A1.2 - NUCLEIC ACIDS
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
djkfasdljfds
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
state the central dogma of biology

what is DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, primary genetic material responsible for storying and transmitting hereditary info
essential for heredity, evolution, and the functioning of living organisms
EXCEPTION: VIRUSES
some use RNA rather than DNA as the genetic material
state the structure of DNA
double helix: molecule is double stranded, linked by complementary base paring between nitrogenous bases (A-T, C-G)
strand orientation: antiparallel strands (2 strands run in oppo direction 5’-3’, 3’-5’), 5’ has a phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of the sugar, 3' end has a hydroxyl group attached to the third carbon of the sugar
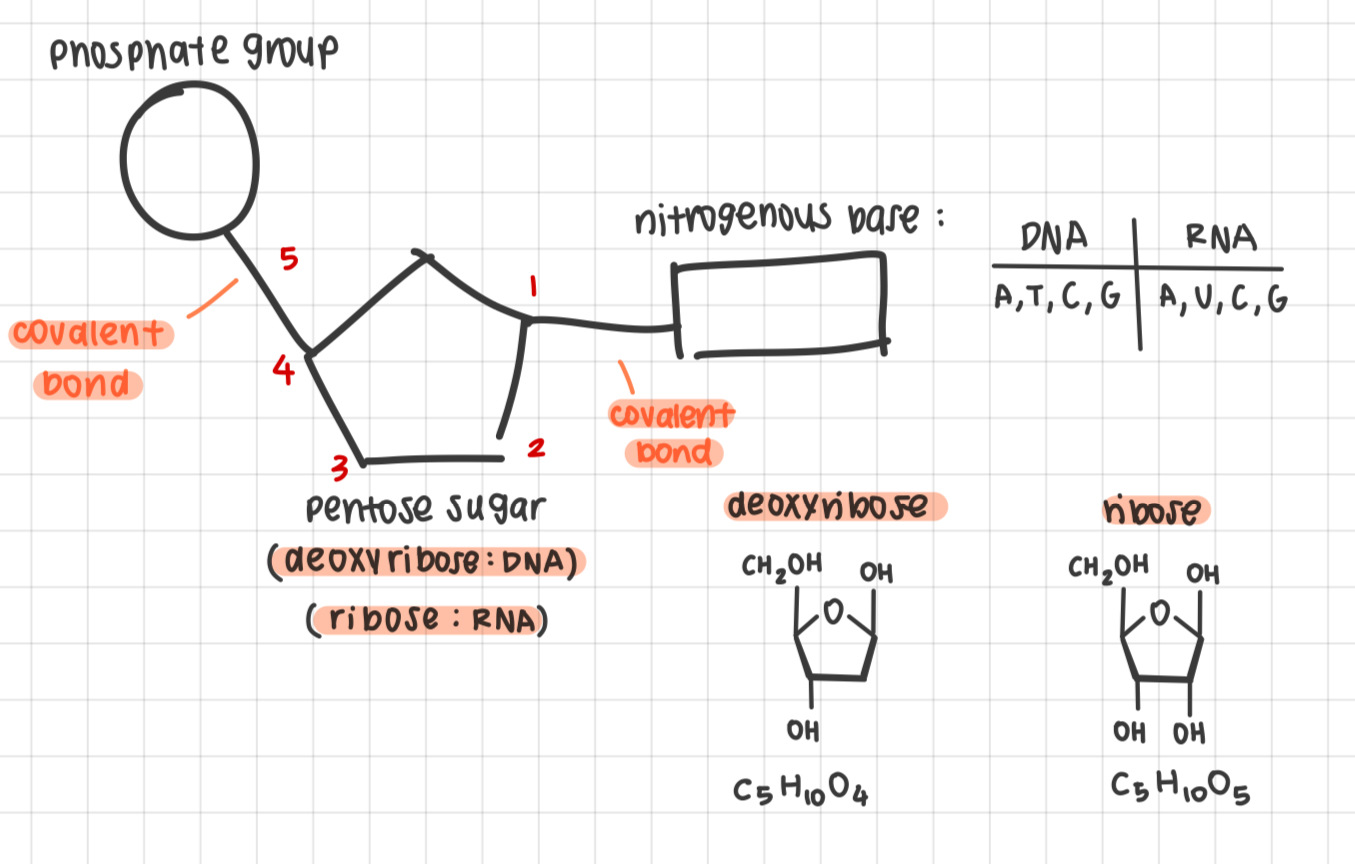
nucleotides: phosphate group, pentose sugar (deoxyribose), nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine)
state the function of DNA
genetic info storage: contains code needed for development, growth, function and reproduction within an organism
gene expression: DNA sequences (genes) transcribed into RNA, then translates into proteins within the cell
state the location of where DNA can be found
eukaryotic cell: nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast
prokaryotic cell: located in a region called the nucleoid
nucleotide to nucleic acids
nucleotides are monomers of nucleic acids
link by covalent bonds
condensation reaction is created
creates sugar phosphate backbone
5’ carbon links to 3’ carbon
hydrogen bonds hold nucleotide bases of opposite strands together
nitrogenous bases
5 types: adenine, thymine, uracil, cytosine, guanine
purines: adenine, guanine (double ring structure - bigger)
pyrimidines: thymine, uracil, cytosine (single ring structure - smaller)
A-T/A-U (2 hydrogen bonds)
C-G (3 hydrogen bonds)
explain why purines always pair with pyrimidines
purines pair with pyrimidines due to complementary structures which enables stable hydrogen bonding and maintaining the structural stability of the DNA double helix
base pairing is important to stabalise the double helic structure of the DNA
what is RNA
