Structural Analysis Introduction
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
refers to a system of connected parts used to support a load. As engineers, we must account for its safety, aesthetics, and serviceability, while taking into consideration economic and environmental constraints.
Structure
is the science and art of planning, designing, and constructing safe and economical structures that will serve their intended purposes.
Structural engineering
is an integral part of any structural engineering project, its function being the prediction of the performance of the proposed structure.
Structural analysis
composed of flexible steel cables are frequently employed to support bridges and long-span roofs.
Tension Structure
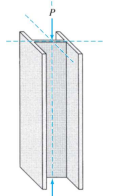
are straight members subjected to axially compressive loads. When a straight member is subjected to lateral loads and/or moments in addition to axial loads, it is called a beam-column.
Compression Structures - Columns
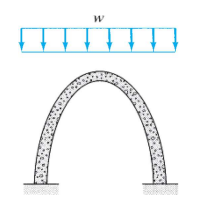
is a curved structure, with a shape similar to that of an inverted cable. Such structures are frequently used to support bridges and long-span roofs.
Compression Structures - Arcs
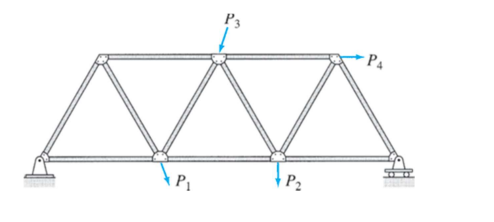
are composed of straight members connected at their ends by hinged connections to form a stable configuration.
Trusses
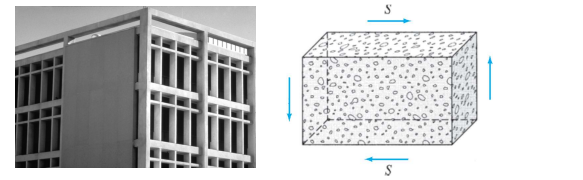
such as reinforced concrete shear walls, are used inmultistory buildings to reduce lateral movements due to wind loads and earthquake excitations.
Shear structures
Some of the most used structures, such as beams, rigid frames, slabs, and plates, can be classified as
Bending Structure
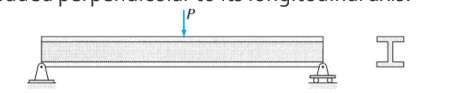
is a straight member that is loaded perpendicular to its longitudinal axis.
Beam
are composed of straight members connected either by rigid (moment-resisting) connections or by hinged connections to form stable configurations.
Rigid frames
The design of horizontal members or beams of rectangular frames is often governed by
bending and shear stresses
are gravity loads of constant magnitudes and fixed positions that act permanently on the structure.
Dead loads
are loads of varying magnitudes and/or positions caused using the structure.
Live loads
induced mainly by wind and earthquakes, are called the lateral loads
Horizontal loads
It is produced by the flow of wind around the structure. The magnitudes of wind load that may act on a structure depend on the:
• geographical location of the structure
• obstructions in its surrounding terrain, such as nearby buildings
• the geometry and the vibrational characteristics of the
structure itself.
Wind loads
It is the horizontal component of ground motion that causes structural damage and that must be considered in designs of structures located in earthquake-prone areas.
Earthquake loads
The portion of the slab area whose load is carried by a particular member is called the
tributary area of the member.
For floor systems with a beam length to spacing ratio of greater than 2.0 (L/s > 2.0)
ONE- WAY SLAB SYSTEM
For floor systems with a beam length to spacing ratio less than or equal to 2.0 ( L/s ≤ 2.0)
TWO- WAY SLAB SYSTEM