AP Bio Unit 2 Organic Chemistry
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
The complexity and variety of organic molecules is due to ___.
the chemical versatility of carbon atoms
their interaction with water
the diverse bonding patterns of nitrogen
the variety of rare elements in organic molecules
the chemical versatility of carbon atoms
Which of the following is true of carbon?
it forms only polar molecules
it can form both polar and nonpolar bonds
it is highly electronegative
it can form a maximum of three covalent bonds with other elements
it can form both polar and nonpolar bonds
how many electron pairs does carbon share to complete its valence shell
2 electron pairs
3 electron pairs
4 electron pairs
8 electron pairs
4 electron pairs
Research indicates that ibuprofen, a drug used to relieve inflammation and pain, is a mixture of two enantiomers; that is, molecules that _____.
have identical chemical formulas but differ in the branching of their carbon skeletons
differ in the arrangement of atoms around their double bonds
are mirror images of each other
differ in the location of their double bonds
are mirror images of each other
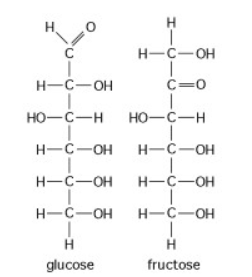
The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These two molecules differ in the _____.
arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
types of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
number of oxygen atoms joined to carbon atoms by double covalent bonds
number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
Which of the following molecules is polar?
C3H7OH C2H5COOH
Neither C2H5COOH or C3H7OH is polar.
C2H5COOH is polar, but C3H7OH is not polar.
C3H7OH is not polar, but C3H7OH is polar.
C3H7OH and C2H5COOH are both polar molecules.
C3H7OH and C2H5COOH are both polar molecules.
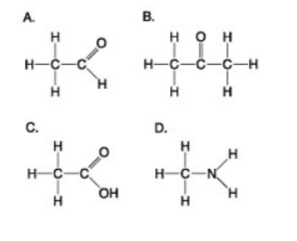
Which molecule shown above would have a positive charge in a cell?
A
B
C
D
D
How many molecules of water are used to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long?
9 molecules of water
12 molecules of water
11 molecules of water
10 molecules of water
10 molecules of water
What does the term insoluble fiber refer to on food packages?
amylopectin
starch
cellulose
polypeptide
cellulose
A glycosidic linkage is analogous to which of the following in proteins?
a disulfide bond
a β-pleated sheet
an amino group
a peptide bond
a peptide bond
Lipids _____.
contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates
are insoluble in water
are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and nitrogen
are made by dehydration reactions
are insoluable in water
Saturated fatty acids _____.
have double bonds between carbon atoms of the fatty acids
are usually liquid at room temperature
are usually produced by plants
are the principal molecules in lard and butter
are the principal molecules in lard and butter
What component of amino acid structure varies among different amino acids?
the glycerol molecule that forms the backbone of the amino acid
the long carbon-hydrogen tails of the molecule
the components of the R-group
the presence of a central C atom
the components of the R-group
Use the following information when answering the corresponding question.
Rhodopsins are light-sensitive molecules composed of a protein (opsin) and retinal (derivative of vitamin A). Opsin is a membrane protein with several α-helical segments that loop back and forth through the plasma membrane. There are two classes of rhodopsins. According to Oded Beje, one class has relatively slow dynamics (a photocycle of approximately 0.5 second) and is well suited for light detection. The second class has faster dynamics (a photocycle of approximately 0.02 seconds) and is well suited for chemiosmosis: pumping of protons or chloride ions across cell membranes. Oded Beje was the first, in September 2000, to report on a rhodopsin (proteorhodopsin) found in the domain Bacteria. [SOURCE: O. Beje et al., Science 289 (2000): 1902.]
Proteorhodopsin consists of a single polypeptide chain. What is the highest level of structure found in this protein?
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
tertiary
What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins?
denaturing protein
tertiary protein
chaperonin
renaturing protein
chaperonin
Nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers?
nucleotides
nitrogenous bases
amino acids
sugars
nucleotides
Which of the following includes all of the pyrimidines found in RNA and DNA?
cytosine, uracil, and guanine
cytosine, uracil, and thymine
cytosine and thymine
cytosine and uracil
cytosine, uracil, and thymine
One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to _____.
act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA
function in the synthesis of proteins
make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity
transmit genetic information to offspring
function in the synthesis of proteins
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
a nitrogenous base and a sugar
a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group
a sugar and a purine or pyrimidine
a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
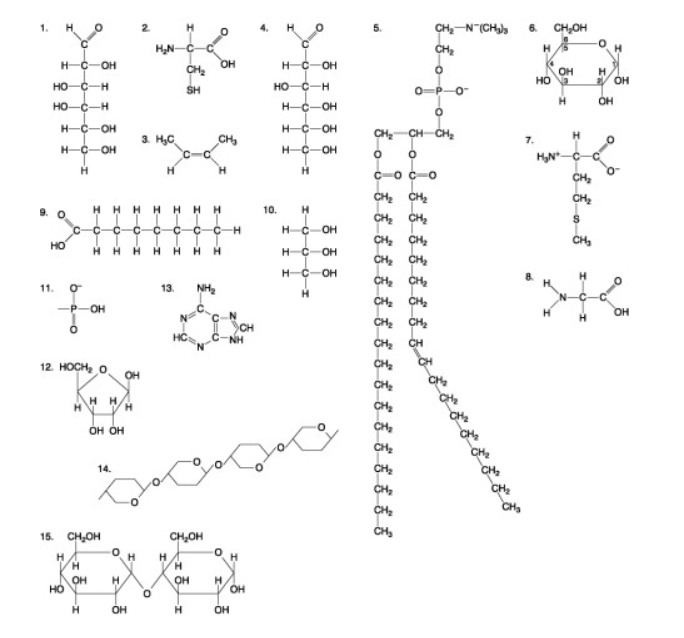
The following question are based on the 15 molecules illustrated in the accompanying figure. Each molecule may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
Which molecule has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and is found in plasma membranes?
