IB Bio HL Yr 1 Unit 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Monozygotic twin
Identical twins
How do monozygotic twins form?
When an embryo divides into two individuals (same DNA)
Carl Linnaeus
Scientist known for morphology and the morphological species concept
The morphological species concept
The idea that organisms in a species share internal and external structure
How is the binomial system for species formatted?
Made of genus and species. Genus is capital, species lowercase. Italicized and can be abbreviated to G. species.
Biological species concept
Two organisms are part of the same species if they can produce fertile offspring
A population
A group of organisms in the same species living in the same place at the same time.
Speciation
The splitting of one species into two or more
Number of chromosomes in humans
46
Number of chromosomes in chimpanzees
48
Diploid cell
A cell with two sets of chromosomes, most body cells (48 chromosomes)
Haploid cell
A cell with one set of chromosomes, sex cells (23 chromosomes)
Karyogram
A method for viewing chromosomes digitally by dividing, staining, and photographing them.
What three characteristics are chromosomes classified by?
Banding pattern, size, and position of centromere
Genome
All the genetic information of an organism (all of it’s DNA)
Gene
A length of DNA with hundreds or thousands of base pairs
SNPs (Single-nucleotide polymorphisms)
Positions in which a more than one gene base can be present in a species (4,000 to 5,000 in humans)
How is genome size measured?
nuclear DNA content of a haploid cell (C-value), mass, or number of base pairs
Whole genome sequencing
Determining all the base sequences in an organisms genome
What is whole genome sequencing used for?
Examining evolutionary relationships and in the future personalized medicine
What organisms does the biological species concept not work for?
Asexually reproducing species and species with horizontal gene transfer
DNA barcode
A short section of DNA from one gene that is enough to identify a species by
What are DNA barcodes used for?
Species identification
Taxon
A group for classifying organisms (e.g. phylum)
Taxonomy
The act of creating groups to classify organisms and assigning them to groups
What is the order of the taxa in the traditional method of taxonomy?
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Cladistics
An alternative approach to taxonomy that used unranked clades and focused on evolutionary relationships
Clade
A group of organisms that have evolved from a common ancestor including the common ancestor
How are organisms place in clades?
By examining base sequences in DNA, amino acid sequences of proteins, and morphological features
Molecular clock
Because mutations in organisms occur at a roughly constant rate, the differences in the genome of two organisms can be compared to determine approximately how long ago they diverged
Cladogram
A visual representation of clades through a tree diagram
What are the three domains?
Bacteria, Archaea (archaebacteria), and Eukarya
Lamarkism
Developed by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, the idea that evolution occurs because of acquired traits being passed down to offspring (e.g. giraffe necks stretched to reach high branches and so their children were naturally born with long necks)
Darwinism
Evolution occurs through random mutations in the genome of an organism which gets passed down to offspring and will go under the influence of natural selection
Artificial selection
When humans have selected to breed organisms with similar traits in order to produce offspring with the desired trait.
Pentadactyl limb
The section of bones that makes up human arms, bird wings, lizard feet, whale fins, and several other animal arm-like structures that came from a common ancestor (homologous structure)
Vestigial structure
A structure passed down from an ancestor that no longer has a use (e.g. appendix)
Homologous structures
Structures with a similar structure but different function, passed from a common ancestor.
Analogous structure
Structures with the same function but different structure and evolutionary origin.
What two processed cause speciation to occur?
Reproductive isolation and differential selection
Reproductive isolation
When two populations of a species because separated reproductively due to geographical separation of behavior and temporal differences (sympatric speciation)
Differential selection
Different pressures in the environment act on the populations in different ways, causing natural selection to take place and lead to different features forming. Examples include climate, predation, and competition
Allopatric speciation
When populations in different geographic locations become different species
Sympatric speciation
When a population living in one location splits due to behavioral or temporal differences
Adaptive radiation
When species evolve to occupy different ecological roles which minimizes competition and increases biodiversity (example: Darwin’s finches)
Polyploidy
When the number of chromosomes in a cell duplicates without the cell dividing, resulting in a cell with double the amount of chromosmes
Allopolyploidy
When individuals from different species cross breed, the resulting cell undergoes polyploidy. Division is successful because there will be two homologous chromosomes of each type (two from each parent) enabling it to overcome fertility problems
What are the three types of biodiversity
Species, ecosystem, and genetic
Richness
The total number of species in an ecosystem
Evenness
How similar the populations of the species are (do they have a similar abundance?)
What caused the first five mass extinctions?
An asteroid, volcanic activity, and climate/atmospheric changes
What is causing the sixth mass extinction?
Human activity
What are the anthropogenic causes of species extinction?
overharvesting, habitat destruction, invasive species, pollution and climate change
What human activities cause ecosystem loss?
Land-use change for agricultural expansion, urbanization, overexploitation, mining and smelting, building of dames and extraction of water, drainage/diversion of water, leaching of fertilizers, climate change
IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Intergovernmental organization that asses biodiversity through monitoring
What does IPBES monitor?
Population size, range of a species, diversity of species in an ecosystem, richness and evenness, area occupied by ecosystem, extent of degradation, number of threatened species within a taxonomic group, genetic diversity with a species
Simpson’s Reciprocal Index
Higher value of D is more diversity
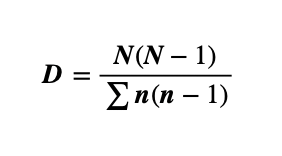
What is the overarching cause of the current biodiversity crisis?
Human population growth and overpopulation
In situ conservation
Conservation of habitats like natural parks or nature reserves that keep species in their native habitat
Management of nature reserves
Includes removal of alien species, reintroduction of species that have become locally extinct (like wolves at Yellowstone), attempts to increase/decrease population of herbivores or predators if needed, prevention of poaching, supplementary feeding, and control of human access
Rewilding
Taking an ecosystem that is very damaged and attempting to restore it to a natural state
Ex situ conservation
When organisms are taken out of the environment into a zoo or botanic garden to breed and keep endangered species safe
Storage of germ plasm in seed or tissue banks
Storing living material for long term that could be used in the future (seeds for plants and tissues, eggs, or sperm for animals)
EDGE
Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered