Living World
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
two types of cell division:
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis:
a cell divides once, resulting in 2 daughter cells. These daughter cells are genetically identical to the original parent cell. Each daughter cell contains the same number of chromosomes as the parent.
Meiosis:
During mitosis, a cell divides once, resulting in 2 daughter cells. These daughter cells are genetically identical to the original parent cell. Each daughter cell contains the same number of chromosomes as the parent.
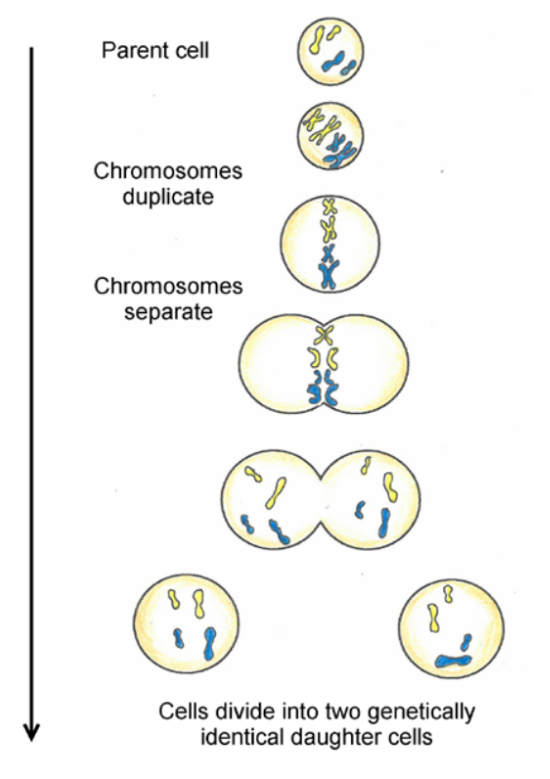
What is this
Mitosis
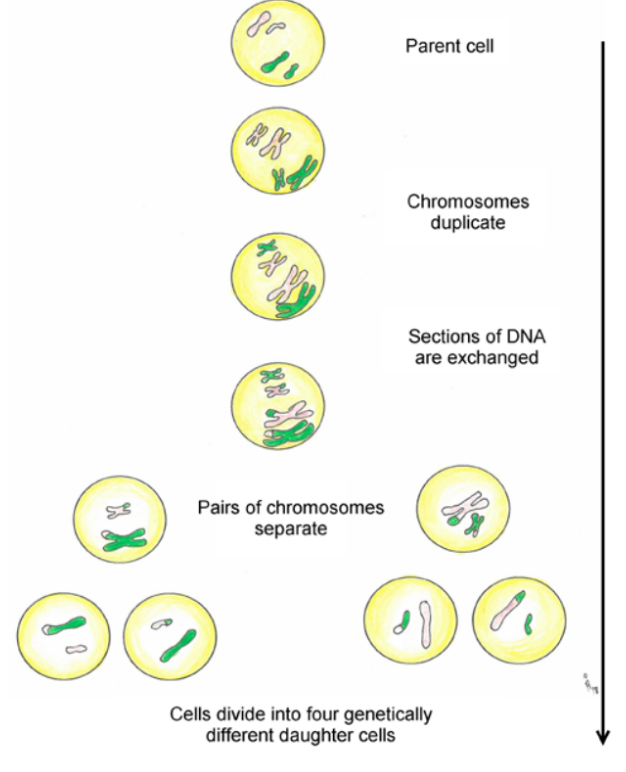
What is this
Meiosis
Function of mitosis:
Growth: increasing the number of cells
Repair: replacing damaged cells
Function of meiosis:
Produce of gametes required for sexual reproduction
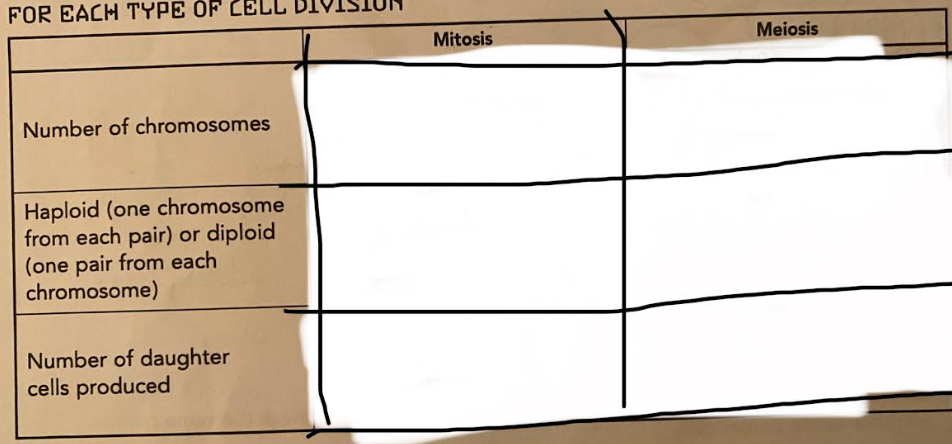
fill in blank
46 chromosomes (2n) 23 (n) chromosomes
diploid Haploid
2 4

46,46,46,46
46,92,92,46
46,46,23,23
46,92,46,23
Number of chromosomes:
Mitosis: same number as parent cell
Meiosis: Half as many as parent cell
Genetic Diversity:
all the possible genetic variations of a species.
