Ch. 1 - 3
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Demographics
characteristics of our population such as its size, distribution of the very old and very young and geographic location
Demographic trends
describe the changes in such characteristics over time
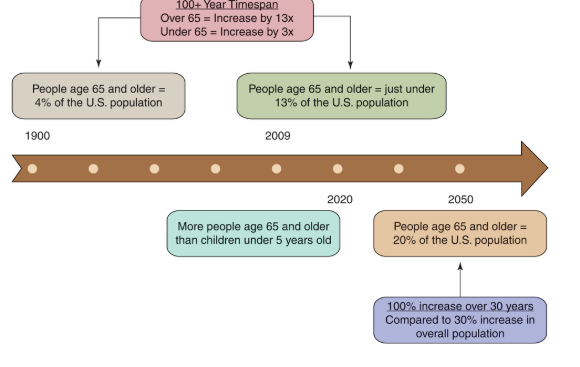
Population aging
sheer increase in the size of population age 65 and older and a gain in the average age of population
fueled by baby boomers; one of the most dramatic demographic changes in the US
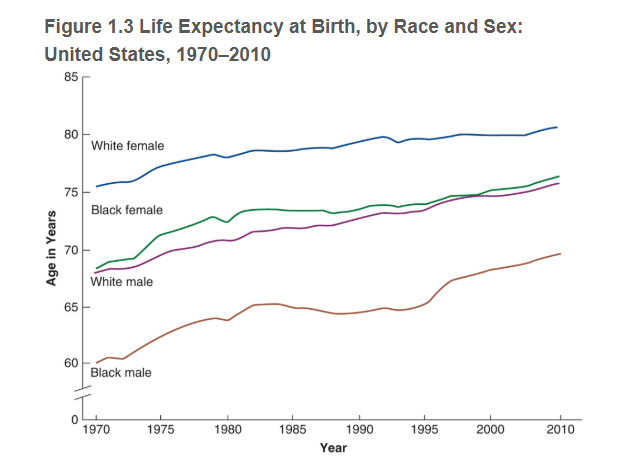
Life expectancy
average length of time one could expect to live if one were born in a particular year and if death rates remain constant
What is the cause of population aging?
falling birthrates: when children are a smaller percent in the population, the average age of the population increases
Which of the two sex lives longer? Why?
Women born today lives 5-6 years longer than men
Two X choromosomes makes women more physiologically more robust
Lifestyle factors such as preventive health behaviors, low rates of smoking, substance abuse and other high-risk behaviors across the life course
Represent 58 percent of the population age 65 and older, and 70 percent over age 85
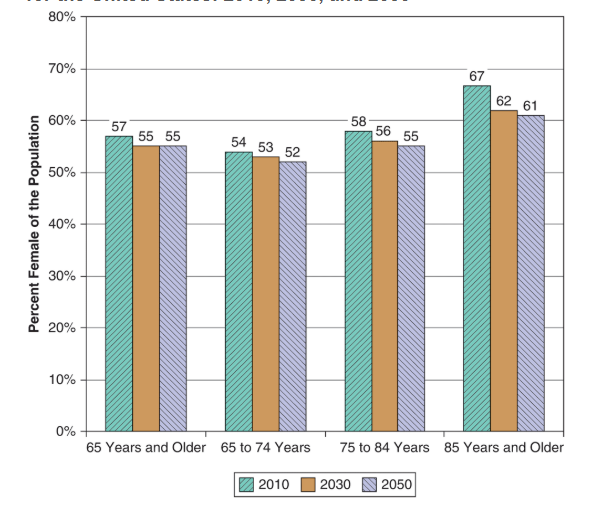
Why do African Americans have lower life expectancy than whites?
Health care disparities, inequities experienced as children and young adults in poverty,, education, and health care are often intensified in old age (more chronic illness)
Older African-American women have a longer average life expectancy than their male-counterparts
Which minority group of women live the longest racially?
Asian women
Maximum life span
length of years a given species could expect to live if all environmental hazards are eliminated (does not go beyond 120 years)
What is the soft limit to the human life span?
