Public Speaking Quiz
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
public speaking
an organized, face-to-face, prepared, intentional (purposeful) attempt to inform, entertain, or persuade a group of people (usually five or more) through words, physical delivery, and (at times) visual or audio aids.
glossophobia
a severe fear of public speaking
communication
sharing meaning between two or more people
culture
the system of learned and shared symbols, language, values, and norms that distinguish one group of people from another
channel
the means through which a message gets from sender to receiver
feedback
direct or indirect messages sent from an audience (receivers) back to the original sender of the message
noise
anything that disrupts, interrupts, or interferes with the communication process
encode
the process of the sender putting his/her thoughts and feelings into words or other symbols
decode
the process of the listener or receiver understanding the words and symbols of a message and making meaning of them
demographic characteristics
the outward characteristics of the audience
audience analysis
examining and looking at your audience first by its demographic characteristics and then by their internal psychological traits
stereotyping
generalizing about a group of people and assuming that because a few persons in that group have a characteristic, all of them do
totalizing
taking one characteristic of a group or person and making that the
“_____” or sum total of what that person or group is
heterogeneous
a mixture of different types of people and demographic characteristics within a group of people
homogeneous
a group of people that are very similar in many characteristics
Psychographic Characteristics
the inner characteristics of the audience; beliefs, attitudes, needs, and values
beliefs
statements we hold to be true
attitude
a stable positive or negative response to a person, idea, object, or policy
needs
important deficiencies that we are motivated to fulfill
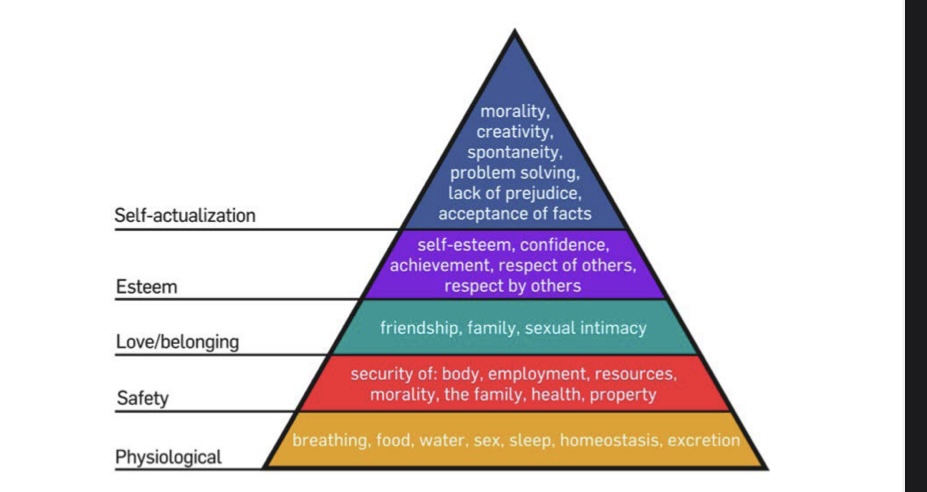
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
hearing
the physical process in which sound waves hit the ear drums and send a message to the brain
listening
an active process where you are specifically making an effort to understand, process, and retain information
comprehensive listening
listening focused on understanding and remembering important information from a public speaking message
empathetic listening
listening for understanding the feelings and motivations of another person, usually with the goal of helping the person deal with a personal problem
appreciative listening
type of informed listening needed to listen to and interpret music, theatre, or literature
critical listening
listening to evaluate the validity of the arguments and information and deciding whether the speaker is persuasive and whether the message should be accepted
planned redundancy
the use of a clear central idea statement, preview of the main points, connective statements, and overall summary in the conclusion to reinforce the main ideas or points of a speech; the deliberate repeating of structural aspects of speech
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for or interpret information in a way that confirms one's preconceptions
Common fears of public speaking
-“all or nothing”
-over generalization
-”fortune telling”
all or nothing
mindset that if your speech falls short of "perfection" (an unrealistic standard), then you are a failure as a public speaker
over generalization
believing that a single event (such as failing at a task) is a universal or "always" event;
fortune telling
the tendency to anticipate that things will turn out badly, no matter how much practice or rehearsal is done.