How is genetic diversity increased
sexual reproduction and having a large and diverse population
Why is genetic diversity important (sexual reproduction)
Since the combination of genes is random in sexual reproduction, each offspring is different and therefore genetic diversity can increase. Want to find offspring with the best genes through natural selection to reproduce species that are better to survive.
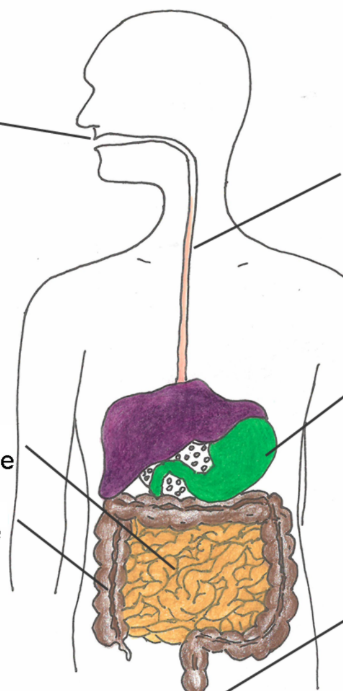
Label parts in order: name of system:
Digestive system: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus.
role of digestive system:
Breakdown of ingested food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed by the body and eliminate undigested food as solid waste.
role of Mouth:
• Ingestion of food
• Chewing and grinding of food with teeth (mechanical digestion)
• Breaking down of starch with saliva (chemical digestion)
Function of stomach
• Churns food (mechanical digestion)
• Breaking down of proteins with gastric juices (chemical digestion)
• Movement of food towards the small intestine
Function of Small intestine
• Breaking down of foods (chemical digestion) with bile, pancreatic
and intestinal juices
• Absorption of fats, carbohydrates, proteins and some vitamins
and minerals
• Movement of food towards the large intestines (with peristalsis)
Function of large intestine
• Absorption of water, vitamins and minerals
• Movement of residual waste products towards the anus
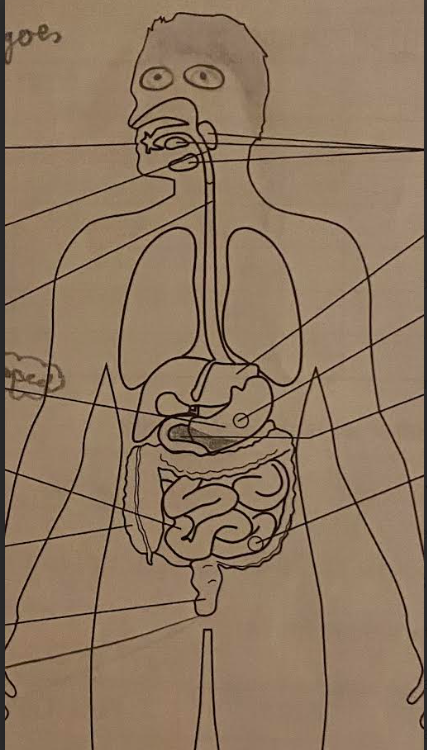
Label:
mouth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, liver, stomach, gastric glands, pancreas, small intestine, intestinal glands, large intestine, rectum, anus
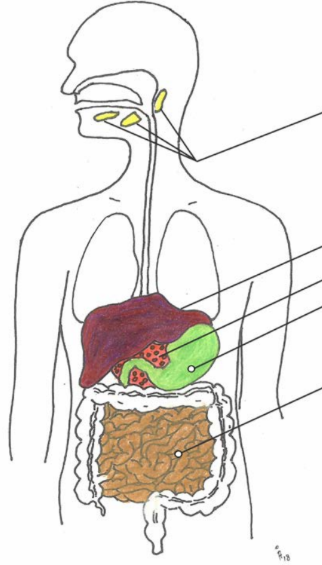
Label
Salivary glands, liver, gastric glands, pancreas, intestinal glands
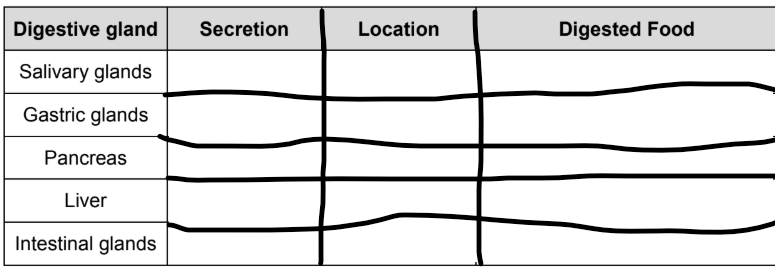
fill in the blank:
saliva mouth starch (complex CHO)
gastric juice stomach proteins
pancreatic juice small intestines carbohydrates, proteins and fats
bile small intestines fats
intestinal juice small intestines carbohydrates, proteins and fats
6 types of nutrients:
