MEDICAL IMAGING TEST 3
1/184
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covering chapters 10-15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
Human Diversity (Cultural Diversity)
Addresses the variety of human societies and cultures, examines their similarities and differences
The wide range of individual differences within the human population such as race, ethnicity, gender, age
Cultures
all of socially transmitted behaviors and patters, arts, beliefs, institutions, and all other products of human work and thoughts by particular classes, communities, or populations
Globalization
The increasing interconnectedness and other independence of different parts of the world.
People now cross borders into other countries to work, go to school, receive medical care, and visit
Theories suggest that human diversity is more important today than ever because of increased globalization
nations, societies, business have become increasingly cross-cultural or multicultural
Characteristics of Human Diversity
age
race
gender and sexual orientation
ethnicity/national origin
religion
mental and physical activity
Generation born 1946-1964
Baby Boomers
Generation born 1965-1980
Generation X
Generation born 1981-1999
Generation Y
Generation born 2000-present
Generation Z
Ethnicity
relates to a person’s distinctive racial, national, religious, linguistic, or cultural heritage
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people who identify with each other on the basis of perceived shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include a people of a common language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, religion, history, or social treatment.
Race
Population that differs from others in relative frequency of some gene or genes ; any of the different varieties of human kind, distinguished by type of hair, color of eyes and skin, stature, bodily proportions, etc
Ethnocentrism
Is regarded as the tendency of some individuals to view norms and values of their own culture as the only acceptable ones and to use them as the standard by which all cultures are measured
Racism
The belief that one race or culture is superior to others and the use of this belief to discriminate against races that the believer considers to be inferior
Assimilation
A person of a diverse culture, over time, give up their original cultural language they identify with,and try to merge into another culture
Biculturalism
Ability of individuals to be able to negotiate competently two or more cultures : the mainstream culture and the individuals culture
Gender
The biologic or chromosomal sexual identity of an individual
Sexual Orientation
A persons identity in relation to the gender(s) to which they are sexually attracted to