85-90 years
How can we achieve maximum life span?
Effectively manage chronic disease such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and kidney diseases as well as obesity (in middle and young-old age); sometimes referred to as an ideal survival curve or a compression of morbidity
What percentage of babies born after 2000 in developed countries are expected to reach age 85?
50 percent
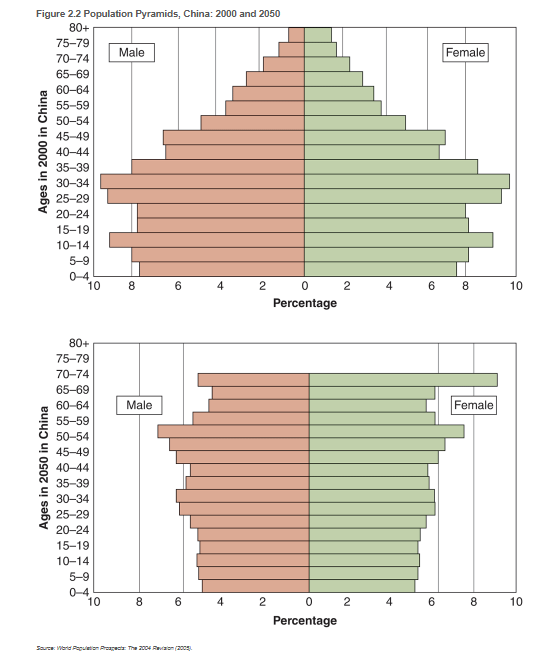
Population pyramids
visually capture the changing age distribution of the American population, the shift in proportion of older adults in relation of younger persons
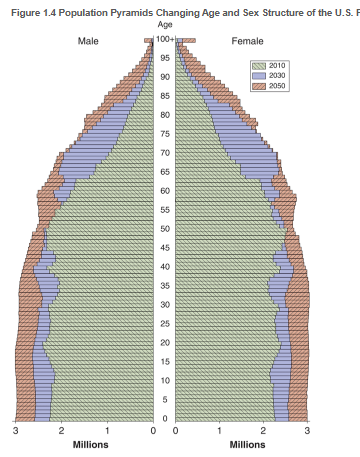
What is the “pig in a python phenomenon mean?”
In the projected resident population of the US, key points in time show a bulge in the area of the pyramid reresenting those residents born during the baby boom period. As years pass, that bulge moves higher up the pyramid, changing the shape of the pyramid into one that widens at the top
Contributions of declining birthrates and reduced death rates for older cohorts
Dependency ratio
changing age distribution in our population, refers to the number of people age 65 and older to every 100 people of traditional working ages; the higher the ratio, the greater the burden of dependent older adults
Ex. In 2010, ratio was 22 people age 65 and older to every 100 people age 18-64, expected to rise to 37 to 100 in 2030
Support ratio
indicates the relationship between the proportion of the population that is employed and the percentage that is not in the workforce
Fewer employed persons support retired older persons today
Ex. 1910, 10 employed per retired older person and now there is fewer than 5
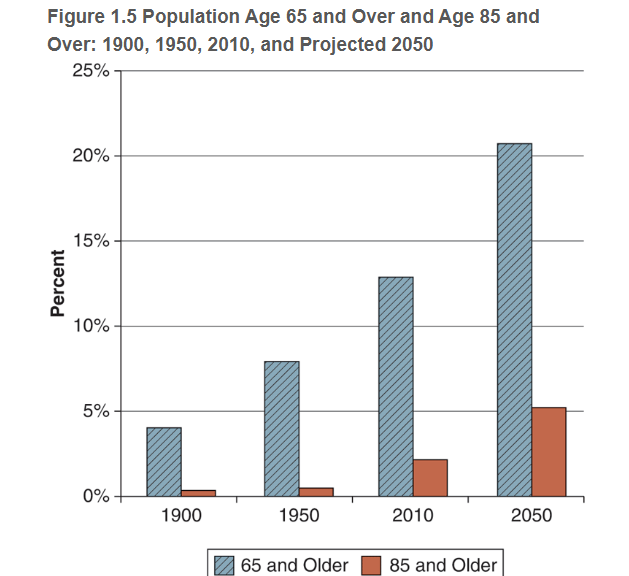
Old-old age group versus oldest-old
Between ages 75 - 84
People age 85+, growing most rapidly due to modern medicine
Demographers
people who study population
projects that the oldest old will reach 19 million or 4 percent of the U.S. population by 2050
Considered to be significant demographic trend because of its impact on social institutions as well as individual lives
What does the term “silver tsunami” means?
