Bio Juncos and Speciation Summative
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Natural Selection
Process in which a population changes based on the successful survival of its offspring with a certain trait.
Adaption-Population change over time,Trait with higher fitness will be seen more.
-Environmental change-Selection pressure will choose which variation survives or dies.
-Variation-different type of trait
-Inheritance-inherit from parent/offspring
-Different survival/reproduction-best in the environmental fitness.Able to survive/reproduce.
Mutation
A trait randomly developed within a population.
Variation
Individuals in a group that have different traits (lactose intolerant and lactose tolerant)
Evolution
The change over time of a population.
Fitness
Individuals in a group with certain traits that are more likely to survive and are able to reproduce and have offspring.
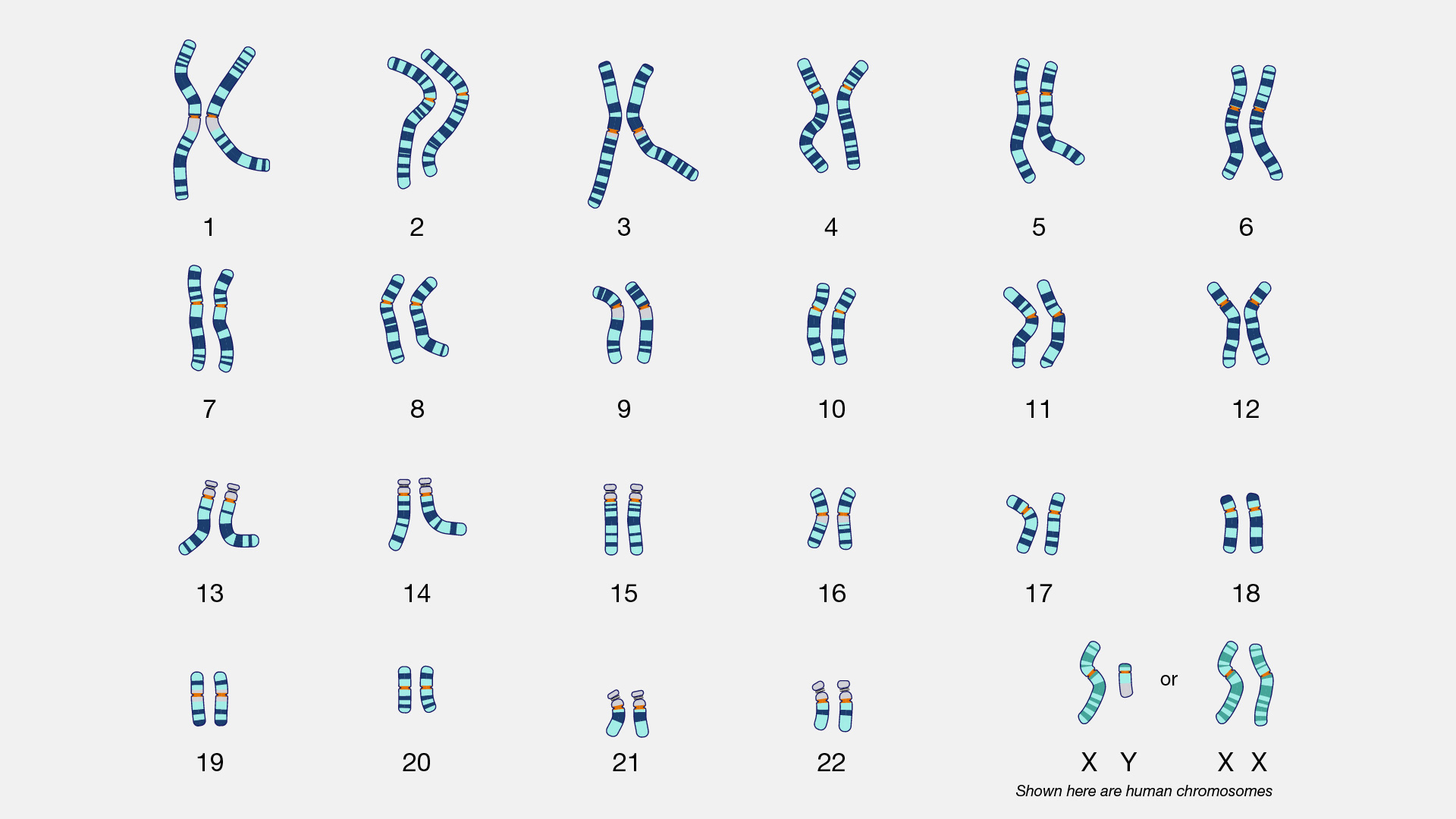
Karyotype
Diagram of chromosomes
Allele
Variation of a trait.