Homophobia
Irrational fear of homosexuality
Americans Disability Act of 1990
Prevents discrimination against people with disabilities
Intelligence quotient (IQ)
Used to determine if individuals have normal, superior, inferior intellectual ability based on standardized tests that measure cognitive abilities and intelligence
Approximately 10% of the worlds population, has some type of disability
Developing Cultural Competency
possessing a set of attitudes, congruent behaviors, and policies that come together in an agency, in a system, or among professionals that enable effective interactions in a cross-cultural or multicultural environment
Valuing diversity (understanding patient attitudes towards sickness and health
Possessing the capacity for cultural self-assessment (aware of own cultural backround and biases)
Having a consciousness of the dynamics of cross-cultural interaction (avoid stereotypes)
Institutionalizing cultural knowledge (obtain info appropriate to culture)
Developing adaptations of service delivery that reflect on understanding of a multicultural environment (drive to be culturally aware)
Six areas of Human Cultural related to Healthcare
Communication- ability to convey and receive information
Space- distance extending in all directions
Time- period of duration
Environmental Control- ability of people to control nature
Biological variations- ethnical or racially related differences in body structure, skin color, hair texture, etc
Social Organizations- patterns of behaviors related to cultures learned through the process of encultration
Anatomical Position
the central concept behind all descriptions of location within the body
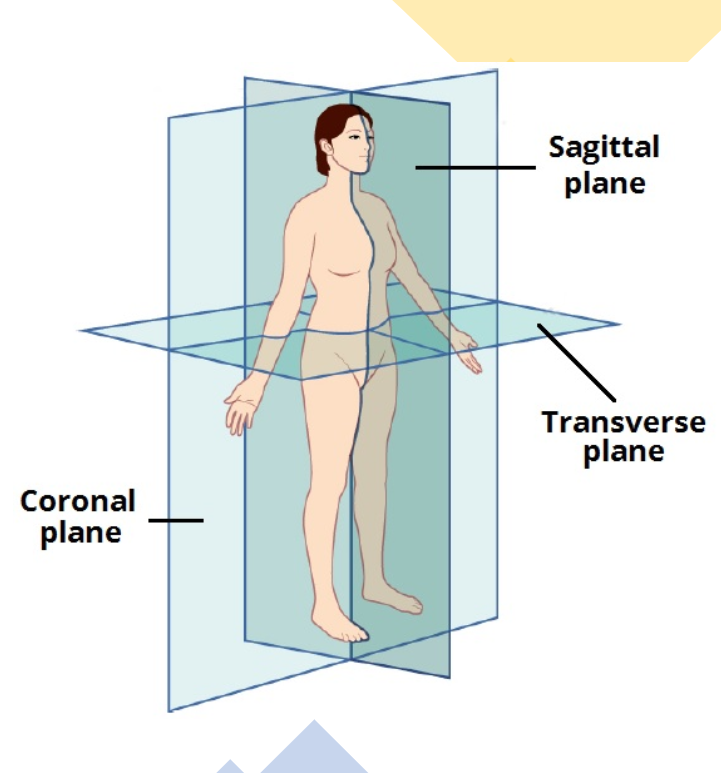
Sagittal
a vertical line which divides the body into a left section and a right section.
Coronal
a vertical line which divides the body into a front (anterior) section and back (posterior) section
Transverse
a horizontal line which divides the body into an upper (superior) section and a lower (inferior) section
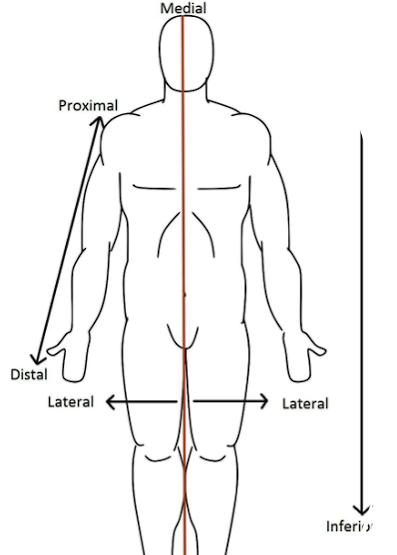
Medial
towards the midline
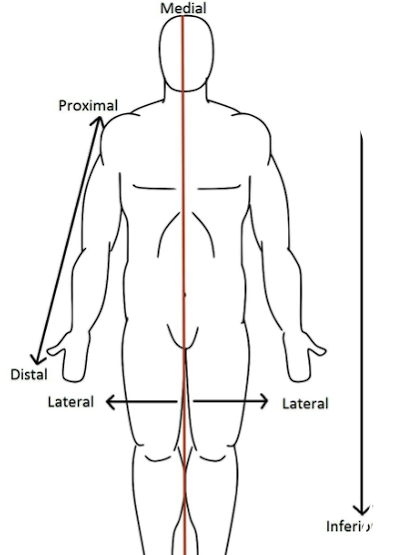
Lateral
Away from midline
Ex : nose is medial to the ears, brachial artery lies medial to the bicep’s tendon
better ex : ears are lateral to nose
Superior
higher in position
Ex : head is superior to neck
Inferior
lower in position
Ex : neck is inferior to head
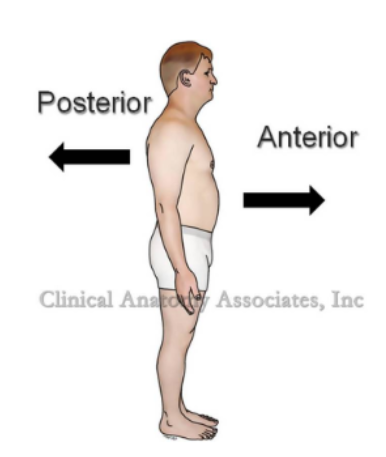
Anterior
refers to the front
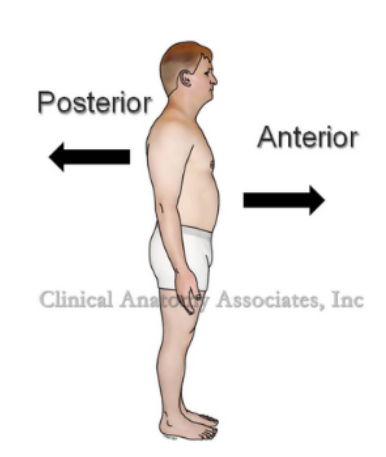
Posterior
refers to the back
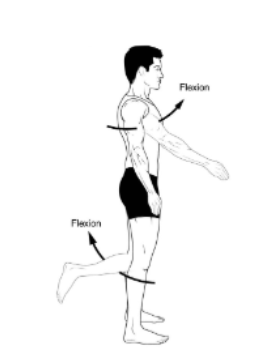
Flexion
movement that causes the angle between two bones of a joint to decrease, such as when a person bends their elbow joint.
(bending; decreasing the angle forward)
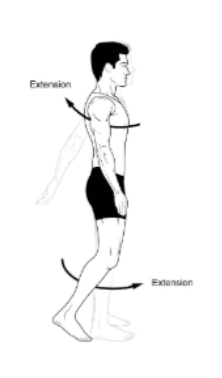
Extension
movement that causes the angle between two bones of joint to increase, such as when a person straightens their elbow joint.
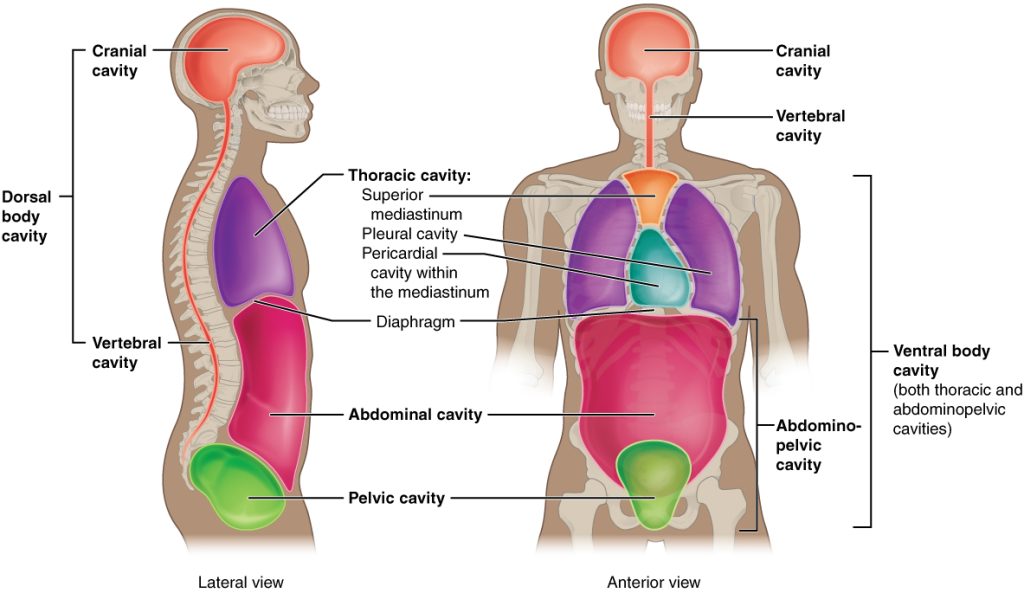
Dorsal Cavity
a continuous cavity located on the dorsal side of the body. It houses the organs of the upper central nervous system, including the brain and the spinal cord
Cranial Cavity
the anterior portion of the dorsal cavity consisting of the space inside the skull. This cavity contains the brain, the meninges of the brain, and cerebrospinal fluid.
Vertebral Cavity
the posterior portion of the dorsal cavity and contains the structures within the vertebral column. These include the spinal cord, the meninges of the spinal cord, and the fluid-filled spaces between them.
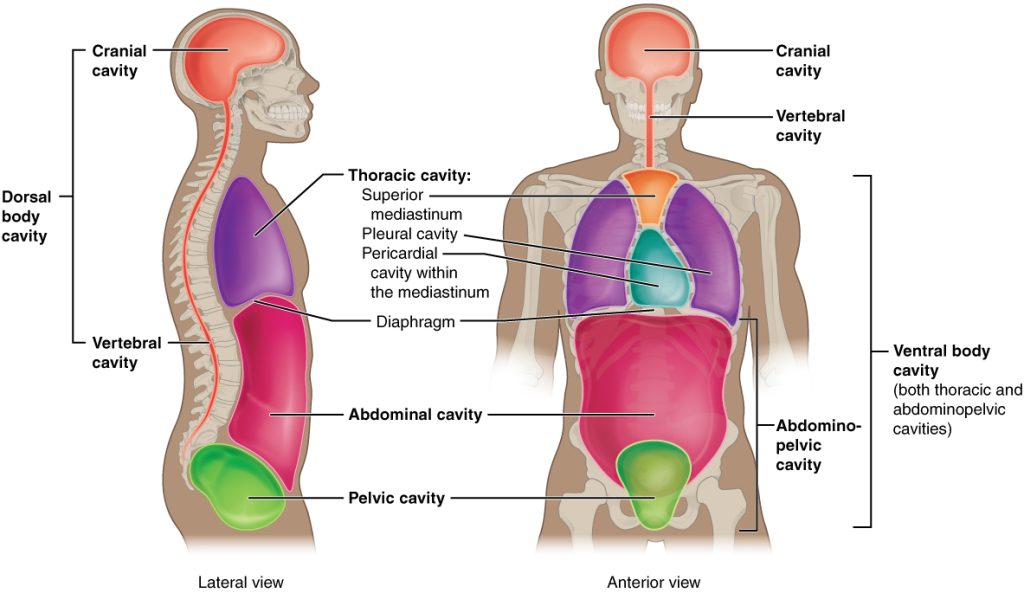
Ventral Cavity
the interior space in the front of the body, contains many different organ systems. The organs within the ventral cavity are also called viscera. The ventral cavity has anterior and posterior portions divided by the diaphragm, a sheet of skeletal muscle found beneath the lungs
Thoracic Cavity
anterior ventral body cavity found within the rib cage in the torso. It houses the primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, such as the heart and lungs, but also includes organs from other systems, such as the esophagus and the thymus gland
Abdominopelvic Cavity
the posterior ventral body cavity found beneath the thoracic cavity and diaphragm. It is generally divided into the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Radiopaque
does not allow x-rays or radiation to pass through
Radiolucent
allows radiation to pass more freely
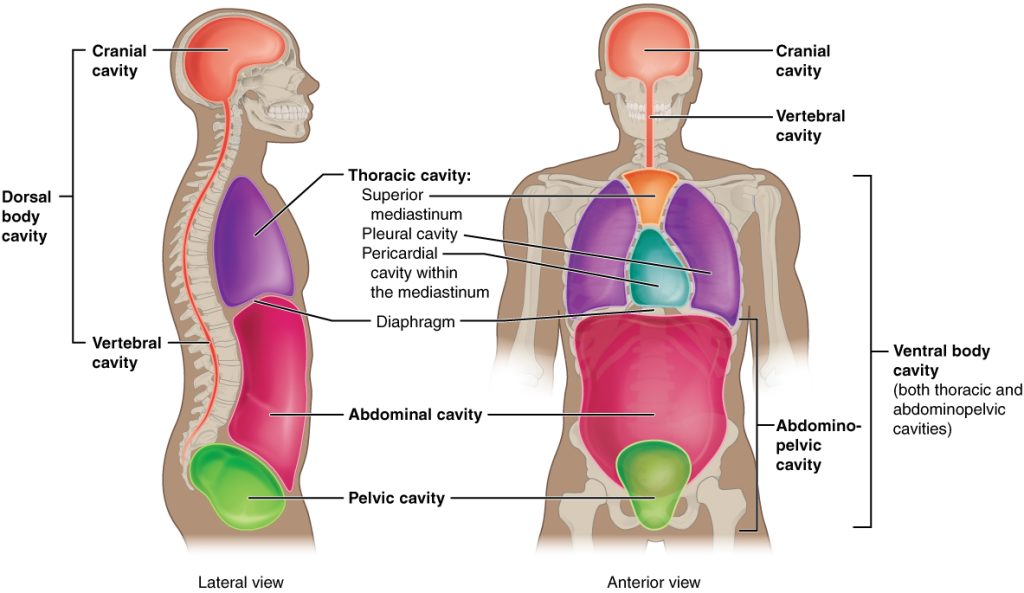
Body Cavity
fluid-filled space within the body that houses and protects internal organs
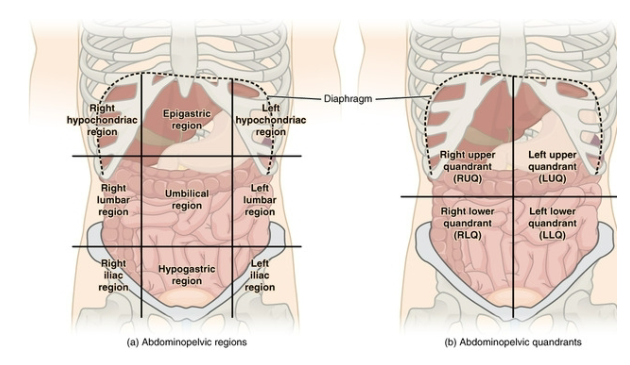
Right Upper Quadrant of the Abdominopelvic Regions
contains the right portion of the liver, the gallbladder, right kidney, a small portion of the stomach, the duodenum, the head of the pancreas, portions of the ascending and transverse colon, and parts of small intestine. Pain in this region is associated with infection and inflammation in the gallbladder and liver or peptic ulcers in the stomach
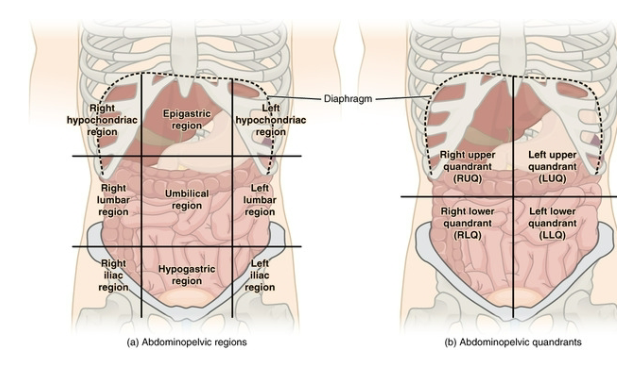
Left Upper Quadrant of the Abdominopelvic Regions
portion of the liver, part of the stomach, the pancreas, left kidney, spleen, portions of the transverse and descending colon, and parts of the small intestine. Pain in this region is associated with malrotation of the intestine and colon
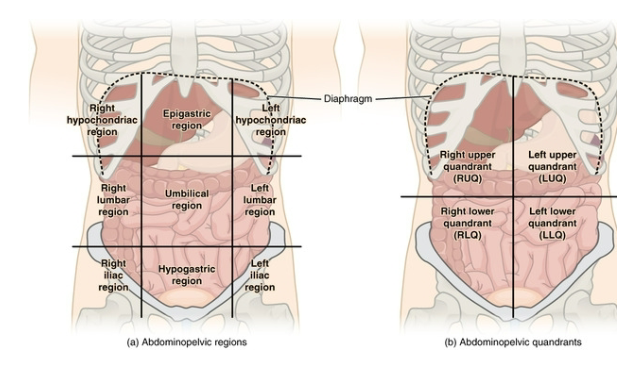
Right Lower Quadrant of the Abdominopelvic Region
the cecum, appendix, part of the small intestines, the right half of the female reproductive system, and the right ureter. Pain in this region is most commonly associated with appendicitis.
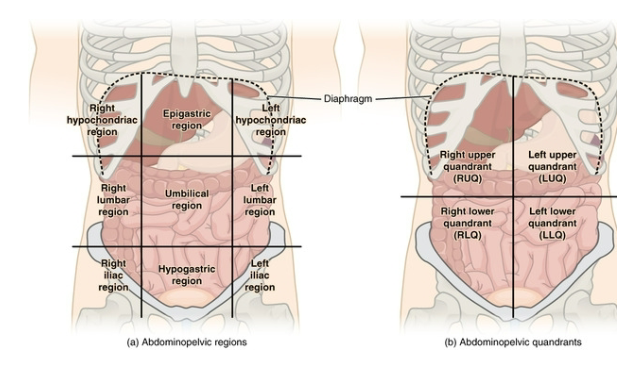
Lower Left Quadrant of the Abdominopelvic Region
houses the majority of the small intestine, some of the large intestine, the left half of the female reproductive system, and the left ureter. Pain in this region is generally associated with colitis
(inflammation of the large intestine) as well as pelvic inflammatory disease and ovarian cysts in females.
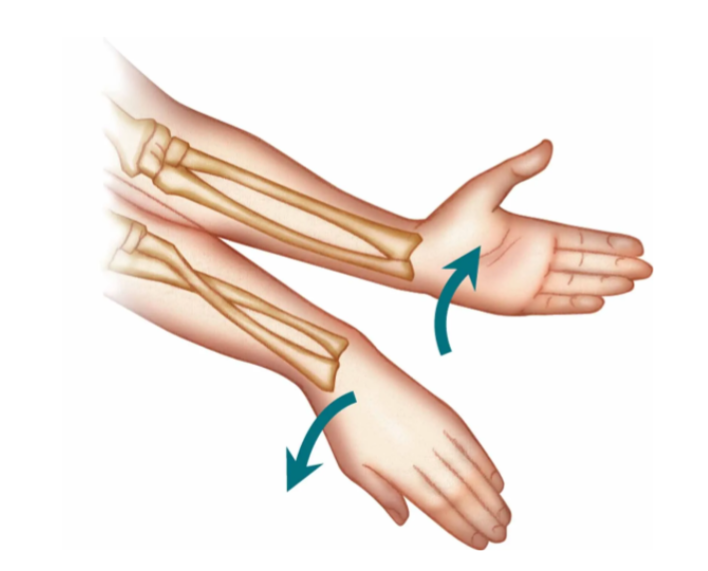
Pronation vs Supination
Rotatory movements of radioulnar joints around a vetrical axis
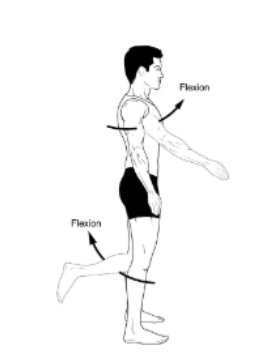
Flexion
the bending of a joint that decreases the angle between two segments of the body.
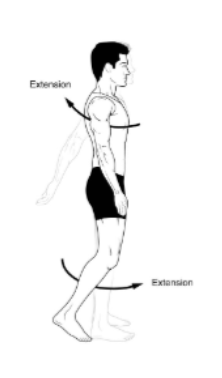
Extension
it's the straightening of a joint that increases the angle between two body parts
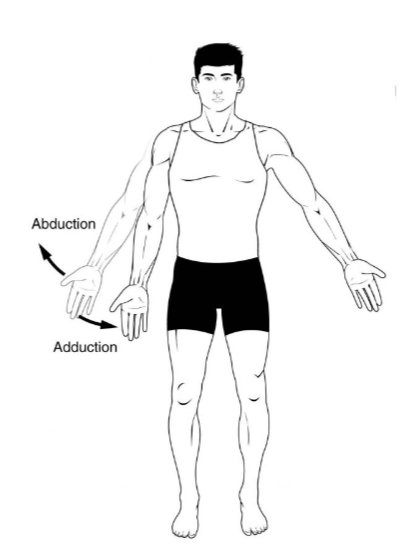
Abduction
refers to the movement of a limb or body part away from the body's midline, the imaginary vertical line down the center of the body.
