Exam 1, Physiology of Exercise 2 II
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Harding University, professor Bland
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
hypobaric
Low pressure
hypoxic
low oxygen
hypoxemia
low blood oxygen
barometric pressure
pressure that the atmosphere exerts on us - changes with altitude
partial pressure (Eg. pO2, pCO2)
pressure that one gas (O2N, etc) exerts in a mix
altitude near sea level
<500 m
low altitude
500-2000 m
moderate altitude
2000-3000 m
high altitude
3000-5500 m
extreme altitude
> 5500 m
As altitude increases, temperature…
decreases
As altitude increases, water vapor pressure…
decreases
Physiological changes at altitude
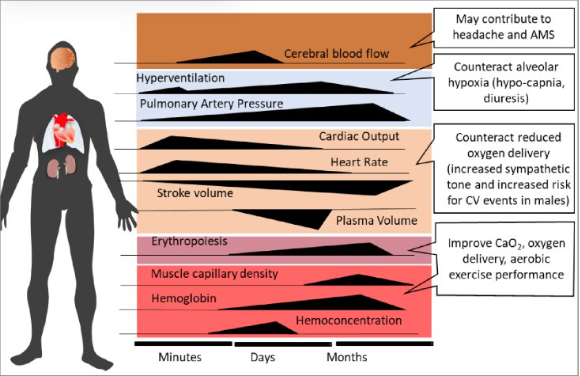
Pulmonary ventilation rate at altitude…
increases: hyperventilation to increase pO2
increased ventilation rate causes pCO2 in the blood to…
decrease; blood alkalizes; called respiratory alkalosis
What is the body’s response when pCO2 declines?
kidneys eliminate some bicarbonate buffer blood, try to rebalance blood pH
Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
Blood essentially moves up and down the hill, along the line as it moves from tissue to heart and back
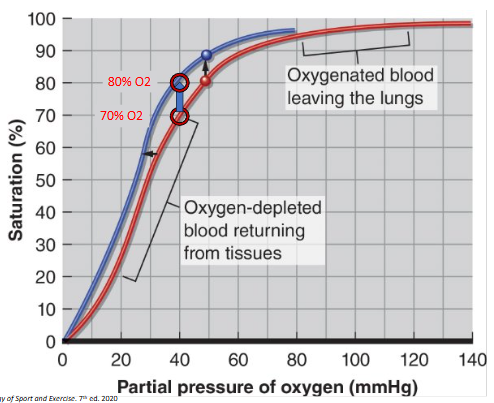
Increase in pH (alkalizing) shifts the Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve…
to the left; lower ability to unload O2 to muscle
Decrease in pH (acidizing) shifts the Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve…
to the right; greater ability to unload O2 to muscle
What does altitude do to blood volume (BV)?
decrease; because low water vapor pressure, increased ventilation and urine output
What does decrease in BV at altitude mean for CO?
Decreased CO at altitude because decreased stroke volume (SV)
What does decreased CO at altitude mean for VO2?
VO2 max is automatically lower despite any maximal efforts. Training capacity is blunted at altitude.
What does altitude do to the nervous system?
Increases sympathetic response to increase HR to maintain CO;
What happens to appetite at altitude?
appetite decreases but basal metabolic rate (BMR) increases, both due to increased sympathetic stress response
What type of substrate is used more at rest at altitude?
CHO (carbohydrates)
Lactate paradox
Initial increase in blood lactate (LA) due to stress + using more CHO.
After training at altitude, huge decrease in maximal LA level, lower than training at sea level.
Paradox because this effect is counterintuitive.
Possibly due to expansion of mitochondria, that would give lactate more places to go to dissipate (decreases LA levels)
Nutritional needs at altitude
Need more fluids
Need more calories
Need more iron - aid RBC production
What amino acid stimulates mTORC (muscle protein synthesis) pathway?
Leucine
At altitude (above 1500m) VO2…
decreases
How long is needed for full acclimation to moderate altitude
3 weeks + 1 more for every 600m added
Increased EPO signals at altitude..
Occur within first few hours at altitude. Increase in RBC takes 2 weeks following.
Blood adaptations at altitude causes blood O2 carrying capacity to…
Increase; but never reaches sea level capacity
Altitude causes muscle mass to…
decrease; due to less mTORC stimulation and decreased appetite
how is mTORC pathway affected when hypoxia ..
inhibited/slowed
Mitochondiral and glycolytic enzyme activity at altitude is..
Decreased; less ability to produce ATP
Those living at altitude (acclimatized) have …
Right ventricular hypertrophy; heart increased blood flow (BF) and BP to lungs