Gamete
Sex cell,egg or sperm,23 cells in egg and 23 cells in sperm.
Zygote
A fertile egg
Fertilization
The sperm getting into the egg,the creation of the offspring inside the womb.
Allopatric speciation
Geographic barrier,river,mountain blocks them off so they are not sharing genes through reproduction,overtime they become different species because their DNA has became to different overtime.
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation occurs even when the organisms live in the same area,something else is isolating them.
Prezygotic Barrier
Barrier before they can even create a fertilized egg.
Examples are)
-Behavioral isolation-Species have different behaviors,ex different bird songs.
-Temporal isolation-species breed at different times,they can breed at different times of the day of different seasons.
-Habitat-Even if two species live in the same area,they live in different parts of their habitat, ex: some frogs may live on land while some live in the water
Postzygotic barrier
Mating and fertilization occurs but it doesn’t make a fertile offspring of the Zygote can’t be born.
-Creation of a non-fertile offspring (they are born to become adults but can’t have their own offspring)they are sterile.
-Weak offspring and can’t survive
-The offspring can’t develop past embryo development.
What is causing sympatric speciation?
Zygotic Barriers
-Prezygotic and Postzygotic
Convergent evolution
Process where organisms,not closely related,independently evolve similar traits as a result of adapting to similar environments of lifestyles.
Analogous structure
Different structure
Similar function
Not from common ancestor
Divergent evolution
Process where other groups from the same ancestor evolve and accumulate differences as they adapt to different types of habitats,resulting in new species.
Homologous structure
Similar structure
Different function
From common ancestor
Analogous structure
Convergent
-Different structure
-Similar Function
-Not from common ancestor.
Homologous structure
Divergent
-Similar structure
-Different function
-From common ancestor
Vestigial structure
Something in your body that you don’t need,something that your ancestors used but aren’t useful today.EX.Wisdom teeth,appendix,tailbone,tonsils
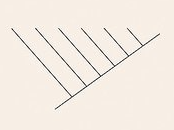
Cladogram
Is a diagram to show the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups of organisms.
-hypothetical
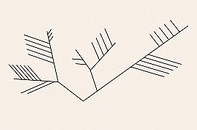
Phylogentic tree
How closely related an animal is to each other,represents the evolutionary relationships among a set of organisms.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondria are structures within cells that convert the energy from food into a form that cells can use. The genetic material found in mitochondrial DNA.
Adaptive Radiation
It is the process in which one species changes and evolves into many different species to adapt to different environments.
Gene flow
Is when there is interbreeding between populations.
Endosymbiotic theory
Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.
Endemic species
An organism that are only found in a specific geographic area.
What is speciation?
The process in which two organisms from the same species develop a new species.
Development of a new species.
How does it speciation occur?
When a population is reproductively isolated in some form.(the organisms do not reproduce to create a fertile offspring.)
Describe how speciation may occured in Darwin’s finches.
Because the finches were living on different islands, they all became isolated, each adapting to its new environment. There was no gene flow/sharing. This caused the species to slowly become so isolated that they couldn’t reproduce with each other, classifying them as distinct species.
Compares the various form of isolation and the pattern of speciation associated with each.
A.allopatric speciation=Geographic Isolation
B.Sympatric speciation
Allopatric speciation happens when the organisms are separated in some way geographically,like a mountain or a river.Mean while sympatric speciation is when the separation occurs when the isolation between the two groups happen on the same habitat,but the difference are the behavioral,temporal and reproducitve,like different birds have different mating songs,even though they live in the same forest.
What is the difference between prezygotic barrier and post zygotic barrier.
Prezygotic barrier is a barrier created before they can create a zygote.Potzygotic barriers are when two species are able to have an offspring or zygote but it isn’t fertile and can’t be born.
Examples of prezygotic barrier and postzygotic barriers.
Prezygotic barrier-Barriers before they can even create a zygote.
Behavioral isolation-species have different behaviors, ex different bird songs.
Temporal isolation- species breed at different times, they can breed at different times of the day or different seasons.
-Habitat-Even if two species live in the same area,they live in different parts of their habitat, ex: some frogs may live on land while some live in the water
Post zygotic barrier-mating and fertilization occurs but it does not make a fertile offspring or the Zygote can’t be born.
Creation of a non-fertile offspring (they are born to become adults but can’t have their own offspring) they are sterile.
Weak offspring and can’t survive.
The offspring can’t develop past embryo development.
Why/how does isolation lead to speciation?
If two groups are isolated long enough,they develop their own environments through natural selection.Overtime,their differences become so great that the two groups can’t reproduce together anymore.
What is a species?
Organisms of a same species can interbreed and reproduce, and their offspring can reproduce (fertile)
What role does the environment play in natural selection?
The environment is the stressor.If there is a change in the environment,the two groups in the population (with and without mutation) get tested to see which group survives better in these new conditions. Those who survive pass down the mutation to their offspring,keeping the mutation “alive”,while those who don’t survive can’t reproduce and die off and take the old traits with them.
TRUE or FALSE: Natural Selection takes place to a population.
True
TRUE or FALSE: Natural Selection takes place over the lifetime of an individual. EXPLAIN
True
If a person is born with a mutation and there is a change in environment.That person with the mutation will be tested to see how the organisms can survive.If the mutation is effective the organism survives and would pass their mutation to their offspring.The population without the mutation will slowly die off and its whole branch will evolved,shows that natural selection has taken place.
What could you look at to figure out if two populations are the same species?
The most important thing someone needs to look at is to decide if two populations are the same species in DNA.Physical traits in an animal could be similar to others.You can’t just decide if two species are the same based on their physical traits.
What investigation can you do to test if two groups are the same species? Be sure to account for variables that need to be held constant. Are there any variables that you are unable to control?
The investigation would be having the same compatible genes and both would produce fertile offspring.What we control is the number of birds that can come for two populations.We can control what would be a decrease in the amount of human interactions,and the food sources for both birds would have to be consistent.What we wouldn’t be able to control would be is if they mate or not.This is why we bring multiple pairs from each species group.
What is adaptive radiation?
Adaptive radiation is how organisms of the same species adapt to different environments and separate.
How are Darwin’s finches an example of adaptive radiation?
The finches have adapted to their specific environment on the island.
Explain why after an environmental change a population might
a.expansion of some species
b.the emergence of new distinct species as populations diverge under different conditions,and the decline and sometimes the extinction of some species.
You can see the species genetic diversity and more genetic diversity increases the chance of survival.
Compare the concepts of homologous structures, analogous structures, and vestigial structures.
Homologous structures have similar structures,different functions and come from a common ancestor.
Analogous structures are the opposite; they have different structures,similar functions and don’t have a common ancestor.
Vestigial structures don’t have a function and are structures from past ancestors.
Compare convergent evolution, divergent evolution and coevolution. Provide an example of each
Convergent evolution is when two species that don’t have a common ancestor develop similar traits based on their environment and lifestyle. (ex.butterfly and bat/both can fly)
Divergent evolution is when two animals from the same ancestor develop different traits because of their different environments. (ex.elephants and mammoths)
Coevolution is when two or more species affect each other’s evolution through the process of natural selection. (ex.bees and flowers)
How can vestigial structures be used as evidence for common ancestry? Examples
If two animals that we think are related and one has a vestigial structure,we can see if the animal from the past had a similar structure.If it appears to have a specific function.If there is a similar structure between two animals,(only the one that is more recent one is vestigial),we can see that the non vestigial structure is the ancestor of the animal with the vestigial structure.
Example)The pelvis of a whale has no apparent function,making it vestigial and if we go back in time and see whales ancestry.We can tell how whale’s ancestors used to have hips, and appear more functionable in the past.In the end ancestors of whales had legs and lived on land before slowly transferring to the sea.
What creates genetic variety from generation to generation?
Mixing genes during reproduction and the creation of new mutations during reproduction.This creates genetic variation.
How is the amount of genetic variety present in a population related to its resilience after an environmental change? Are they more or less likely to adapt/evolve? For Example, say there is a population of humans that are genetically identical, what would happen to those humans if a virus came into their population that could kill them. What would happen to that population?
If the organism has Genetic variation,then it has an advantage when it comes to encountering changes in environments of that specific population. This gives the population a better ability to adapt to one of its different traits.It will be able to survive in the new environment.
What is the difference between phylogeneic trees and cladograms?
The difference between phylogenetic trees and cladograms are, Phylogenetic trees can show the facts and the evolution history of species.ANd a cladogram can only show a theory of how a species came to be based only on physical characteristics/traits.
What sources of evidence can be used to determine common ancestry?
Fossils,DNA,and genetic code.
Are some sources of evidence more reliable than others? What is the most reliable source of evidence?
DNA