Human diversity consists of characteristics associated with-
age
ethnicity
race
gender/sexual orientation
lifestyle
Individuals born between 1981 and 1995
Millennials/ Gen Y
Over the next three decades, which age group is expected to be the fastest-growing segment of the population?
85+
Relate to a person’s ethnicity?
language
religion
race
What is NOT one of the ways that culturally different individuals have interacted with the US majority culture in the past?
assimilation
biculturalism
Approximately what percentage of world’s population has some type of disability?
Approximately 10%
Which act is considered the most profound step that the United States has ever undertaken to prevent discrimination toward people with a disability?
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA)
which one is not considered an element that may contribute to the ability of an organization to become culturally competent?
ignoring cultural norms and values
Emotional Intelligence (EI)
one of the best ways to learn to communicate effectively with others is to understand emotions
Patients exhibits a wide range of emotions
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
self-actualization
aesthetics
need to understand
esteem
belongingness and love
safety
physiologic (food, shelter, clothing, sexual gratification
Two types of patients
Inpatients and outpatients
Inpatients
those occupying a bed
Outpatients
those not occupying a bed
Patient assessment is in 2 forms
reading the patients charts
verbal communication
Patient Interaction
Inpatients or outpatients can come to the radiology department with family or friends – Friends will not be allowed in the room
■ Patient information and history – Family members are allowed in the room
■ Elderly patient may have a son or daughter to help the hx and explaining the exam
■ Patient does not speak English, but a family member does
Patient interaction (2)
– Family members are allowed in the room (cont)
■ If the patient is not cooperative, a family member may help position the
patient
■ If there is a need to hold the patient in a certain position
– Chest x-ray on a cart
– Upright toddler
■ If the patient is a minor and the patient request that mom or dad stay
with them
■ Police officers are allowed in the room in the event the patient is a
prisoner
■ Mental health workers are allowed in the room
– Family members are not allowed in the room
■ Family members who may be pregnant or suspect that they
are
– Regardless of pregnancy all patients must wear a lead
apron
■ Non family members
Methods of Effective Communication
Verbal skills
Humor
Verbal skills
It is what you say and how you say it
different tones of voice may mean different things
what you say may have different effects on different cultures
Humor
Many patients use their illness or disease as a humorous event and others will get angry
Non-verbal communication
Patients receive signals about them by the radiographers attitude such as
tone
pitch
pauses
rate of speaking
volume
Palpation
Using finger tips
Traumatized patients
may be in shock
may not be aware of where they are
may not be aware of what they are saying
may be combative
Nonresponsive patients
stat chest example
technologist should try to communicate while determining their coherence level
work quickly and effectively while continuing to communicate
letting the patient know what is going on during the procedure
watch for visual indications of changed in vital signs
Visually Impaired patients
giving clear instructions before the exam
reassuring the patient through gentle touch
establish someone is near if needed
Hearing impaired patients
write out the instructions
write out questions
Non English speaking patients
interpreters
Mentally impaired patients
usually have someone with them
communicate with gentle tones and smiles will often illicit a positive response
Intoxicated Patients
Unpredictable
Gerontology
geriatrics
study of aging and diseases of older adults
at the end of 20th century, more than 33 million Americans were over 65 years of age-more than 12% of the population
referring to older patients as geriatric
Terminally ill patients
– Closed awareness
■ Patient is unaware of condition
– Open awareness
■ Patient is aware of condition
Stages of Dying
Denial and Isolation
Anger
Bargaining stage
Depression
Acceptance
Advance Directives
means of a patient to direct their health care they are unable to make decisions on their own.
BE
Barium Enema
BID
twice daily
BP
Blood pressure
CXR
Chest X-ray
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease