Overview of the Human Digestive System
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Mouth
The entry point of the digestive system where mechanical digestion (chewing) and chemical digestion (saliva) begin.
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach and moves food using peristalsis.
Peristalsis
Wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
Stomach
A muscular organ where food is mixed with gastric juices; protein digestion begins here.
Small Intestine
The site of most digestion and nutrient absorption; consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large Intestine (Colon)
Absorbs water and electrolytes; forms and stores feces.
Liver
Produces bile, which helps digest fats; also processes nutrients and detoxifies substances.
Bile
A substance produced by the liver that emulsifies fats for digestion.
Gallbladder
Stores and releases bile into the small intestine.
Pancreas
Produces digestive enzymes and bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid in the small intestine.
Amylase
An enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates; found in saliva and pancreatic juice.
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine, where feces are stored before being expelled.
Anus
The opening at the end of the digestive tract where solid waste leaves the body.
Mechanical Digestion
Physical breakdown of food (e.g., chewing, stomach churning).
Chemical Digestion
Breakdown of food by enzymes and chemicals.
Absorption
The process by which nutrients pass from the digestive system into the bloodstream or lymph.
What are the Accesory Digestive Organs
Salivary Glands, Teeth, pancreas, liver, gallbladder
What is the difference between the Alimentary Canal and the Accessory digestive organs.
Digested food comes out the Alimentary and non-digested food comes out the accessory digestive organs.
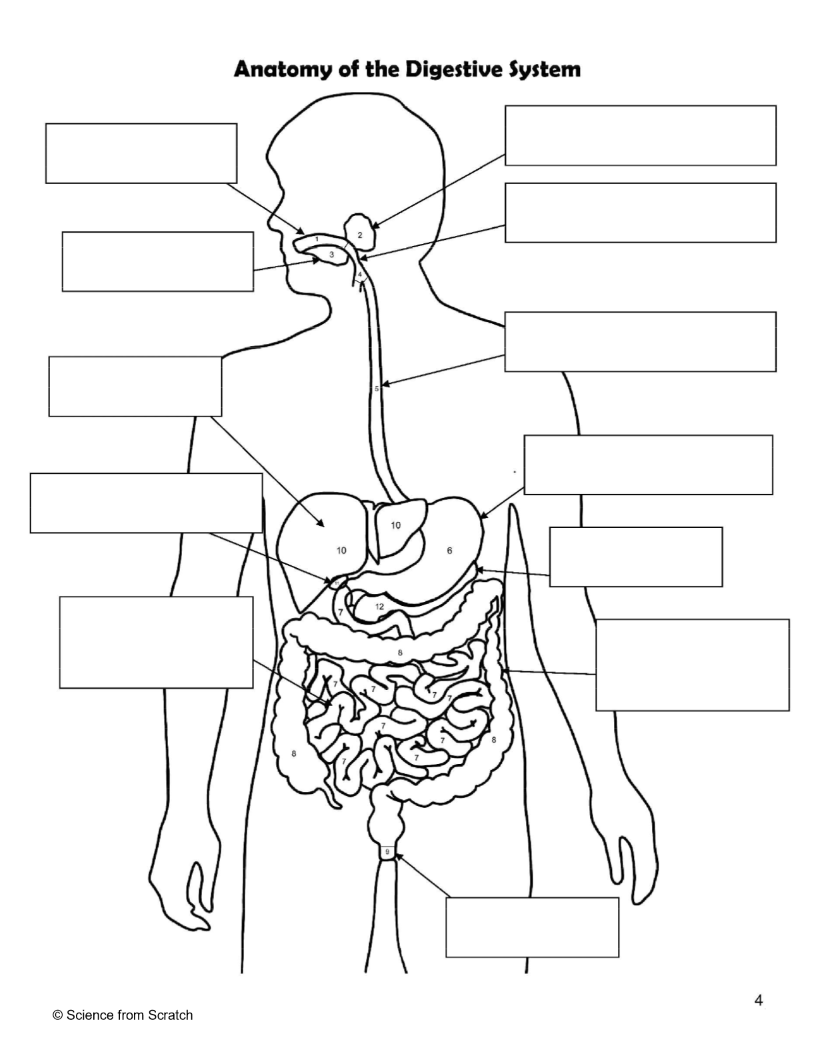
