Part 1: Skin Cancer- Epidemiology & Etiology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the largest organ of the body?
The skin
The skin measures ____sq feet, and weighs ___ lbs on the average person
22 ft²
10-12 lbs
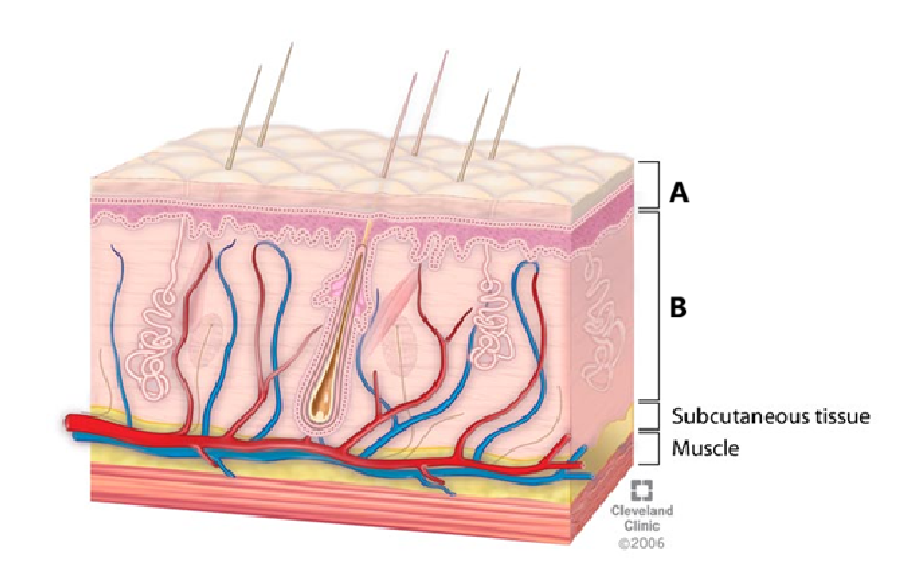
label
A. Epidermis
B. Dermis
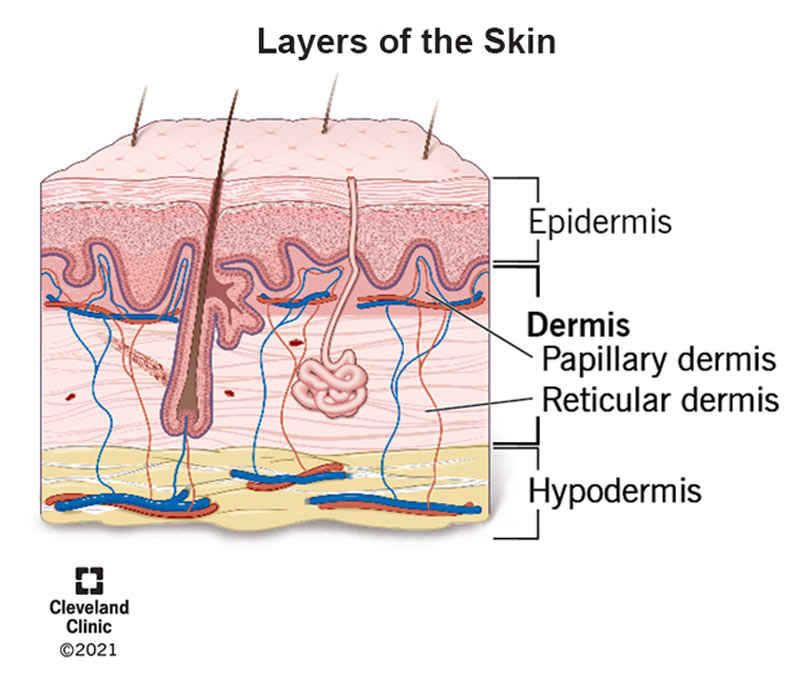
term. dermis
def. the connective tissue layer of the skin
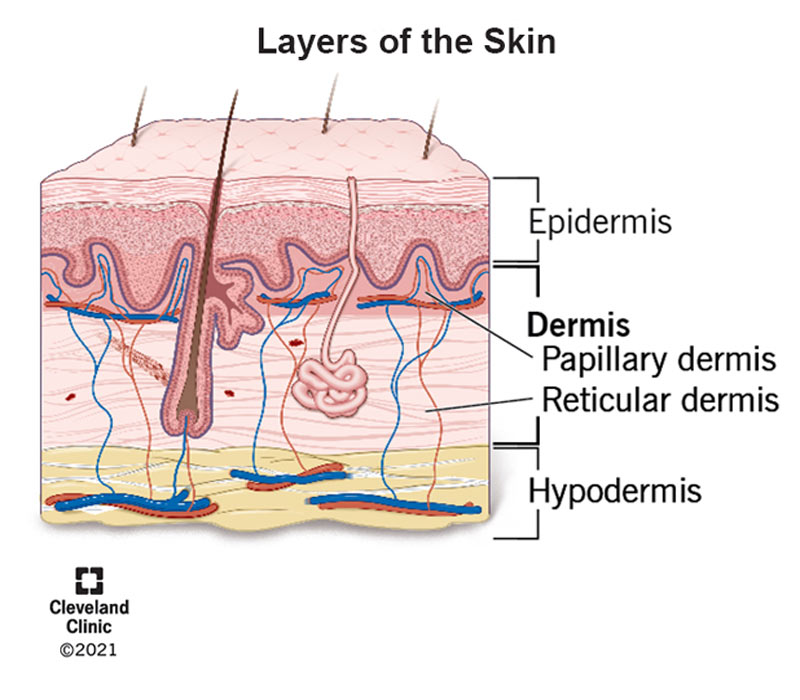
term. epidermis
def. the epithelial layer of the skin
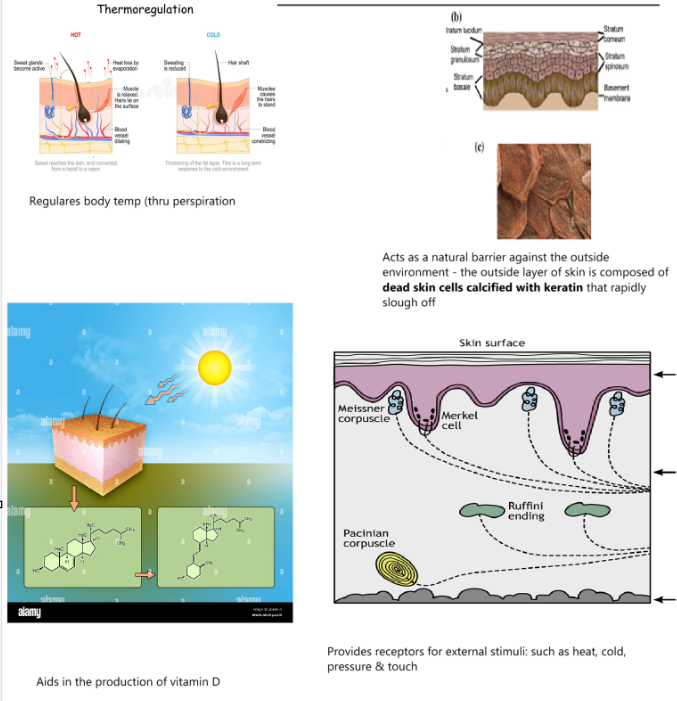
What are the 4 functions of the skin
Temperature
Barrier
Vitamin D
External Stimuli Receptors
Skin cancer has a (low/ high) incidence, and an overall (low/high) death rate
high, low
FYI: this is why we leave skin cancer out of cancer statistics
True or False: Skin cancer commonly metastasizes
False, it rarely does
How many cases of skin cancer per year?
Over 1M/ year
Skin Cancer Epidemiology (excluding Melanoma) (4)
Male predominant (but women have been catching up) FYI: cuz men have outdoorsy jobs, women: tanning
More common in:
fair skin
red hair
well-freckled people - 10x higher risk of skin cancer
people of Irish or Scottish descent
people with xeroderma pigmentosum - frequently get skin cancer on exposed surfaces
Rare in black people
Peak age is 7th decade in life (people in their 60s)

Why is skin cancer rare in black people?
