A & P nervous system flashcards
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what two parts is the nervous system divided into?
CNS
PNS
What is the PNS comprised of?
all other nerves that are in the brain or the spinal cord.
What is the CNS comprised of?
consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
clinical application: Migraine
signs: pounding head, nausea, aura light or sound sensitivity
treatment: drugs that block neurotransmitter release from certain neurons
What is sensory division (Afferent)?
sends impulses from the senses to the CNS
What is motor division (Efferent)
sends impulses from the CNS to the muscles and the glands
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic?
Symp: used in emergency situations (fight or flight)
Parasymp: reduces sympathetic response and provdies resting functions
Autonomic vs Somatic?
Auto: involuntary muscle control
Soma: voluntary muscle control
NS: sensory input
it detects changes inside and outside the body
NS: Integration
processing and interpreting the information
NS: Response
activation of muscles (motor output) or glands
What are the 2 types of nerve cells
Neurons: conduct impulses around the body
Neuroglia: support, insulate, and protect neurons
What percent of nerve cells do neurons make up?
10%
What percent of nerve cells do neuroglia make up?
90%
what does the cell body of a neuron contain?
nucleus
cytoplasm
organelles
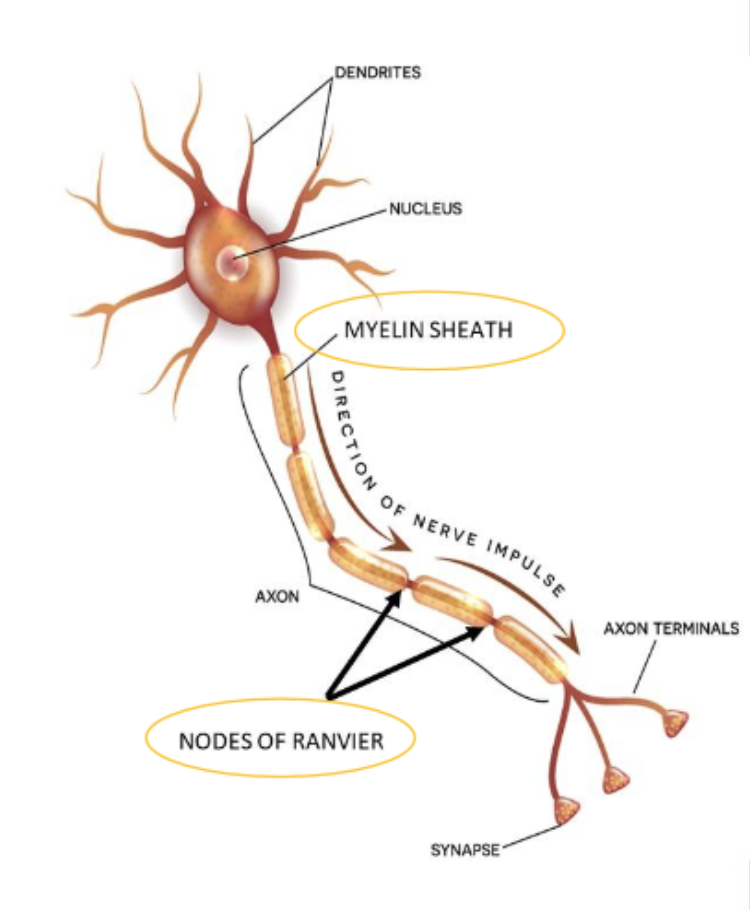
what is a dendrite?
brings impulses towards the cell body
(the little branches protruding off the neuron)
What is an axon?
send impulses away from the cell body
(the long chain which follows the flow of nerve impulses)
What is an axon terminal?
they release neurotransmitters to pass an impulse to the next neuron.
What are the 3 types of neurons?
unipolar: one process
bipolar: two processes
multipolar: many processes
What are the 3 types of neuron functions?
afferent neurons: carry impulses towards the CNS
efferent neurons: carry impulses away from the CNS
interneurons: connect afferent and efferent neurons
what are axons wrapped in?
Myelin, which is like a waxy insulation → helps nerve impulses to travel more quickly.
