Space exploration (i MIGHT just off myself)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What happened to Copernicus’s heliocentric model
It wasn’t 100% complete and was later revised by several scientists
What did Kepler propose
That the motion of celestial bodies would be more accurate if the orbits were elliptical rather than circular
What does the ellipse shape look like
A squashed circle
The planets of our solar system move in what around the sun
Ellipses
What are the 3 observations Galileo make with his telescope
The moon has craters on the surface, the sun has sunspots that change over time (suggesting that the sun rotates), suns are much farther away than we previously thought
How many years later did Kepler propose his ideas
80 years later
What did newton explain
Why the planets orbit in ellipses
What was newtons universal law of gravity
Gravity between objects pulls them together. When no forces act on an object it will move in a straight line at a constant speed.
What is universal gravitation
All objects attract other objects based on their mass, and this provides an explanation for the planets elliptical orbits.
What can sunspots eject
Large masses of energetic, magnetized plasma
What did Richard Tousey make an observation about
solar flares
In what year did Richard Tousey make his important observation
1973
What are solar winds
High energy particles steaming off the sun
What protects planets from solar winds
The atmosphere
What does the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram show
Surface temperature and luminosity/brightness
What axis is the surface temperature on
X-axis, increases when moving left
What axis is luminosity/brightness on
Y-axis, increases when moving up
What positions does the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram show
Positions of the different types of stars
What is the sun classified as in the context of its future life cycle
A red giant
What is the sun currently
A main-sequence star
What are the major regions of the
Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram
Main sequence, red giants, white dwarves
what are the contributions of space travel to our understanding of space
enabling direct observation of celestial bodies, leading to discoveries about the formation of stars, galaxies, and planets, and the search for extraterrestrial life
How are satellites used for gps
by broadcasting time and location signals
How are satellites used for communications
relaying radio signals between distant points on Earth, overcoming the planet's curvature
How are satellites used for weather forecasting
by taking measurements and creating images of Earth's atmosphere from space, using instruments that detect visible light, infrared radiation, and microwaves
What are rockets
A tube containing combustible material at one end
What are the components of rockets
