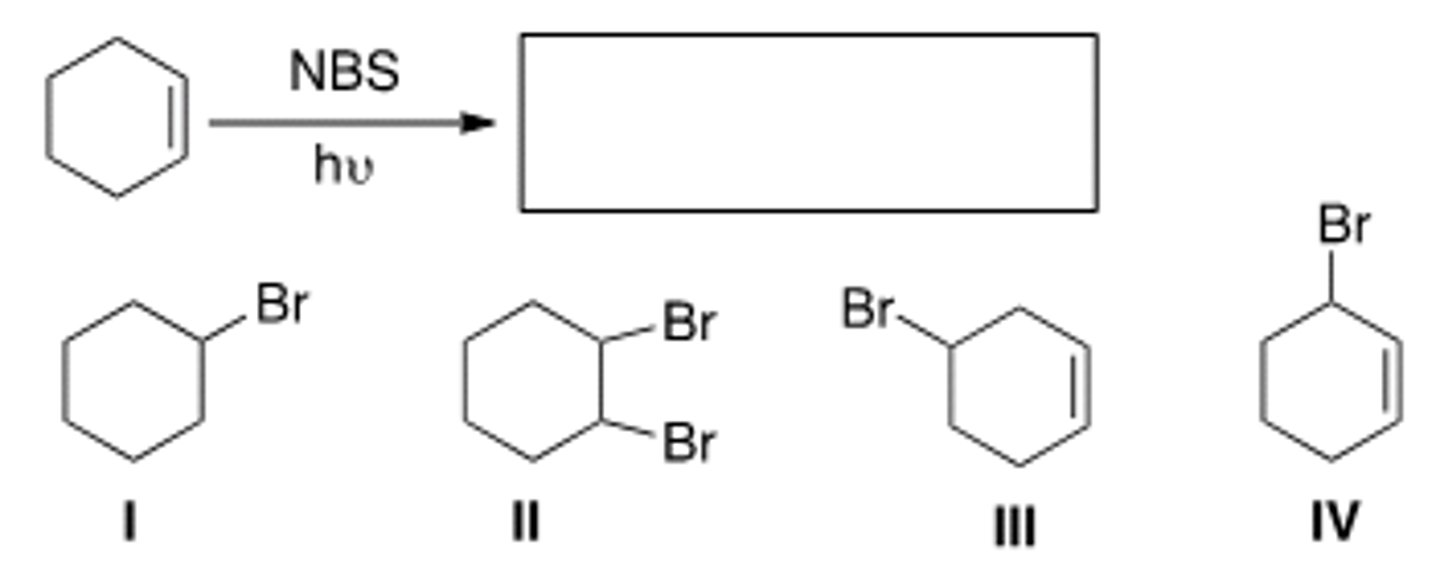
B
What is the product of the following reaction?
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
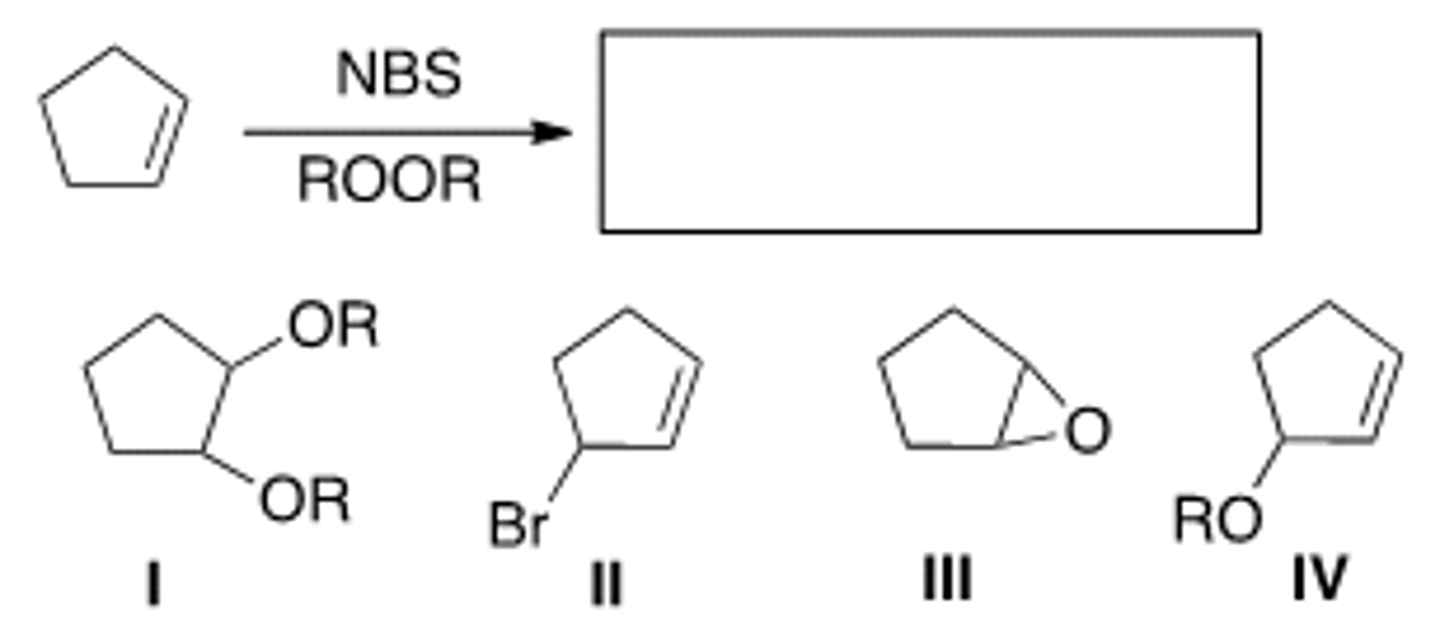
D
How many allylic halides can be formed when 3-methycyclohexene undergoes allylic
halogenation with one equivalent of NBS and light?
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
A
What is the product of the following reaction?
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
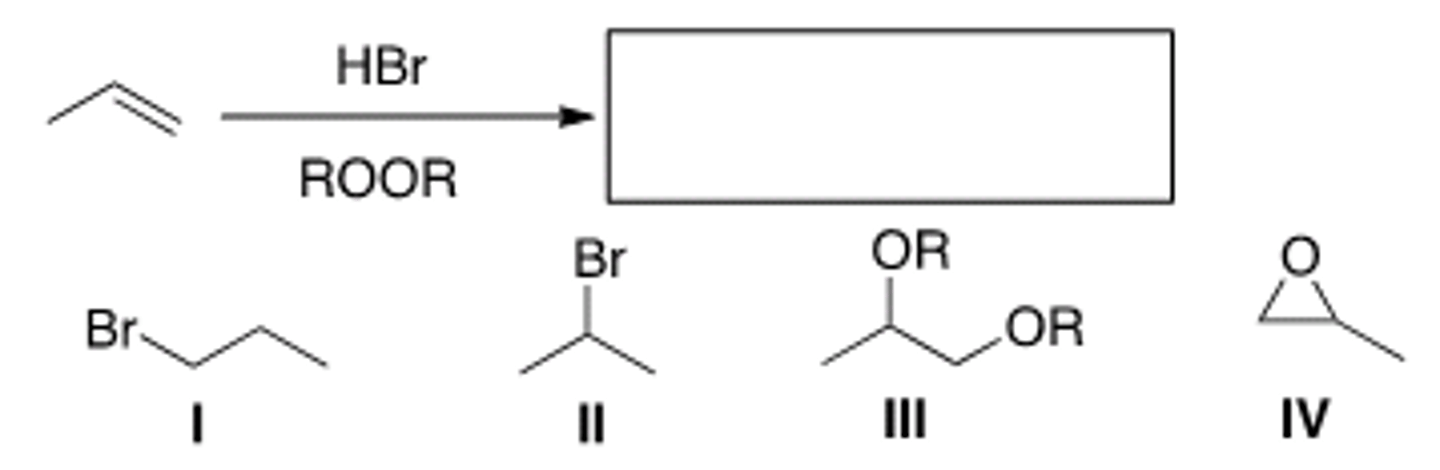
A
Identify the monomer used to make the following polymer.
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
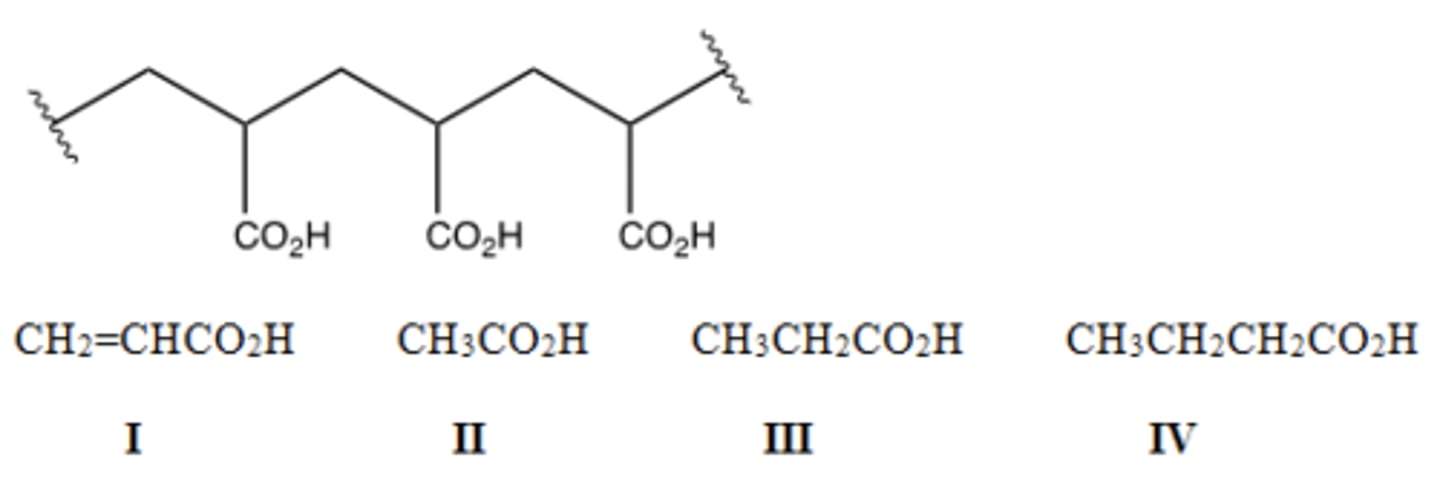
B
Identify the monomer used to make the following polymer.
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
C
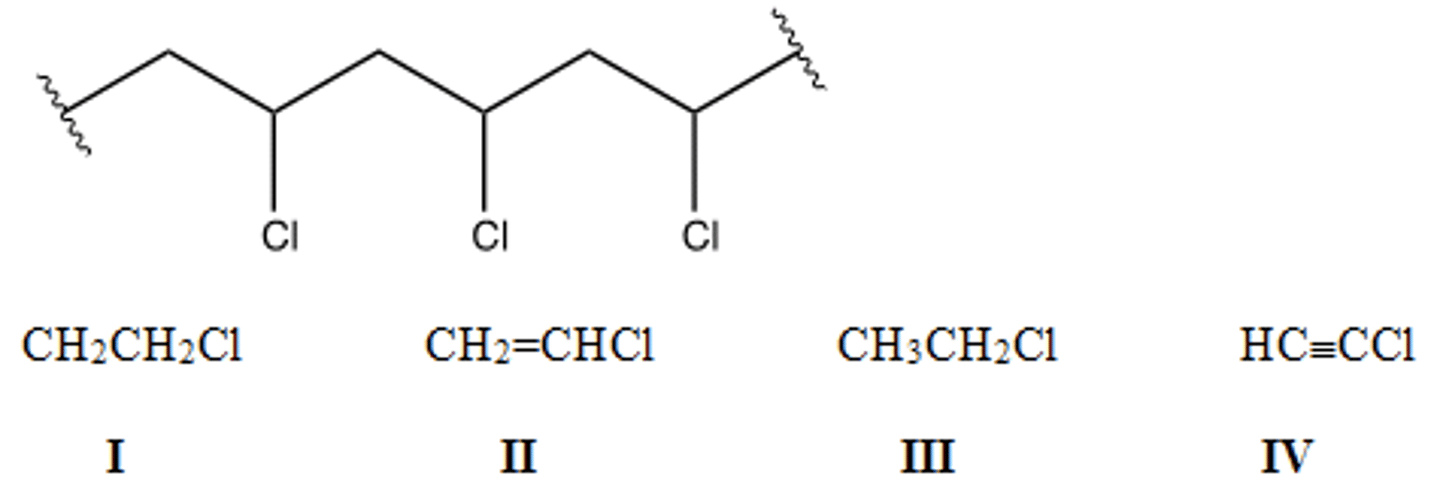
Identify the monomer used to make the following polymer.
