IB Chemistry S3.2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Half Equation
An equation that happens to one reactant, in terms of electrons.
Oxidation
gain of oxygen, loss of electrons, loss of hydrogen or increase in oxidation number
Reduction
loss of oxygen, gain of electrons, gain of hydrogen or decrease in oxidation number
Redox
Reactions involving Oxidation and Reduction.
Oxidation Number
The measure of electron control atoms in molecules have relative to atoms of the pure (non-ionic) element. Often the same as ionic charge
Oxidising Agent
A reactant that is reduced so that another can be oxidised
As you go up group 7...
the halogens become stronger oxidising agents because their reactivity increases
Reducing Agent
A reactant that is oxidised so that another can be reduced
The more reactive a metal...
the better reducing agent it is because it lose valence electrons more readily
Displacement Reaction
A reaction where an ion in a solution is displaced through oxidation of an element added to the solution.
Aside from a displacement reaction how can you know if one metal is more reactive than other?
Measure the temperature because displacement reactions are exothermic
Spectator Ion
An ion that takes part in displacement reactions, but isn't chemically changed
Electrode Potential
The charge difference between metal ions and the solution containing them.
Voltaic Cell (Battery)
A type of electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy from a spontaneous reaction into electrical energy
Anode
The electrode where oxidation occurs.
VAN
voltaic anode negative
What charge is the anode in an electrolytic cell?
positive
1 multiple choice option
Cathode
The electrode where reduction occurs. It's positive in a voltaic cell and negative in an electrolytic cell.
What are the typical components of a voltaic cell?
Anode, cathode, salt bridge, wires and voltmeter
In what direction do electrons flow in a voltaic cell?
Anode → Cathode
Salt Bridge
A glass tube or paper strip that prevents charge buildup so the solutions remain neutral, ions can be transferred and voltage can be generated
How can the voltage generated by a voltaic cell be altered?
Use different metals (changes difference in reactivity), different concentrations, change temperature or pressure if gases are present
In a cell diagram, what does a single line represent?
a phase boundary
In a cell diagram, what does a double line represent?
a salt bridge
What is a secondary cell?
cells that involve redox reactions that can be reversed using electrical energy which makes the cell rechargeable
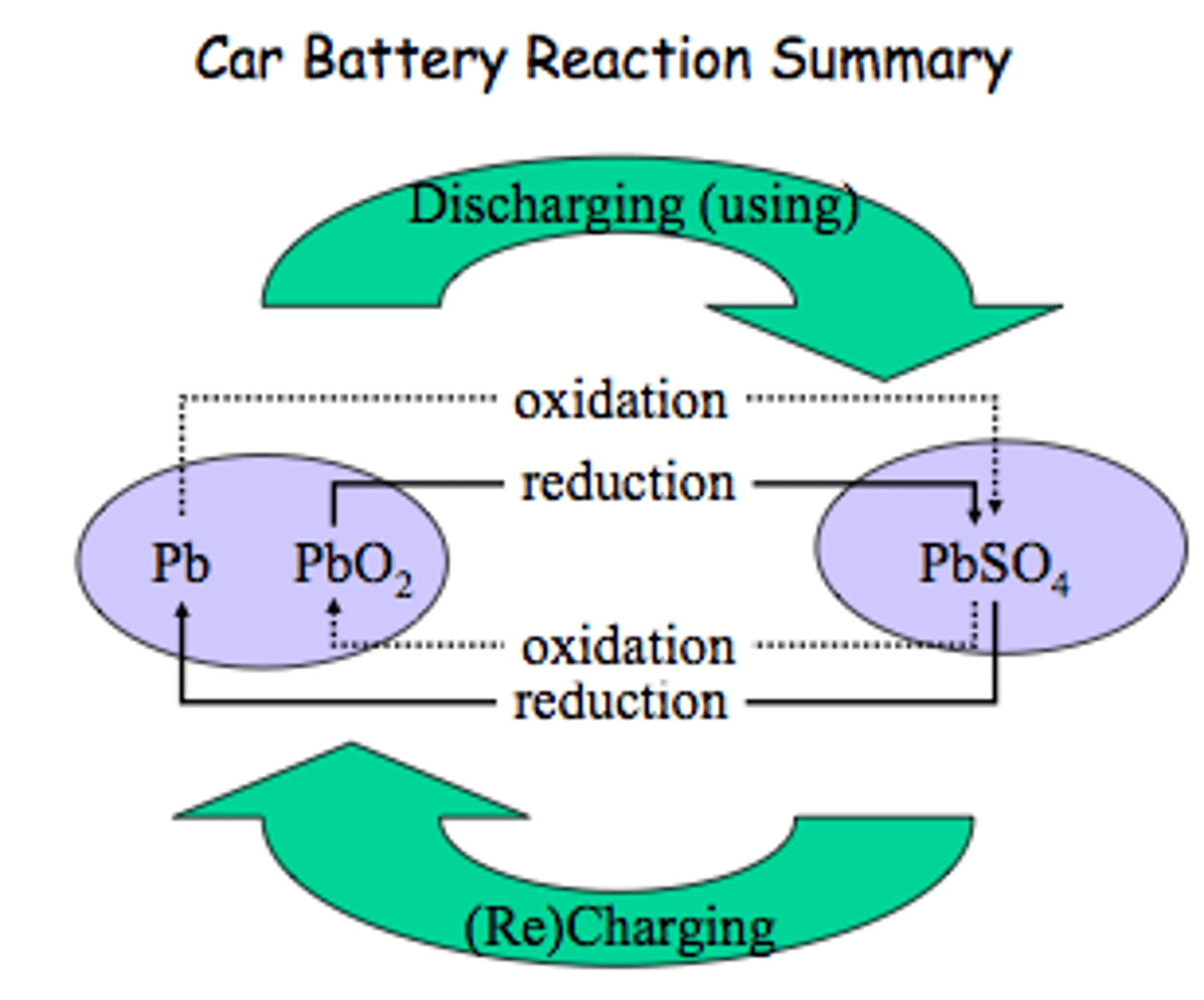
Give an example of a secondary cell?
Lead-acid car batteries that power the engine's motor. The anode is lead and the cathode is lead oxide which both sit in sulfuric acid
How is the reaction reversed in a lead-acid battery?
the chemical energy from combustion
What kind of electrochemical cell is a lithium-ion battery?
a secondary cell
Evaluate secondary cells
Compared to voltaic cells, they satisfy higher current demands but have a higher rate of self-discharge
What are fuel cells?
Fuel cells convert methanol, ethanol or hydrogen into water, carbon dioxide and heat
Evaluate fuel cells
Very efficient as more energy is converted into kinetic energy. Little pollution. But they aren't rechargeable so they require a constant supply of fuels. It's also expensive to transport and store these fuels which can require energy to make e.g hydrogen
What is an electrolytic cell?
Cells that converts electrical energy into chemical by bringing about non-spontaneous reactions with an external power source
Electrolysis
Breaking down a compound by inducing an electrical charge.
Electrolyte
A substance that dissolves in water to make a solution with ions that conduct electric current
Where does the electrical energy come from in an electrolytic cell?
The electrodes are suspended in an electrolyte which is typically a molten or aqueous ionic compound. Therefore, the ions are mobile which allows current to flow
What are the components of an electrolytic cell?
