Oligopoly
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Oligopoly diagram
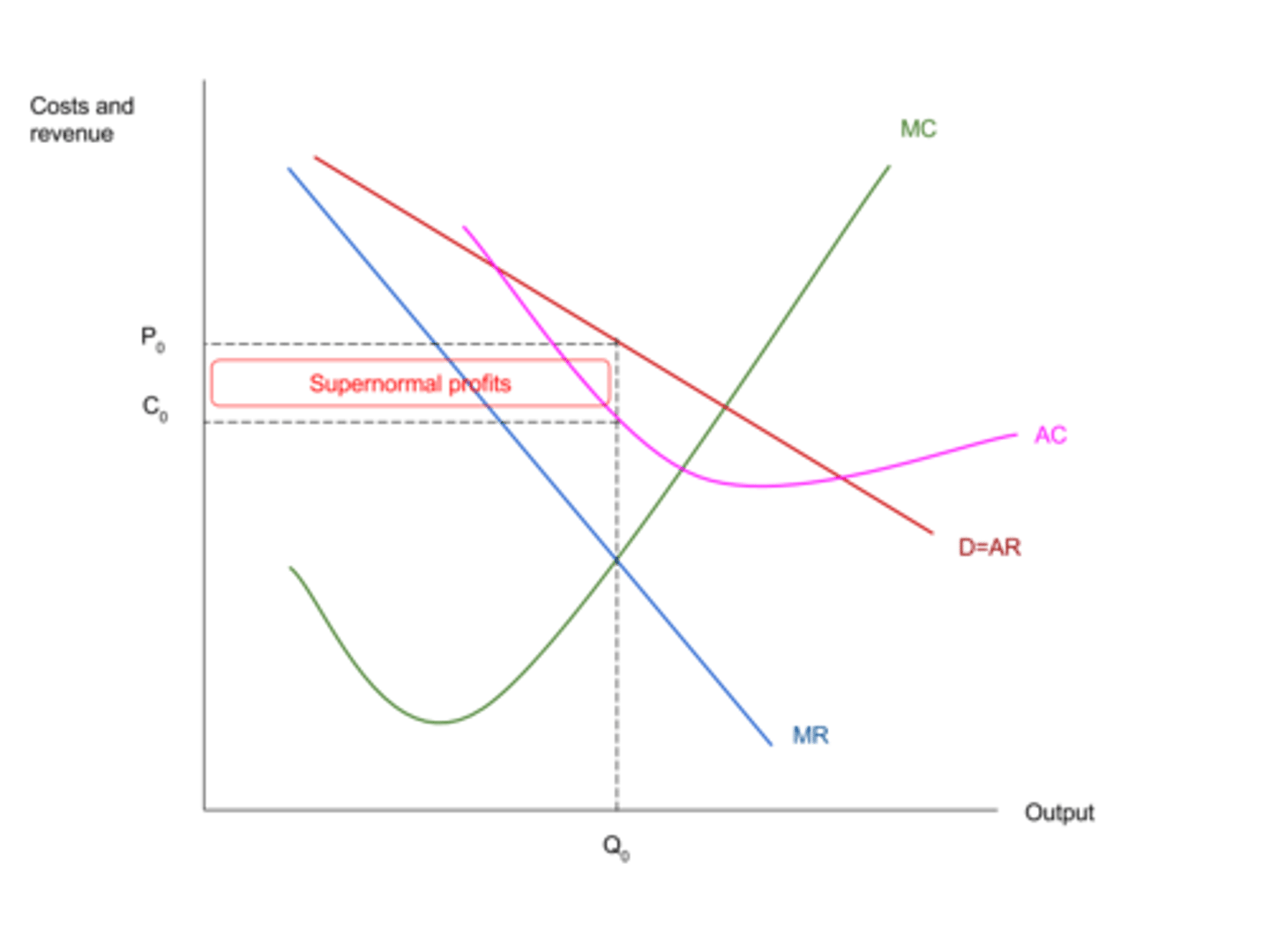
Firms operating in oligopolistic markets tend to keep what
prices stable
Firms in oligopolistic markets are what
interdependent
Oligopoly firms have an incentive to work together through what
Collusive agreements
what level of market competition is there
high
oligopoly exists when the top five firms in the market account for more than how much market share
60%
Characteristics of an oligopoly (3)
- high barriers to entry
- interdependent decision making
- non price competition
Kinked demand curve
a perceived demand curve that arises when competing oligopoly firms commit to match price cuts, but not price increases
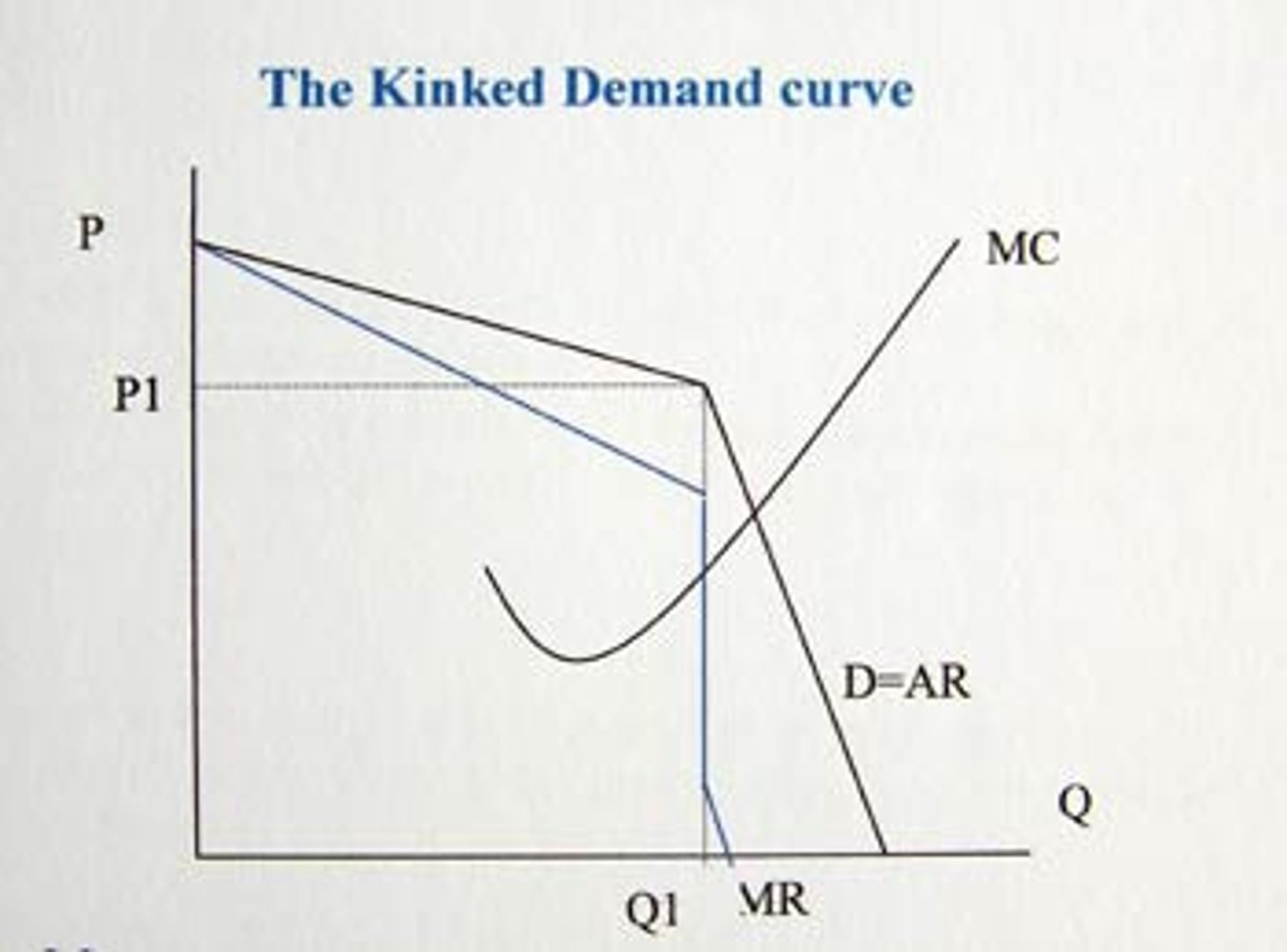
Price leadership
a form of implicit collusion in which one firm in an oligopoly announces a price change and the other firms in the industry match the change
Prisoners dilemma
a game in which pursuing dominant strategies results in noncooperation that leaves everyone worse off
Rivals within an oligopoly are assumed not to follow a price increase by a firm, so the acting firm will lose market share and therefore demand will be relatively what leading to what
elastic and a rise in price will lead to less revenue
Rivals within an oligopoly are likely to match a price fall by one firm to avoid losing what
market share
if firms match a price fall, demand will be more inelastic and a fall in price will also lead to a what
fall in total revenue
Key predictions of the kinked demand curve theory is that prices will be what even when there's what assuming firms are what
sticky even when there is a change in the marginal costs of supply assuming firms are profit maximising
Price wars
a series of competitive price cuts that lowers the market price below the cost of production
Who are the winners from price wars
- regular consumers
- managers from higher sales
Who are the losers from price wars
- shareholders as lower profits
- suppliers may get squeezed
Limit pricing diagram
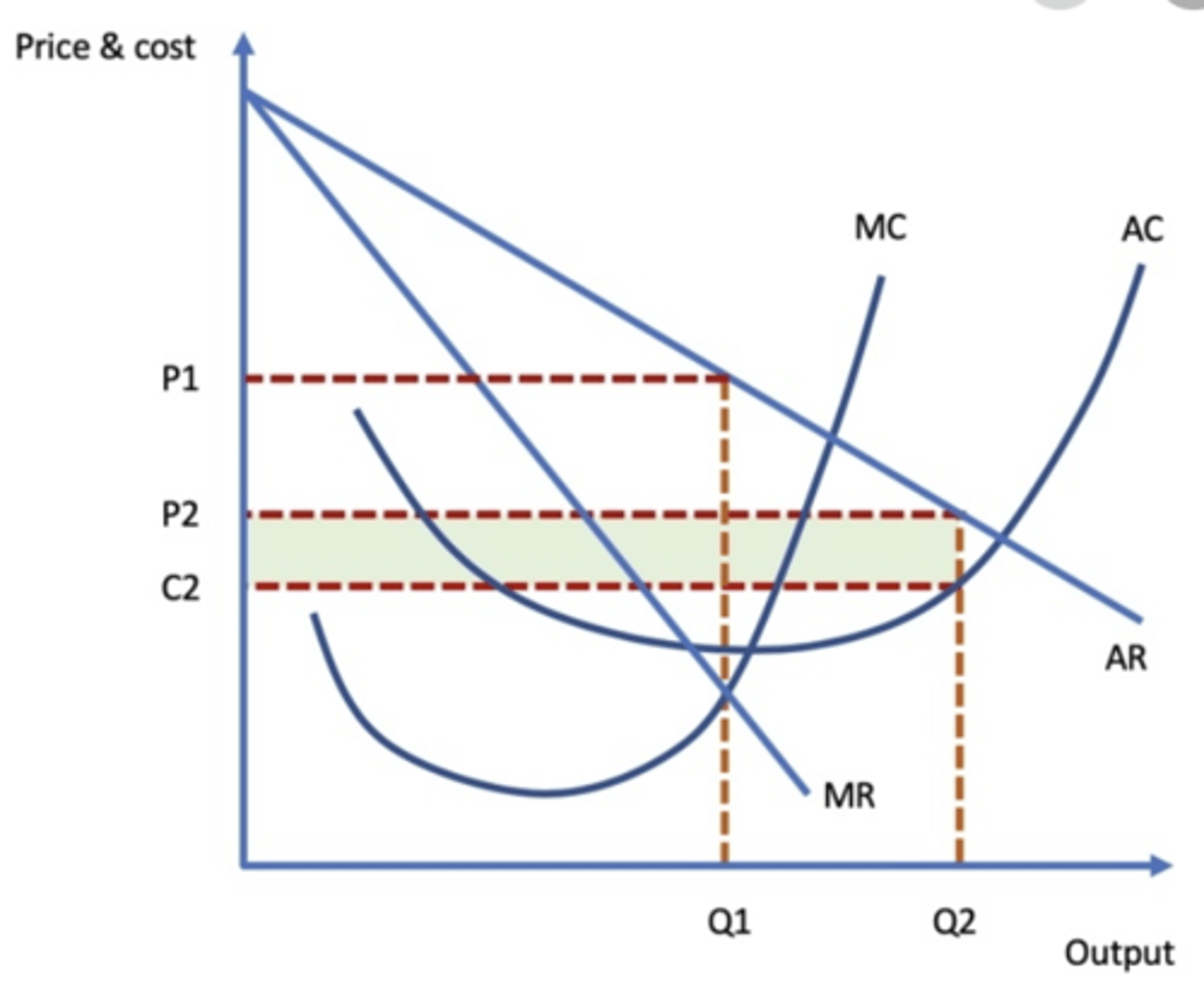
Limit pricing