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
D
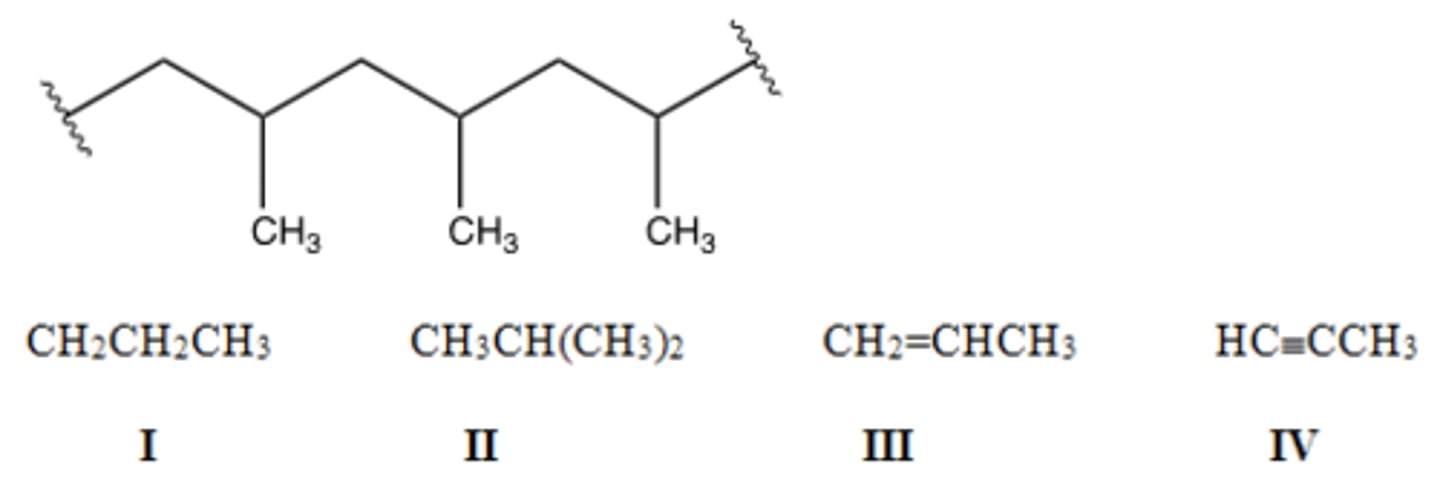
Determine the monochlorination product(s)
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only I and II
D
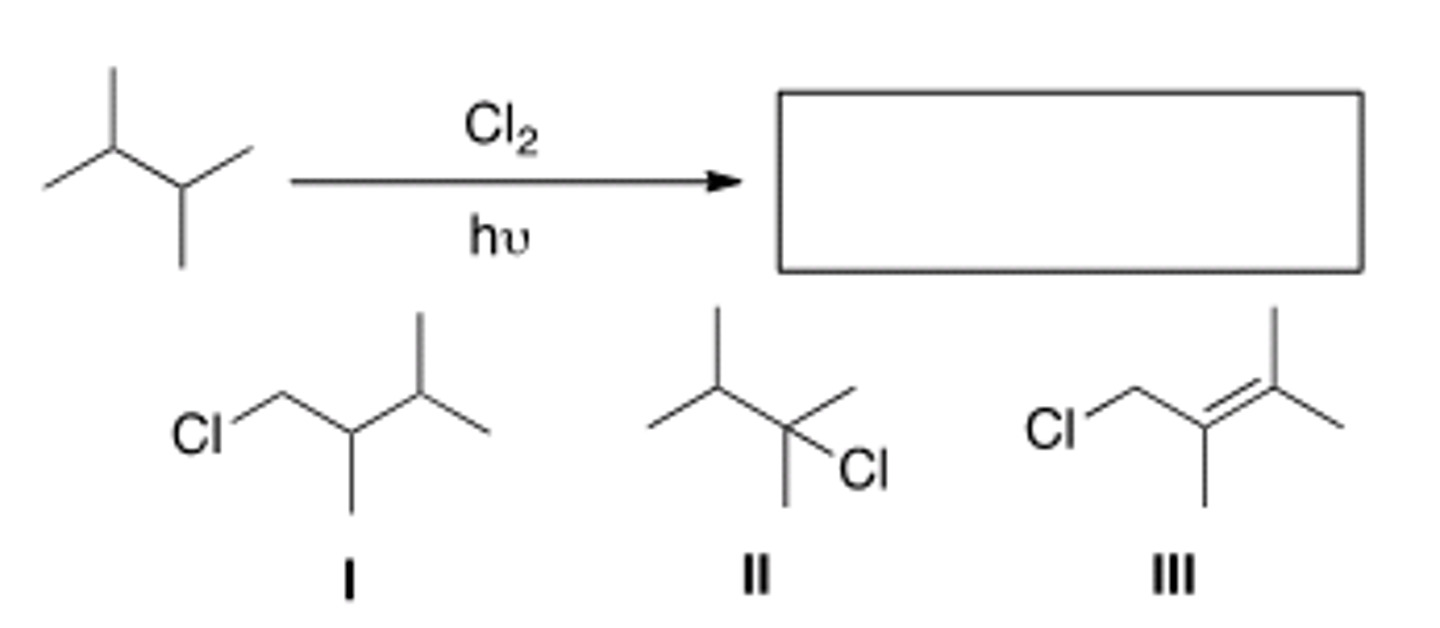
Determine the product of the following reaction.
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D
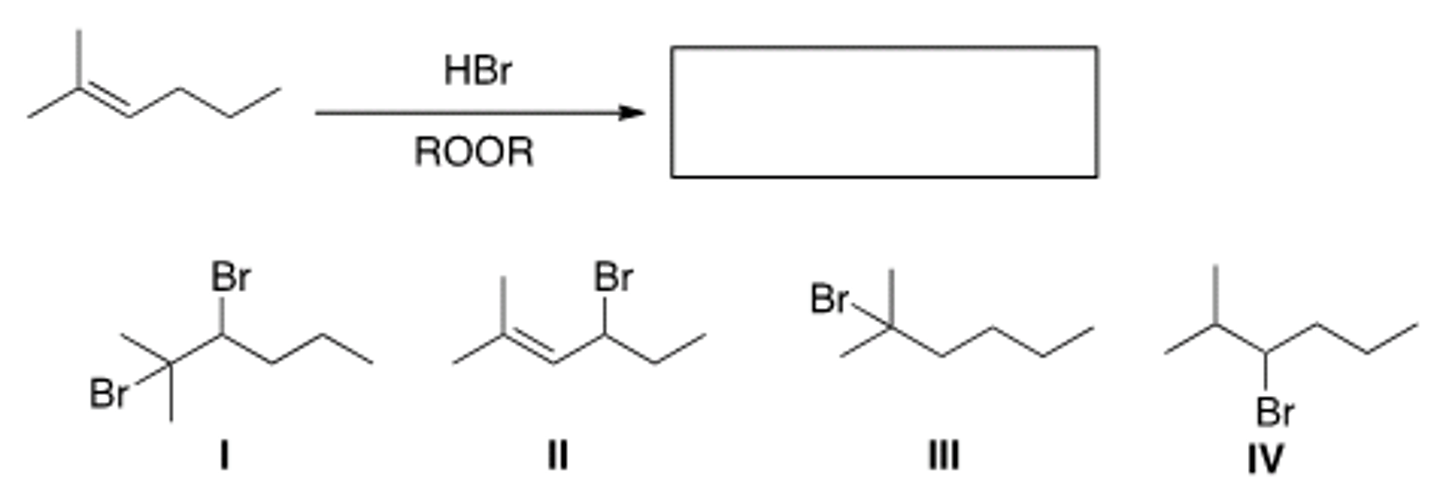
Determine the product(s) of the following reaction.
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only I and II
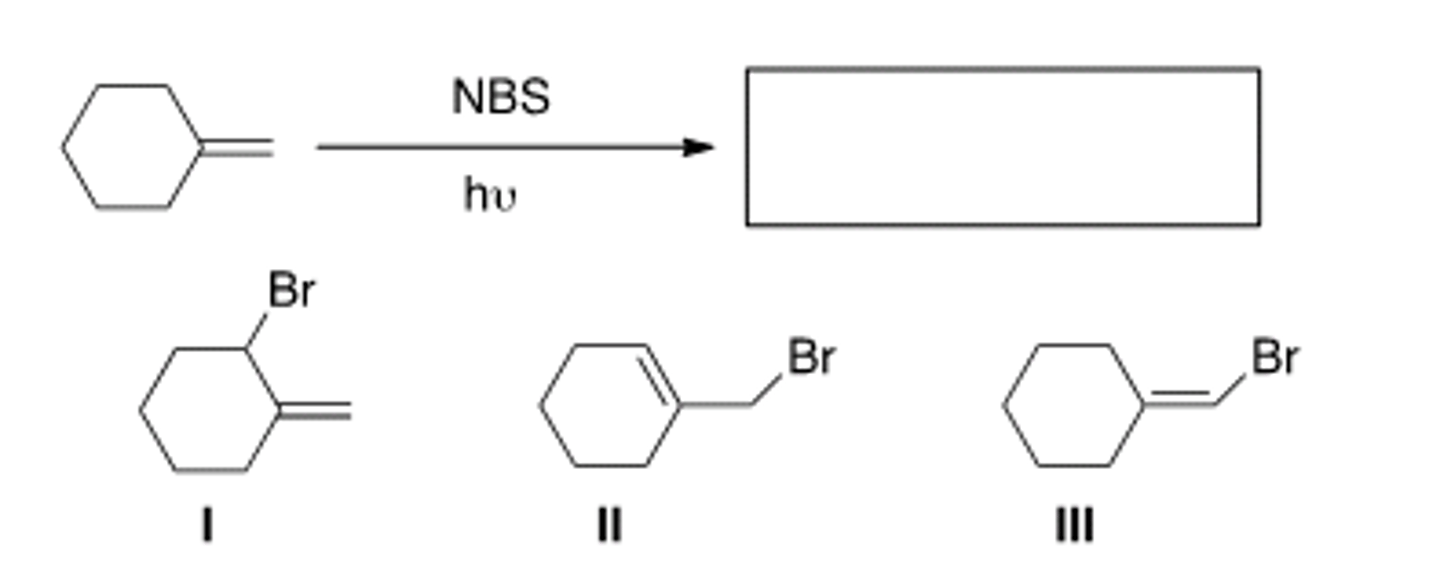
D
Which of the following statements is (are) true about free radical halogenation of
alkanes?
A) The first of the chain-propagating steps is rate-determining.
B) The reaction proceeds by way of a flat sp2 hybridized free radical.
C) The chain-initiating step involves cleavage of a carbon-hydrogen bond to afford a
carbon radical and a hydrogen atom.
D) Statements (The first of the chain-propagating steps is rate-determining) and (The
reaction proceeds by way of a flat sp2 hybridized free radical) are both true.
B
Which of the labeled hydrogens is most easily abstracted in a free radical bromination
reaction?
A) Ha
B) Hb
C) Hc
D) Hd
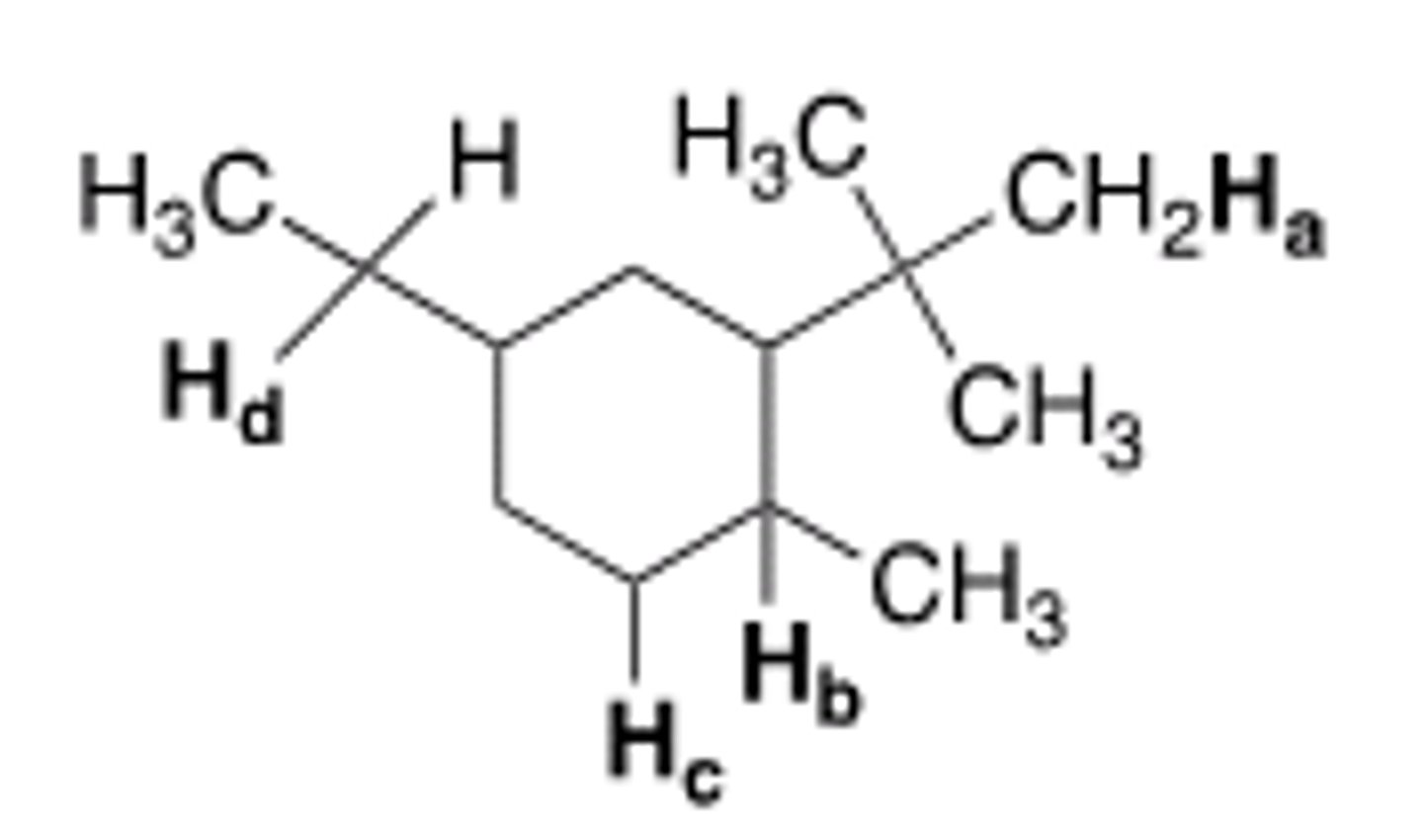
C
Which of the indicated hydrogens is most readily abstracted in a free radical
halogenation reaction?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
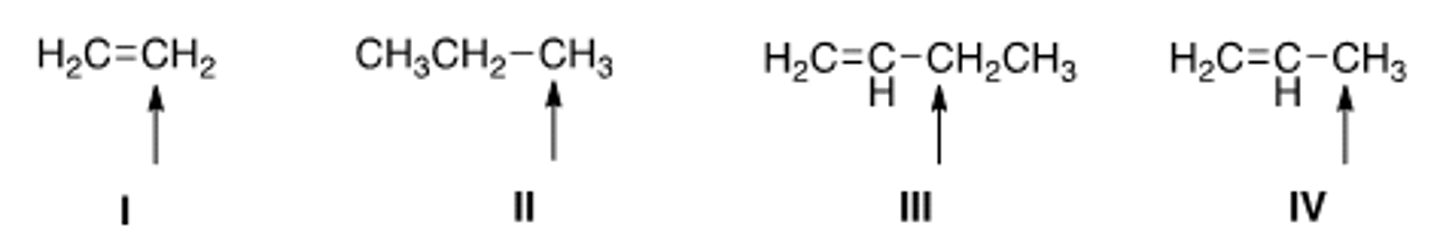
A
This reaction could conceivably occur by the following chain mechanisms [1], [2], and
[3]. The chain initiating step(s) is (are) _____.
A) Only [1]
B) Only [2]
C) Only [3]
D) Only [1] and [2]
![<p>This reaction could conceivably occur by the following chain mechanisms [1], [2], and</p><p>[3]. The chain initiating step(s) is (are) _____.</p><p>A) Only [1]</p><p>B) Only [2]</p><p>C) Only [3]</p><p>D) Only [1] and [2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3cc01b22-e39d-48ff-9fa3-3ee76738e1db.jpg)
B
This reaction could conceivably occur by the following chain mechanisms [1], [2], and
[3]. The chain propagating step(s) is (are) _______.
A) Only [1] and [2] B) Only [2] and [3] C) Only [1] and [3] D) Only [3]
![<p>This reaction could conceivably occur by the following chain mechanisms [1], [2], and</p><p>[3]. The chain propagating step(s) is (are) _______.</p><p>A) Only [1] and [2] B) Only [2] and [3] C) Only [1] and [3] D) Only [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cc9a0d6a-c499-42a8-be83-d078574d1699.jpg)
B
Determine ∆H for step 1
A) -5 kcal/mol
C) -28 kcal/mol
B) +58 kcal/mol
D) None of the choices are correct.
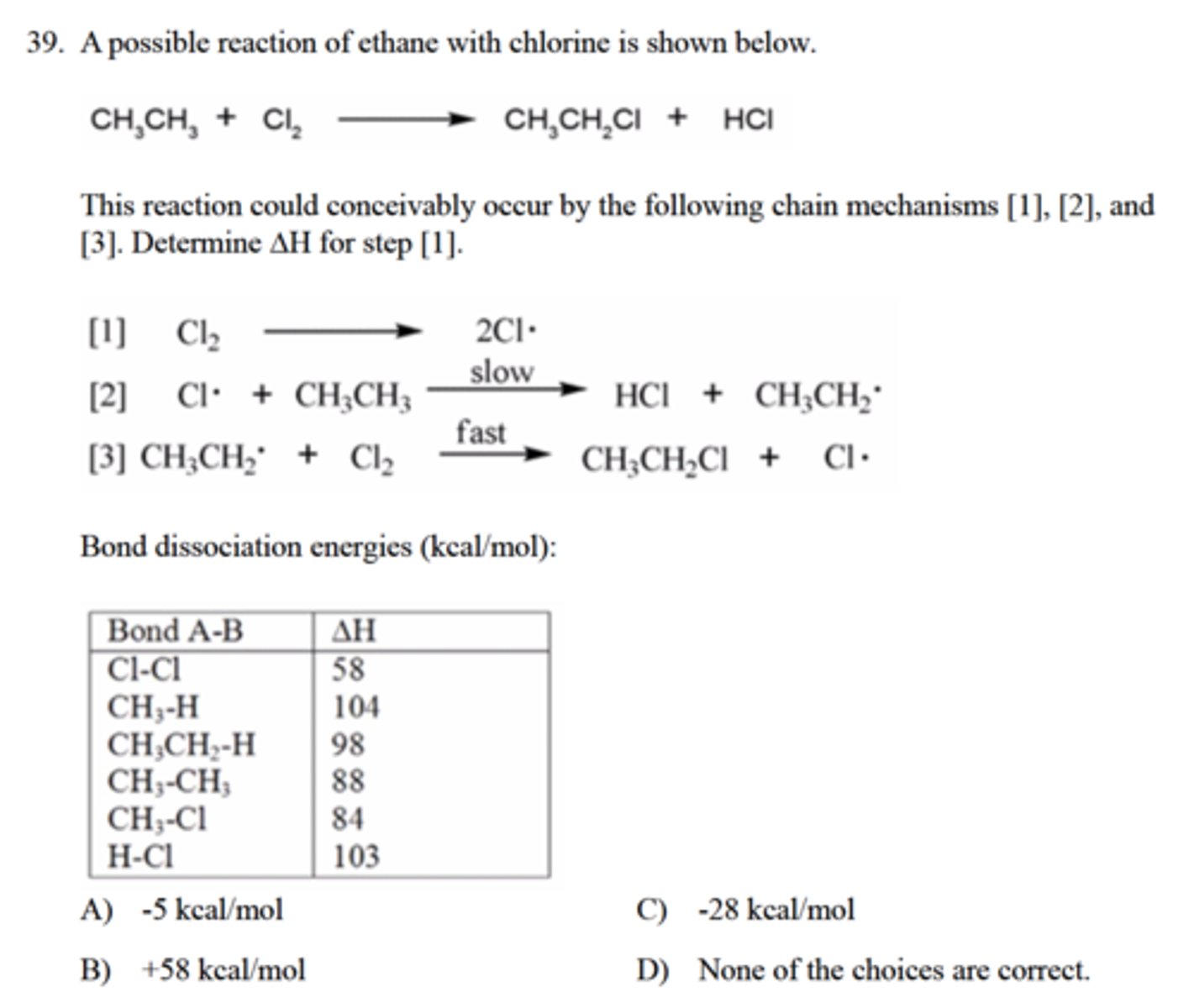
A
Determine ∆H for step 2
A) -5 kcal/mol
C) -28 kcal/mol
B) +58 kcal/mol
D) None of the choices are correct.
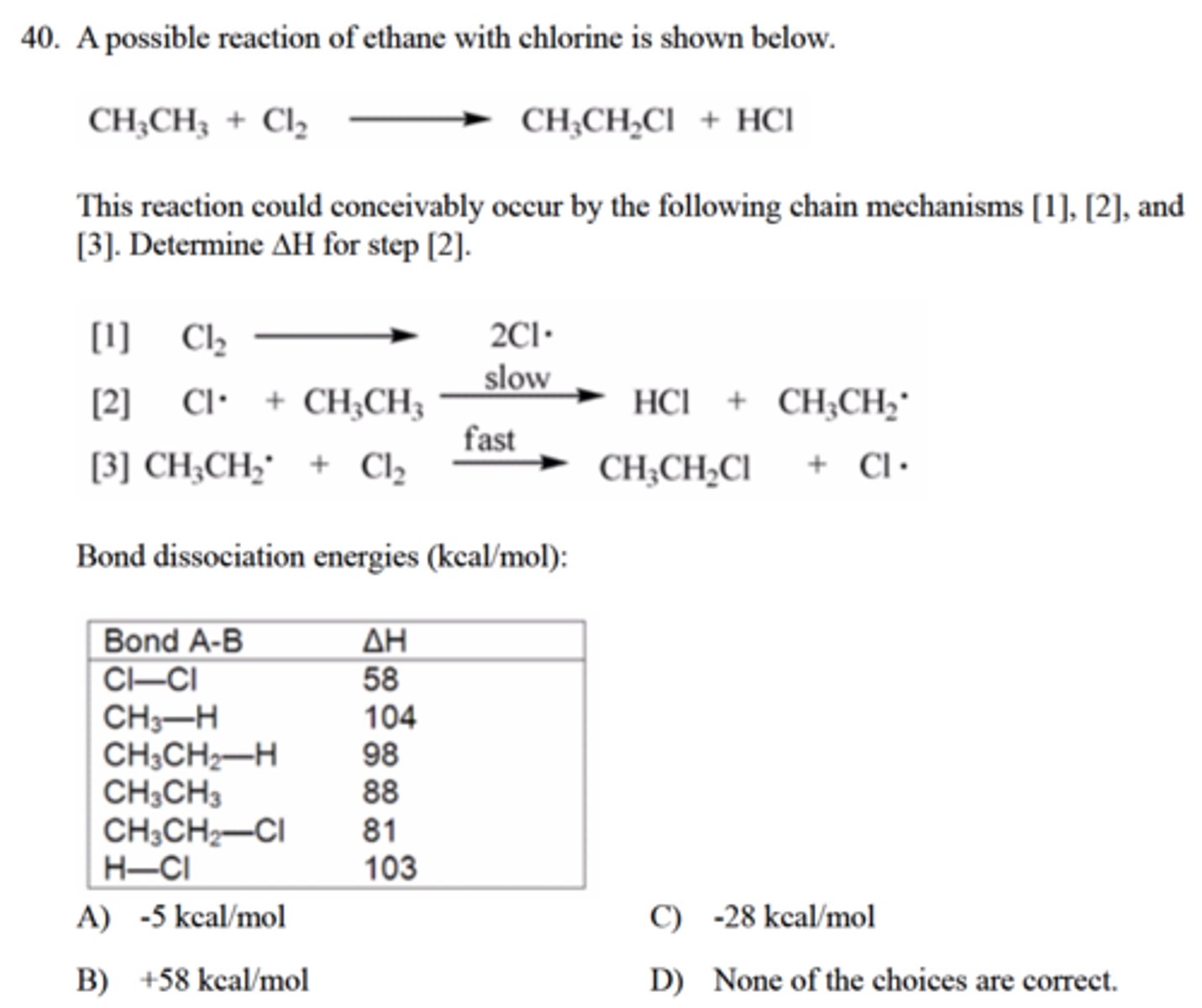
D
Select the route that would most likely produce the desired results from the given
starting material.
I. (1) H2SO4 and heat; (2) HBr
II. (1) KOH in ethanol; (2) HBr
III. (1) H2SO4 and heat; (2) HBr + peroxides
IV. (1) potassium tert-butoxide in tert-butanol; (2) HBr + peroxides
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
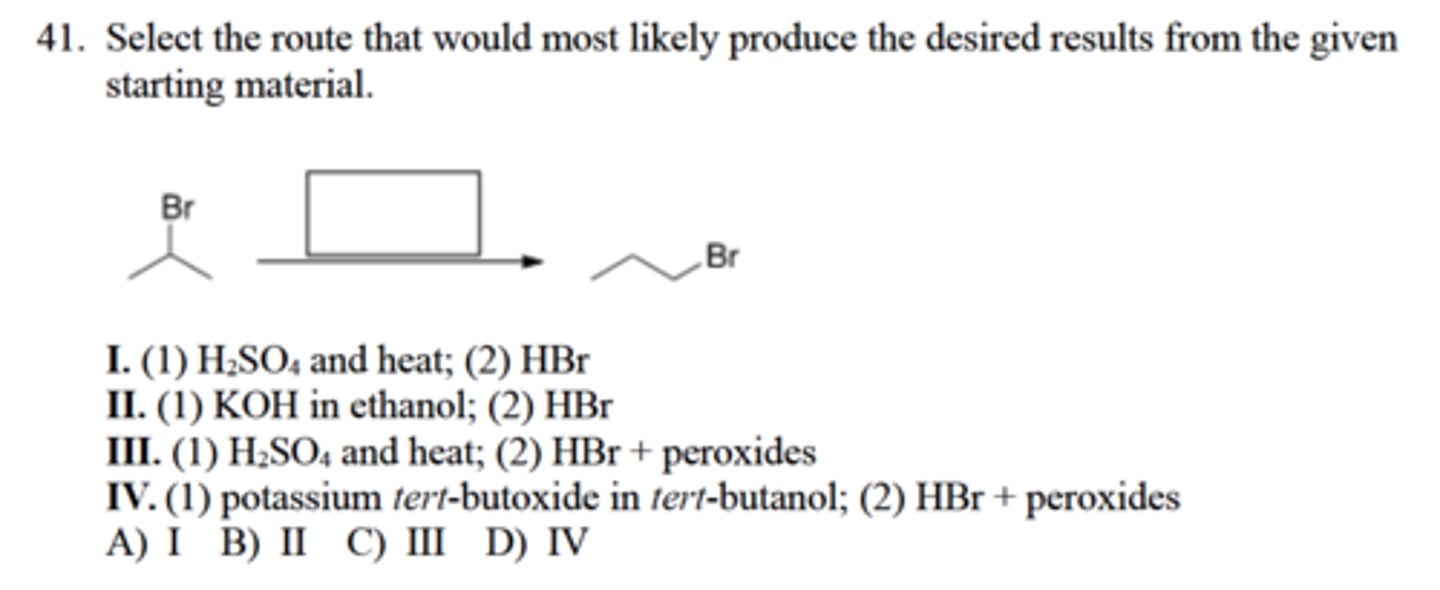
D
What type of reactive intermediate is formed in the reaction of propene with Nbromosuccinimide
(NBS) to give 3-bromo-1-propene?
A) Cyclic bromonium ion
B) Allylic carbocation
C) Allylic carbanion
D) Allylic radical
A
Which of the following alkenes undergoes allylic bromination to form a single
monobrominated product?
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
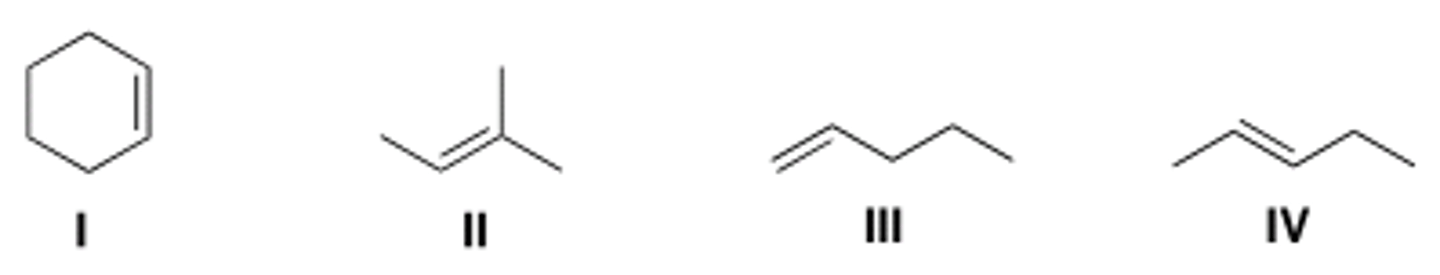
C
Which of the following dienes contain conjugated double bonds?
A. Only I and II
B. Only II and III
C. Only I and III
D. Only II and IV
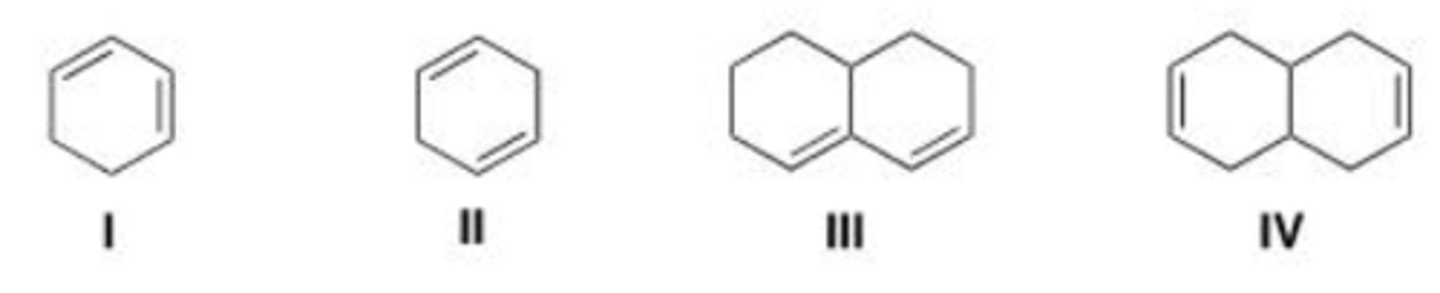
D
Which of the following dienes contain isolated double bonds?
A. Only I and II
B. Only II and III
C. Only I and III
D. Only II and IV
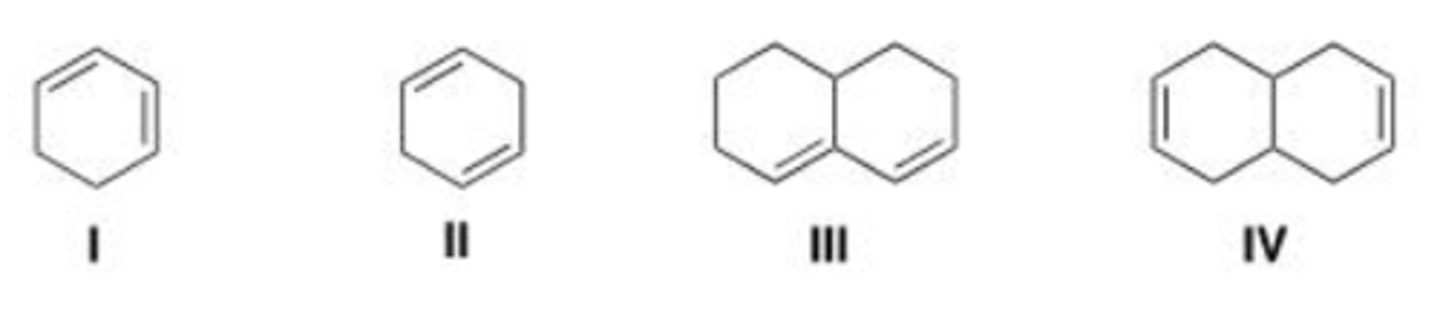
B
Which of the following statements about resonance structures is true?
A. The placement of atoms is different.
B. The placement of p bonds is different.
C. The placement of s bonds is different.
D. The placement of nonbonded electrons is the same.
B
What is the hybridization around the indicated carbon atom in the following anion?
A. sp3
B. sp2
C. sp
D. p
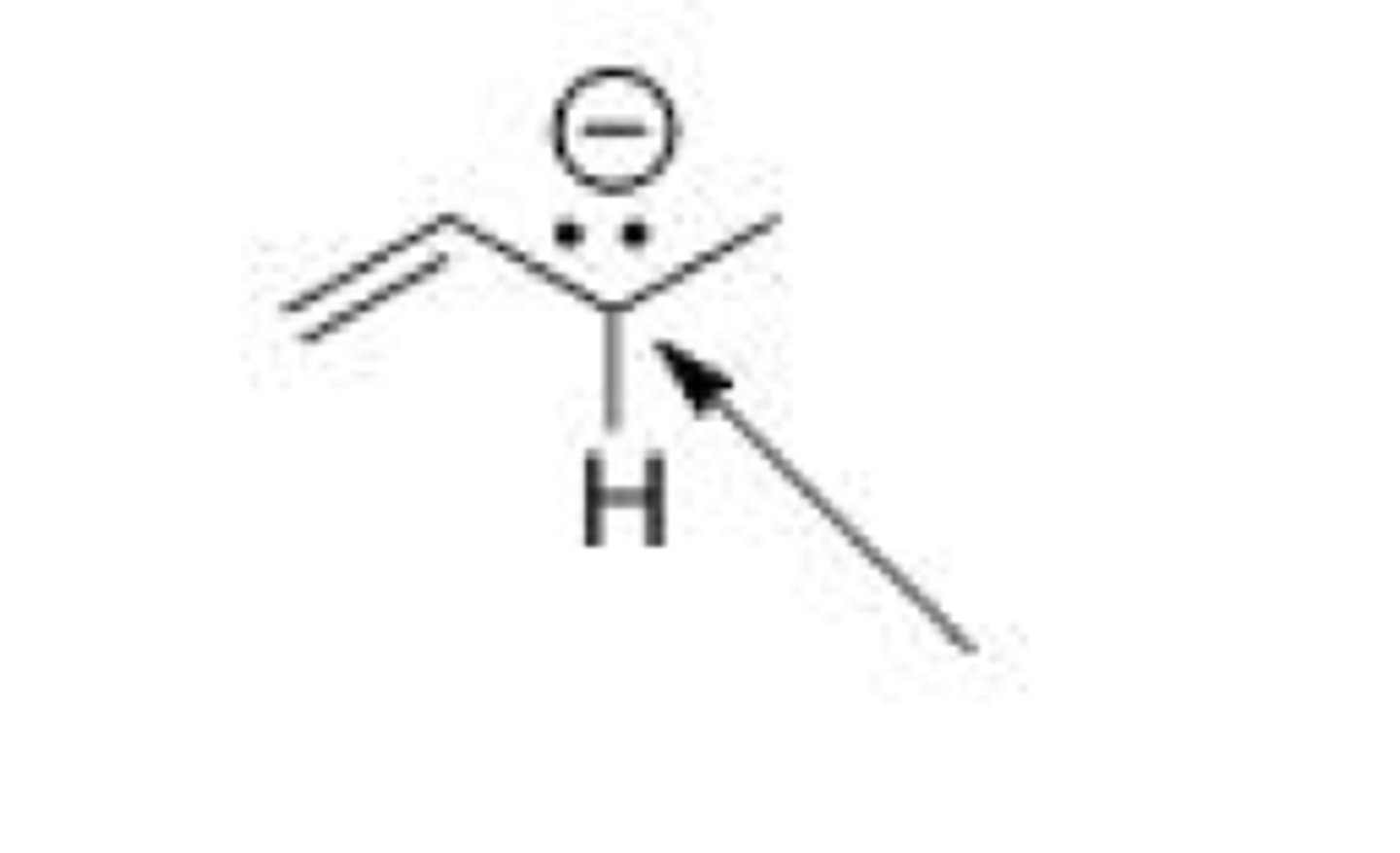
B
What is the hybridization around the indicated oxygen atom in the following anion?
A. sp3
B. sp2
C. sp
D. p
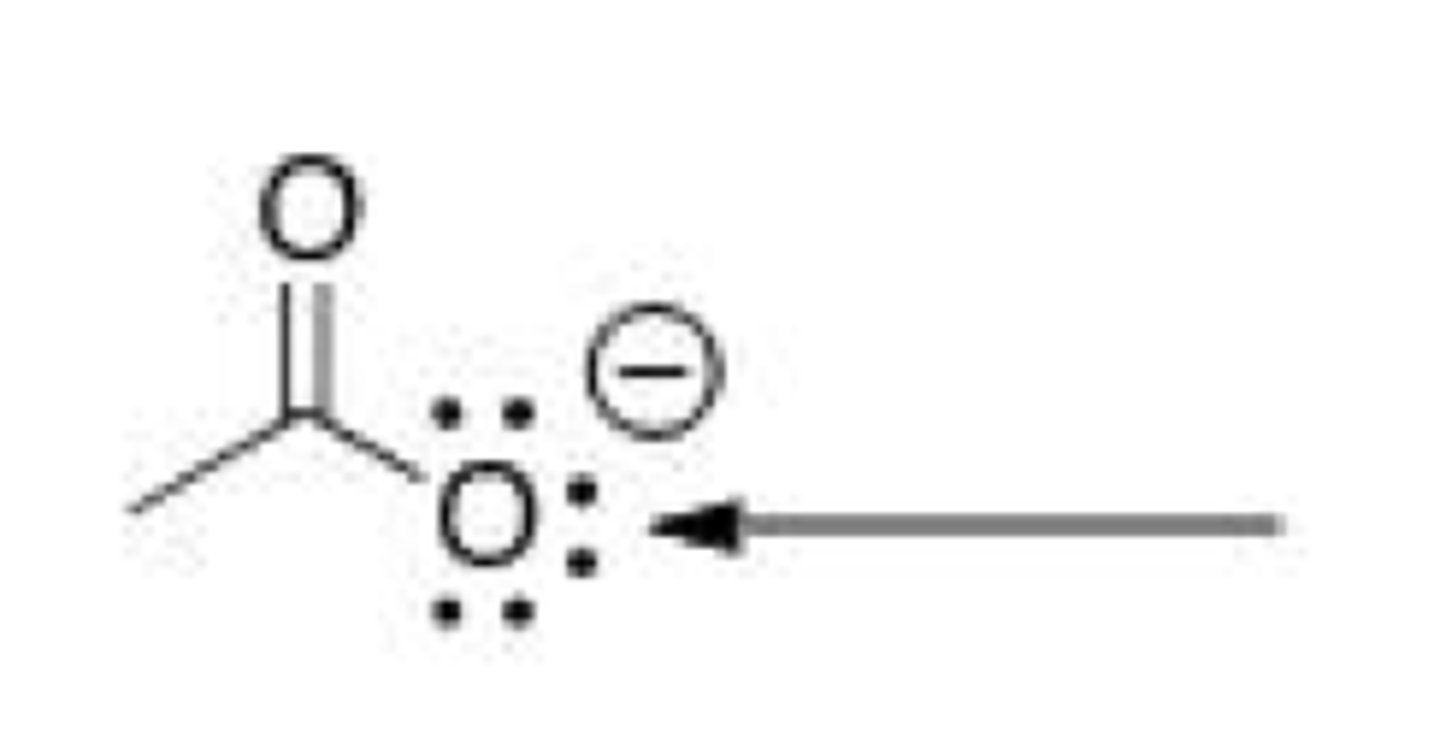
B
Which of the following is (are) conjugated dienes?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only I and II
D. I, II, and III
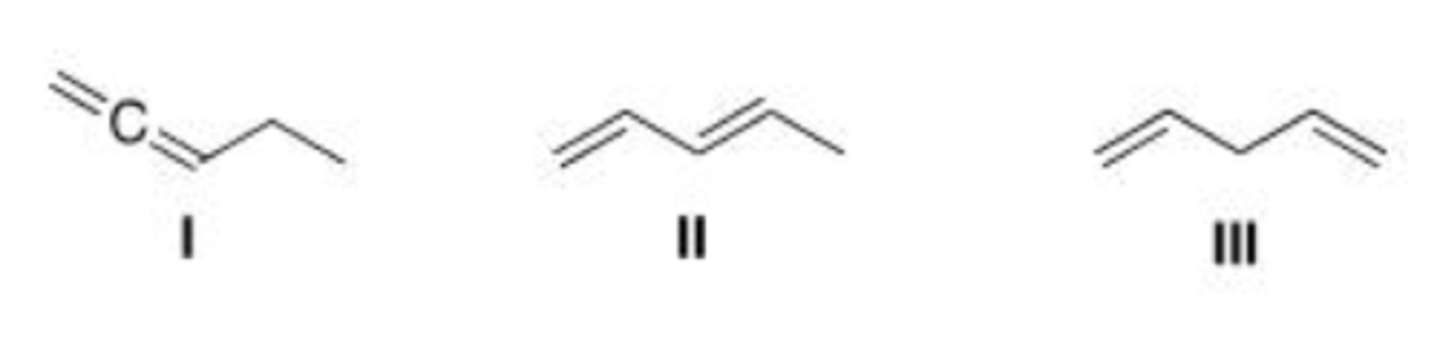
D
Which of the following compounds is conjugated?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
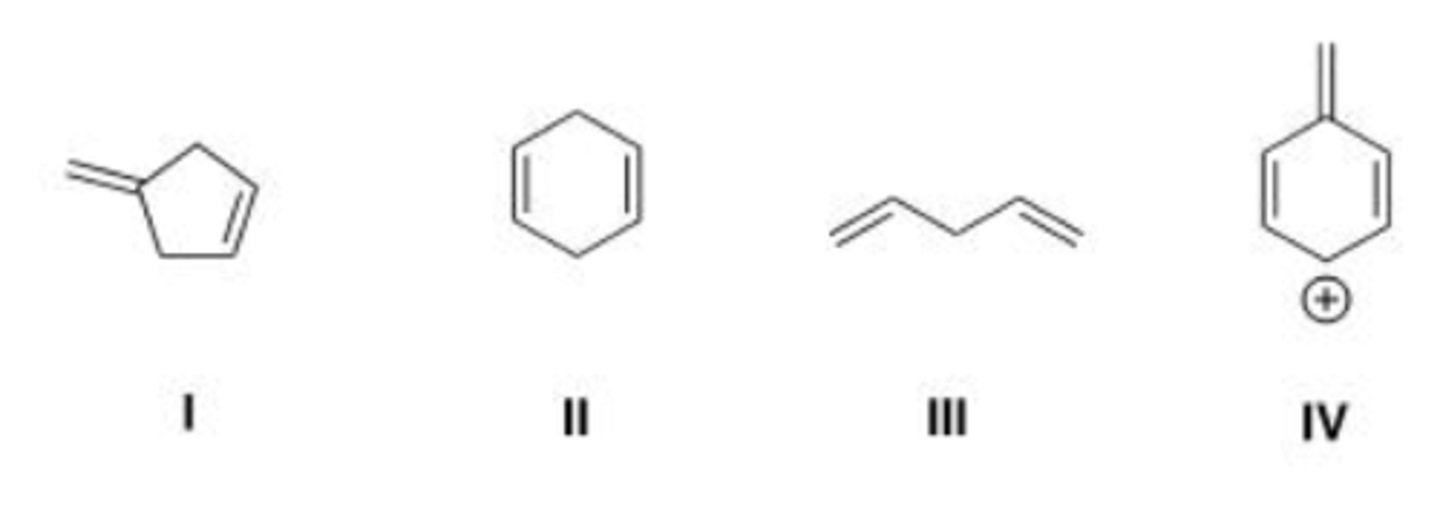
C
Which of the following conjugated dienes represent two conformations?
A. Only I and II
B. Only I and III
C. Only II and III
D. None of the choices
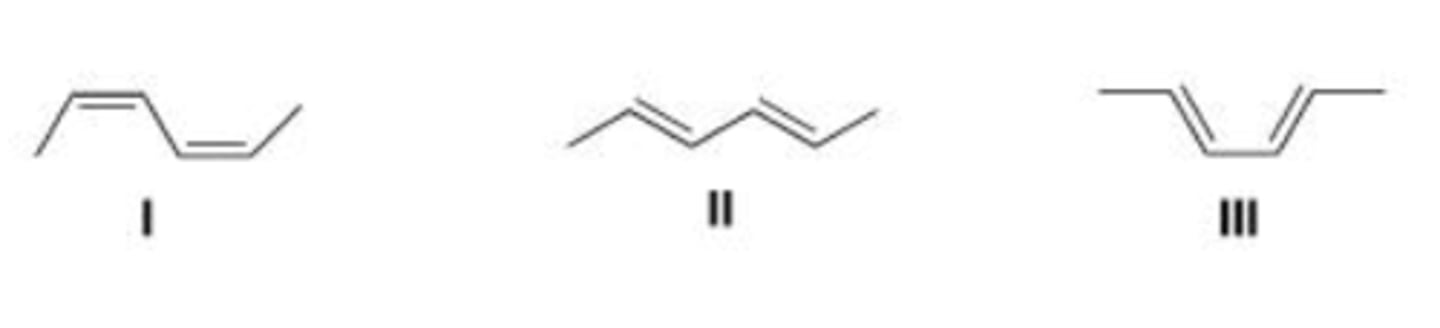
III > I > II
Rank the following dienes in order of decreasing heat of hydrogenation, putting the diene with the highest heat of hydrogenation first.
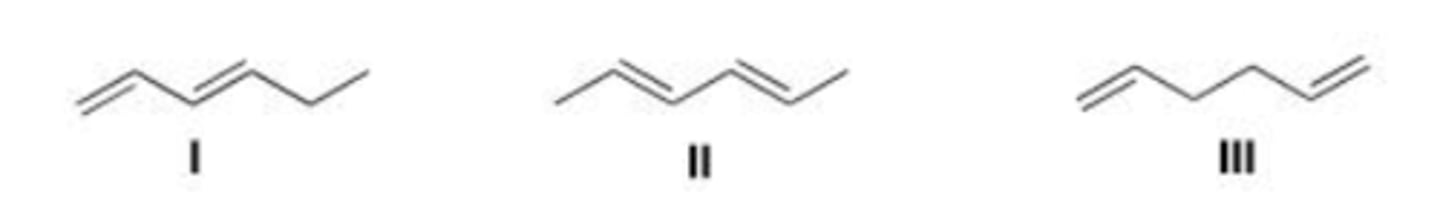
I < II < III
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing stability, putting the least stable first.
D
What is the reactive intermediate in the reaction of 1,3-diene with HBr, resulting in 1,4-addition?
A. Allylic radical
B. Cyclic bromonium
C. Dienophile
D. Allylic carbocation
B
Which of the following is the appropriate term for the mechanism of the addition of HBr to 1,3-dienes?
A. Nucleophilic addition
B. Electrophilic addition
C. Free radical addition
D. Conjugate addition
B
What is (are) the major product(s) of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only II and IV
C. Only I and III
D. Only I, II, and III
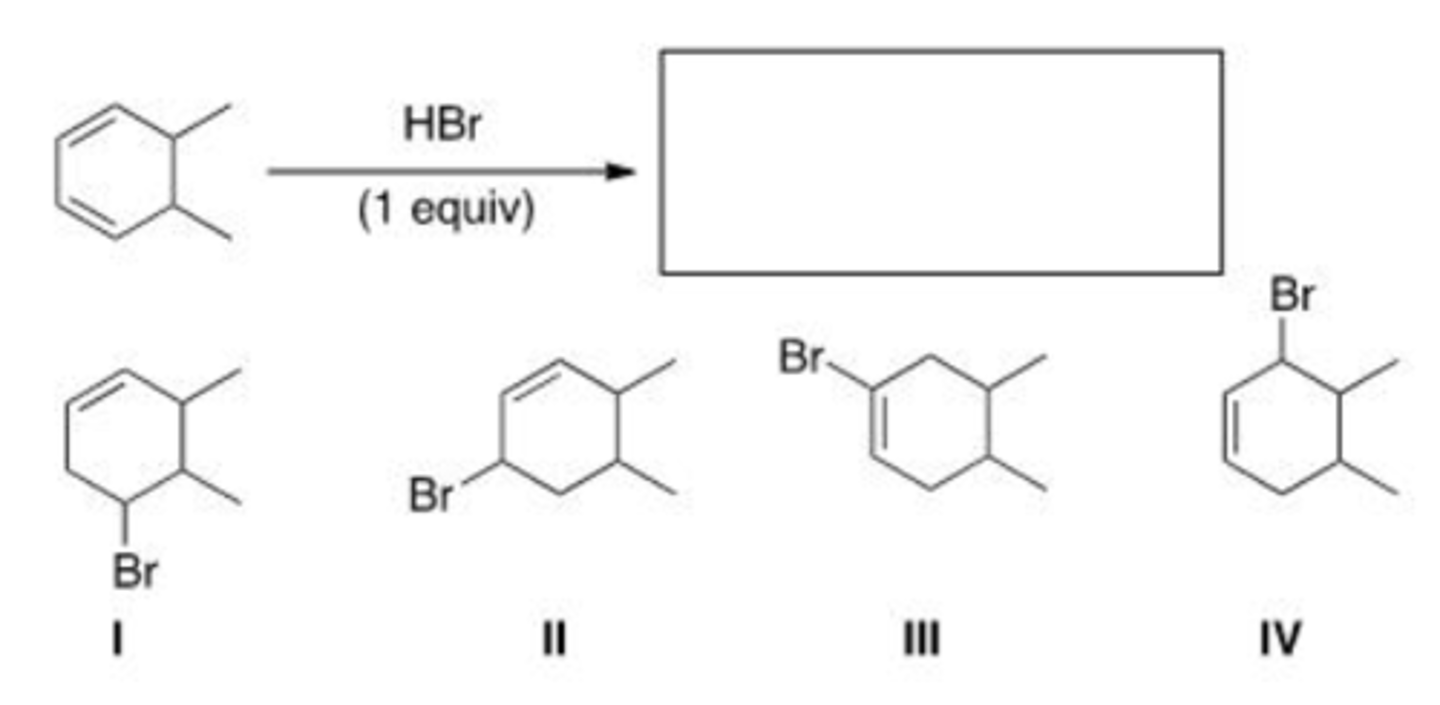
D
What is (are) the major product(s) of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only I and III
C. Only II and IV
D. Only I, II, and III
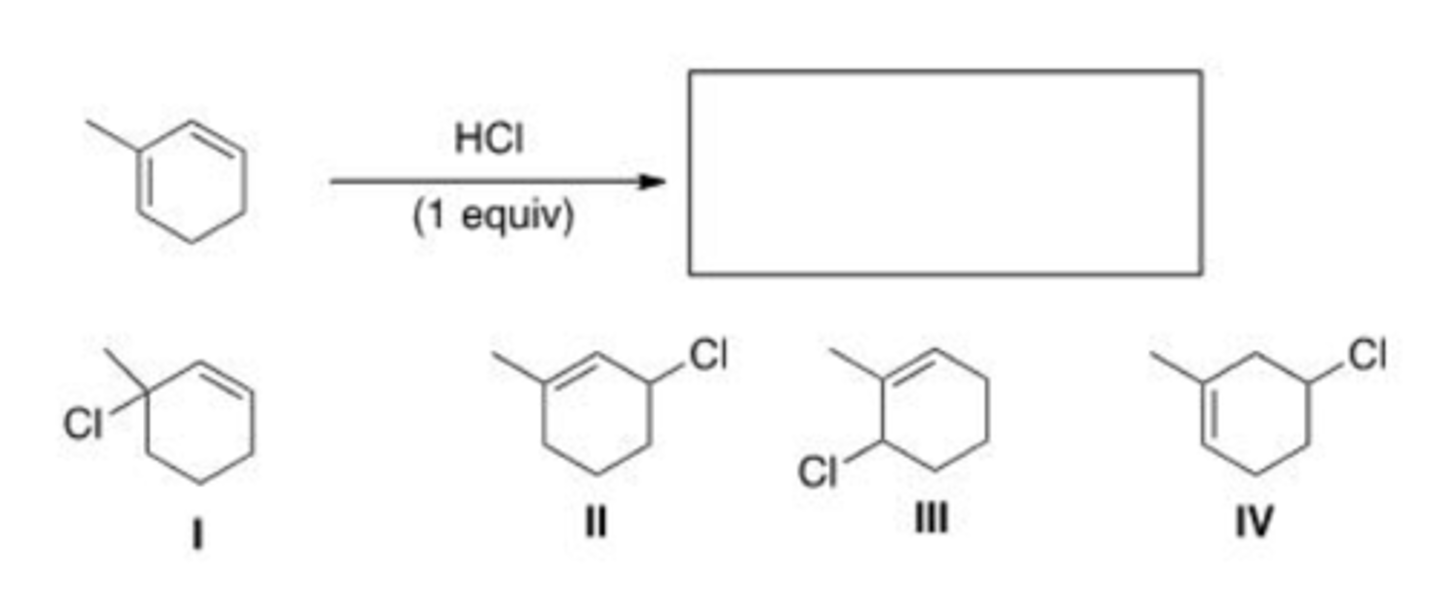
C
What is (are) the major product(s) of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only I and II
D. I, II, and III
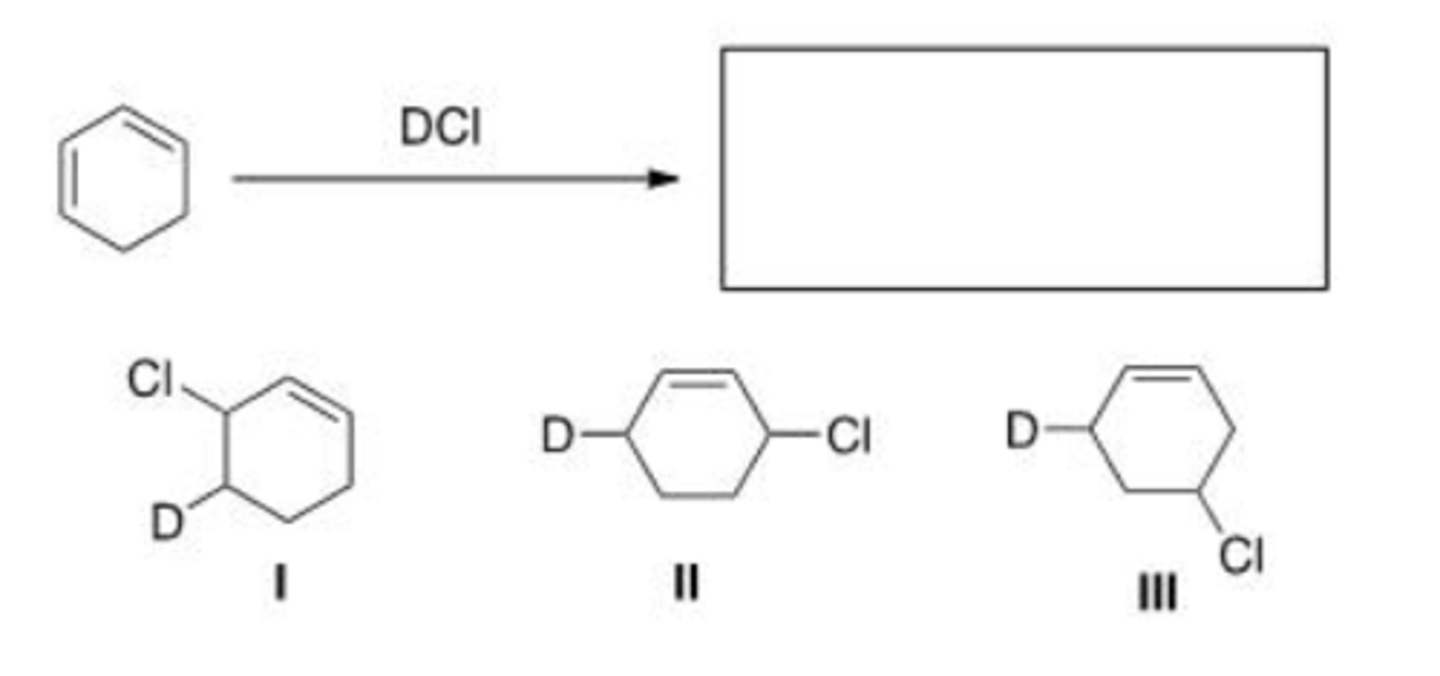
D
Which of the following is not a product obtained from the addition of 1 equivalent of HBr to (E)-1,3-pentadiene?
A. (E)-4-Bromo-2-pentene
B. (E)-1-Bromo-2-pentene
C. 3-Bromo-1-pentene
D. (E)-3-Bromo-2-pentene
B
What is the thermodynamic product obtained from the addition of 1 equivalent of HBr to 1,3-butadiene?
A. 3-Bromo-1-butene
B. 1-Bromo-2-butene
C. 2-Bromo-2-butene
D. 2-Bromo-1-butene
A
What is the kinetic product obtained from the addition of 1 equivalent of HBr to 1,3-butadiene?
A. 3-Bromo-1-butene
B. 1-Bromo-2-butene
C. 2-Bromo-2-butene
D. 2-Bromo-1-butene
B
Which of the following statements about kinetic vs. thermodynamic products is true?
A. The product that is formed faster is the thermodynamic product.
B. The kinetic product predominates at low temperature.
C. The product that predominates at equilibrium is the kinetic product.
D. The thermodynamic product is less stable.
A
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of the Diels-Alder reaction is true?
A. Three π bonds break; two σ bonds and one π bond form.
B. Three π bonds break; one σ bond and two π bonds form.
C. Two π bonds break; one σ bond and one π bond form.
D. Two π bonds break; two σ bonds and one π bond form.
A
Which of the following is not a feature of the Diels-Alder reaction?
A. They are initiated by peroxides.
B. They form new six-membered rings.
C. Three π bonds break.
D. They are concerted.
III < I < II
Rank the following dienes in order of increasing reactivity in a Diels-Alder reaction, listing the least reactive first.
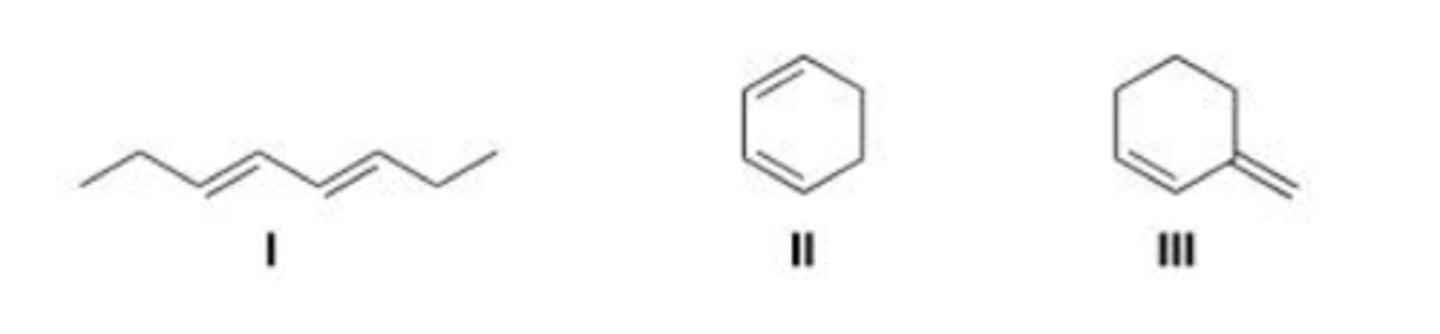
D
Which of the following is the least reactive diene in a Diels-Alder reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
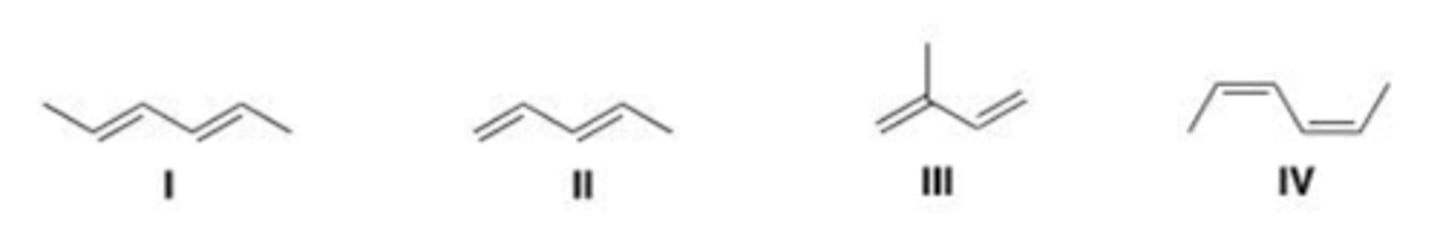
D
Which of the following statements about the Diels-Alder reaction is true?
A. The diene can react only when it adopts the s-trans conformation.
B. Electron-withdrawing substituents in the diene increase reaction rate.
C. Electron-donating substituents in the dienophile increase the reaction rate.
D. The stereochemistry of the dienophile is retained in the product.
III < I < II
Rank the following dienophile in order of increasing reactivity in a Diels-Alder reaction, listing the least reactive first.
