DNA, rNA, Protein Synthesis, and Mutations Test
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
determines an organism’s traits (ex. hair colour, eye colour)
holds the information for life
List the nitrogenous bases
Purines:
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines:
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
What is Chargraff’s Rule?
Adenine MUST pair with Thymine
Guanine MUST pair with Cytosine
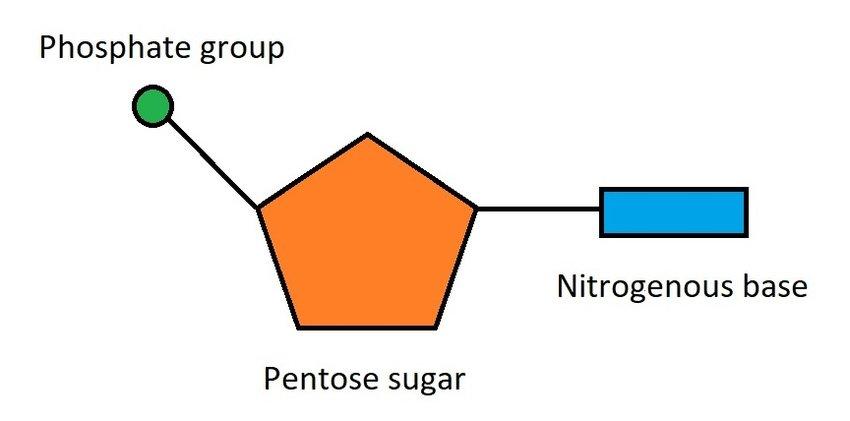
What are nucleotides?
Repeating units of large DNA molecules
What is a nucleotide composed of?
1 sugar, 1 phosphate, 1 nitrogen base (A,T,C,G in DNA; U,A,G,C in RNA)
Enzyme
macromolecule acting as a catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction in our bodies
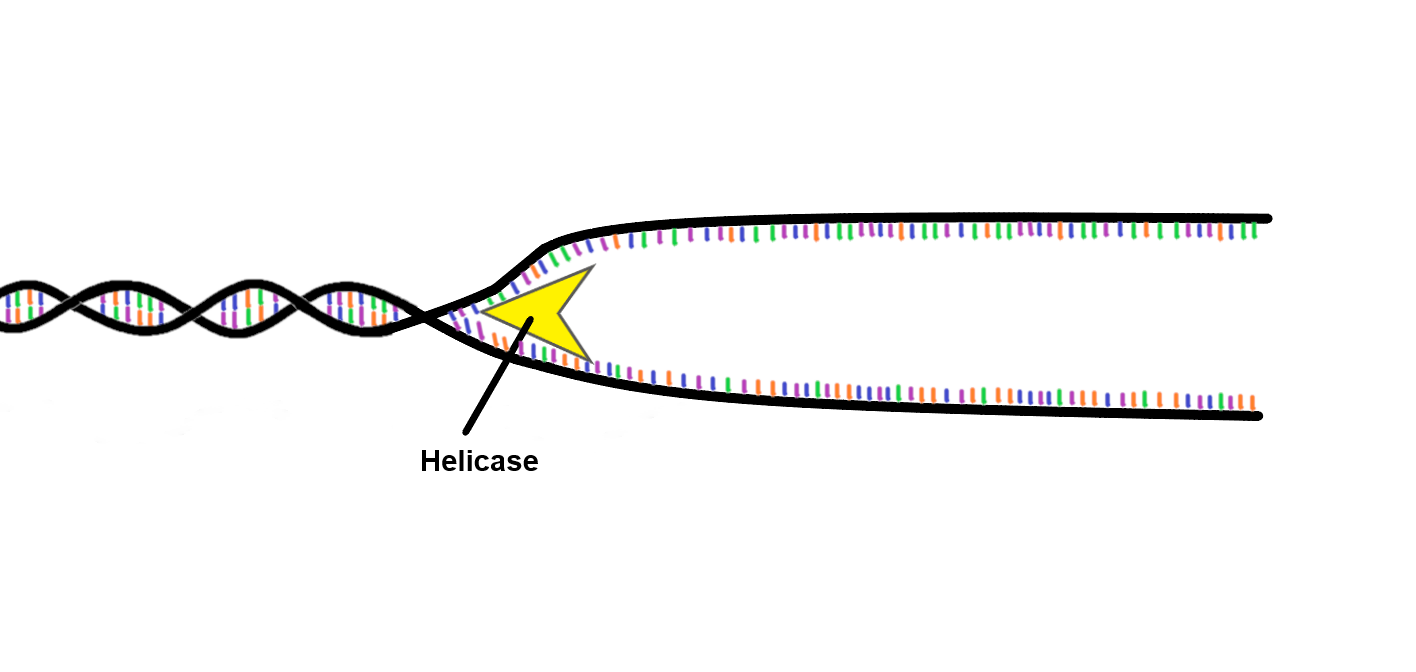