water, minerals, vitamins, proteins,carbohydrates, fats
Function of water and sources:
• Transports nutrients and
waste products
• Regulates body temperature
• Allows chemical reactions to
occur
ex: Water, fruits, vegetables, soups,
drinks
Function of vitamins and sources:
• Regulate the metabolism
• Molecules that help in chemical reactions
helps fight infections
Ex: Fruits, vegetables, dairy products, liver
Function of minerals and source:
• Building blocks for many tissues
• Help in chemical reactions
Ex: Vegetables, fruits, fish, dairy
products, legumes
function of protein and sources:
• Build and repair tissues and cells
• Last resort energy source
ex: Meat, fish, eggs, nuts, legumes,
milk and dairy products, tofu
function of carbohydrates and sources:
• Body’s main energy source
Ex: Complex carbohydrates
(starch): rice, cereals, bread,
potatoes, pasta
Ex: Simple carbohydrates (sugars):
granulated sugar, fruits and fruit
juice, candy
function of fats and sources:
important energy source, energy from fats accessed once energy can no longer be extracted from CHO
Protects organs and insulates the body
ex: Butter, cheese, and other dairy
products, Plant-based oils, fatty meats
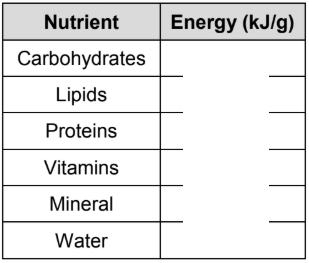
fill in the blanks
17, 37, 17 ,0 ,0 ,0
two types of transformation of food in the digestive system
mechanical and chemical
mechanical transformation in digestive system:
physical breakdown of food into smaller particles to prepare it for chemical digestion
Examples of mechanical transformation:
Chewing: process of crushing and grinding food-mouth
Churning: muscle contractions mix the food with secretions from the digestive glands
chemical digestions:
chemical reaction occur to transform the larger/more complex molecules into simpler molecules.
example of chemical digestion:
Saliva in the mouth that transforms starch into simpler carbohydrates. Located in salivary glands, gastric glands, intestinal glands, pancreas, liver
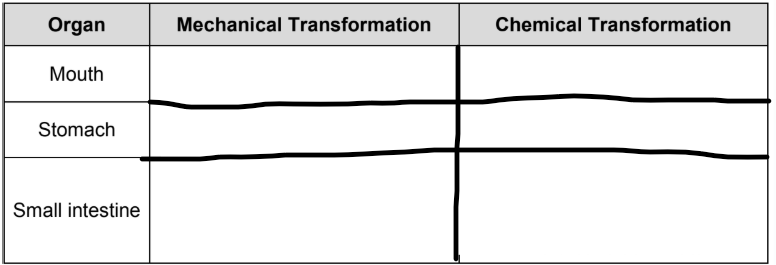
Mouth: MT=Chewing action of teeth tears apart food. CT=Saliva breaks down starch.