What is 1 as labeled
mouth
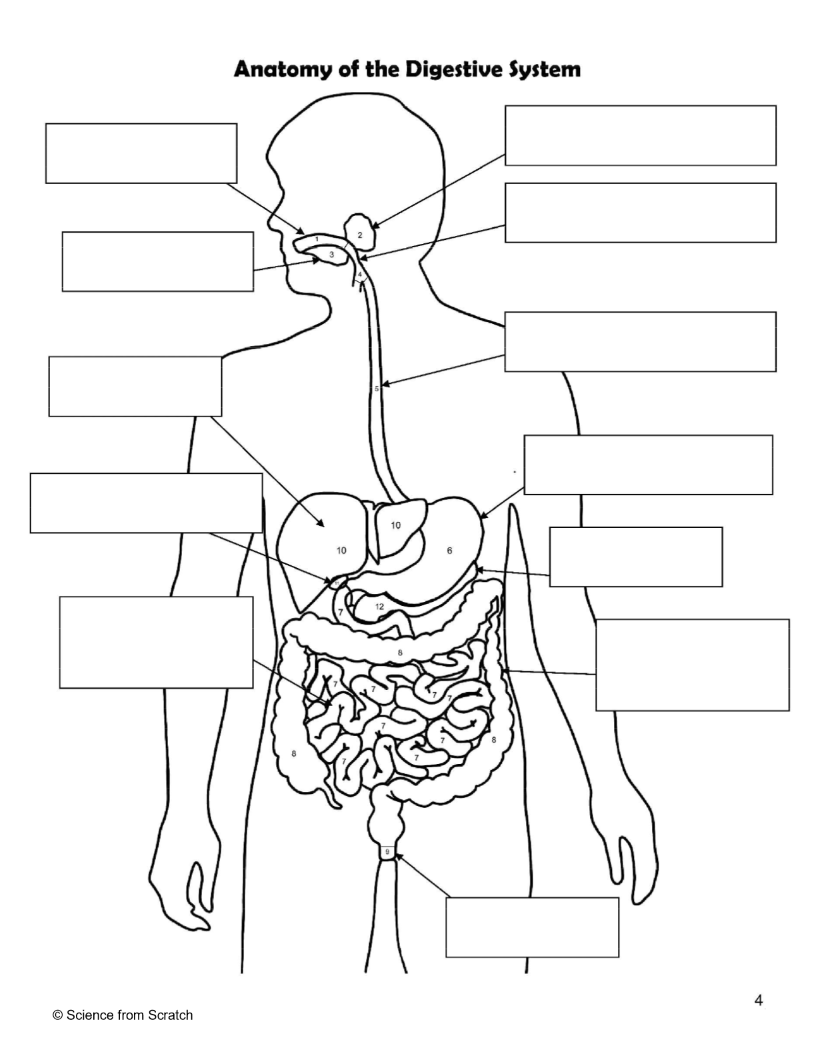
What is 2 as labeled
Salivary Glands
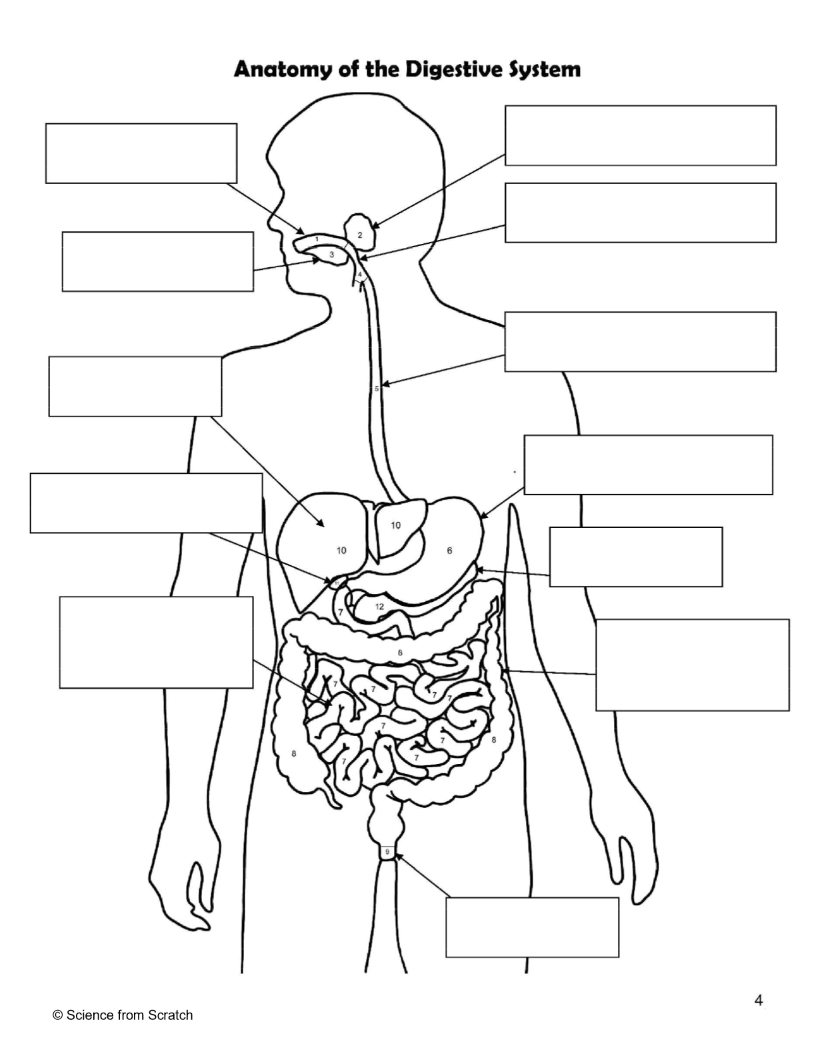
What is 3 as labeled
Tongue
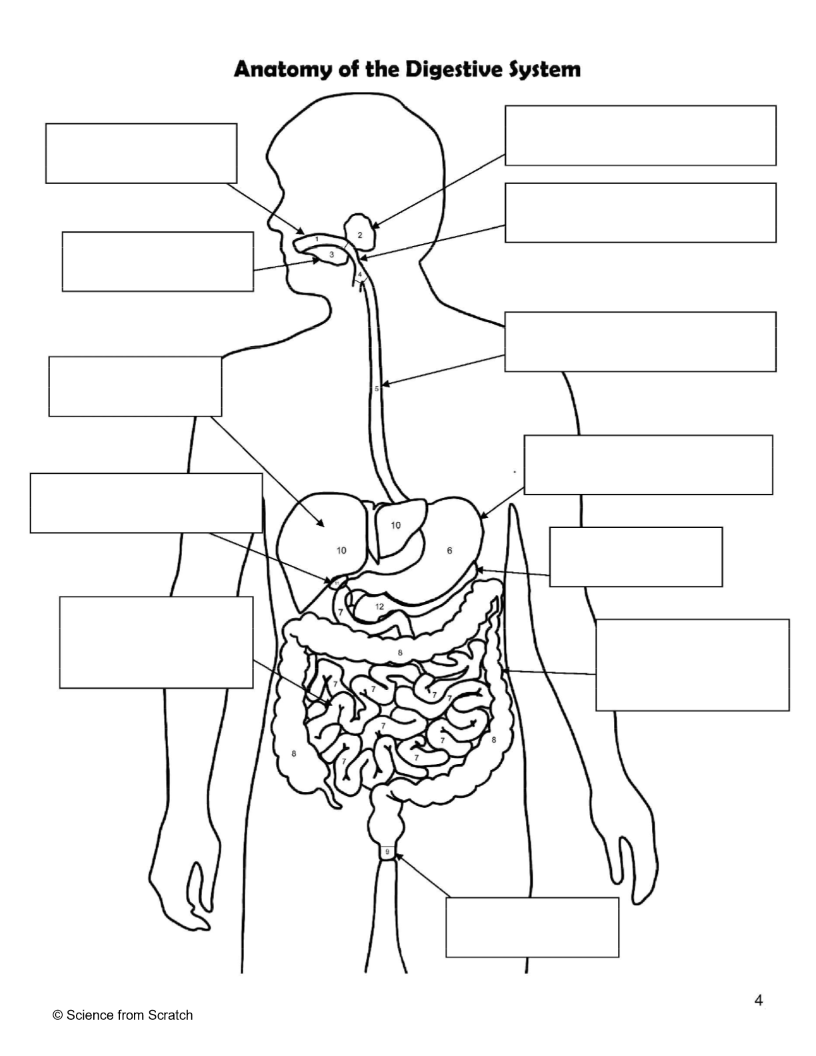
What is 4 as labeled
Pharnyx
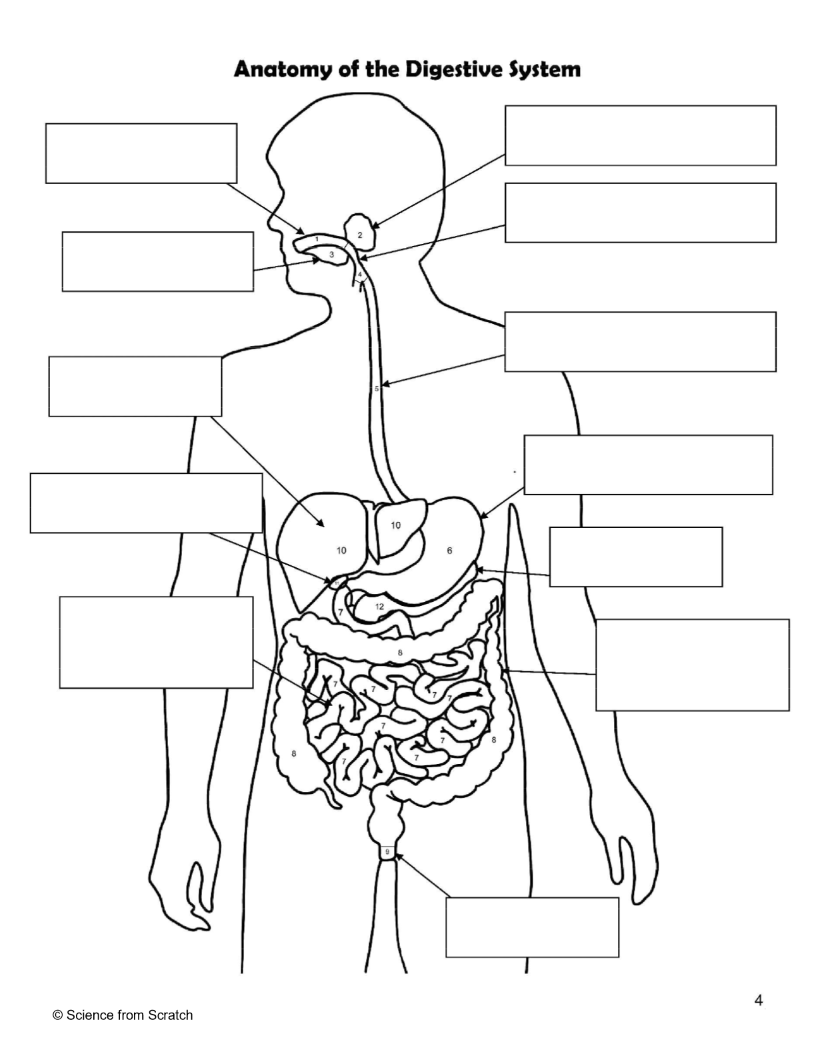
What is 5 as labeled
Esophagus
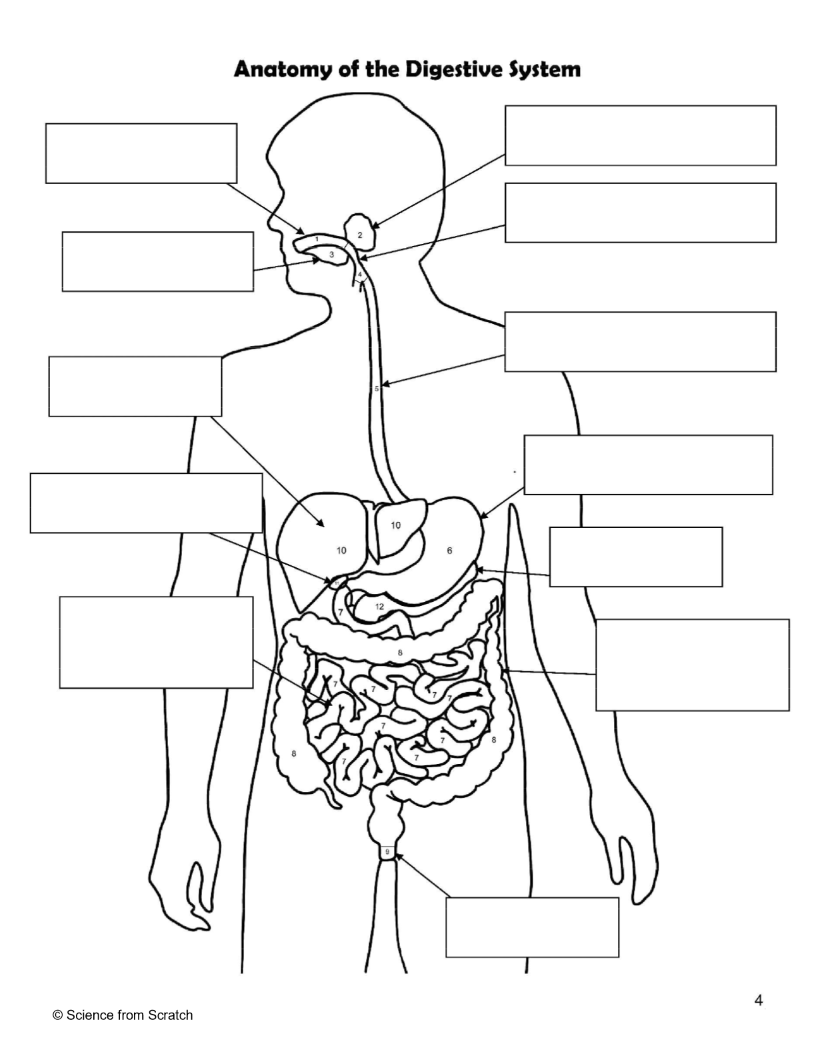
What is 6 as labeled
Stomach
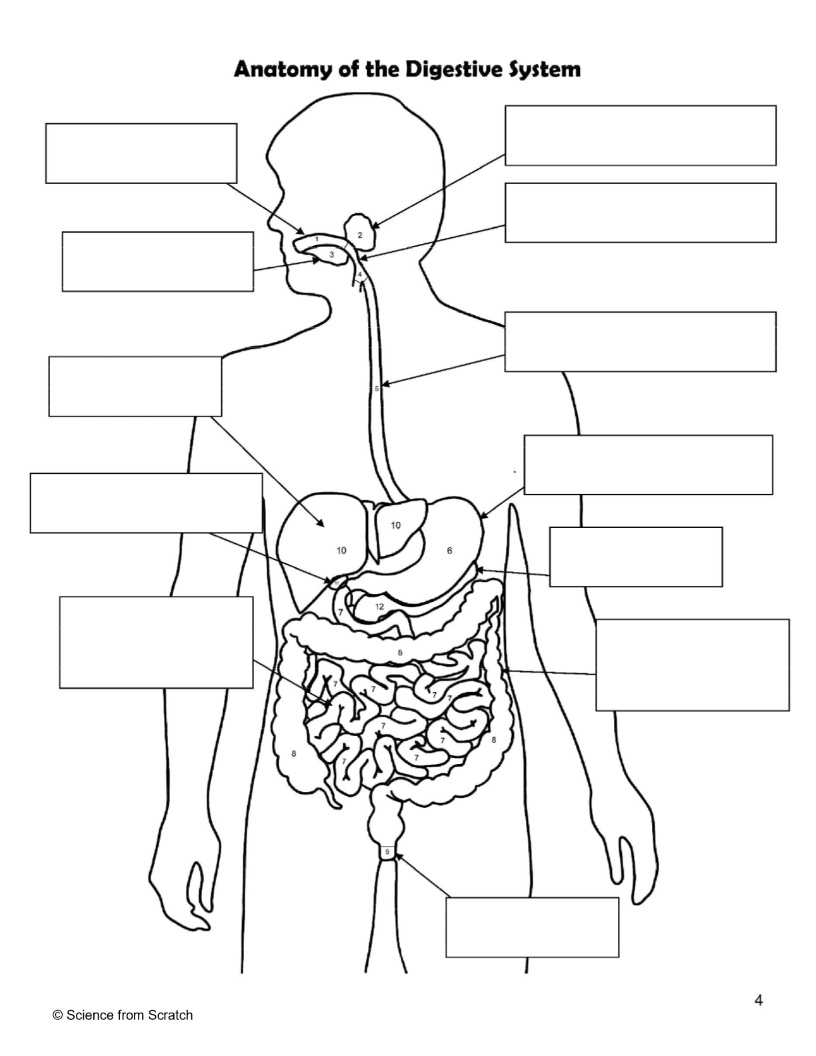
What is 7 as labeled
Small Intestine
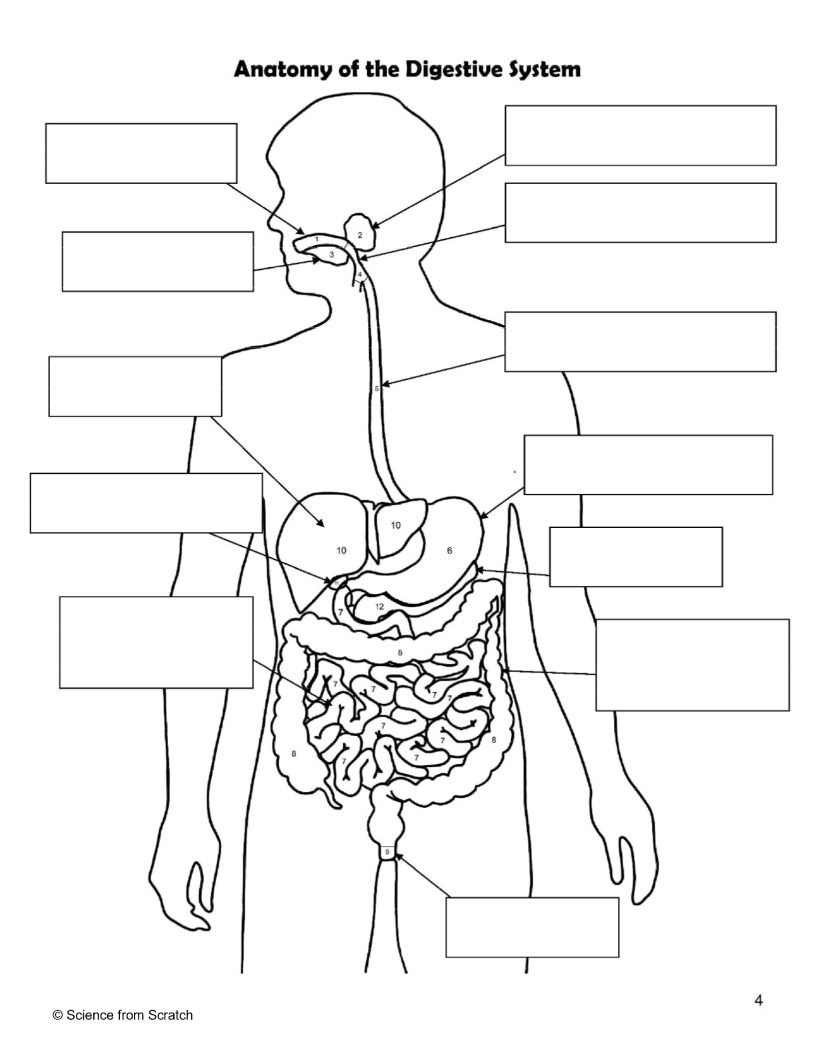
What is 8 as labeled
Large Intestine
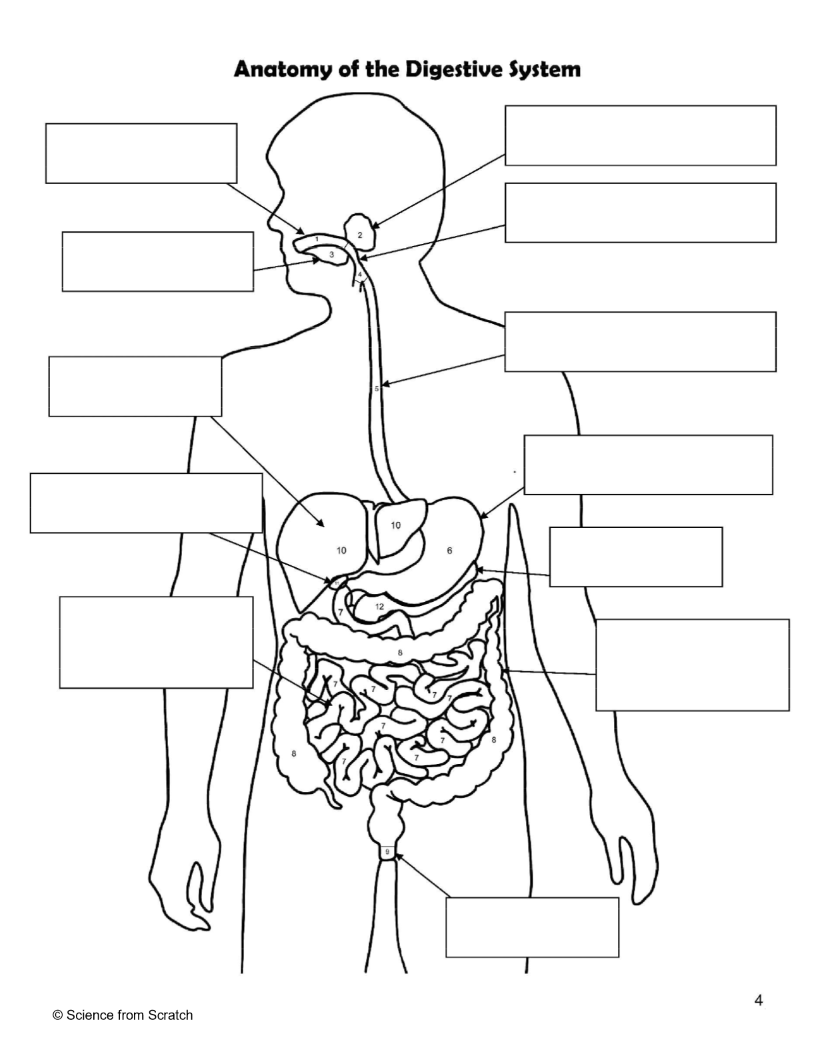
What is 9 as labeled
Anus
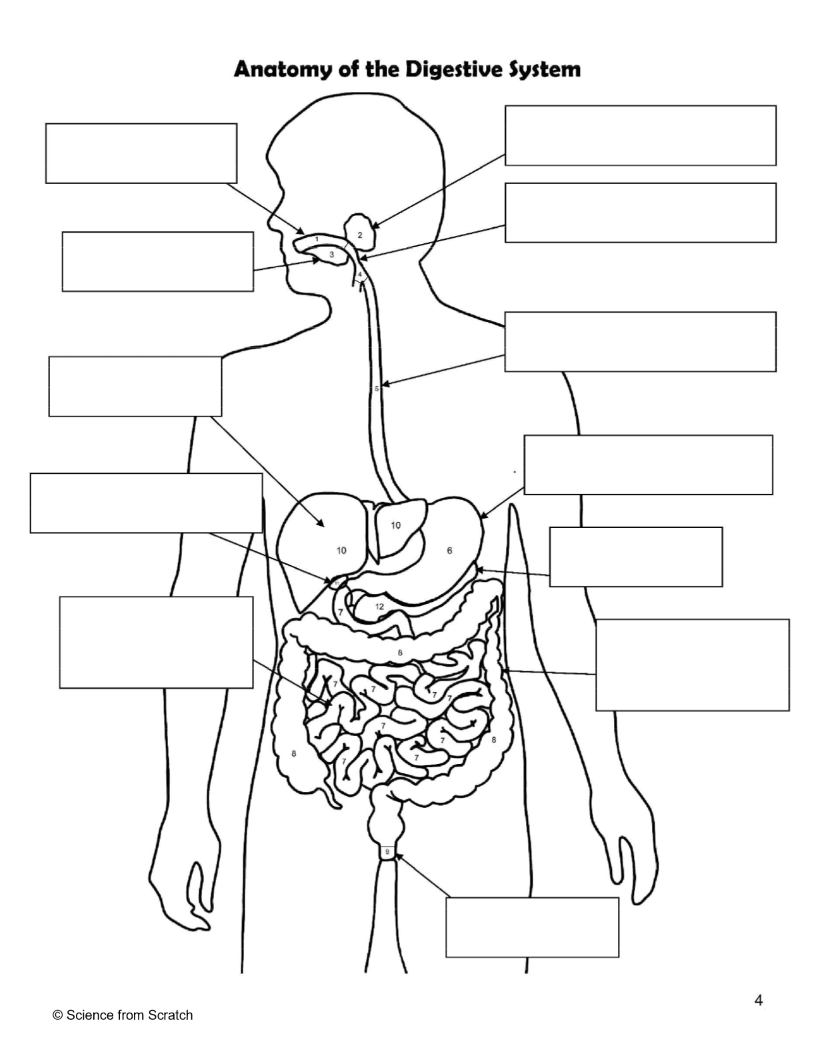
What is 10 as labeled
liver
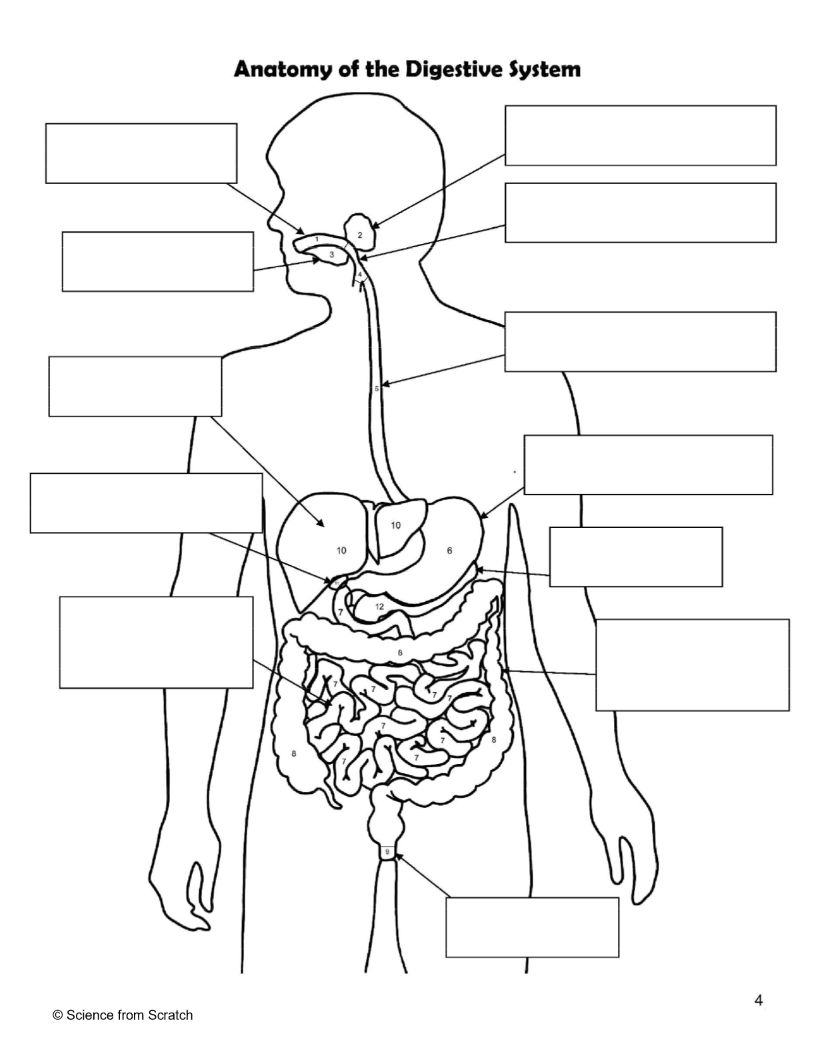
What is 11 as Labeled
Gallbladder
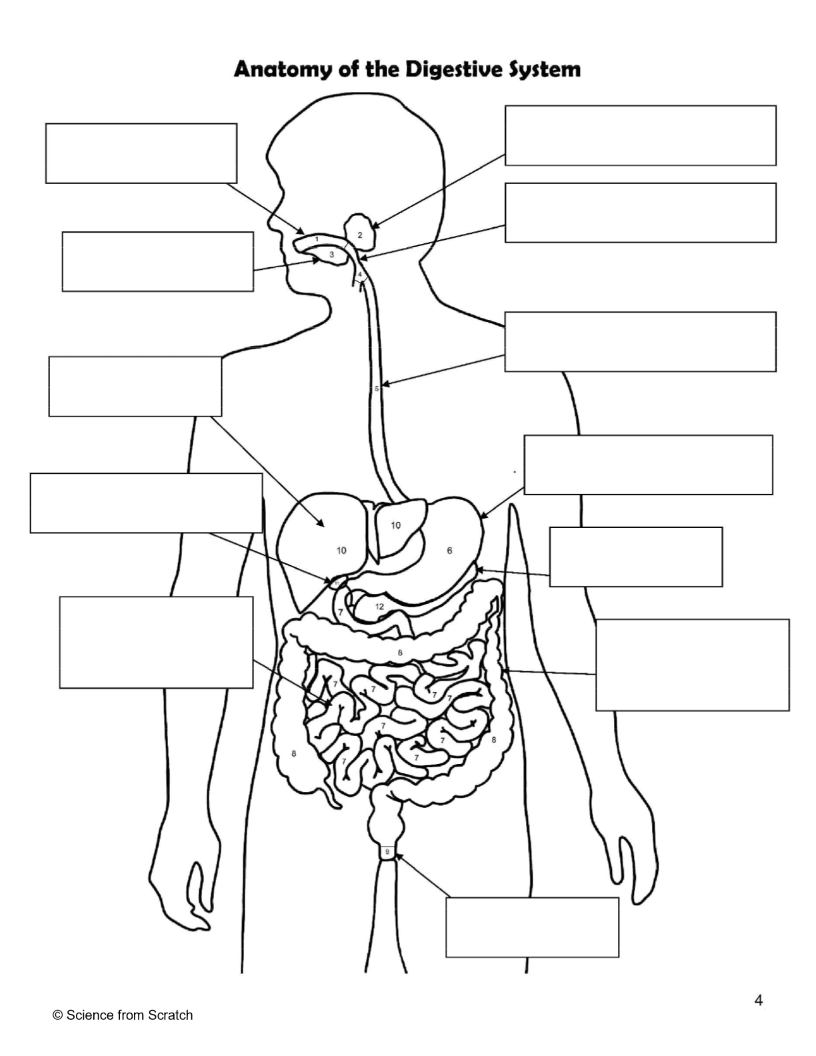
What is 12 as Labeled
Pancreas
What is defecation?
Defecation is the process of eliminating waste from the digestive tract through the anus.
What is ingestion?
is the process of taking in food and liquids into the body through the mouth.
Secretion
digestive organs release enzymes and acids
propulsion
is the movement of food through the digestive tract