They have more melanin, which serves as a protectant
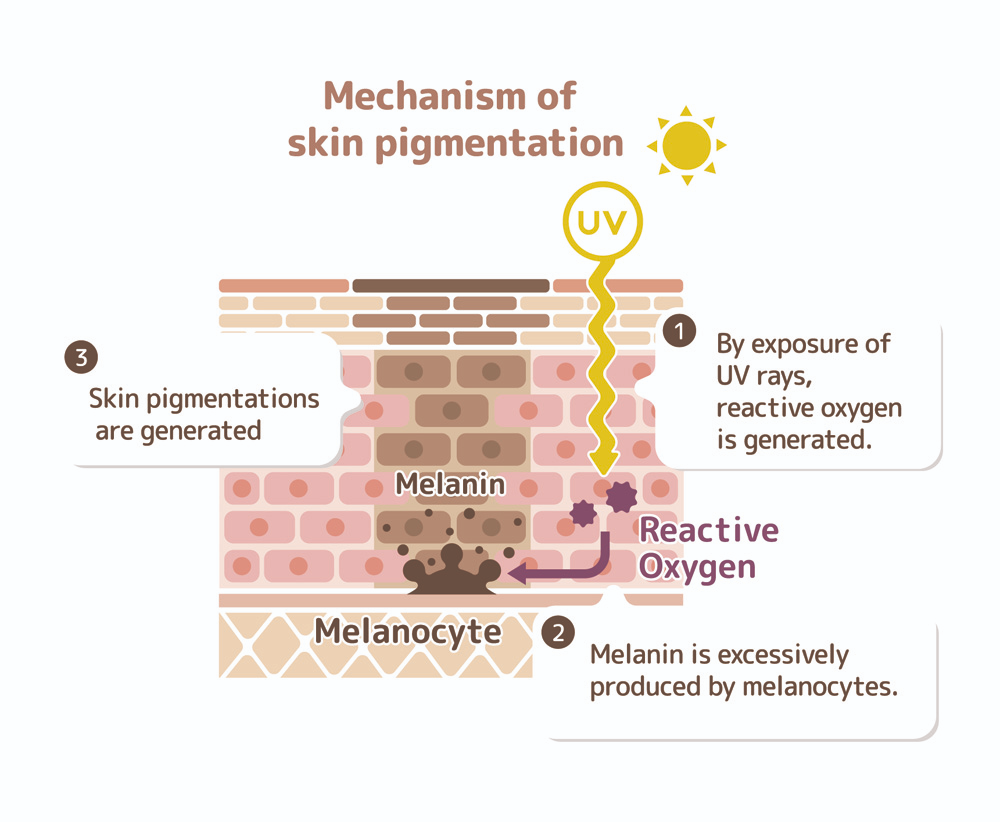
If skin cancer does occur in black people, in what areas of the body does it tend to appear? What type of skin cancer is it?
non-pigmented areas
palms of hands
soles of feet
and tends to be a melanoma

What is xeroderma pigmentosum?
genetic condition of pigment abnormalities
Etiology of skin cancer (6)
UV radiation
Medical radiation- more likely in squamous cell
Some chemicals- specially arsenic
HPV virus- specially in squamous cells cancers
Scars or Chronic Inflammatory Conditions- in squamous cell cancers
Genetic disorders including albinism
What is the major risk factor for skin cancer?
UV radiation
Which cancers are more likely to result from radiation exposure?
squamous cell cancers
basal cell cancers
squamous cell
What is another etiology factor listed in some text books for skin cancers? Why don’t we list it as one?
immune system deficiencies
HOWEVER, immune system deficiencies contribute to ALL CANCERS, it is not specific to skin cancers or any cancer
Which 2 sun components are harmful? Why?
UVA- once thought to be harmless. Penetrate deep enough to result in malignant transformations & act as a co-factor, encouraging tumor development initiated by UVB
UVB- damages DNA → causing mutations → result in cancer
Tanning beds use (UVA/ UVB) rays
UVA
T/F: A sun burn is the skin’s response to damage, but tanning is not
F: both are a response to damage
T/F: People living in the equator have a higher risk of skin cancer
True
Related to etiology are social/ cultural factors that can cause skin cancer, including:(3)
popularization of the “golden tan”
Fashion/ clothing trends that allow more skin exposure
Depletion of ozone layer allows more UV rays the atmosphere → higher exposure
What prevention program did Australia develop to reduce skin cancer?
Slip, slap, slop
What do the following stand for:
Slip
Slap
Slop
Slip on protective clothing
Slap on a hat
Slop on the sunscreen
SPF stands for
Sun Protection Factor
An SPF of at least ___ is recommended, but anything higher than ___ is trash
15, 25
What does an SPF of 15 mean
with sun protection of 15 SPF, 15 hrs of exposure is equivalent to 1 hr of exposure without sunscreen
How often should you reapply sunscreen?
Every 2 hours &
After swimming or heavy physical activity (Sweating)