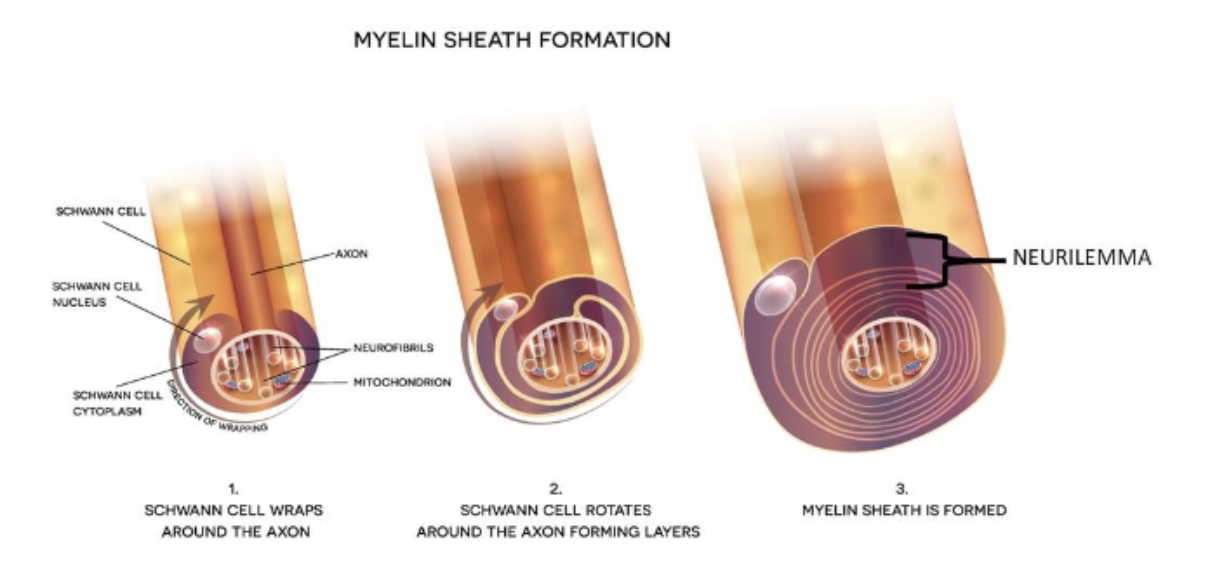
how is a myelin formed?
a Schwann cell wraps itself around axon, like a coil.
(^ outside layers of a schwann are called a neurilemma)
what are the myelin wrappings called?
myelin sheath; since this is formed from many Schwann cells, it has gaps called Nodes of Ranvier
What are satellite cells?
support clusters of neuron cell bodies (ganglia)
what are astrocytes?
support and anchor neurons to surrounding capillaries
what are microglia?
provide immune response to the CNS
what are ependymal cells?
secrete and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
what are oligodendrocytes?
provide myelin insulation to neurons in the CNS
How is a nerve impulse passed along a neuron?
an electrical signal that travels along the neuron. It arises from the movement of ions causing a change in electrical charges.
What happens when a neuron is at rest?
its intracellular space is negatively charged and the extracellular space is positively charged. this is called resting potential
What happens when a neuron is stimulated?
Sodium rushes into the neuron and quickly reverses the charges (depolarization) → this is known as an action potential
^ This process moves down the length of a neuron
what happens as an impulse passes (neuron stimulated)
potassium diffuses put of the neuron (re polarization)
then, the sodium-potassium pump then restores the ion concentrations to normal and the resting potential returns.
What are the steps of a nerve impluse
1. impulse arrives and threshold is met → 2. voltage gated Na+ channels are opened and Na+ enters the cell → 3. voltage gated K+ channels are opened and K+ leaves the cell; Na+ begin to rest → 4. channels ( K+) are still open; while Na+ are at resting state → 5. Na+/K+ pump restores orginial levels of voltage in the cell.
What event occurs at the synapse?
where two neurons meet
these two neurons do not touch, the space between them is called the synaptic cleft.
T OR F: does the impulse cross the axon terminal once it reaches?
FALSE; it does not cross the gap
what does the impulse stimulate?
the vesicle to release the neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft
these neurotransmitters cause channels to open in the next neuron, continuing the action potential from one neuron to the next.
overview steps of synaptic transtion? (cards: 36,35,34)
action potential arrives at presynaptic terminal
Ca2+ channels open on presynaptic terminal
synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron
Na+ channels open on the posthypnotic neuron
what are the structures protected by three layers of connective tissue called the meninges
dura mater: thick, tough layer
arachnoid membrane: thin, cobweb-like layer
pia mater: thin layer containing lots of blood vessels
where is the cerebrospinal fluid and what is its function?
between the arachnoid layer and the pia matter
it protects the brain by preventing it from contacting the skull.
it also maintains the blood-brain barrier (this controls homeostasis for the brain and prevents infection
how many ventricles are in the CSF system
4 ventricles
2 lateral
How is the myelin sheath created?
from a Schwann cell; this wraps itself around the axon like a coil.
The outer layers of a Schwann cell are called the neurilemma.
What is the overall purpose of a myelin?
they help nerve impulses travel more quickly
provide insulation
What are Satellite cells? What are Schwann cells?
Support clusters of neuron cell bodies (ganglia) → in the PNS
Provide myelin insulation → in the PNS
Where are neuroglia found?
Either in the CNS or the PNS
What is the #1 kind of neuroglia in the CNS that supports and anchors neurons to surrounding capillaries?
Astrocytes
What is the #2 kind of neuroglia in the CNS that provides immune response?
Microglia
What is the #3 kind of neuroglia in the CNS that secretes and circulate cerebrospinal fluid?
Ependymal cells
What is the #4 kind of neuroglia in the CNS that provides myelin insulation to neurons?
Oligodendrocytes