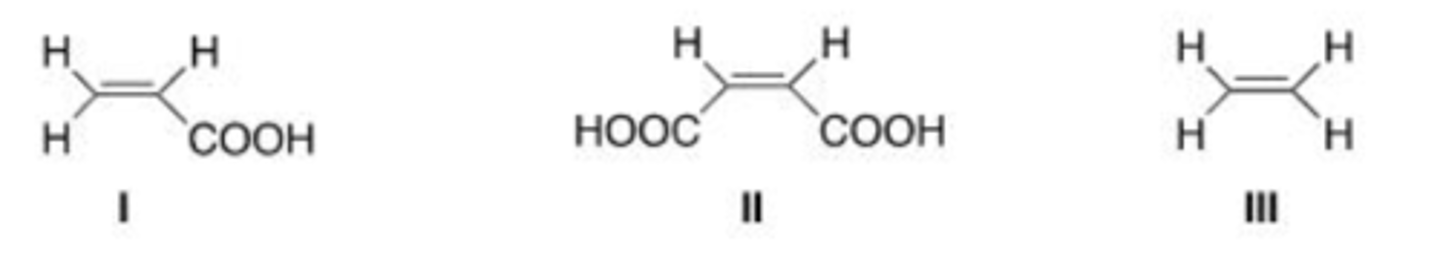
D
Which of the following compounds is the least reactive dienophile in a Diels-Alder reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
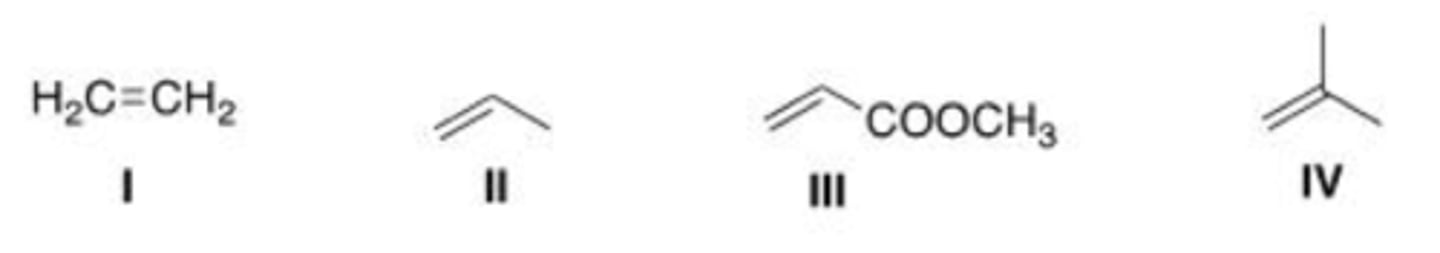
C
Which of the following compounds is the most reactive dienophile in a Diels-Alder reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
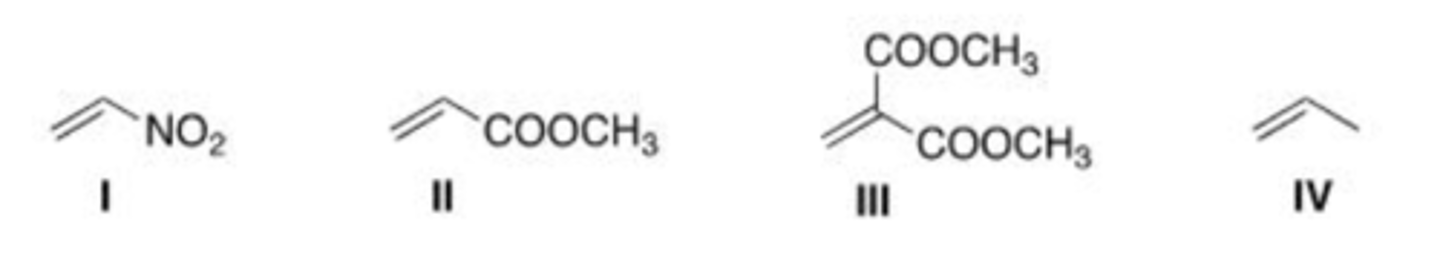
D
Which of the following is the most reactive diene in a Diels-Alder reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
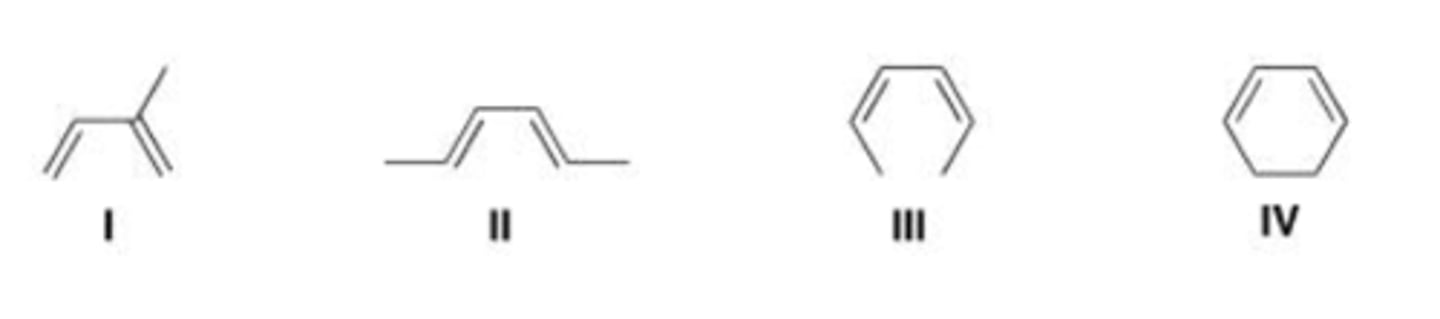
C
Which of the following is the least reactive diene in a Diels-Alder reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
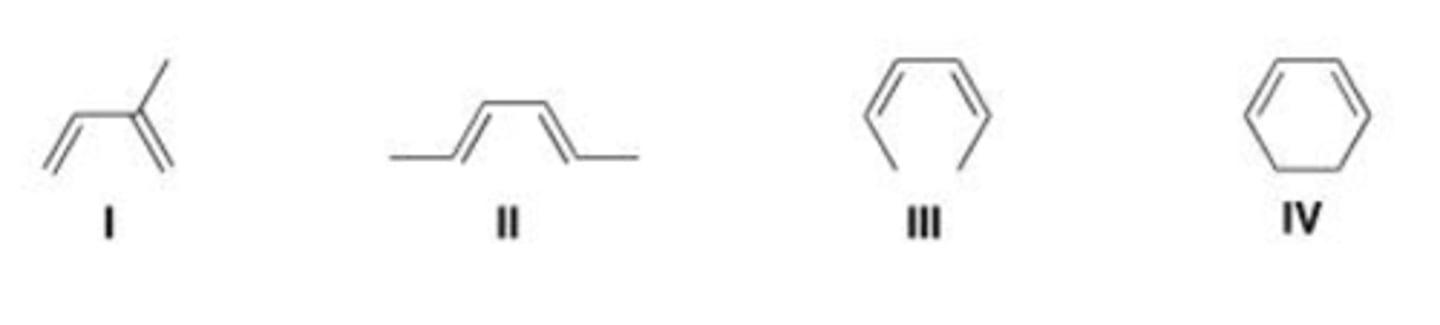
D
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
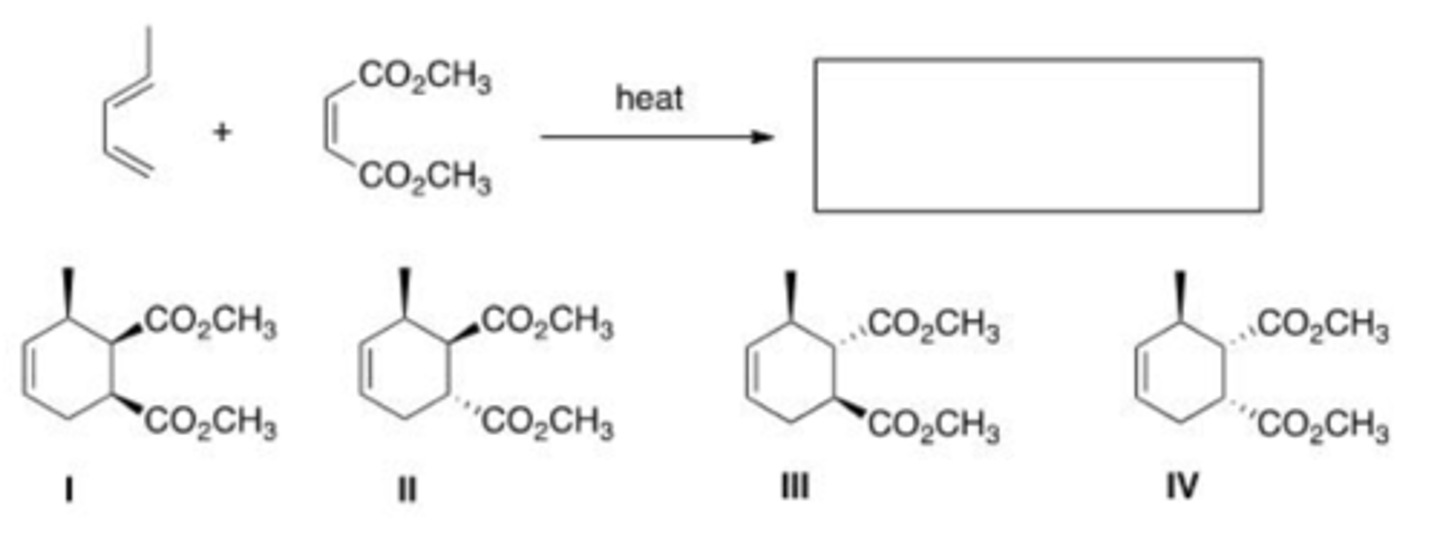
C
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Only I and II
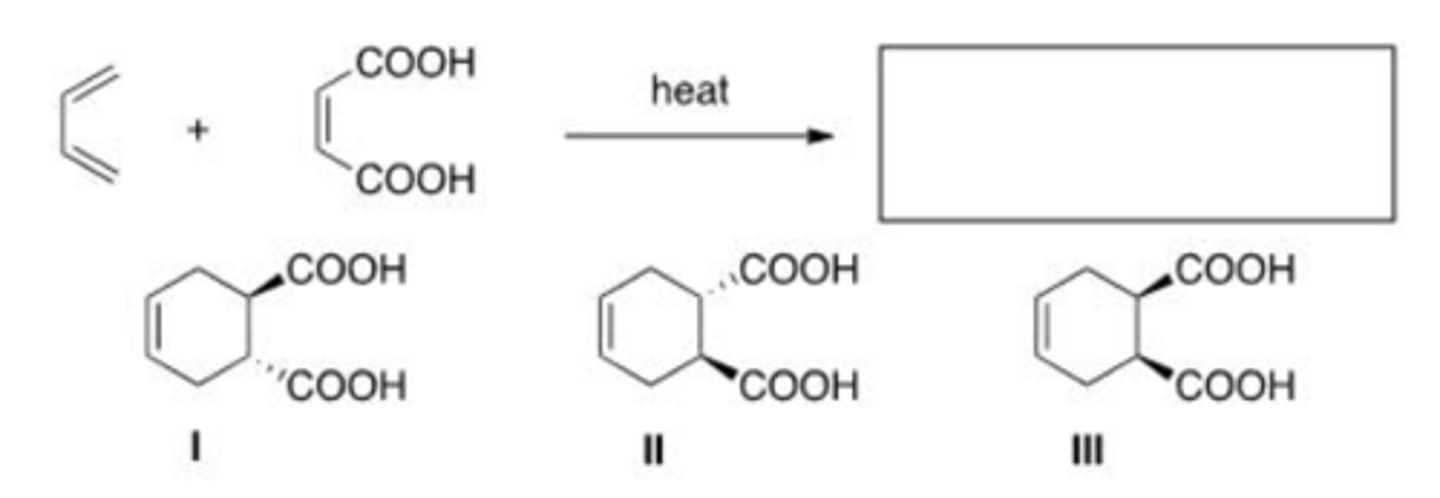
D
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Only I and II