reducing the price of a good to just above average cost to deter the entry of new firms into the market. Prices are set at levels which are likely to make it unprofitable for potential entrants who might consider coming into the market
Predatory Pricing diagram
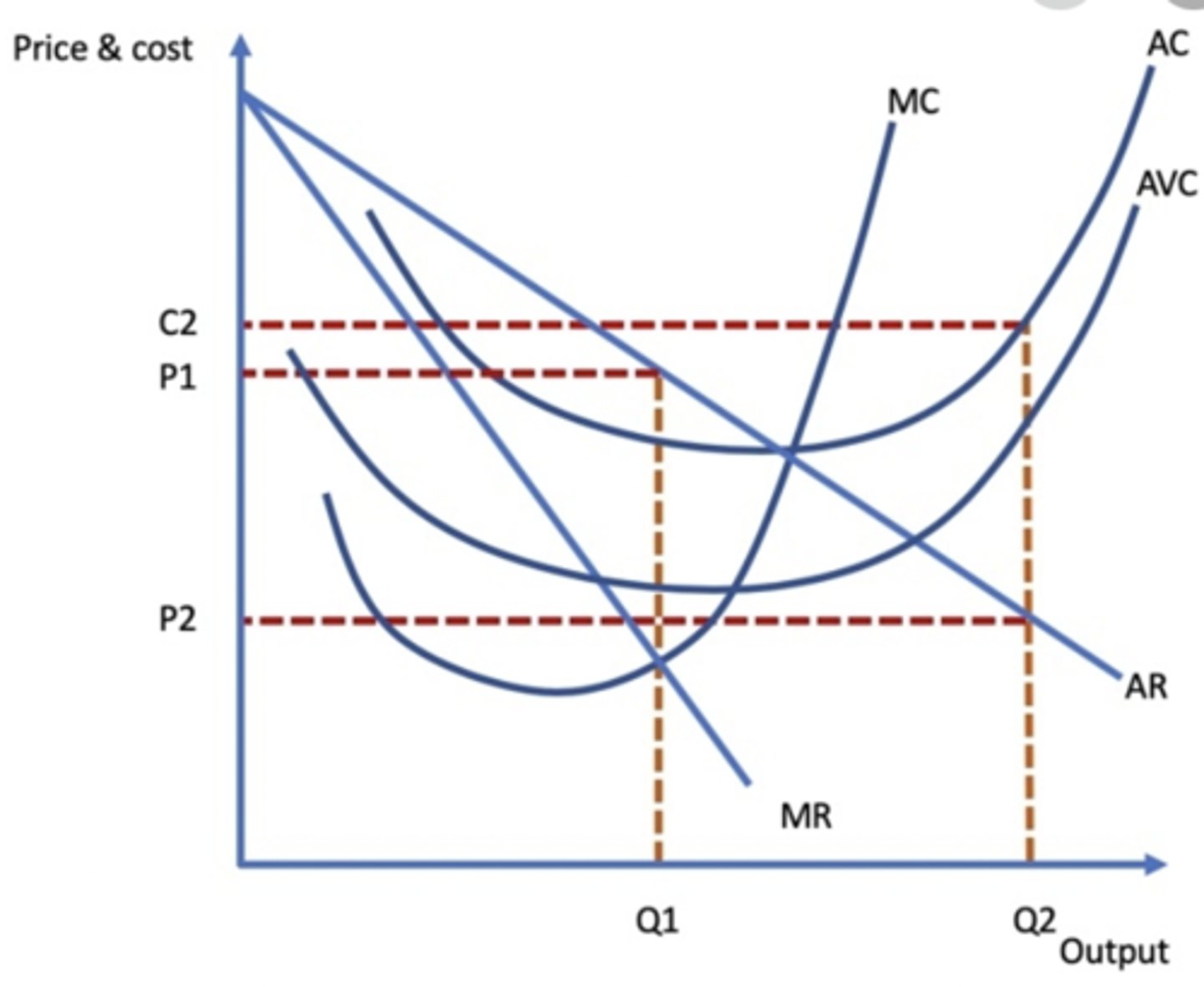
predatory pricing
the practice of charging a very low price for a product with the intent of driving competitors out of business or out of a market
two types of oligopolistic markets
collusive and non-collusive
collusive oligopoly
- explain via game theory and pay-off matrix
- game theory is concerned with predicting the outcome of games of strategy in which the participants have incomplete information about the intentions of the other
Non-collusive oligopoly
explain via kinked demand curve theory of sticky prices.
