Synapses & Sensory Receptors
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is a synapse
It s a junction between the synaptic terminal and another cell.
List the types of Synapses
Electrical
Chemical
What is an electrical Synapse and how does it work?
A current flows direclty from cell to cell and it is a less common one.
What is a chemical synapse and how do they work?
They involve neurotransmitters that travel between the pretsynaptic cell → synaptic cleft → postsynaptic receptor.
What are neurotransmitters?
They diffuse accross the synaptic cleft, then bind + activate specific postsynaptic receptors
What role does the presynaptic neuron play in chemcial synapses
Presynaptic Neuron:
Synthesizes neurotransmitters which are stored in synaptic vesicles.
An AP causes voltage gated CA2+ channels to open.
Ca 2+ enters
Vesicles then fuse wiht the “bottom” of the presynaptic neuron
This finally releases neurotransmitters.
What are postsynaptic potentials?
It is a change in membrane potential of postsynaptic cells.
Which are triggered by a ligand-gated ion channel (ligand = something that binds neurotransmitters )
The neurotransmitter does not open the cell but a postsynaptic potential is generated that can stimulate or inhibit.
List the types of postsynaptic potentials
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP): Depolarizes
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP): Hyperpolarizes
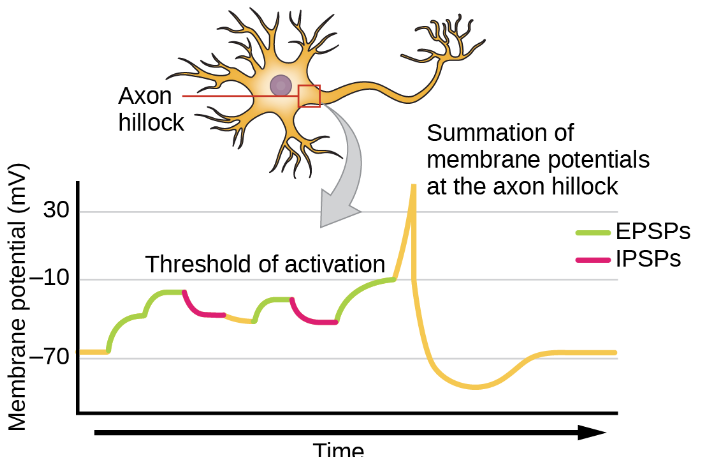
What is Temporal Summation
There are 2+ EPSPs at 1 synapse in rapid succession
the @nd epsp arrives before the membrane potntioal resets → leads to a stronger depolarization.
What is Spatial Summation?
2+ EPSPs nearly simultaneously
Different synapses
Same postsynaptic neuron → leads to stronger depolarization.
What is the importance of the Axon Hillock for interactions?
It is the neuron’s integration center.
The membrane potential at the axon hillock = Summed effect of all EPSPs (excitatory) and IPSPs (inhibitory).
All of the signals addup at the axon hillock and it is the “discisuion point” of the neuron.
What is Neuronal Plasticity?
It is the response of the nervous system to activity.
Remodeling happens through competition among neurons for growth-supporting factors.
Synapse elimination occurs — only required synapses are kept.
Lastly, follows the use it or lose it principle.
What are the two types of memory?
Short Term Memory
Info is held for a short time, & is essential for quireing memories, but not maintaing.
Is acesses by tempory links in the hippocampus
Long Term Memory
It is permenat connections in the cerebral cortex, stored memories.
Temporay links are replaced by connections within the cerebral cortex → making permenalt
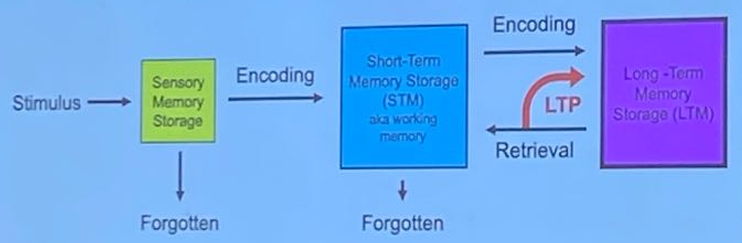
What is Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)?
It is a lasting increase in the strength of synaptic transmission.
A fundemental process of memory storage and learning.
Stimulus → Sensory [info could be forgotten] → Encoding → STM [info can be forgotten] → encoding → LTM [consistent retrieval [LTP] → remember better].
![<p>It is a lasting increase in the strength of synaptic transmission. </p><p><em>A fundemental process of memory storage and learning. </em></p><ul><li><p><span style="font-family: "EB Garamond", serif">Stimulus → Sensory [info could be forgotten] → Encoding → STM [info can be forgotten] → encoding → LTM [consistent retrieval [LTP] → remember better].</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4997e559-6764-4506-8504-aff518c14eb3.png)
What are the two conditions required for LTP?
High-frequency series of APs
Depolarization from another stimulus at the same time
-→ It strengthes the synapse whose activity coincides with that of another.
List the types of Sensory Pathways.
Snesory Reception
Sensory Transduction
Transmission
Perception.
What is Sensory Reception?
A sensory receptor detectes change.
Often times a sense organs’ receptors + associated cells (eyes)
What is Sensory Transduction?
Energy of stimulus is converted to receptor potential -stimulus → AP
A Unstimulated receptor is at → resting potential
A stimulated receptor is → depolarized → which triggers an AP
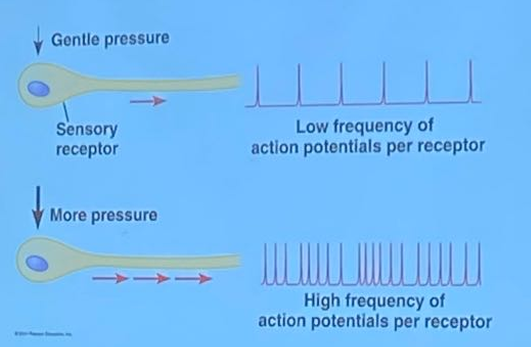
What is Transmission? (Sensory Pathway)
The Sensory information travels as an AP-receptor → brain
Larger receptor potential means → more freqent AP
What is Perception?
Simply the brain processing information.
List the types of sensory receptors
Its characterized by type of stimulus transduced
Chemoreceptors
Photoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Thermoreceptors
What are some of the functions of the Human Ear?
Its for hearing AND balance.
Works via mechanoreceptors
Sound: presuse waves in the air or water
Hearing: ability to sense changes in pressure & intrepret them as sound.