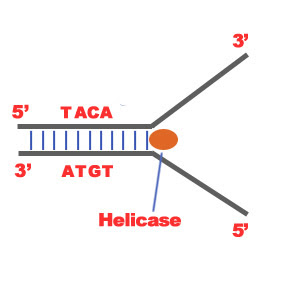
Helicase
An enzyme that unzips the DNA molecule by breaking the hydrogen bonds between base pairs
DNA polymerase
Adds new nucleotides to build the new complementary strand; checks for mistakes
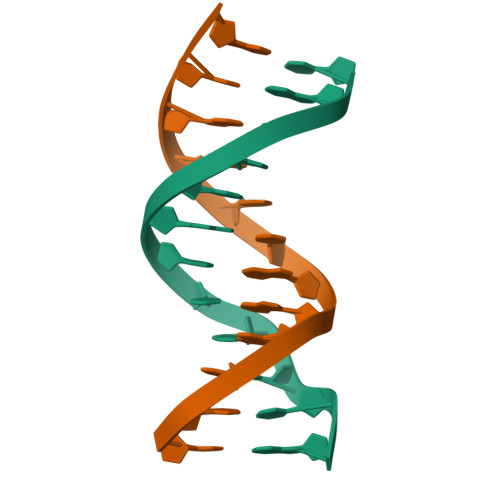
Double Helix
twisted-ladder shape of DNA formed by two strands

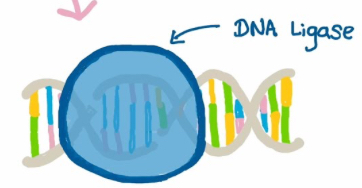
Ligase
enzyme that joins pieces of DNA together
Template Strand
The original DNA strand serving as as guide for building a new complementary strand
What is the name of the process shown in the diagram?
DNA replication
When does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication occurs during the process of meiosis and mitosis
Why does DNA replication happen?
