A Framework to Address Maternal Mortality: Global and US Context
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Why maternal mortality is so importnat in poublic jealth?
A powerful warning sign about how well a society protects pregnant people and families, how strong its healthcare system is, and how much it values human rights—and it’s now recognized as a top U.S. public health priority.
not in HP2020 but in HP2030
Maternal Death – definition
the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of the end of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and the site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management, but not from accidental or incidental causes.
Maternal mortality ratio (MMR)
MMR = (# of maternal deaths)/(# of live births)
represents the risk associated with each pregnancy
Maternal death - direct cause
Deaths resulting from obstetric complications of the pregnant state (pregnancy, labor and puerperium), from interventions, omissions, incorrect treatment, or from a chain of events resulting from any of the above.
Maternal death - indirect cause
Deaths resulting from previous existing disease or disease that developed during pregnancy and which was NOT due to direct obstetric causes, but which was aggravated by physiologic effects of pregnancy.
leading causes of maternal death (globally) [direct causes]
HOUSE
H - Hemorrhage (28%)
O - Obstructed labor (8%)
U – Unsafe abortion (13%)
S – Sepsis (15%)
E – Eclampsia / hypertensive disorders (14%)
Hemorrhage
Massive bleeding during pregnancy/after birth due to uterine or placental issues,
trauma, or blood clotting issue. Leads to shock or death
Obstructed labor
Malpresentation (breech, transverse); cephalopelvic disproportion (inability of
head to fit through pelvic canal). Can lead to fetal death and maternal death.
Unsafe abortion
Can lead to uterine perforation, other trauma, hemorrhage, and infection.
Sepsis
AKA puerperal infection or fever (temperature ≥38°C during pregnancy, labor, or after childbirth.
Eclampsia / hypertensive disorders
High blood pressure, protein in urine, and other symptoms During late pregnancy or postpartum. Can lead to liver rupture, stroke, seizure or death
leading causes of maternal death (globally) [indirect causes]
Anemia, Malaria, HIV, heart disease
hemorrage - direct or indirect?
direct
Anemia - direct or indirect?
indirect
Pregannt mom not knowing she has pre-eclampsia symptoms - delay?
delay in recognizing
Long distance to provide - delay?
delay in reaching services
Shortage of equipment and supplies - delay?
delay in receiving quality care
Proportion of maternal deaths considered preventable
80-85%
MMR in low-income countries vs. developed countries vs. sub-saharan africa
MMR in low-income countries: 240
MMR in developed countries: 16
MMR in Sub-Saharan Africa: 500
Maternal Mortality [1990 vs 2015] [globally]
fell by almost half btwn 1990 and 2015
what prevents maternal mortality
access
access - community levels and rural areas for maternal mortality
Community levels: someone who has 2 or 3 jobs and don't get pto they have less access
Rural Areas: federal cuts impact state levels too and rural areas are impacted the most
Investments in infant health vs maternal health
Investments in infant health, may not always improve maternal health
Investments in maternal health WILL improve infant health
causes of death in mothers and infants …
overlap
Rates since 2015 [globally]
Stagnating
This means improvements in maternal mortality have slowed or stopped.
After years of decline, progress plateaued around 2015 instead of continuing to improve.
COVID-19 - possible contributing factor
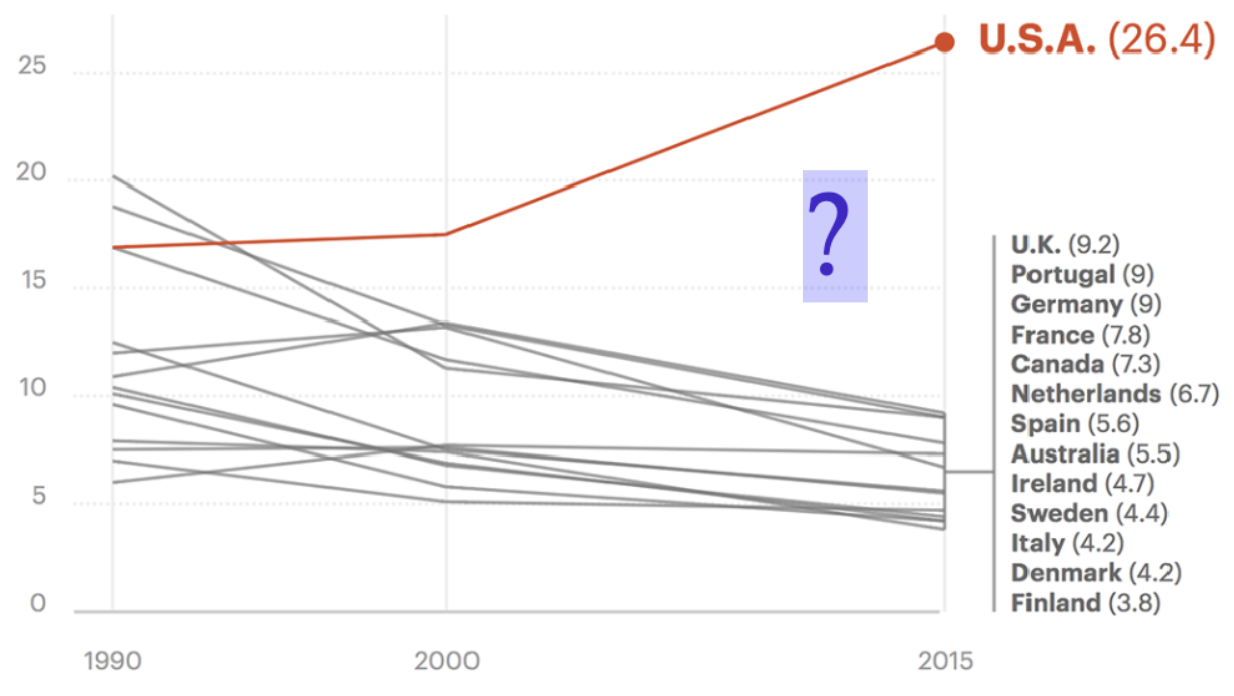
Maternal mortality in U.S versus globally
rising in the U.S while it declines everywhere else
Maternal mortality post COVID [globally]
increased in most countries during COVID but began to decline since then
racial/ethnic disparities in maternal mortality rates
higher pregnancy-related mortality ratios among Black and American Indian/Alaskan Native women.
These gaps DID NOT CHANGE OVER TIME
US maternal mortality rate
highest maternal death rate, with the rate for black women being the highest of any group
when do most U.S pregnancy related deaths occur (what period of pregnancy)
2/3 occur during post partum period
when is a death considered preventable
if there was at least some chance
of the death being prevented by
one or more reasonable changes
to patient, family, provider,
facility, system, and/or
community factors.