BIOL 211- Lecture 3- Microtubules Draft
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are the long tubules in the cytoplasm of cells ?
Microtubules
How are microtubules composed?
Microtubules are composed of of α- and β-tubulin heterodimers - assembled into hollow, tube-like cylinder approximately 25nm in diameter.
What is the role of microtubules ?
Microtubules provide structural support and are involved in cell division, intracellular transport, cell motility and help generate cell polarity.
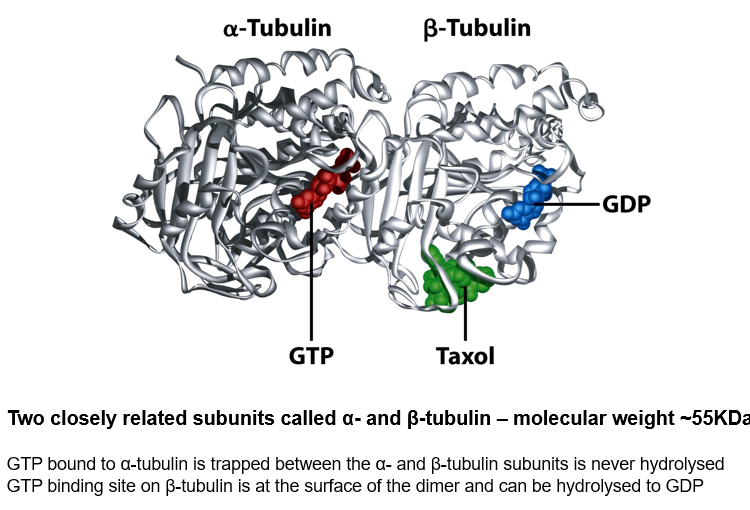
Ribbon diagram of the Tubulin dimer
Two closely related subunits called α- and β-tubulin – molecular weight ~55KDa
GTP bound to α-tubulin is trapped between the α- and β-tubulin subunits is never hydrolysed
GTP binding site on β-tubulin is at the surface of the dimer and can be hydrolysed to GDP
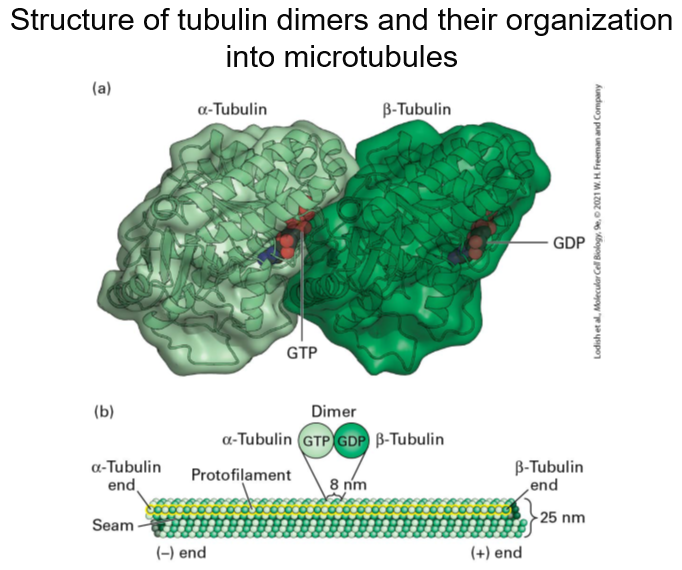
Structure of tubulin dimers and their organization into microtubules
In assembly
Define protofilaments in the context of microtubules.
Protofilaments are formed by the alignment of α-tubulin and β-tubulin dimers end to end, which pack side by side to create the wall of the microtubule.
They are staggered so α-tubulin in one protofilament is in contact with α-tubulin in the neighbouring protofilaments, except at the seam, where an α-subunit contacts a β-subunit
Microtubules display a structural polarity, and subunits are added preferentially at the end where β-tubulin monomers are exposed
This end of the microtubule is known as the (+) end - microtubule motors can ‘read’ the polarity of microtubule (see later)
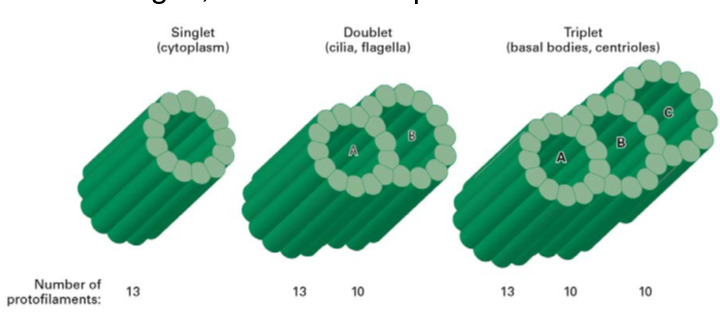
What are single doublet and triplet microtubules
Singlet microtubule - a simple tube built from 13 protofilaments
Doublet microtubule - an additional set of 10 protofilaments form a second tubule (B) by fusing to the wall of a singlet (A) microtubule
Triplet microtubule - attaching another 10 protofilaments to the (B) tubule of a doublet microtubule creates a (C) tubule
How do microtubules display structural polarity?
