lec 6 greenhouse gases, atmospheric circulation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
atmosphere becomes mostly transparent to long wave radiation around
8-10 km, water vapor can’t be held because it’s cold
weather occurs in
troposphere
hot air warmed by surface
rises, keeps rising until it is same temp as surroundings
moist air is less dense than dry air because
water vapor is less massive than the other fasses
when moist air rises and gets to colder temps
it condenses into clouds
hadley cell
warm moist equatorial air rises and moves towards the poles
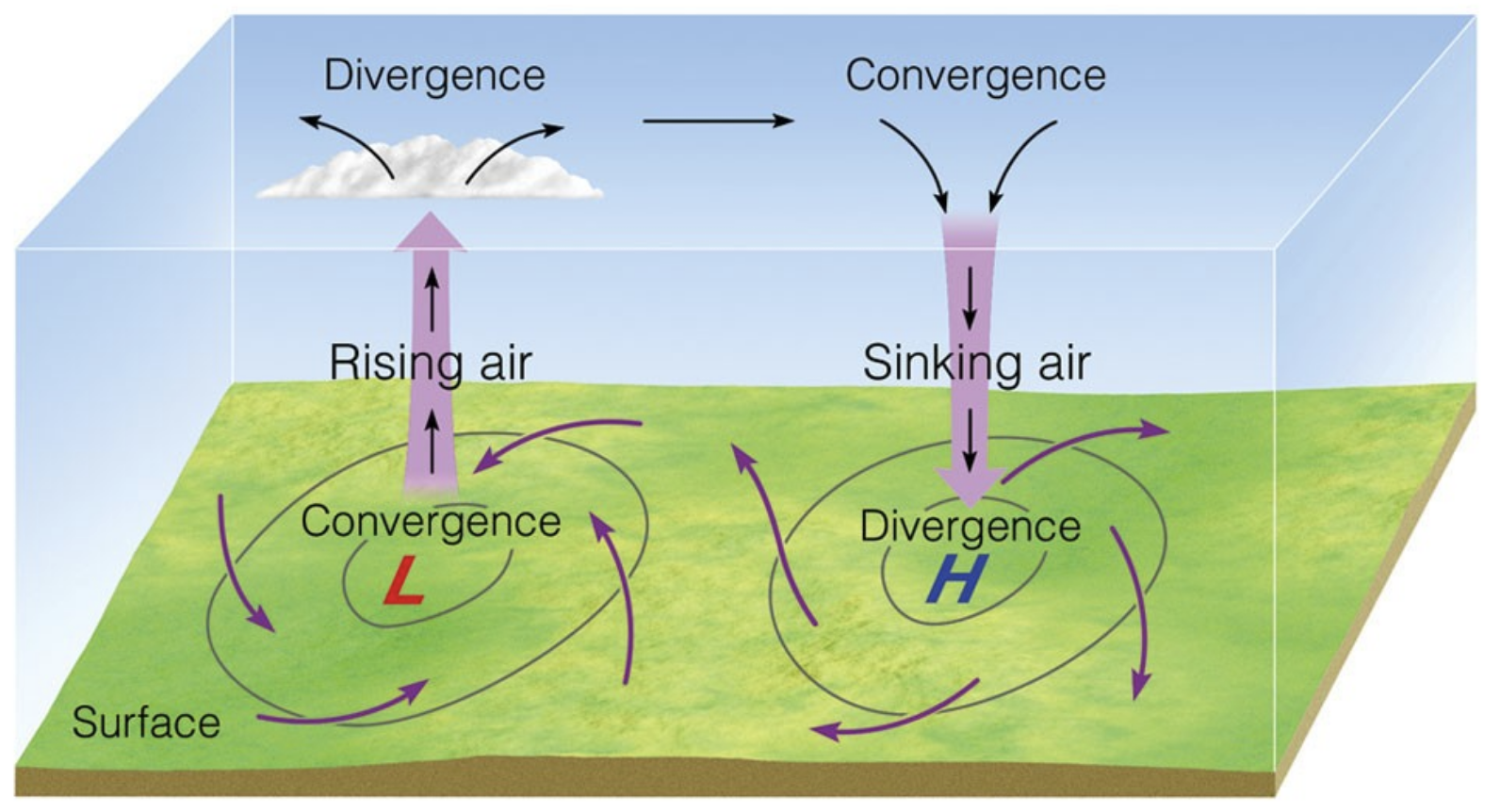
low pressure areas
convergence with counterclockwise rotation → rising air → divergence and cloud formation

high pressure areas
convergence → sinking air → divergence with clockwise rotation
westerly winds driven by
temp contrast between the poles and equator
jet streams
narrow ribbons of high winds at boundaries between the cells
as arctic warms more than equator, polar vortex
becomes weaker and likely to move