growth and repair
First step of DNA replication:
Enzyme (helicase) breaks hydrogen bonds between base pairs
Second step of DNA replication:
DNA helix unwinds — two strands separate (unzip)
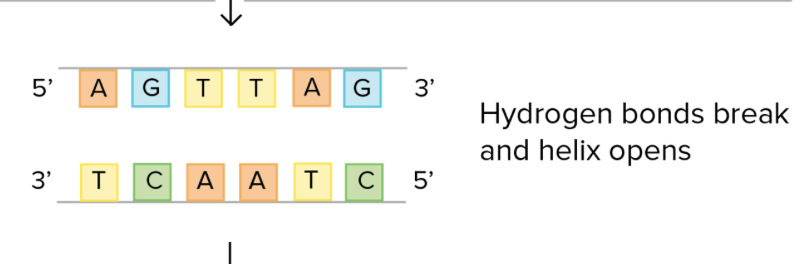
Third step of DNA replication:
Free nucleotides from the cytoplasm enter the nucleus with the help of DNA polymerase; they bond to complementary bases on the DNA strands
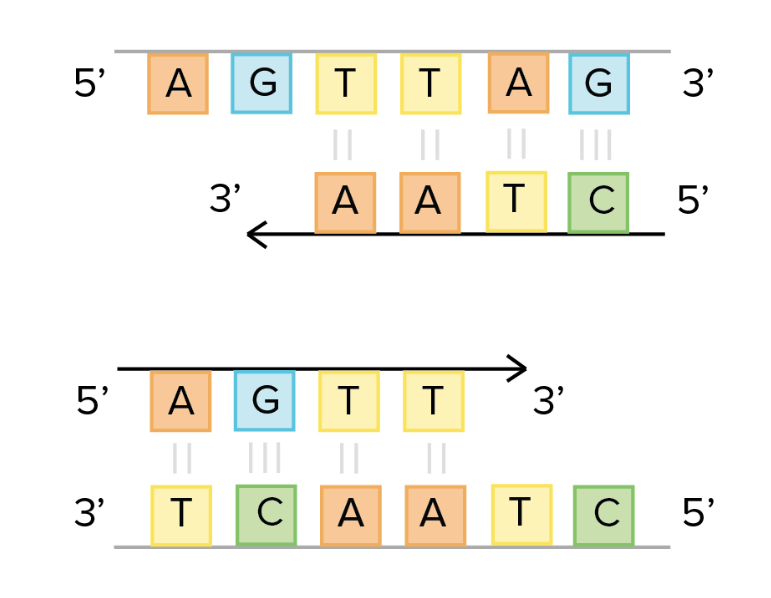
Result of DNA replication?
two identical DNA molecules that are EXACT copies of the original
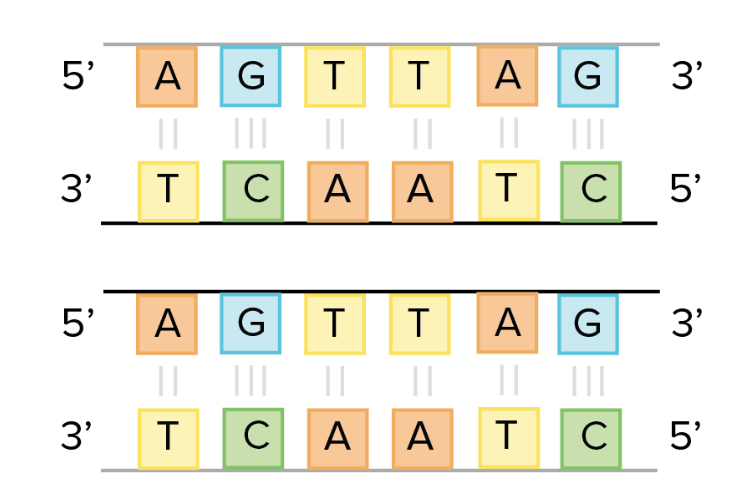
What is semiconservative?
Two DNA molecules that each consist of one “old” strand and one “new” strand.
What is antiparallel?
One strand goes 5’ to 3’; the other goes 3’ to 5’
What is recombinant DNA?
A technique used in genetic engineering; to make large quantities of the product coded by the gene
Define vector.
Vector: a plasmid (bacterial DNA) or virus. Something to “host” the gene of interest
List the examples of rDNA:
Gene therapy
Cloning
Transgenic “pharm” animals
Transgenic/GMOs
Gene therapy
Inserting a functioning gene to help an individual with a dysfunctional gene (ex. fixing defective genes to help sick people get better)
Cloning
Making copies of genes and/or inserting genes into cells (ex. making an exact copy of an animal (Dolly the Sheep))
Transgenic “pharm” animals
Using animals/bacteria to make vaccines and drugs (ex. goats producing medicine (anti-clotting factors) in milk)
Transgenic/GMOs
Giving organisms traits they don’t naturally possess (ex. Golden Rice containing extra vitamin A)
Contrast DNA and RNA
DNA:
double-stranded helix
deoxyribose
ATCG
nucleus
permanent
RNA:
single-stranded
ribose
UAGC
nucleus and cytoplasm
temporary
Compare DNA and RNA
both are nucleotides
both has adenine, guanine, and cytosine
both carry genetic information
both are needed for making proteins
What is protein synthesis?