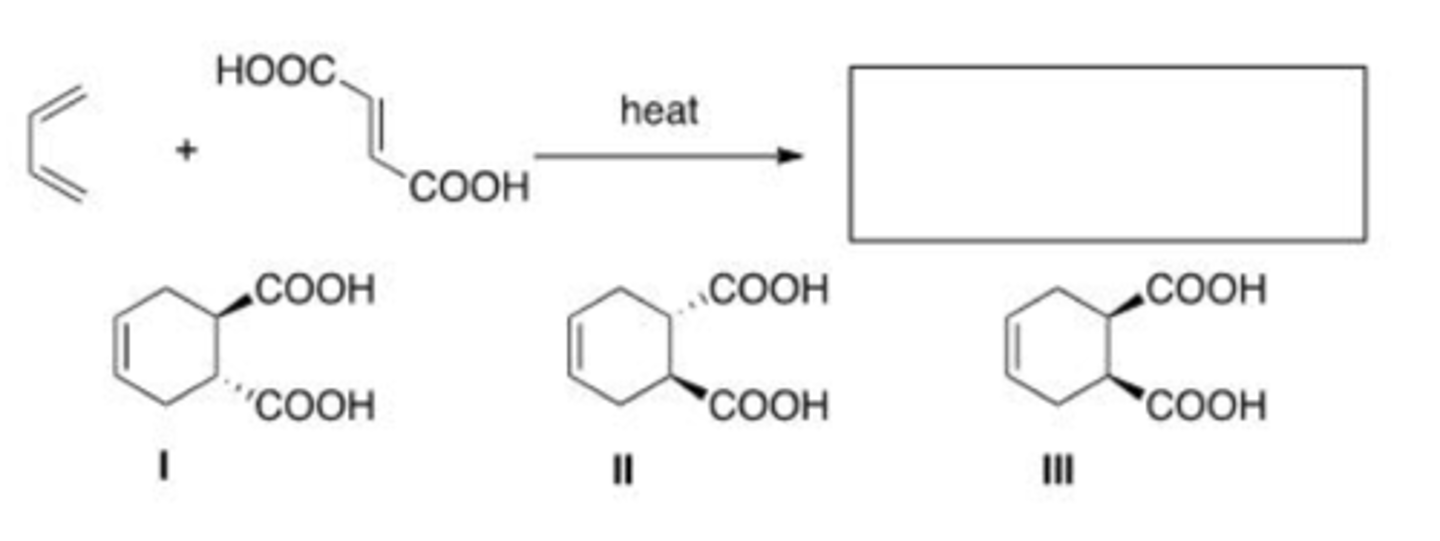
A
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only I and II
C. Only II and III
D. I, II, and III
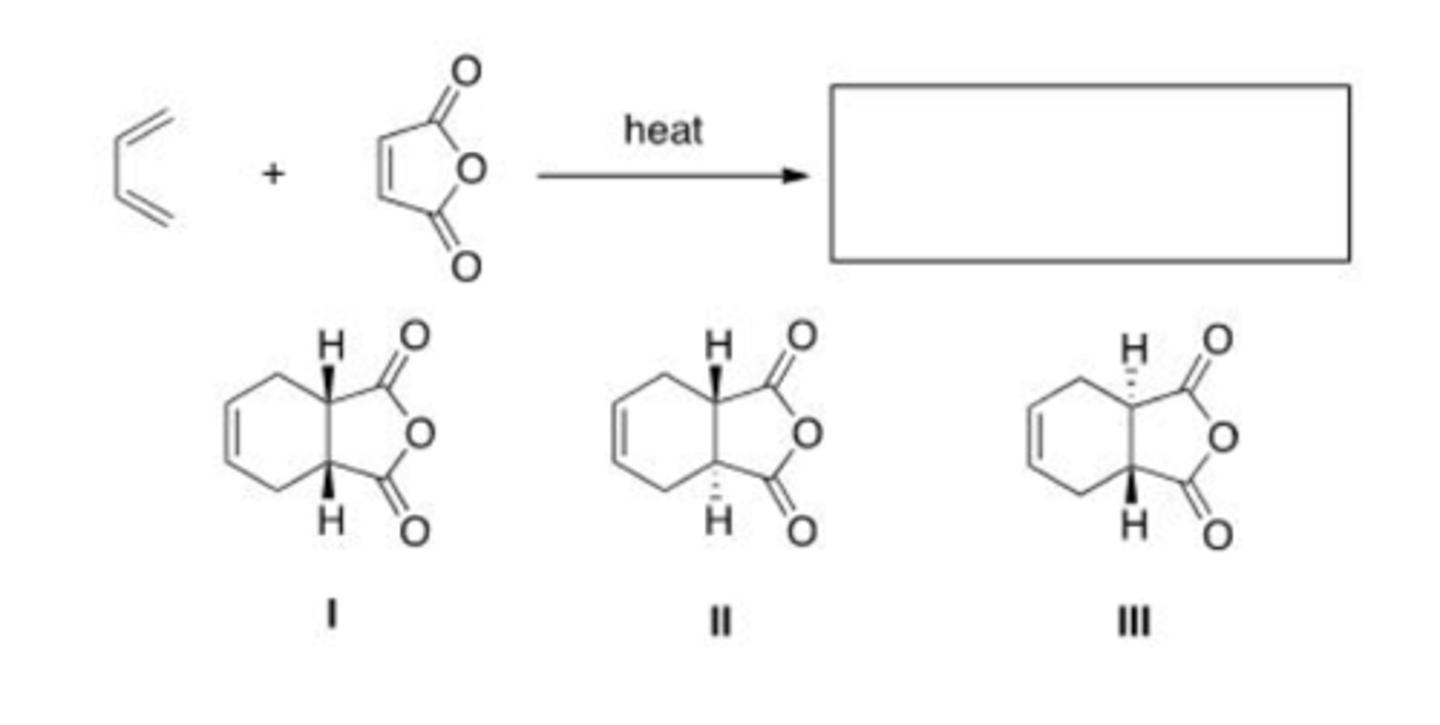
B
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
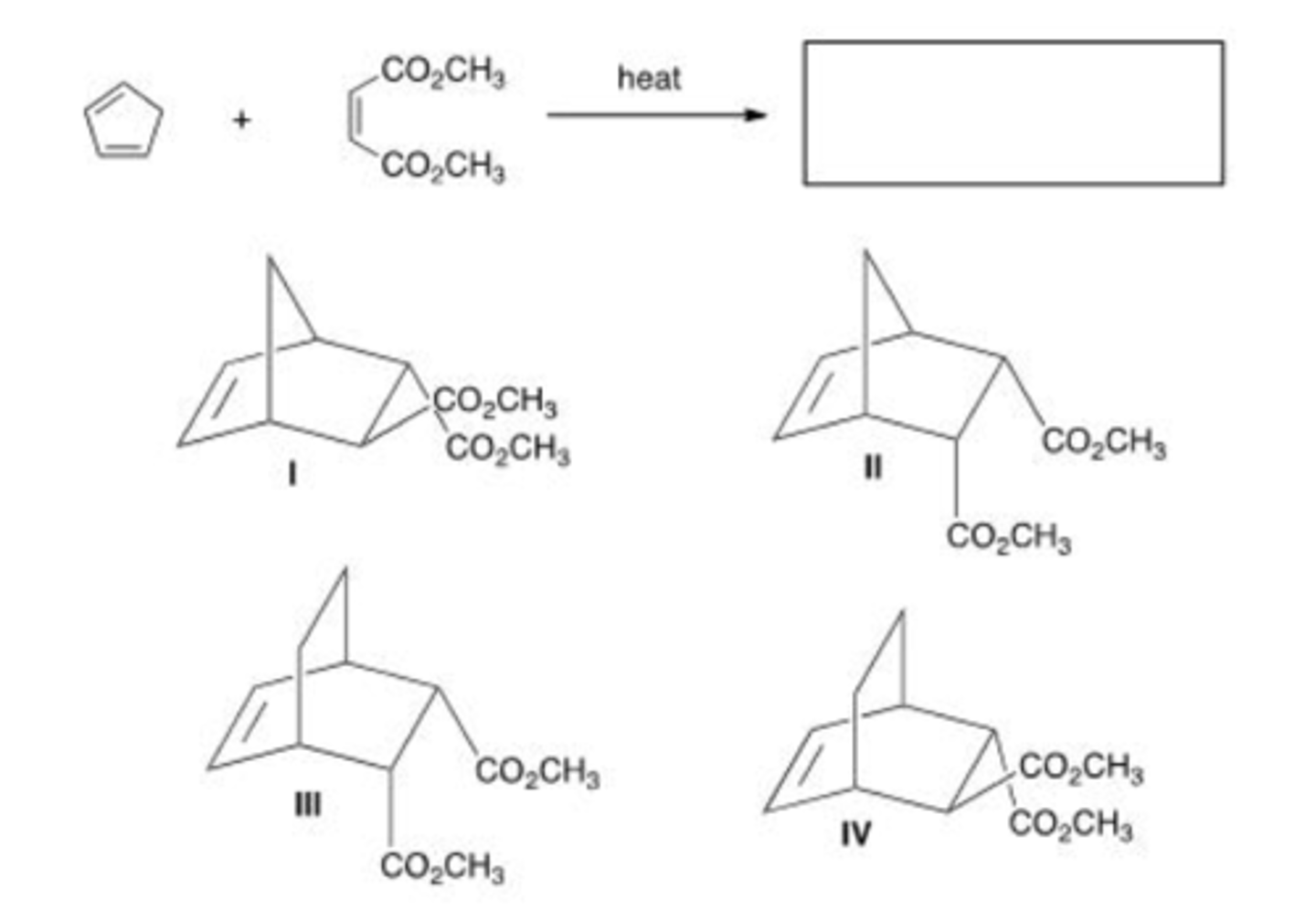
D
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
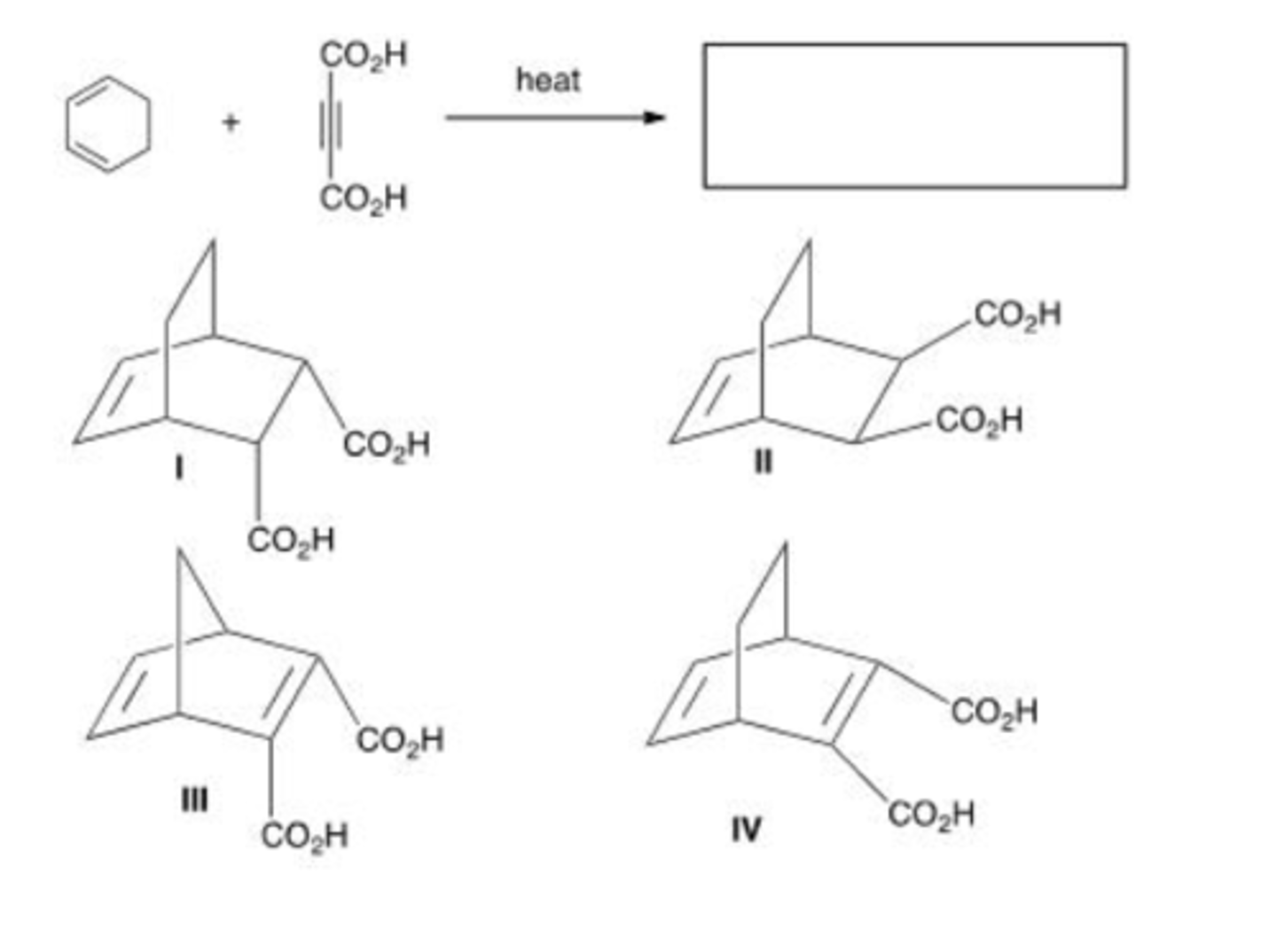
D
What diene and dienophile are used in a Diels-Alder reaction to prepare the following compound?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
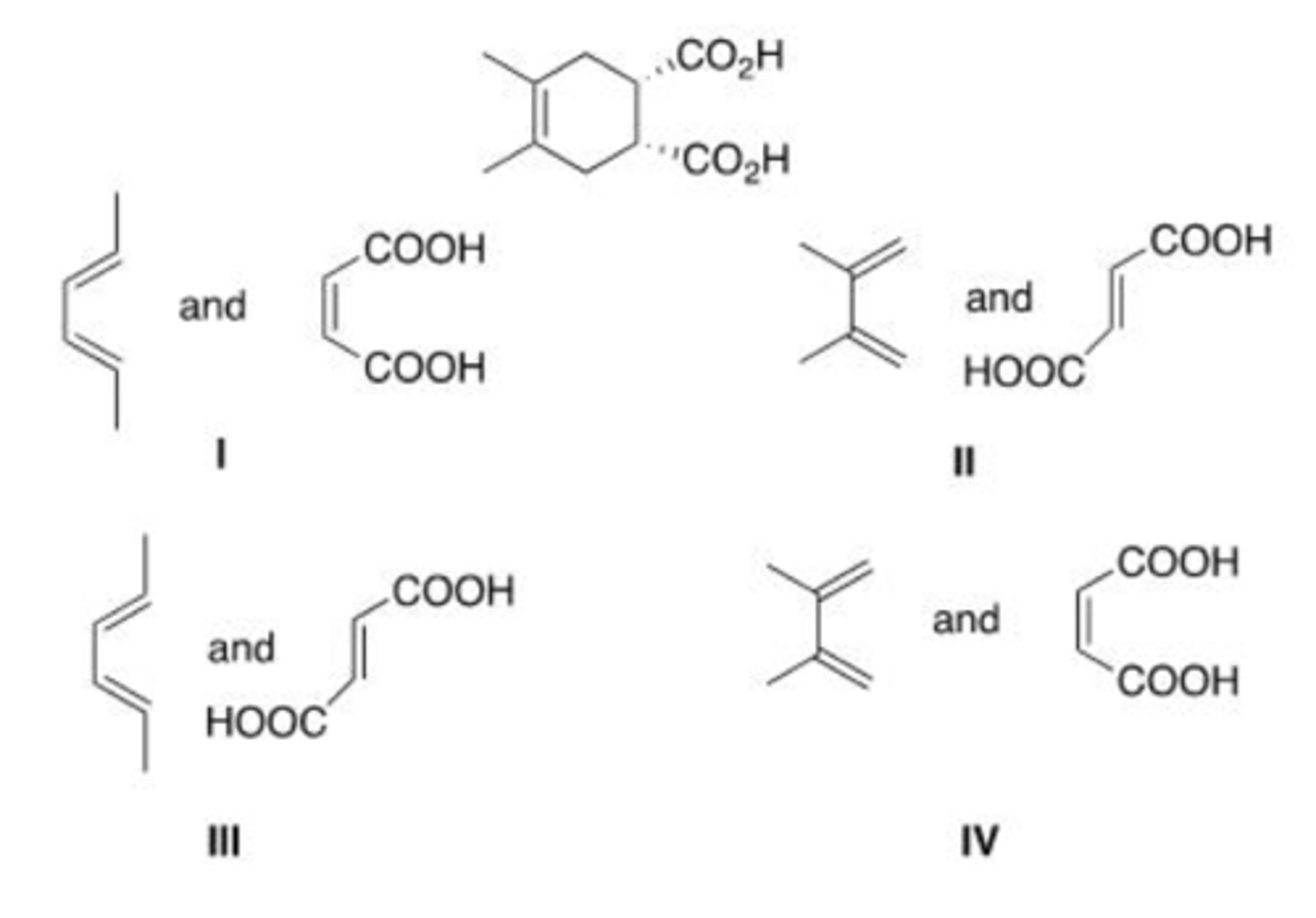
B
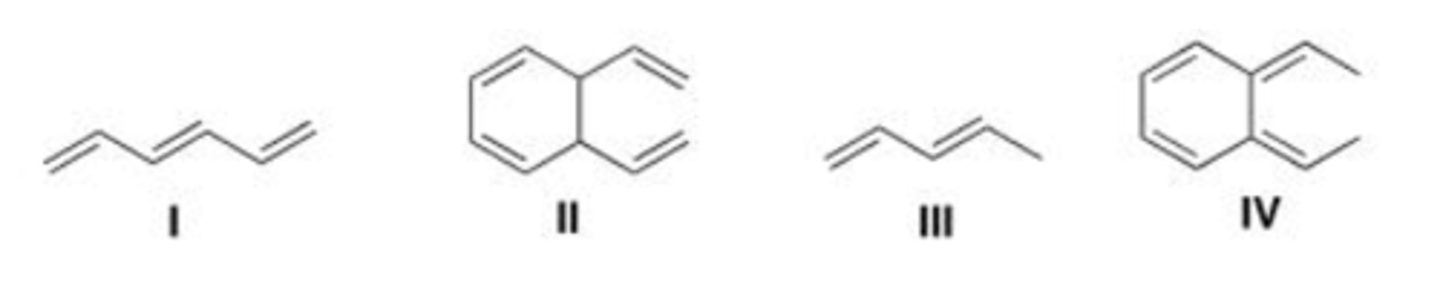
Which of the following compound absorbs UV light at the longest wavelength?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
D
Which of the following compound absorbs UV light at the longest wavelength?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
D
Which of the following electronic transitions is common in the UV spectrum of 1,3-butadiene?