two inert electrodes, an electrolyte, direct current power source
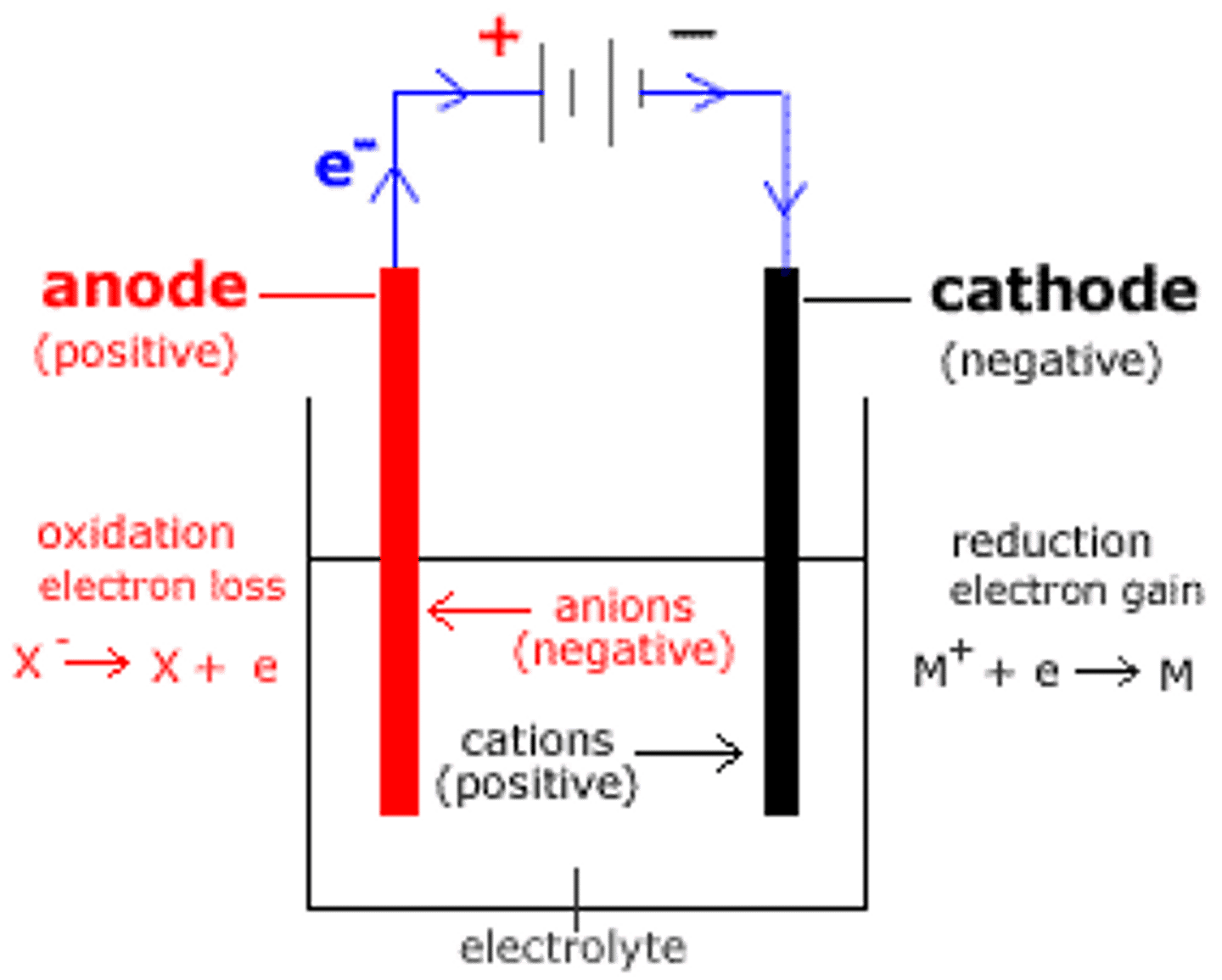
What materials can inert electrodes be made of?
platinum or carbon e.g graphite
In molten electrolysis, what happens at the anode?
Anions are oxidised into atoms
In molten electrolysis, what happens at the cathode?
Cations are reduced into atoms
In the electrolysis of aqueous solutions, what happens at the anode?
the non-metal ion or water will be oxidised
In the electrolysis of aqueous solutions, what happens at the cathode?
the metal ion or water will be reduced
Which 3 factors determine what products are formed during the electrolysis of aqueous solutions?
- concentrations of the ions in the electrolyte
- nature/material of the electrodes
- E° values of the ions
How do the E° values of the ions affect the products formed during the electrolysis of aqueous solutions?
At the cathode and the anode, the reaction with the more positive electrode potential will occur
Selective Discharge
The process in an electrolytic cell by which only one ion at an electrode is oxidised or reduced, and only one product is given off. This depends on which is oxidised or reduced more easily.
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode
An electrode with an electrode potential of 0.00V to act as a reference point by which from electrode potentials can be compared.
What are the features of the standard hydrogen electrode?
platinum electrode, 1.00 mol/dm^-3 acid, hydrogen gas, 100kPa at 298K
2H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ↔ H₂(g)
The reaction occurring in the Standard Hydrogen Electrode.
Standard half-Cell
A half cell in standard conditions.
Standard Electrode Potential (E°)
the potential (voltage) of the reduction half-equation under STP relative to SHE
Negative standard electrode potentials indicate that...
reduction is unlikely to occur but it can act as a reducing agent
Positive standard electrode potentials indicate that...
reduction is more likely to occur than the reduction of hydrogen ions so it can act as an oxidising agent
How is E^Θcell calculated?
= E^Θhalf-cell of reduction - E^Θhalf-cell of oxidation
If E^Θcell is positive...
the reaction is spontaneous
If E^Θcell is negative...
the reaction isn't spontaneous but the reverse reaction will be
Electroplating
The process of coating one metal (the cathode) in another through electrolysis because the metal at the anode will erode due to oxidation. These ions will move to the cathode and become solid atoms again
What's an example of using electrolysis to purify a metal?
Impure copper as the anode and pure copper as the cathode in a solution of copper sulphate
What are common oxidising agents and why do they work well?
acidified potassium manganate and potassium dichromate because they are transition metals with lots of oxygen
How are oxidation agents denoted in equations?
[O]
What happens when a primary alcohol is oxidised by distillation?
It becomes an aldehyde and water is released
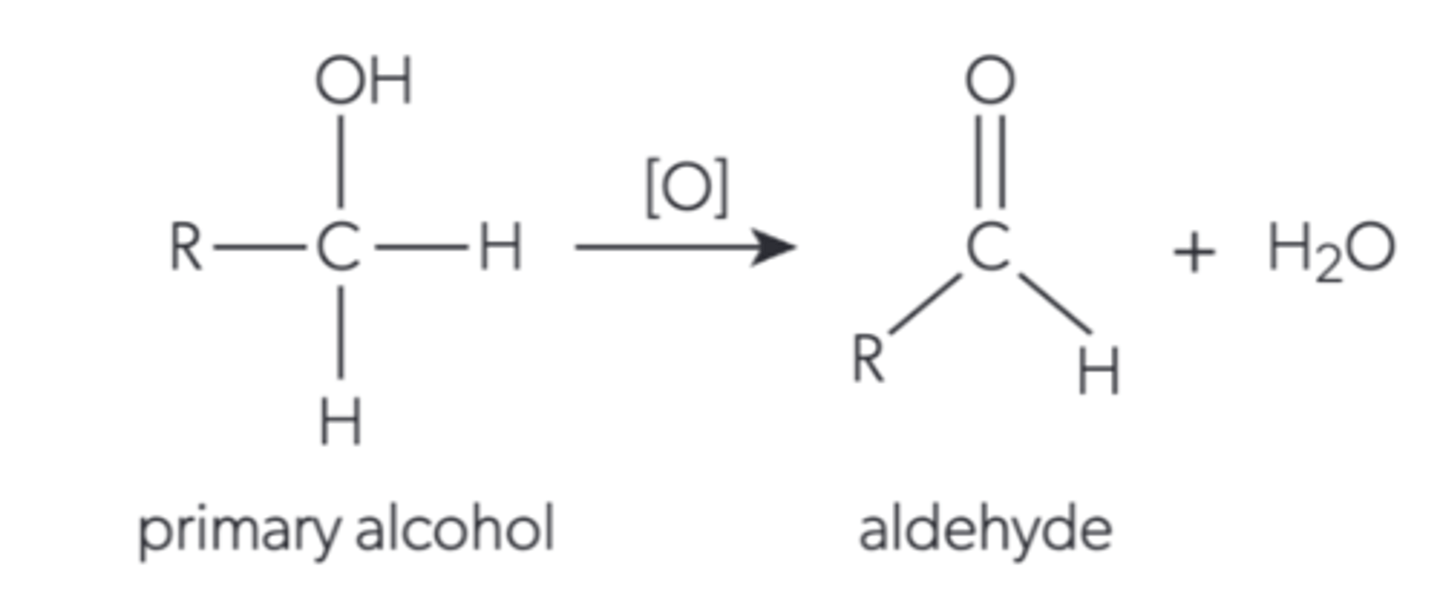
Describe how a primary alcohol is oxidised by distillation?
The alcohol and oxidising agent are gently heated in a flask to the boiling point of the aldehyde so that it becomes gaseous. This vapour passes through the condenser so it condenses and the liquid is collected in a flask
What happens when a primary alcohol is oxidised by reflux?
An aldehyde forms initially, then it becomes carboxylic acid
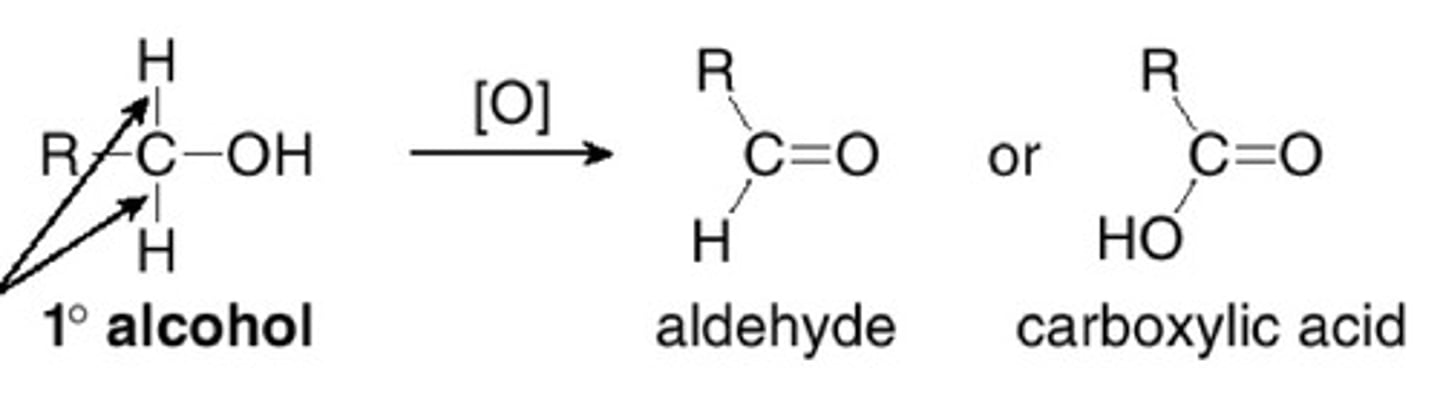
Describe the process of oxidation by heating under reflux?
The reflux condenser condenses any gases and forces them back into the reaction vessel. This puts the aldehyde back in the flask to be oxidised again.
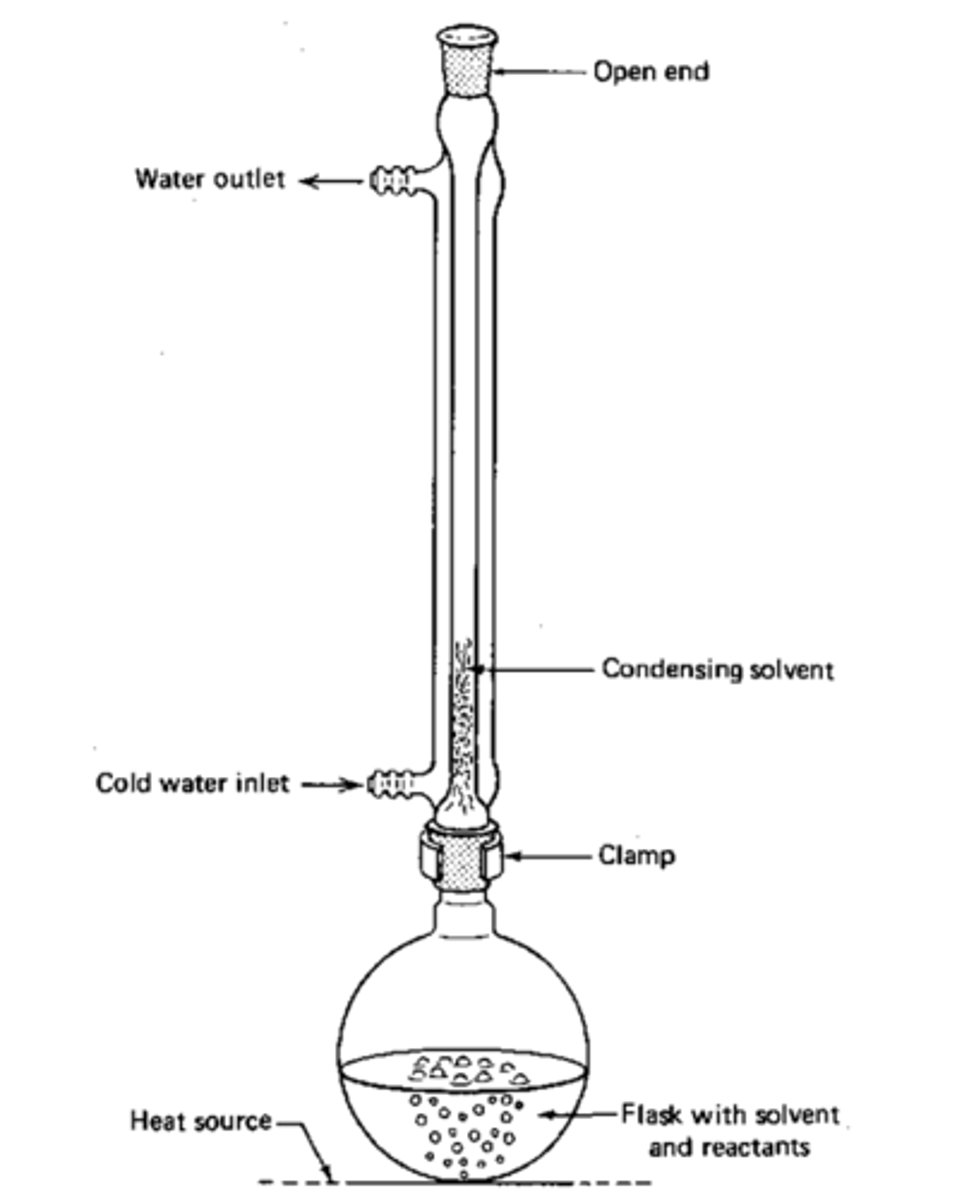
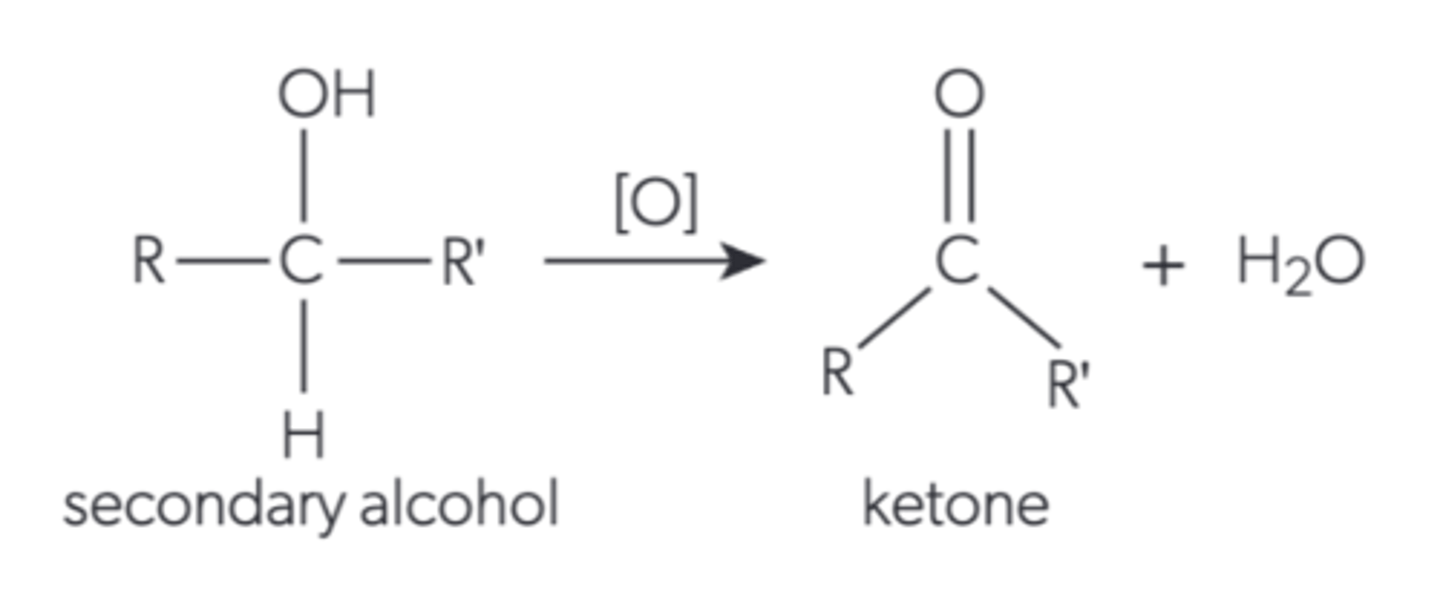
What happens when a secondary alcohol is oxidised by reflux?
it becomes a ketone because the hydroxyl is oxidised into a carbonyl and water is lost
Can tertiary alcohols be oxidized?
No
How can the oxidation of alcohols be reversed?
Using reducing agents which are good sources of hybride ions (H-)
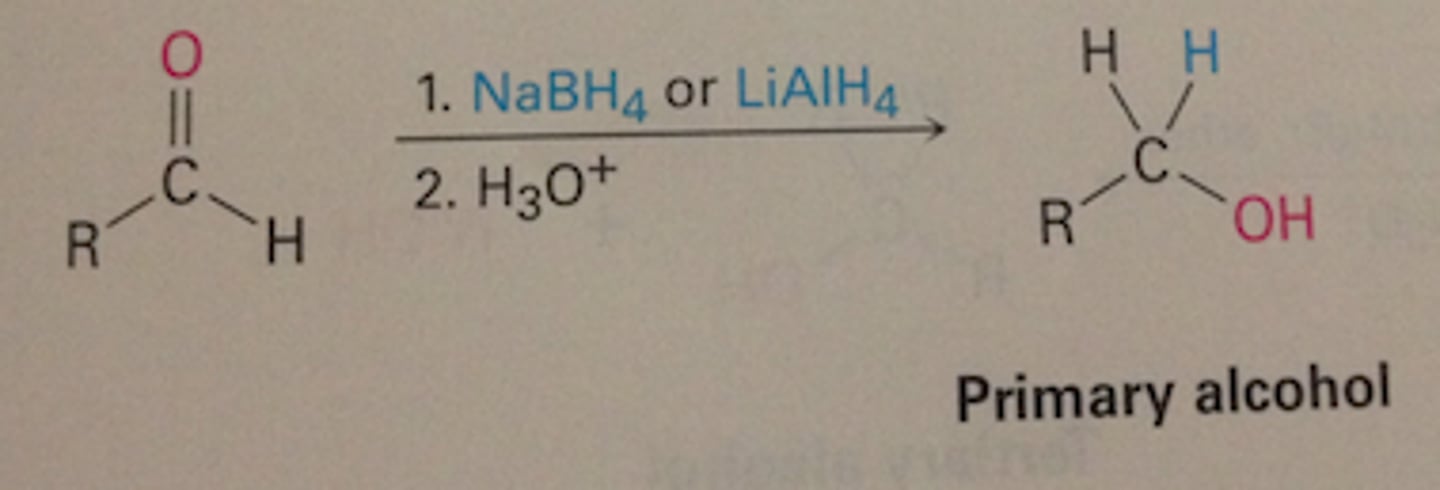
How are hybride ions represented?
[H]
How are alkenes and alkynes reduced?
Because they are unsaturated, the addition of hydrogen, in the presence of a transition metal catalyst e.g nickel will reduce carbon's oxidation state and the degree of unsaturation
What is formed when an alkyne is reduced?
An alkene is formed
What is formed when an alkene is reduced?
An alkane is formed
How can alkynes be directly reduced to alkanes?
Reacting them with excess hydrogen in the presence of transition metal catalyst