process of making proteins
involves transcription and translation
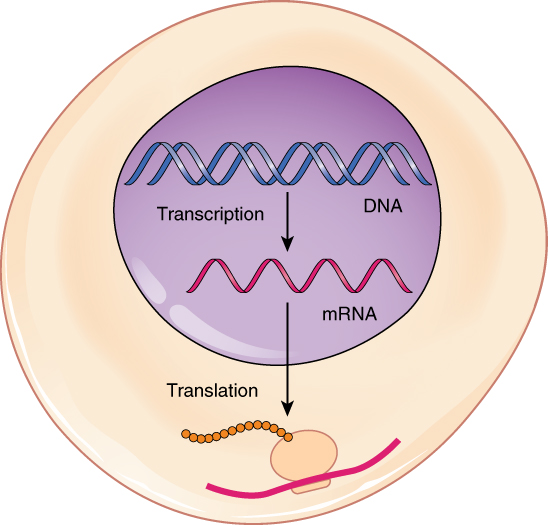
What is transcription?
mRNA (messenger RNA)
DNA → mRNA
process of making mRNA from a DNA template to take the DNA info outside of the nucleus
DNA too fat to leave nucleus
mRNA carries info encoded in DNA out of nucleus to the ribosomes located in the cytoplasm in a cell
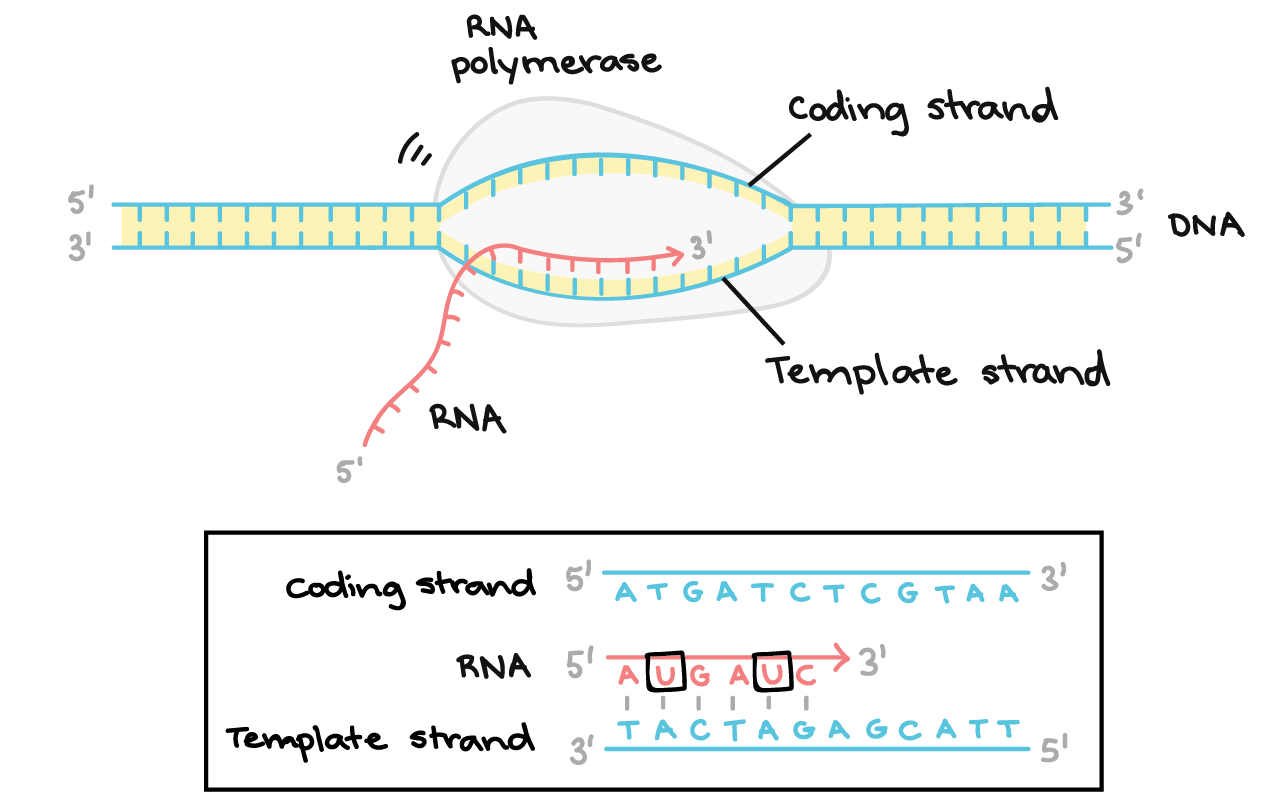
First step of transcription:
DNA strands unwind and separate
Second step of transcription:
DNA strand containing a specific gene serves as a template strand
Third step of transcription:
RNA nucleotides are matched to complementary DNA bases
Fourth step of transcription:
mRNA molecule is complete and DNA rewinds
DNA and RNA
DNA: A T C G
=
RNA: U A G C
PRACTICE: CTG TAC GGA
GAC AUG CCU
What is translation?
mRNA → protein
process of making proteins from info on mRNA
mRNA travels out of nucleus to the ribosomes located (rRNA), which “reads” the mRNA as a series of 3 letter words called codons
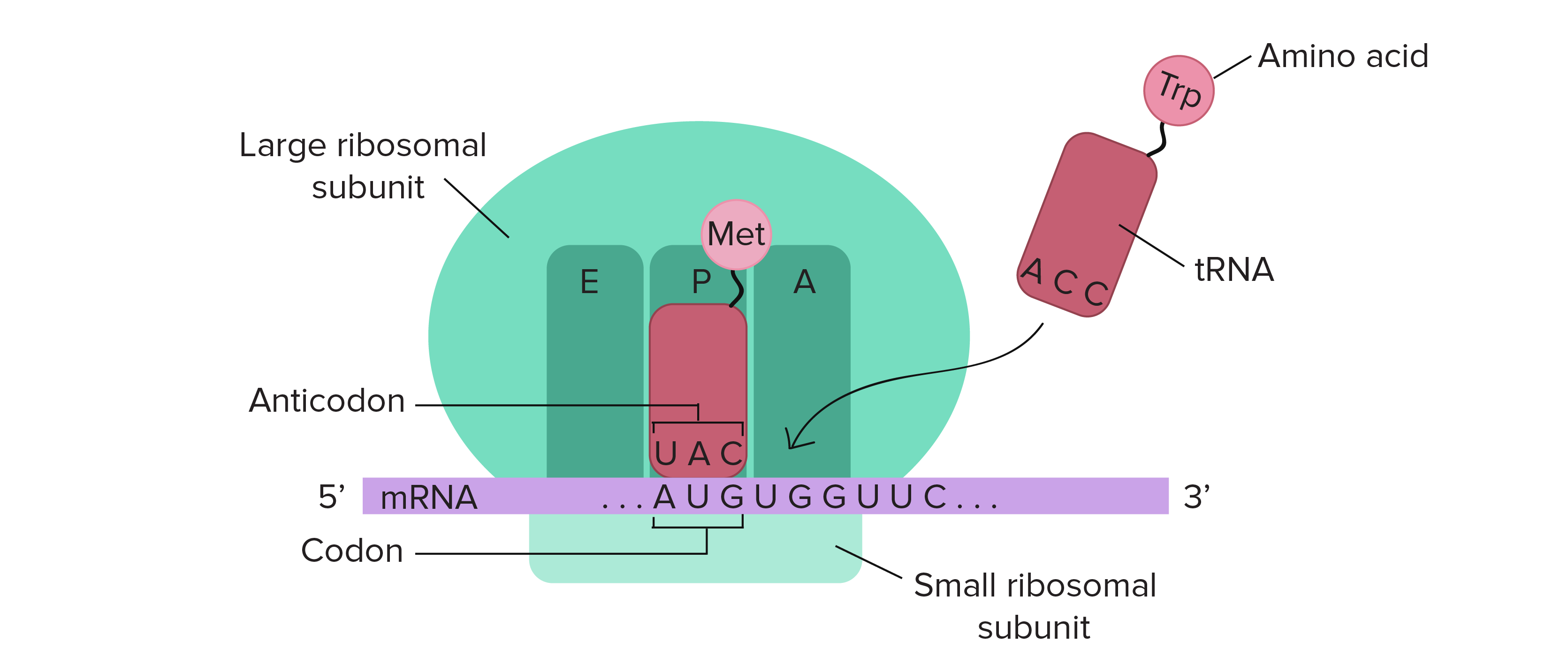
Define codon.