how to draw the payoff matrix
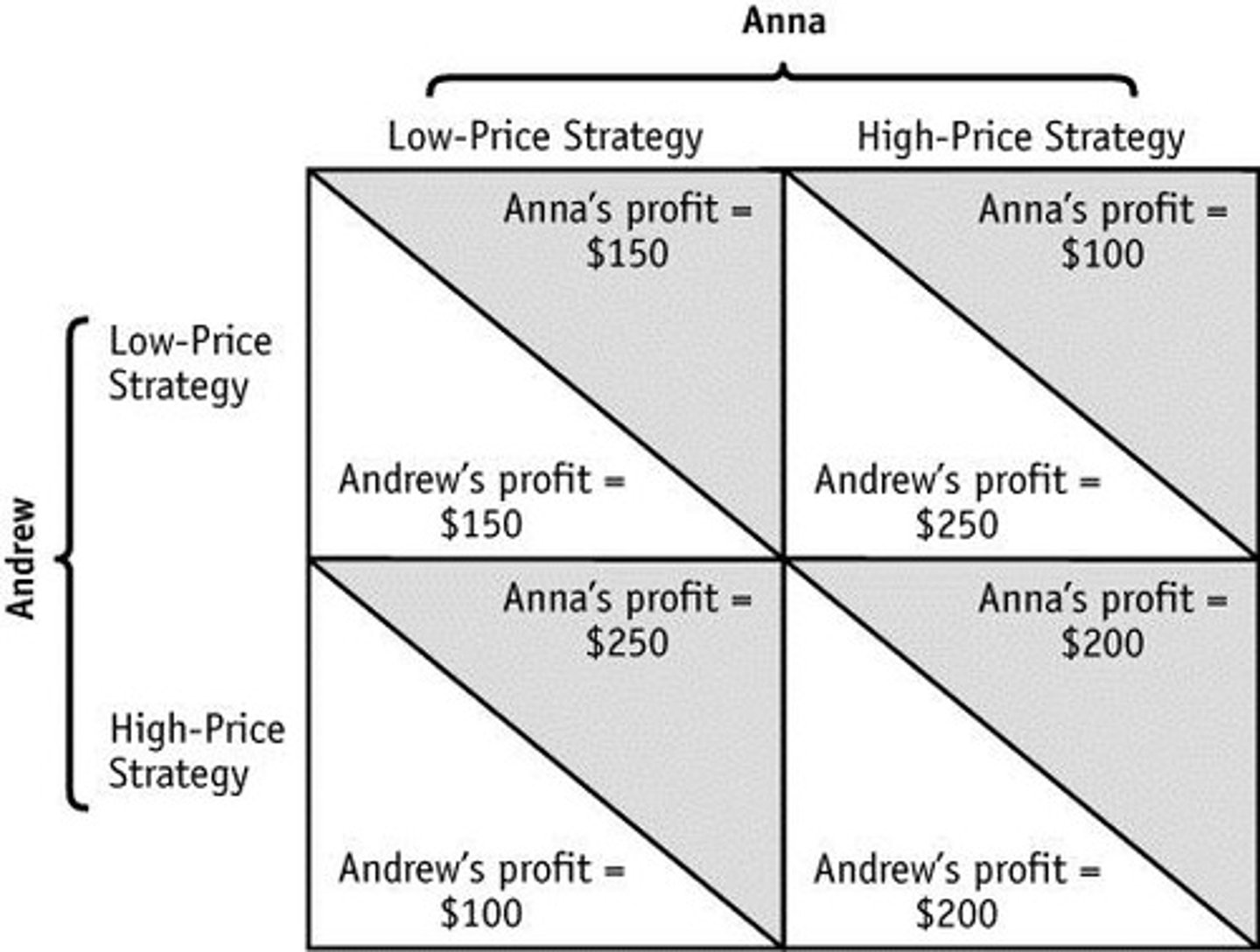
no collusion where do you end up on the payoff matrix
low low
therefore it is much better for firms to collude and set what price
high high
Prisoner's dilemma explained
it is definitely worth colluding but also worth breaking the collusive agreement first. Once broken, it is worth colluding again. This is the prisoner's dilemma, this explains why cartels form but also break down inevitably
what else can firms collude on aside from the price
geographical segmentation of markets, quantity and restriction of supply, marketing agreements
When is collusion likely to break down?
- under collusion there is always an incentive for a firm to cheat because an individual firm could increase its profits by exceeding its quota and undercutting its rivals
- if there are incentives for businesses to admit their part in collusion in order to receive a lower fine
- there are lots of firms involved and therefore trust becomes an issue
- one firm is much more profitable than the other
- there are lower barriers to entry and new firms can join the market and threaten the cartel