physics final mock 2
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
efficiency
useful energy transferred by the device/total energy supplied to the device
wave speed
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
formula for inertial mass
force = mass x acceleration
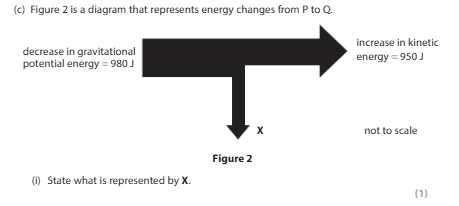
energy dissipated
explain one factor, other than the time of the collision, that would affect the force on the car in the collision
magnitude of the change in momentum influenced by the cars initial speed and mass as a greater change in momentum means a greater force for a given collision time
explain why UVC is potentially the most dangerous ultraviolet radiation but does not cause harm to people
due to its highest energy, it doesn't harm people as it is completely absorbed by the Earth's ozone layer and atmosphere before reaching the surface
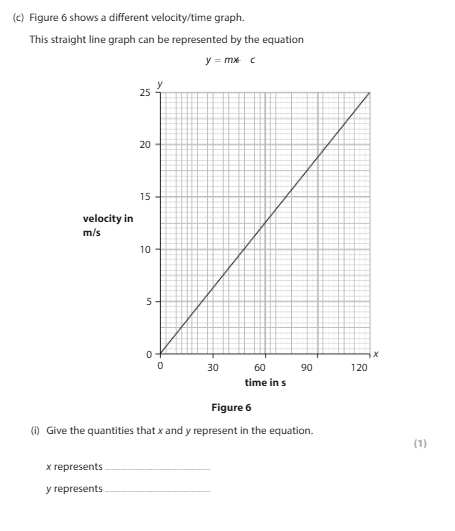
x = time y = velocity
ionising meaning
removing an electron form an atom or molecule creating a positive ion or adding an electron to an atom creating a negative ion
explain how to determine a value for the background radiation count rate
use a GM tube and counter to measure counts over a set time, take several readings to ensure reliability and calculate the average count rate from these readings
the teacher now investigates the absorption of beta radiation by different thicknesses of aluminium
a) name independent variable
b) name constant variable
thickness of aluminium
distance between source and detector
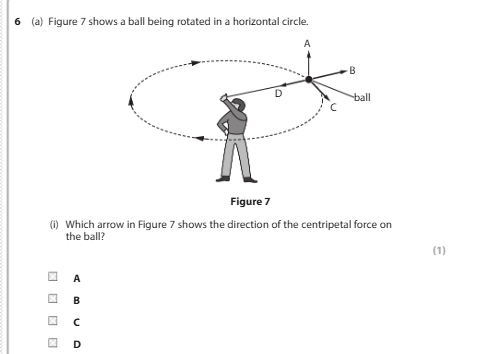
D
the ball is moving at constant speed, give one reason why the velocity of the ball is continuously changing
velocity is a vector quantity meaning it has both magnitude and direction, for an object moving in a circle even if its speed is constant its direction of motion is always to the circle and therefore continuously changing, since the direction component of velocity is changing, the velocity itself is changing
explain how momentum and energy is conserved in this collision
Momentum is a vector quantity with magnitude and direction, before trolley P has momentum to the right and trolley Q has momentum to the left, before the total momentum is zero, after the collision the trolleys stick together and stop meaning their combined velocity is zero therefore the total momentum after the collision is zero meaning it is fully conserved. Before collision both trolleys have kinetic energy, after they collide and stop their kinetic energy is zero, the lost kinetic energy is converted to sound energy from impact and heat energy due to friction from collision, the total energy of the system is constant so energy is conserved overall.