Microtubules display structural polarity with subunits added preferentially at the end where β-tubulin monomers are exposed, known as the (+) end.
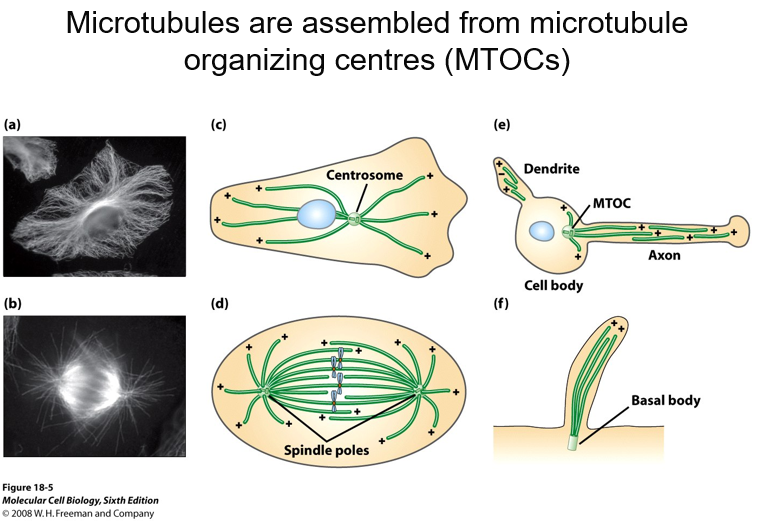
What are microtubule organising centers (MTOCs)
Microtubules are nucleated from MTOCs
Since spontaneous nucleation of microtubules is an energetically unfavourable reaction and does not play a significant role in microtubule assembly in vivo.
These MTOC serve to nucleate and organise microtubules and the (-) ends of microtubules remain associated with the MTOC.
In animal cells, the centrosome is the main MTOC.
Microtubules are assembled from microtubule organizing centres (MTOCs)
All the negatiive ends are in contact with the centrosome
Structure of centrosomes
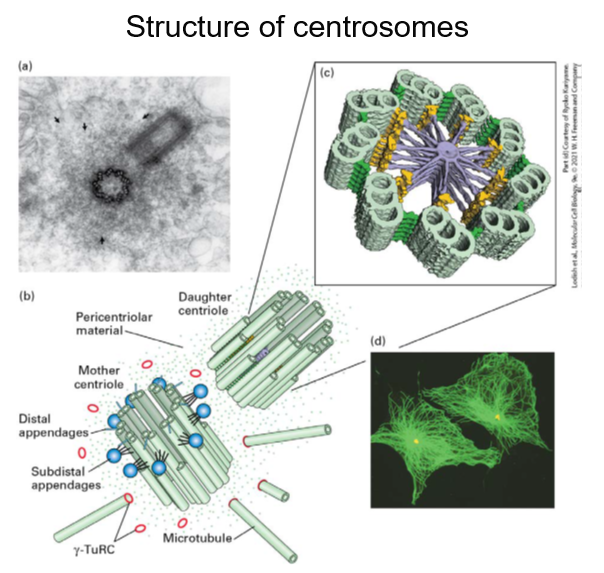
Identify the main microtubule-organizing center in animal cells.
In animal cells, the main microtubule-organizing center is the centrosome.
Centrosomes – summary
Each centrosome consists of a pair of orthogonally arranged cylindrical centrioles surrounded by amorphous material called pericentriolar material
Centrioles are about 0.5μm long and 0.2μm in diameter
Highly organised and stable structures that consist of 9 triplet microtubules
The centrioles themselves do not nucleate the cytoplasmic microtubule array - factors in the pericentriolar material do this
BUT the outer doublet MTs in cilia and flagella are extended from A and B tubules of the triplet basal body structure
A critical component is the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) located in the pericentriolar material - consists of many copies of γ-tubulin associated with several other proteins
Explain the structure of centrosomes.
Centrosomes consist of a pair of orthogonally arranged cylindrical centrioles surrounded by amorphous material known as pericentriolar material.
They are about 0.5μm long and 0.2μm in diameter
They are highly organised and stable structures that consist of 9 triplet microtubules.
How many microtubules are in a centrosome
9 triplet microtubules