ribonucleic acid, carries genetic information, regulates gene expression, participate in protien synthesis
state the structure of RNA
single stranded: RNA is single-stranded, connected by phosphodiester bonds
state the function of RNA
1) mRNA (messenger RNA): carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes
2) tRNA (transfer RNA): brings amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis
3) rRNA (ribosomal RNA): part of the ribosome structure and plays a role in protein synthesis
4) RNA in viruses: serves as genetic material, encodes information required for viral replication and infection
state the location of where RNA can be found
eukaryotic cell: nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosome, mitochondria, chloroplasts (in plant cells)
state the function of a nucleosome
regulate transcription and gene expression
condense long strands of DNA into a more compact form, allowing it to fit within the nuclei
keeps them organised: protect DNA from damage and prevent it from becoming tangled
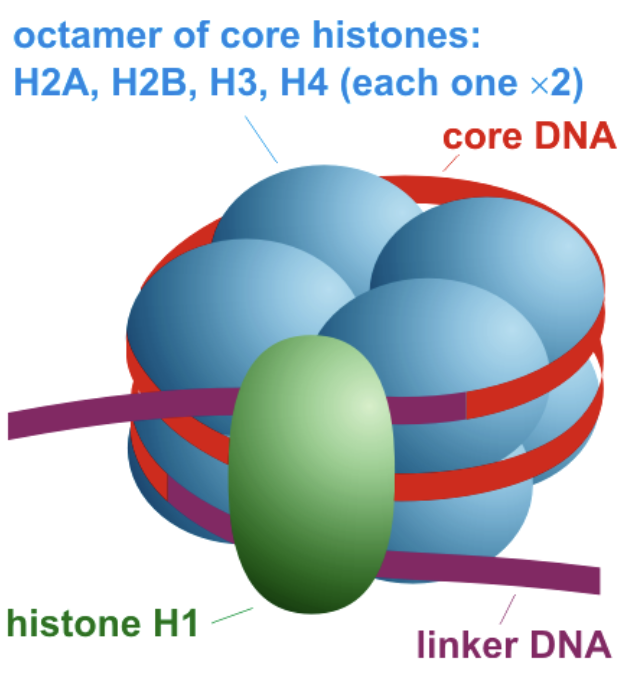
state the structure of a nucleosome
found in eukaryotes
consists of DNA wrapped around histone protiens
eight histones in core (octamer)
“linker” histone attaches to DNA to bind DNA to the core
histone H1 binds to the linker DNA and helps stabilize the nucleosome structure
outline the results of the Hershey and Chase experiment
study that provided crucial evidence for DNA as the genetic material, proved that DNA is the genetic material, not protein (1952)
outline how radioisotopes provide technological breakthroughs in science
“labels” the molecule and can “track” the location and movement of the labelled molecule
allowed scientists to trace atoms and molecules in bodies and cells
explain how Chargaff’s data falsified the tetranucleotide hypothesis
the “tetranucleotide” hypothesis early idea about the structure of DNA
presented that nucleotides were arranged in repeating sequences of the four bases: ATCG, ATCG, etc
%A = %T = %C = %G, %AT = %GC
chargaff proved this hypothesis wrong as he extracted and analyzed the nucleotides from a variety of species
led him to discover that:
A ≈ T , C ≈ G in a given DNA sample
A pairs with T and C pairs with G in the DNA structure
total amount of A, T, C, and G varied among different organisms