Stomach: MT=Churning action breaks apart food. CT=Gastric juices break down protein.
Small intestine: MT=None. CT=Intestinal and pancreatic juices break down carbohydrates, fats and proteins.Bile breaks down fats.
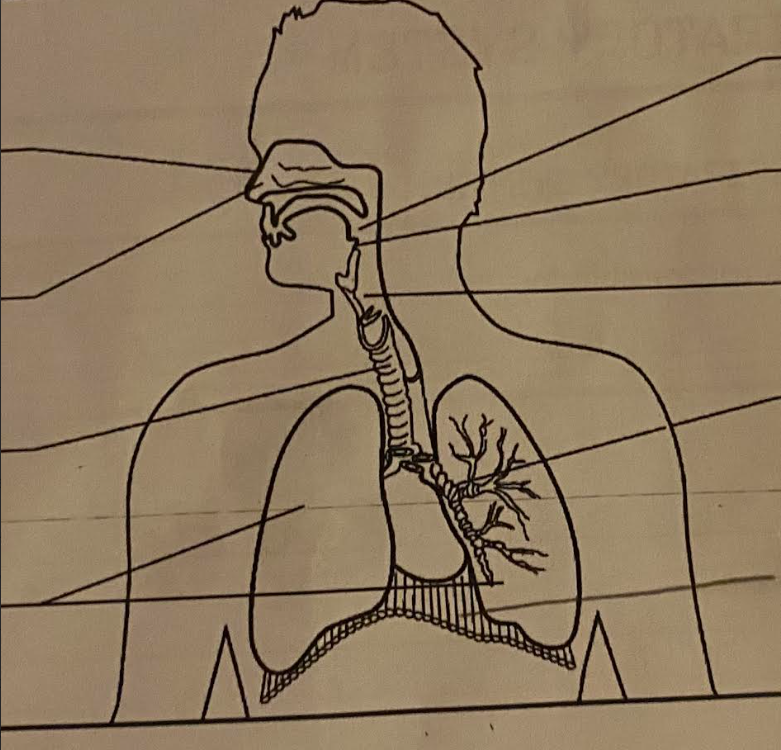
label parts:
nose, nasal passage, pharynx, eppiglottis, larynx, trachea, Bronchus, lungs, Diaphragm
Respiratory system:
responsible for exchange of oxygen gas and carbon dioxide gas and the subsequent release of energy, and elimination of carbon dioxide gas.
Nasal cavity:
where air is filtered throught cilia, warmed, and moistened through mucus and numerous blood vessels.
Lungs:
elastic organs, on each side of the heart, cotain millions of alveoli, ensures gas exchange between body and its surroundindg
formula for cellular respiration
C6H1206 + 602= 6C02 + 6H20 + energy
what determines blood type:
due to the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of the red blood cells.
4 different blood types groups and antigen present on surface:
A: a antigen B: b antigen AB: a + b antigen O: none
all possible blood types
A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+, O-
compatibility of blood types
A person CANNOT receive blood which has antigens that are not present in their own blood.