growth of the oldest-old has profound consequences for families, health and social services, long-term services and supports, retirement and workplace policies, political power, etc.
Centenarians
people age 100 and older
They are remarkably healthy, mentally alert, free of major disability, able to perform most daily activites, and engaged in their communities
What percentage of age is heritable?
one-third, we are partly responsible for our own old age
Hardiness
genetic factors determines how well an older person copes with disease or other stressors in their lives
Ex. oldest-old have higher threshold for disease and a lower risk of autoimmune diseases
Do women or men score higher on cognitive function tests after age of 90?
Men, women do score higher between ages 65 and 89
What is factors of lower rates of disease among centenarians in Okinawa?
Low-calorie diet with high intake of vitamins B6, B12, D, calcium, omega-3 fats, and high-fiber foods.
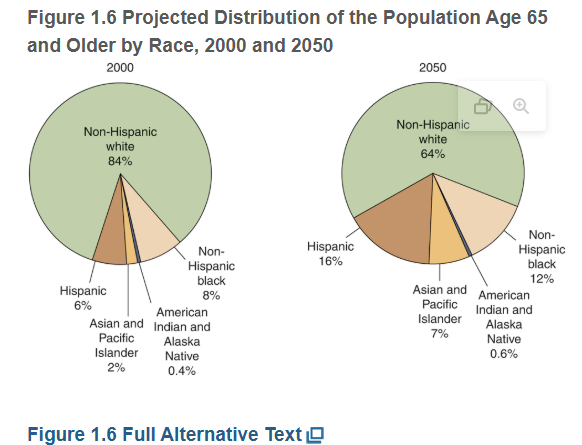
What is the percentage of the population in person of color over age of 65?
slightly more than 20 percent due to higher fertility and mortalitity rates among the younger nonwhite population and high rates of immigration of younger adults
will double from 20 percent to 40 percent in 2050 in the US
Which group is the general invisibility of being old?
LGBT due to stigma
What is the aging experience like for LGBT adults?
High rates of social isolation and mental distress and health disparities
Low percentage of 3 percent and the highest it can go is 18-20 percent
Compression of morbidity
lengthening the period of youthful vigor and experiencing only a few years of major illness in very old age
What is the concept of compressed morbidity?
Premature death is minimized because disease and functional decline are compressed into a brief period of 3-5 years before death
Population aging
older adults grow in both real numbers and in proportion to the larger population
What affects a country’s population aging?
Life expectancy, median age
Demographic divide
dichotomy between the needs of young and old between developed and developing countries
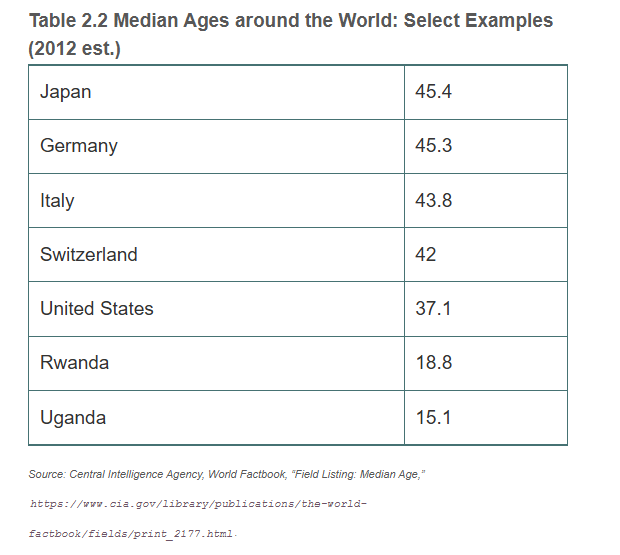
Median age
the age at which half the population is older and half is younger
What affects the country’s median age?
Birthrate because it adds to the number of people younger than the median age in a given country
Ex. Africa’s median age will increase from 19 to 27.4 in 2050 due to fertility rates being 3 times higher and high mortality rates
What is the estimate percentage of increase in 65+ in 2040?
14 percent
Why is China projected to have a population increase of people 60 years or older?
One child policy
Economic implications of population aging
increase in pension or retirement age, baby bonsuses and benefits to increase fertility rates, aiding the economy through immigration and other incentives
Traditional societies view older adults as
wisdom, security (wealth and property rights), power (civil and political), traditions (culture passed down), services provided (childcare), honor and respect
Filal Piety
everyone should respect and care of their elders
In modern societies, older people do not share the same status because of decline in respect, power, prestige, and influence
Theory of modernization
transformation of society from relatively rural way of life toward urban, industralized centers
all parts of the world increasingly urbanizing, 50% of the world population now living in urban areas
What happens in modernization?
young people move from rural areas to cities to seek better opprotunities; older adults remain
residential segregation impacts family interactions (distance, isolation, decline of intergenerational support, education)
older adults have lower social status and position
How many of foreign-born residents are 65+?
12 percent of US population
Grown from 2.7 to 4.3 million
Which state is one of the top states for older adult immigrants?
California
What percentage of older immigrants do not speak English and what is the impact?
75 percent, social isolation, grief and loss over leaving home country
Elder immigrants have twice the poverty levels, lack of health insurance when needed the most, dependency on younger family members
Biculturalism
intergrating two cultures into one’s lifestyle
intergration often means loss of filal piety, less likely to be sent to retirement homes, may choose to live in an ethnic enclave
Which country makes it illegal to not fiancially support your parents?
Singapore
Biological aging
Or senescence is the normal process of alterations over time in the body and its organ systems that eventually affect our functioning but do not necessarily result in disease or death
What are two general orientations that most biological theories of aging have?
Aging occurs due to random genetic mutations and oxidative stress
Aging is the result of programmed senescence
Four Primary theories of biological aging
Wear-and-tear theory, cellular aging theory, immunological theory, radical theory
Wear-and-tear theory
Like a machine, the organism simply wears out over time influenced by environmental stress
Cellular aging theory
aging occurs as cells slow their number of replications; cells are programmed to follow a biological clock and stop replicating after a fixed number of times
Immunological theory
aging is a function of body’s immune system becoming defective; less efficient in making the body resistant to pathogens and infections that attack and interfere with normal functioning
Radical theory
Or oxidative stress model states that the progressive, irreversible accumulation of oxidative damage to cells explain loss of physiological functions as we age
when organism cannot easily detoxify or repair the damage caused by free radical
Prolongevity
extending the length of healthy life and eliminating some disease associated with aging
Healthy life span
expanding the number of years we spend in good health
What are some of the ways we can reverse aging?
Growth hormones: increase lean muscle mass and bone density and reduced fat levels
Caloric restriction: reducing the intake of fat, protein, or carbohydrates is found to extend the life of experimental animals without causing malnutrition
What leads to changes in body composition?
lean body mass in muscle tissue is lost, whereas the proportion of fat increases
muscle fibers steadily decreases after age 50 leading to muscle tissue losing its elasticity and flexibility and muscle mass declines
What is the 4 causes of changes in skin?
Ultraviolet light from the sun, which damages the elastic fibers beneath the skin’s surface
Cell replacement in epidermis (outer layer of skin) slows down, the connective tissue that makes up the second layer of the skin (dermis) thins leading to reduced elasticity and fullness of our skin increasing sagging and wrinkling
Sweat glands deteriorate, deep skin layers lose fat and water
Skin’s blood circulation is diminished making temperature-regulating mechanism damaged (which is why elders feel cold all the time)
How many inches do we lose per year after the age of 30?
1/16th inch
Why do old people shrink?
Loss of bone mineral density and strength in our trunk, arms, and legs, the spine becomes more curved, and disks in vertebrae become compacted
Kyphosis
crush fractures of the spine cause the vertebrae to collapse
Kinesthetic system
lets us know our position in physical space
Age-related changes in the central nervous system as well as muscle weakness and diminished vision makes older people less able to judge the position of their bodies in physical space
Respiratory system
Decrease in vital capacity which is the require coordination of the respiratory, nervous, muscular systems
Oxygen in lungs declines by 50 percent for men between ages 25 and 70
Atherosclerosis
Arterial and vessel walls become increasingly lined with fats
What happens to our urinal system?
Kidneys lose their capacity to absorb glucose and their concentrating and diluting ability leading to increased problems with dehydration
Urinary incontinence
Bladder capacity reduced as much as 50 percent and sensation of needing to empty the bladder is delayed resulting from medications, acute illness, urinary tract infections
Gastrointestinal system
Changes in esophagus include a decrease in contraction of the muscles and more time for the cardiac sphincter (allows food to pass into the stomach) to open — more time for food to reach the stomach — sensation of being full before finishing a meal
What leads to chronic inflammation of the stomach lining and greater risk for colon stomach cancer?
diminish of secretion of digestive juices in stomach
Menopause
reduced production of two important hormones in women, estrogen and progesterone
What is the affect of neuronal loss?
reduced blood flow do slightly impair cognitive and motor function, resulting in a slower reaction time
Normal physiological changes in women and men
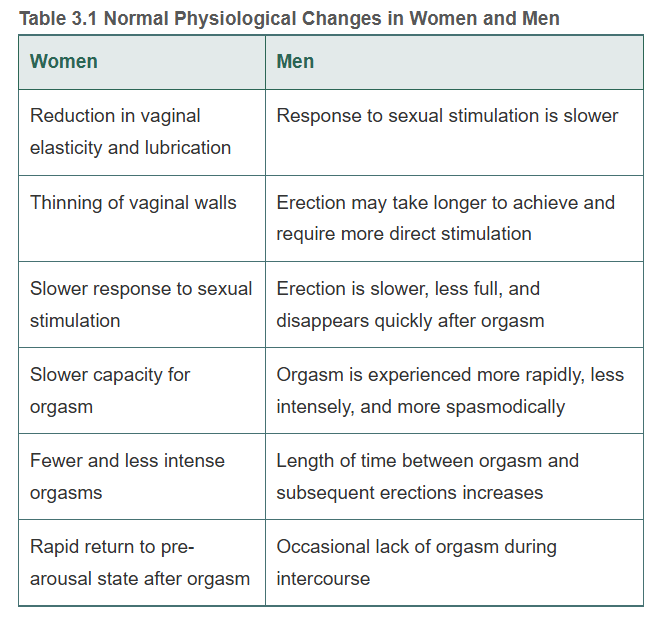
Health status
presence or absence of disease and the degree in level of functioning
Functional ability
what someone can do - or think they can do - and how healthy they are
Disability
impairments in the ability to complete daily tasks that may need assistance is required
Instrumental Activites of Daily Living
measures of functional ability based on point of level of care they may need
Why do we have more chronic illness?
Life expectancy is increasing, treatment advances, higher rates of unhealthy behaviors, and increased public awareness of conditions
What is the leading cause of injury-related deaths in older adults?
Fall; increasing fall rates since 1990, if it leads to hip fracture — 20 percent die within a year
Older Drivers
90 percent of people 65+ drive
only cause about 7 percent of accidents but high death rates
Use of Physician Services
adults 65+ average 7 doctor visits yearly
on average have 3x as many hospital days
take 8-9 medications on average
geriatricians can better serve older adults