3-base code on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid
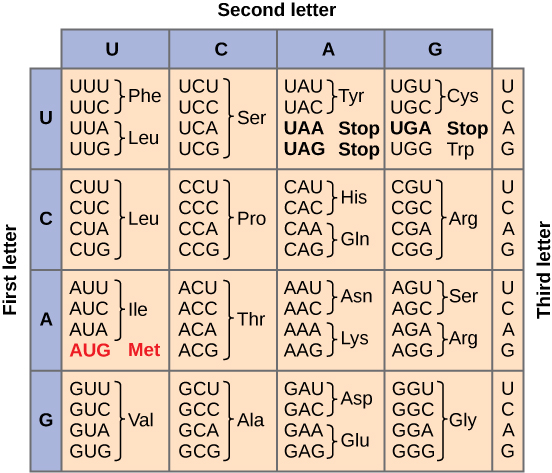
Define protein.
peptide bonds connecting amino acids
Define mutation
A change in the DNA sequence
How can mutations occur?
errors during DNA replication
radiation
chemicals
viruses
What are ways mutations can occur?
Substitution
Deletion
Insertion
Inversion
Reciprocal translocation
Chromosomal rearrangements
Substitution
base is replaced by one of the other three bases (ex. A → G)
Deletion
a base is removed (ex. ATC → AC)
Insertion
a new base is added (ex. ATC → ATGC)
Inversion
a section of DNA flips around 180°
Reciprocal translocation
two chromosomes change places (ex. chromosome 1 gives part of its DNA to chromosome 3)
Chromosomal rearrangements
big mutations that change the structure or order of parts of a chromosome
What are the consequences of mutations?
Missense mutation
Nonsense mutation
“Silent” mutation
Frameshift mutation
Missense mutation
changes an amino acid to another amino acid
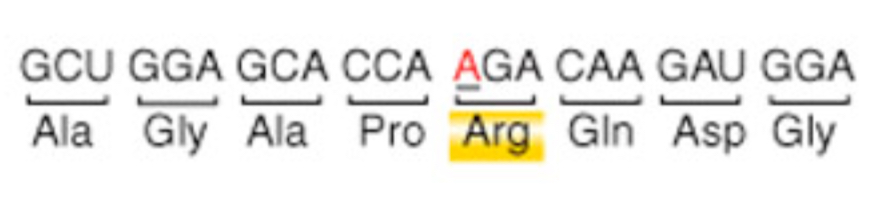
Nonsense mutation
changes an amino acid to a STOP codon; premature termination of translation

“Silent” mutation
doesn’t change an amino acid, but in some cases can still have a phenotypic effect (ex. speeding up or slowing down protein synthesis)

Frameshift mutation
deletion or insertion of a number of bases that is not a multiple of 3. Usually introduces premature STOP codons in addition to lots of amino acid changes

Mutation impact on protein function
loss of function
complete loss of the protein
gain of function
increase in the protein’s function