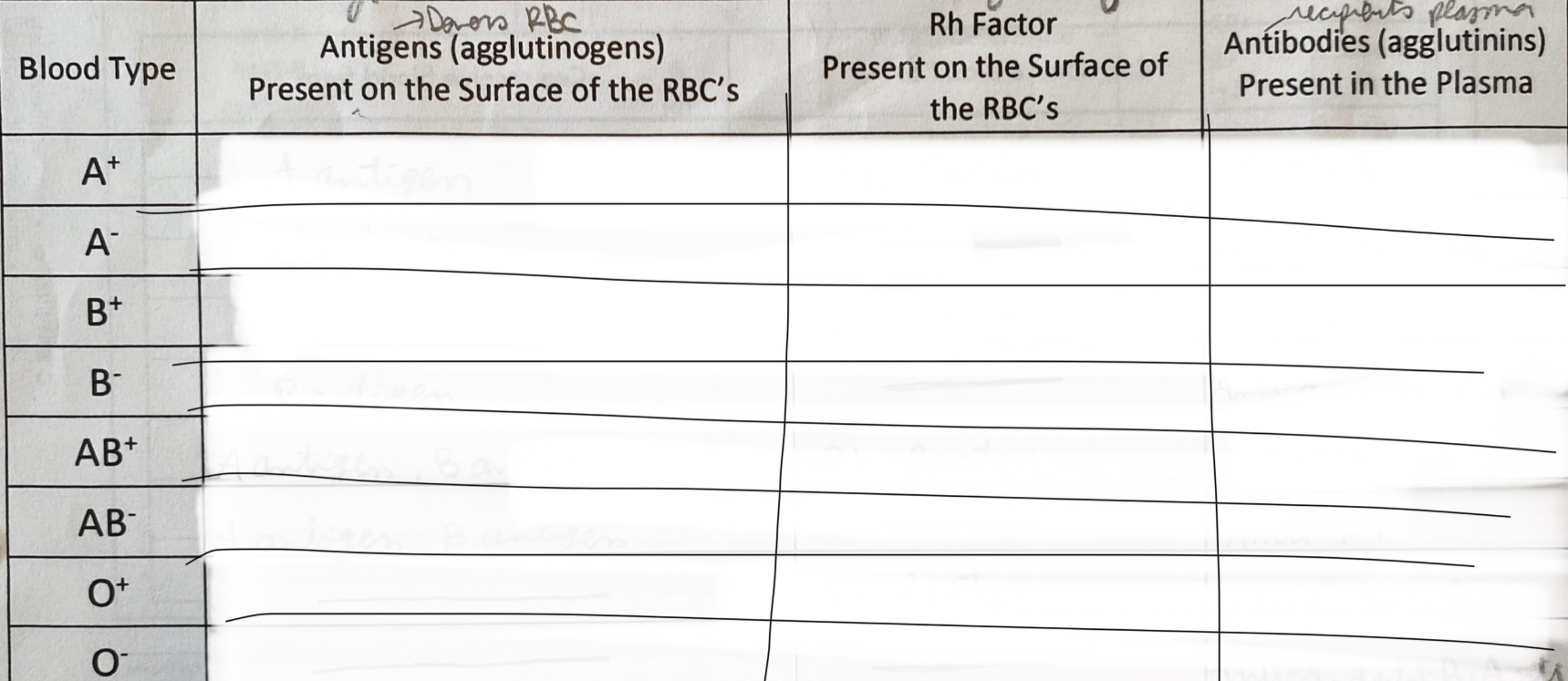
fill in blanks
A+: A-antigen, Rh factor, Anti-B
A-: A-antigen, ————, anti-B, anti-Rh
B+: B-antigen, Rh factor, Anti-A
B-: B-antigen, ————-, anti-A, anti-Rh
AB+: A + B antigen, Rh factor, ————
AB-: a + B antigen, —————, anti-Rh
O+: ———-, Rh factor, Anti-A, Anti-B,
O-: ———-, ————, anti-A, anti-B, anti-Rh

fill in the blanks:
A+: A+, AB+ / A+, A-, O+, O-
A-: A+, A-, AB+, AB- / A-, O-
B+: B+, AB+ / B+, B-, O+, O-
B-: B+, B-, AB+, AB- / B-, O-
AB+: AB+ / A+, A-, B+, B-’ AB+, AB-, O+, O-
AB-: AB+, AB- / A-, B-, AB-, O-
O+: A+, B+, AB+,O+
O-: A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+, O- / O-
role of the circulatory/ cardiovascular system
serves to transport blood throughout the body and exchange of gases, nutrients and waste.
what is the lymphatic system:
The lymphatic system is a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins and waste and is necessary in maintaining your body’s defenses.
role of lymphatic system:
evacuate waste products from the cells and aids in the circulation of antibodies. Transport lymph, which contains antibodies and white blood cells,
immunity
ability of an organism to resist a desease or ingections by the action of specific antibodies produced.
Active immunity
Active immunity is a type of immunity developed by the body's own immune system in response to exposure to a pathogen or antigen.
two types of active immunity:
natural immunity and artificial immunity
Natural immunity:
acquired naturally when an organism recovers from an infectious agent through the bodies process of creating antibodies.
Artificial immunity:
artificially acquired by injecting a small quantity of a
weakened infectious agent through a process of vaccination wich wil cause body to produce antibodies for that particular disease.
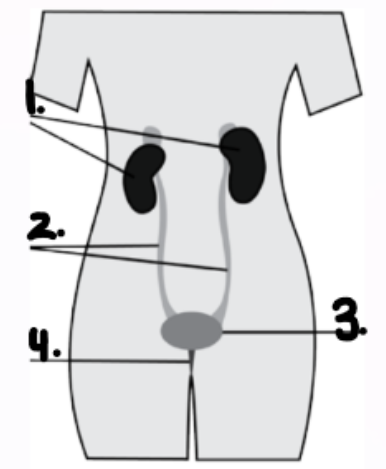
label parts and name system:
excretory system: 1. bladder 2. ureters 3. bladder 4. urethra
Role of excratory system:
Filter blood and eliminate cellular waste:
Filtering the blood: the kidneys filter out urea from the blood to form urine.
Eliminating cellular and other waste: removing waste from the body (through urination,exhalation and perspiration).
role of Kidney: (functional unit= nephron)
eliminate waste and maintain equilibrium in blood through production of urine
function of urethers:
Transport urine produced in kidney to the bladder
Function of bladder:
muscular sac which stores urine until it’s released through urination.
Function of Urethra:
Transports urine from bladder to the outside
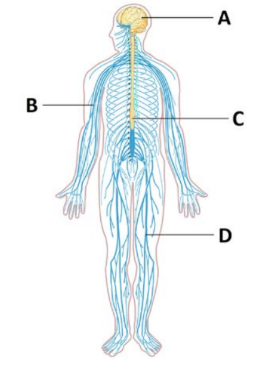
What system is this
Nervous system
Peripheral nervous system:
Connects different parts of the body to the cns
role of peripheral nervous system:
transportation of nerve impulses from the senses to the brain and from the brain to the muscles
Sensory receptor:
detect stimuli and transform the information into nerve impulse
Sensory nerves:
transmit information from receptor in body to the cns
Motor nerves:
transmit information form the cns to the body in order for the body to respond appropriately to the stimulus (producing voluntary and involuntary movement)
order of information through nervous system
stimulus—sensory receptors—sensory nerves—CNS—motor nerves—muscles
voluntary act
act is one that you choose to do consciously.
Reflex
A reflex is an action that is involuntary, meaning you do not choose to do it. It is done
automatically for you. Most reflexes serve to protect the body.
sensory receptors imvolved in hearing:
cochlea
sensory receptor for balance:
Vestibule and semicircular canals
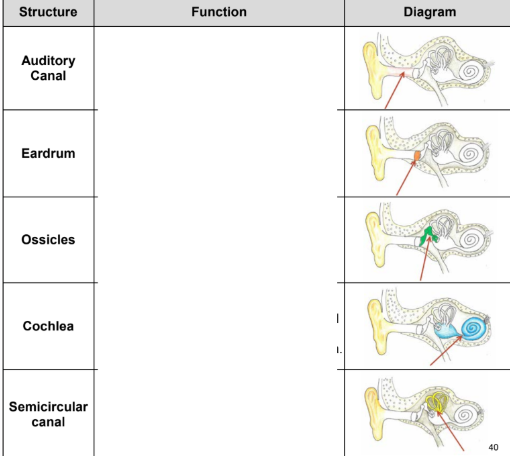
Pinna: captures sound wave
Auditory canal: carries sound wave to eardrum
Eardrum: vibrates in response to sound waves and transmits the vibration to the ossicles.
Ossicles: 3 small bones which transfer the vibrations from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Cochlea: fluid filled structure shaped like a snail, tiny cilia that line inside move in response to vibrations and concerts these into nerve impulses
semicircular canals: 3 fluid-filled rings oriented in different planes. Movement in the fluid send information about movement and body position to help maintain balance.
sensory receptor for smell
olfactory epithelium
define olfactory epithelium, olfactory bulb and olfactory nerve
olfactory epithelium: contains chemoreceptor nerve cells which are sensitive to odorant molecules. Converts the chemical information in the odorant molecules into nerve impulses.
Olfactory bulb: locaed at tip of olfactory nerve, contains 15 million nerve cells. conveys nerve impulse to olfactory nerve
Olfactory nerve: transports nerve impulse to olfactory cortex
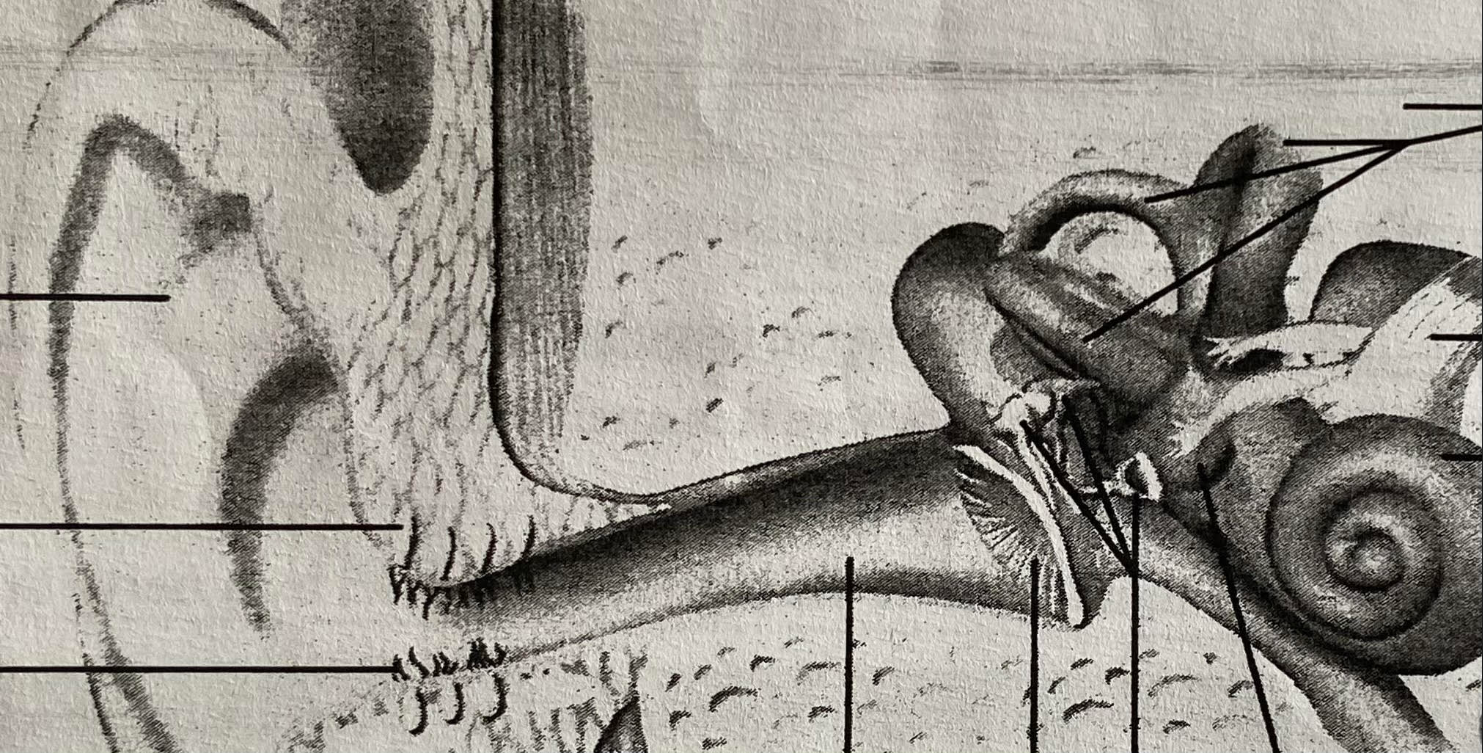

pinna, auditory canal, eardrum, ossicle, vestibule, Eustachian tube, cochlea, autitory nerve, semicircular canals.
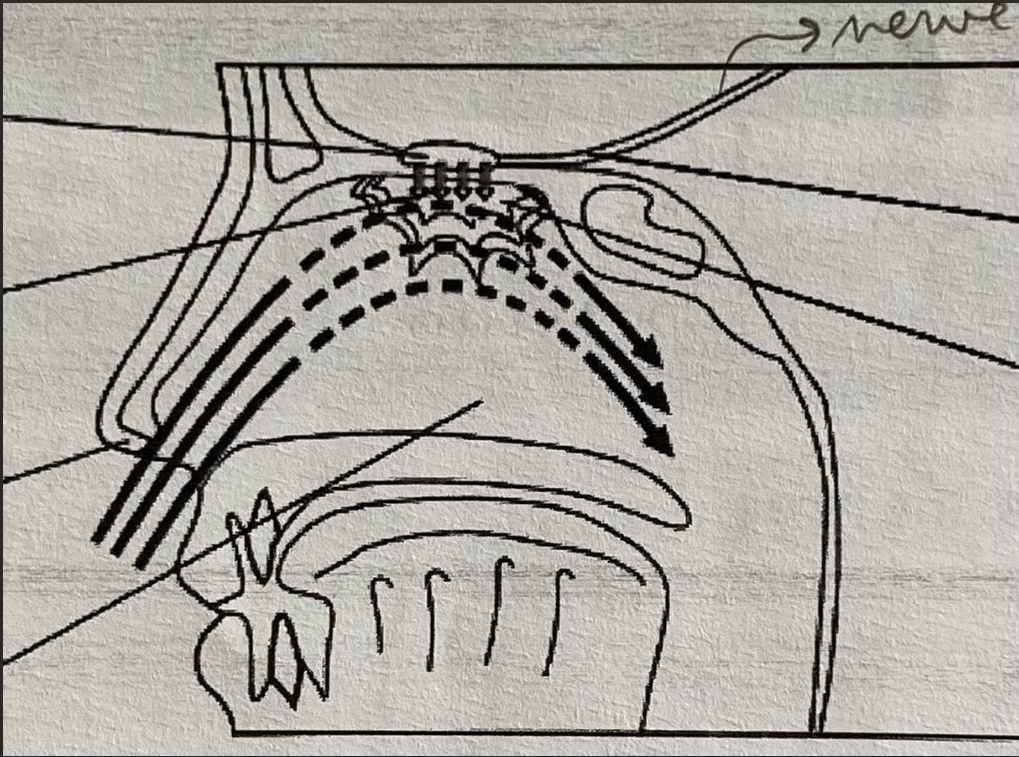
olfactory bulb, olfactiry nerve, olfactory cilia, olfactory epithelium, nostrils, nasal cavities
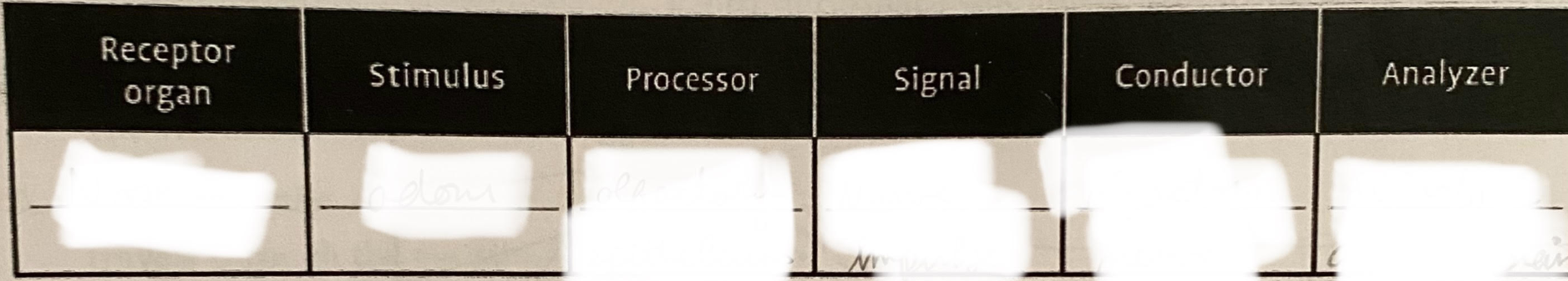
ear:
sound, cochlea, nerve impulse, auditory nerve, aiditoru cortex

nose:
odeur particles, olfactory epithelium, nerve impulse, olfactory nerve, olfactory cortex
3 types of muscles:
striated or skeletal muscles
Smooth muscles
cardiac muscles
skeletal muscles:
attached to bone. It may contract voluntarily or involuntarily (reflex response) to move bones.
smooth muscles:
involuntary muscles found in internal organs.
Cardiac muscles:
found in the heart. It contracts involuntarily.