the structural system, which is the outer frame; the payload system, which carries the cargo; the guidance system, which uses computers and sensors to steer the rocket; and the propulsion system, which generates thrust through a combination of the engine, propellants, pumps, and nozzle
What is on the opposite side of the rocket
The payload
What is the payload
The device or material the rocket transports.
What are all the things the payload can be
A person, a measurement device, equipment, an explosive
What does the nose cone do
Helps the rocket moves smoothly
What is the order from top to bottom of the parts of a rocket
Nose cone, payload, guidance system, first stage, engines, exhaust
What does the guidance system do
Steers the rocket
What is the main body of the rocket
First stage
What ones the first stage of the rocket contain
Fuel tanks
What do the engines do
Provide the thrust for liftoff
What does the exhaust on a rocket do
Hot gases pushed out by the engines
What is a stage rocket
A stage is a section of a rocket that drops off once its fuel has been used up, this makes the remaining part of the rocket lighter
What happens to a rocket with more than one stage
It would fly faster and higher
Why did scientists develop gravitational assist
Because we are unable to send heavy spacecrafts on long journeys throughout the solar system
What are voyager one and two
Space probes built by NASA in the 1970s
What happened after the 2 voyagers were launched
They used gravitational assists from other terrestrial planets to send them as far as possible to collect data
What did voyager one do
It was faster and reached Jupiter in 1979, then went towards Saturn
What did voyager 2 do
Went slower, on a fixed path, reached Jupiter 4 months after voyager 1
Which voyager has traveled farther and why
Voyager 2 because it later reached Neptune and Uranus, it has visited farther out planets
What could we do now that we ave fund out how a way to reliably get into space
We could use things into orbit around earth to help us better understand the planets and universe
What is an example of things we can put into orbit around space
Satellites
What is an artificial satellite
A satellite made by humans, like a spacecraft or telescope that will stay in the orbit
What are examples of a naturally occurring satellite
Moon & earth
What are some ways that a satellite can orbit
Geosynchronous, low earth orbit
Geosynchronous orbit
Move in the same rotation as earths orbit, take 24 hours to orbit earth, synchronized with earths rotation, appear to be motionless over a point on earths surface
Low earth orbit
Satellites are placed 200-800km high above the ground, they complete one orbit of the earth in about 1.5 hours, satellites circle earth faster than earth rotates
Remote sensing
The science of taking measurements (of earth or other planets) from space
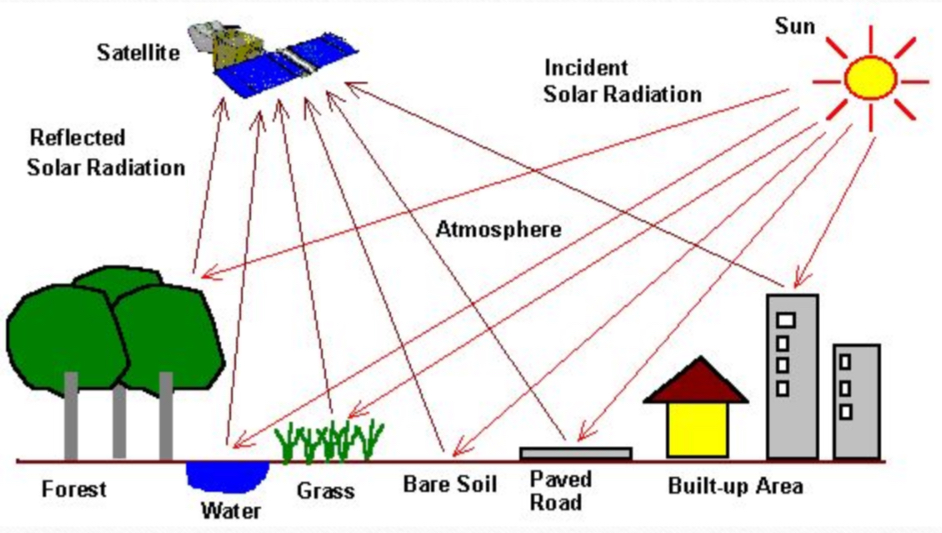
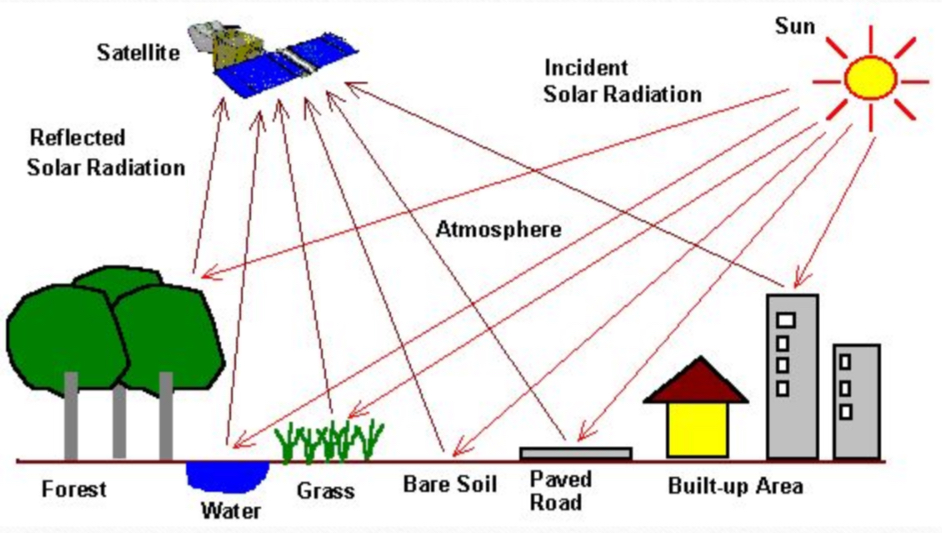
How can satellite images show healthy vegetation
By being computer processed
What do images of vegetation or forest degradation show when its unhealthy/degraded
Lots of purple on the thingy