Molecule 1
Molecule 14
Molecule 5
Molecule 12
Molecule 5
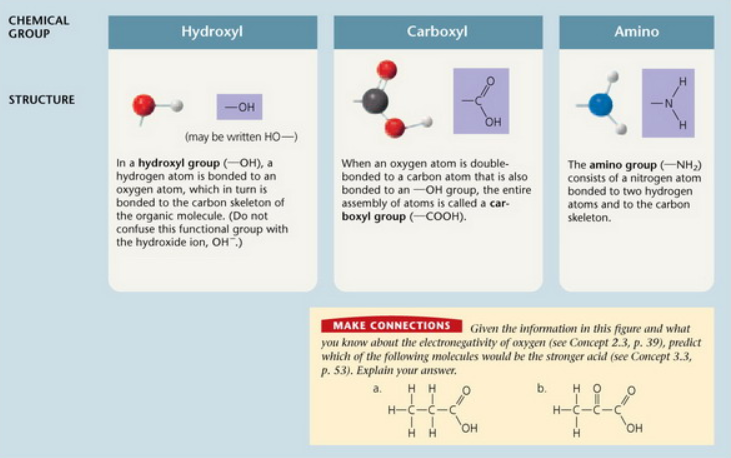
Which of the functional groups shown above is most likely to gain a proton and become positively charged?
The amino group is most likely to gain a proton.
The hydroxyl group is most likely to gain a proton.
The carboxyl group is most likely to gain a proton.
The amino group is most likely to gain a proton.
How do isomers differ from one another?
Isomers differ in the arrangement or bonding of atoms.
Isomers differ in charge.
Isomers differ in molecular formulas.
Isomers differ in the arrangement or bonding of atoms.
Which statement about isomers is correct?
Enantiomers differ in biological activity.
Structural isomers differ in the position of double bonds within the molecule.
Cis-trans isomers are mirror image isomers.
Enantiomers differ in biological activity.
Which of the following statements about functional groups is TRUE?
DNA and RNA are functional groups.
Lipids and proteins are functional groups.
Amino and carboxyl are functional groups
Amino and carboxyl are functional groups
Which statement about a methyl functional group is correct?
A methyl group is polar.
A methyl group may be negatively charged.
A methyl group consists of a carbon bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
A methyl group consists of a carbon bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
Which molecule is a nucleotide
the amino acid glycine
deoxyribose
ATP
ATP
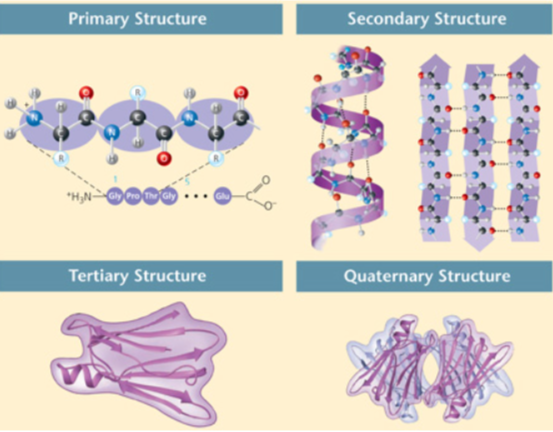
These figures show the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. Which level of protein structure is characteristic of some, but not all, proteins?
Secondary level of protein structure
Quaternary level of protein structure
Tertiary level of protein structure
Quaternary level of protein structure
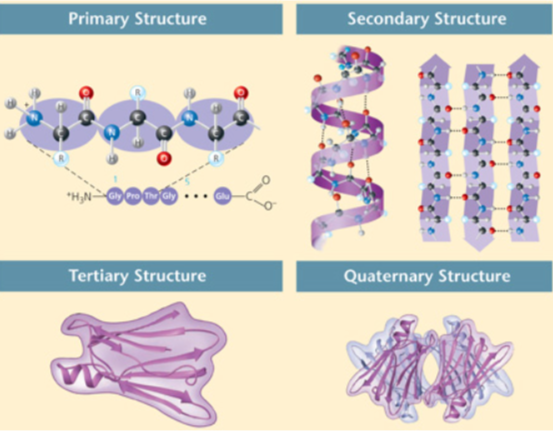
There are four levels of protein structure. These figures show primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure. Which level(s) of protein structure may be stabilized by covalent bonds?
Primary, tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure
Secondary level of protein structure
None of the levels of protein structure is stabilized by covalent bonds.
Primary, tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure
What structural difference accounts for the functional differences between starch and cellulose?
Starch and cellulose differ in the glycosidic linkages between their glucose monomers.
Starch is a polymer of glucose, whereas cellulose is a polymer of fructose.
Starch can be digested by animal enzymes, whereas cellulose cannot.
Starch and cellulose differ in the glycosidic linkages between their glucose monomers.
Which feature of large biological molecules explains their great diversity?
The many ways that monomers of each class of biological molecule can be combined into polymers
The many classes of large biological molecules
The diversity of elements found in large biological molecules
The many ways that monomers of each class of biological molecule can be combined into polymers