A. s®p
B. s®p*
C. n ®p*
D. p®p*
C
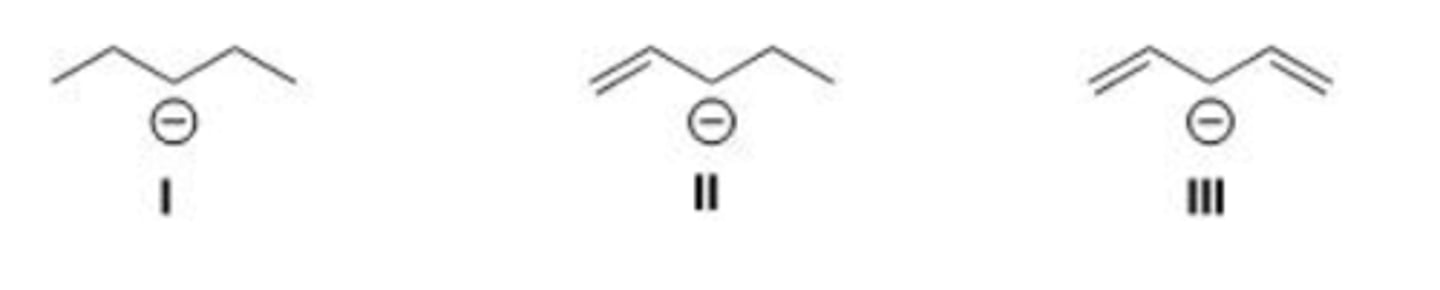
What is the definition of a resonance structure?
A. Compounds with the same molecular formula.
B. Compounds with different carbon frameworks.
C. Structures that differ only in the placement of π and nonbonding electrons.
D. Structures that differ only in the location of bonds.
III > II > I
Rank the following anions from most to least stable, listing the most stable first.
C
How would you favor the formation of the kinetic product of the following reaction?
A. Excess HBr
B. Long reaction time
C. Low temperature
D. High pressure
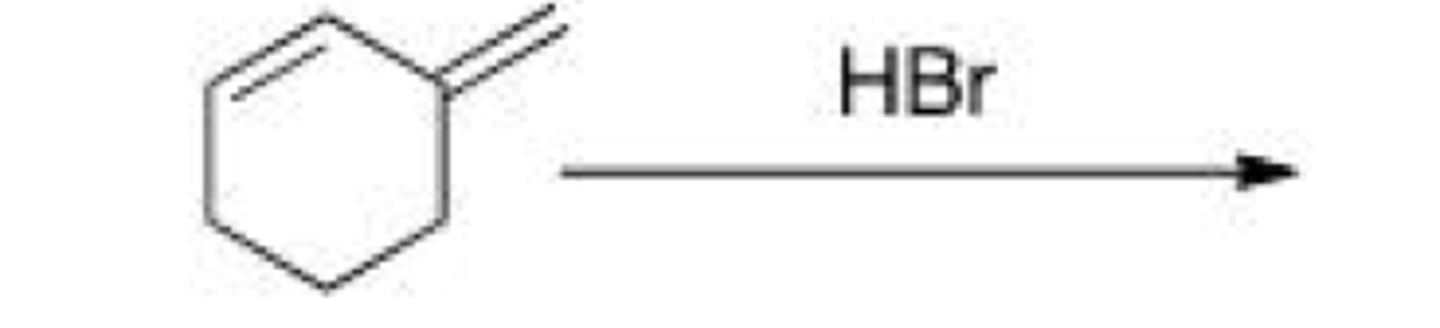
C
Which of the following is an example of a bridged bicyclic system?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
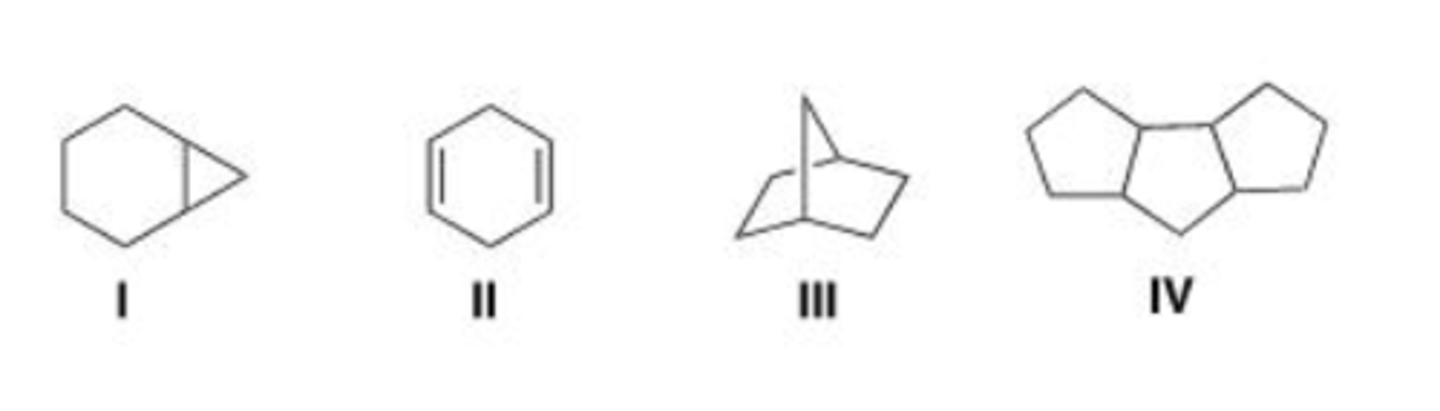
D
Why would the compound below not react with a dienophile in a Diels-Alder reaction?
A. The compound is not a conjugated diene.
B. There are no electron withdrawing groups on the compound.
C. There are no electron donating groups on the compound.
D. The compound cannot adopt the s-cis conformation.
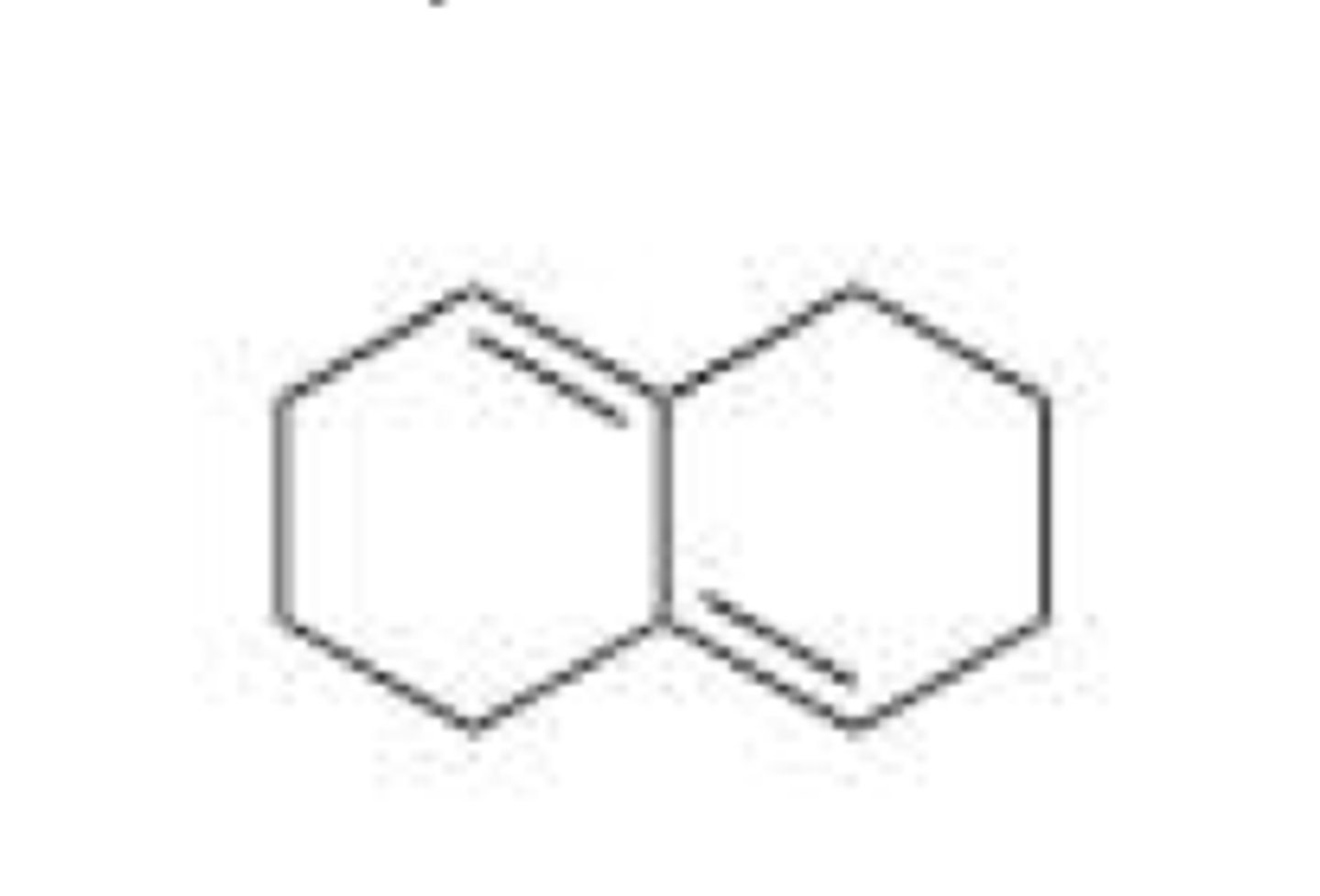
C
Which of the following is not a resonance structure of acetic anhydride?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
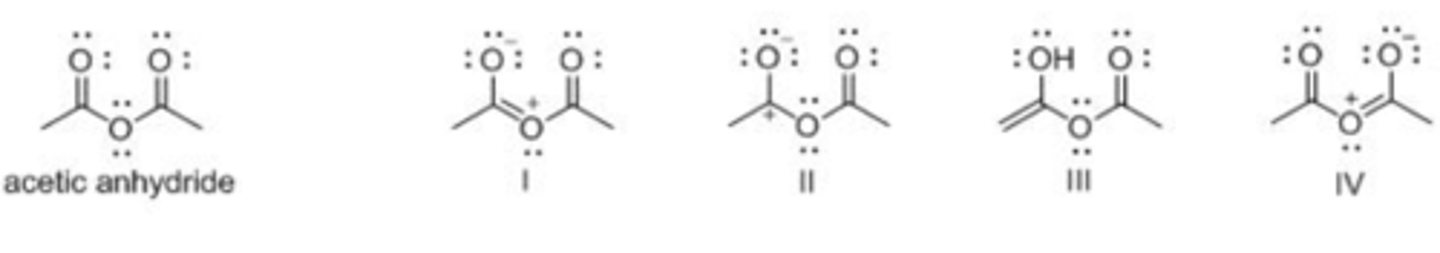
D
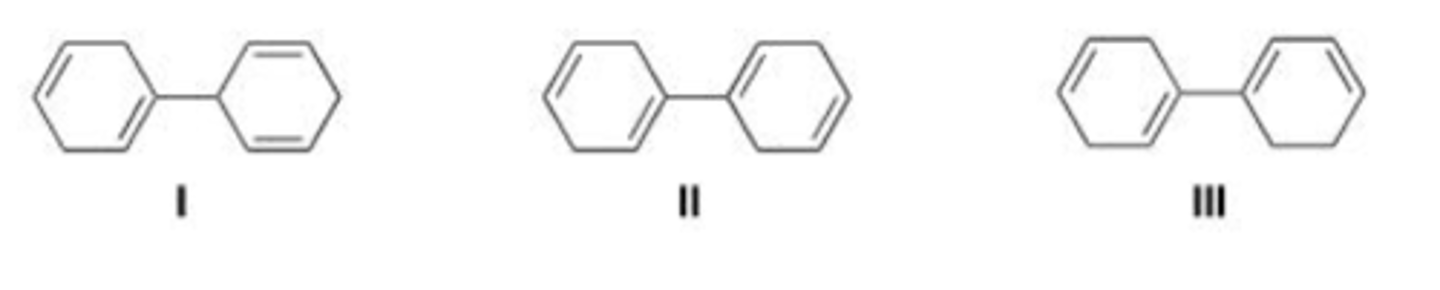
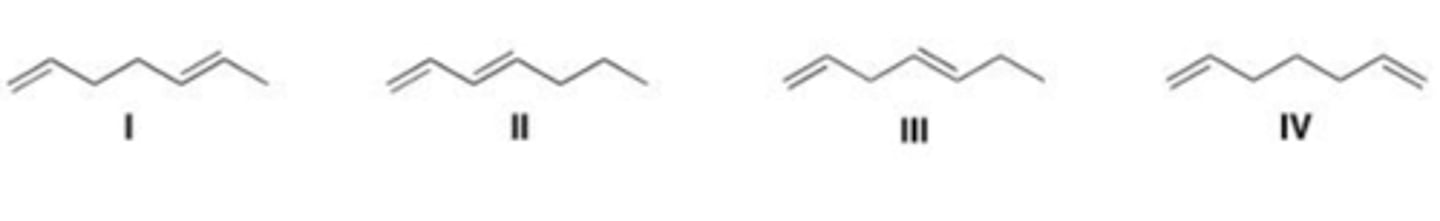
Which triene has the largest heat of hydrogenation?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
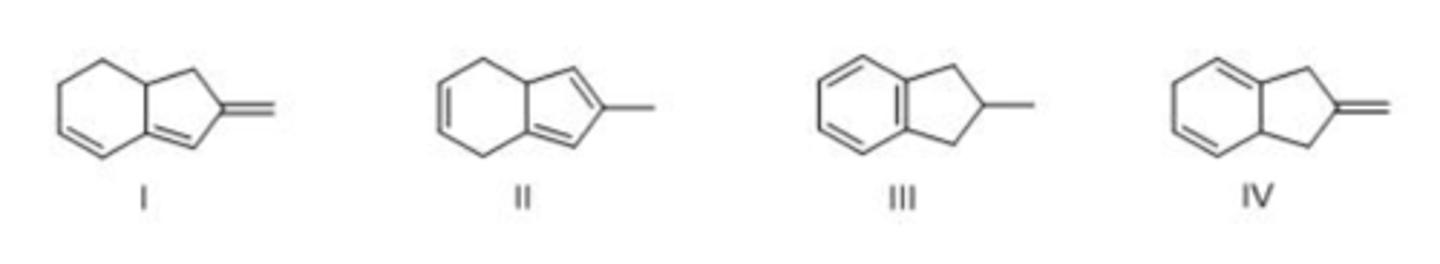
A
Which triene has the smallest heat of hydrogenation?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
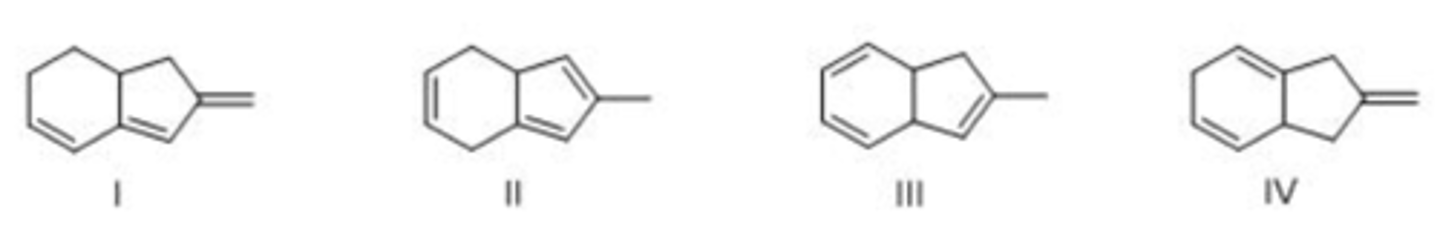
A
Which triene absorbs the longest wavelength of UV light?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV