Developmental Psych Exam 1 Uark- Alwood
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Development
Process by which we grow and change , and the ways in which we stay the same over time
Cohort
A group of individuals of the same age.
Cohort study
-a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period of time.
-the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation.
perform a cross-sequential study.
what is a way to guard against cohort effects in research
Theory
A way of organizing sets of observations into general explanations of how something works
-must be falsifiable
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Context
-where and when a person develops
-has 3 parts
1. physical and social environment
2. intangible factors such as values, culture, or ideas
3. peer group, school, neighborhood, or community
Culture
-a broad aspect of culture
-a set of customs, knowledge, attitudes, and values that are shared by members of a group and are learned early in life through group interaction
Scientific Method
-a process of using and answering questions by making careful and systematic observations and gathering information
-identify the problem and make a hypothesis
-replication is very important
Nature vs Nurture
-name for a controversy in which it is debated whether genetics or environment is responsible for driving behavior
-questions how they interact
active vs passive
-children play an active role in guiding their own development
-children interact with and change the context of their development
-they create experiences that influence all areas of development (manufacturers of their own development)
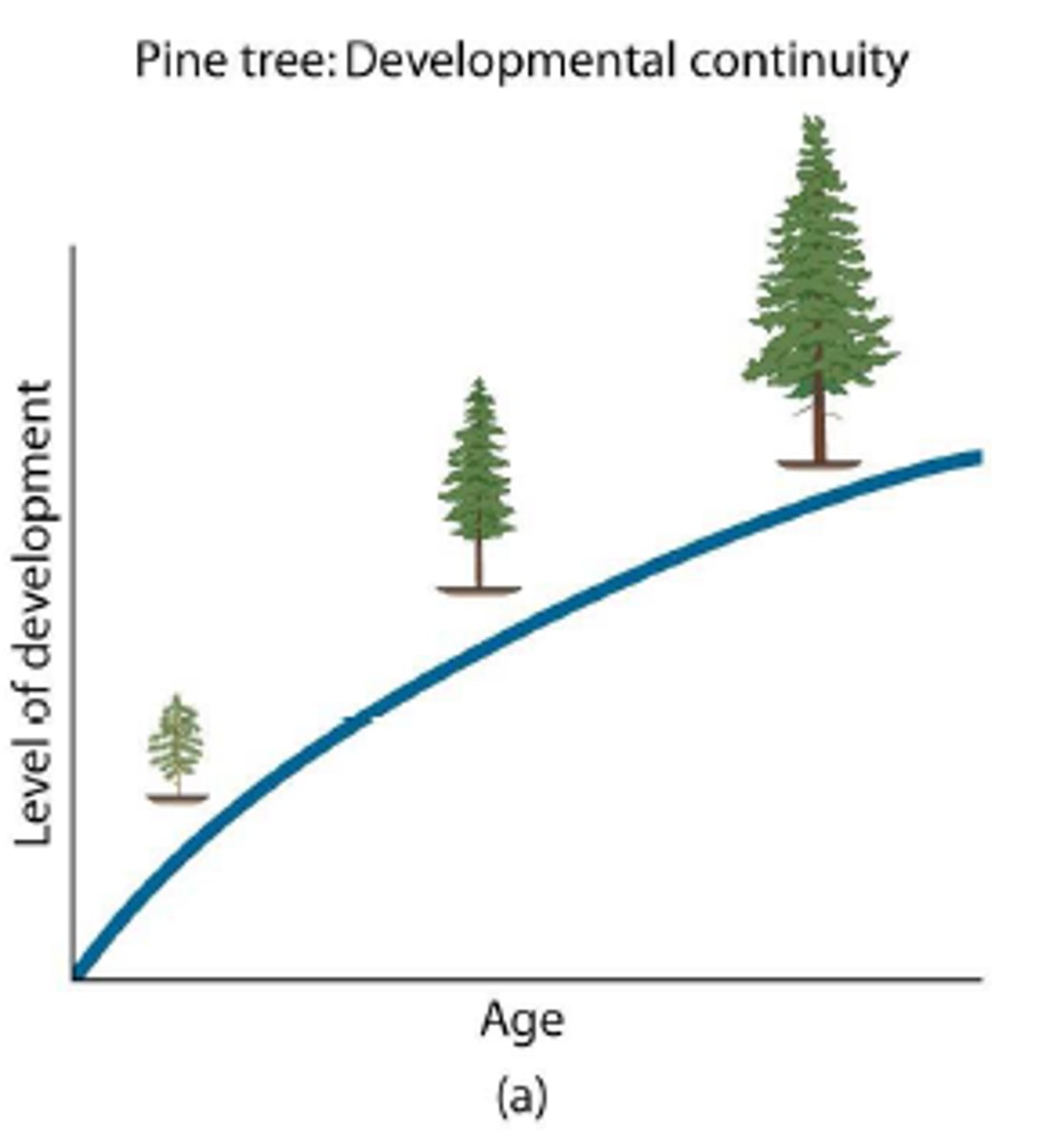
Continuous Development
gradual development overtime (quantitative)
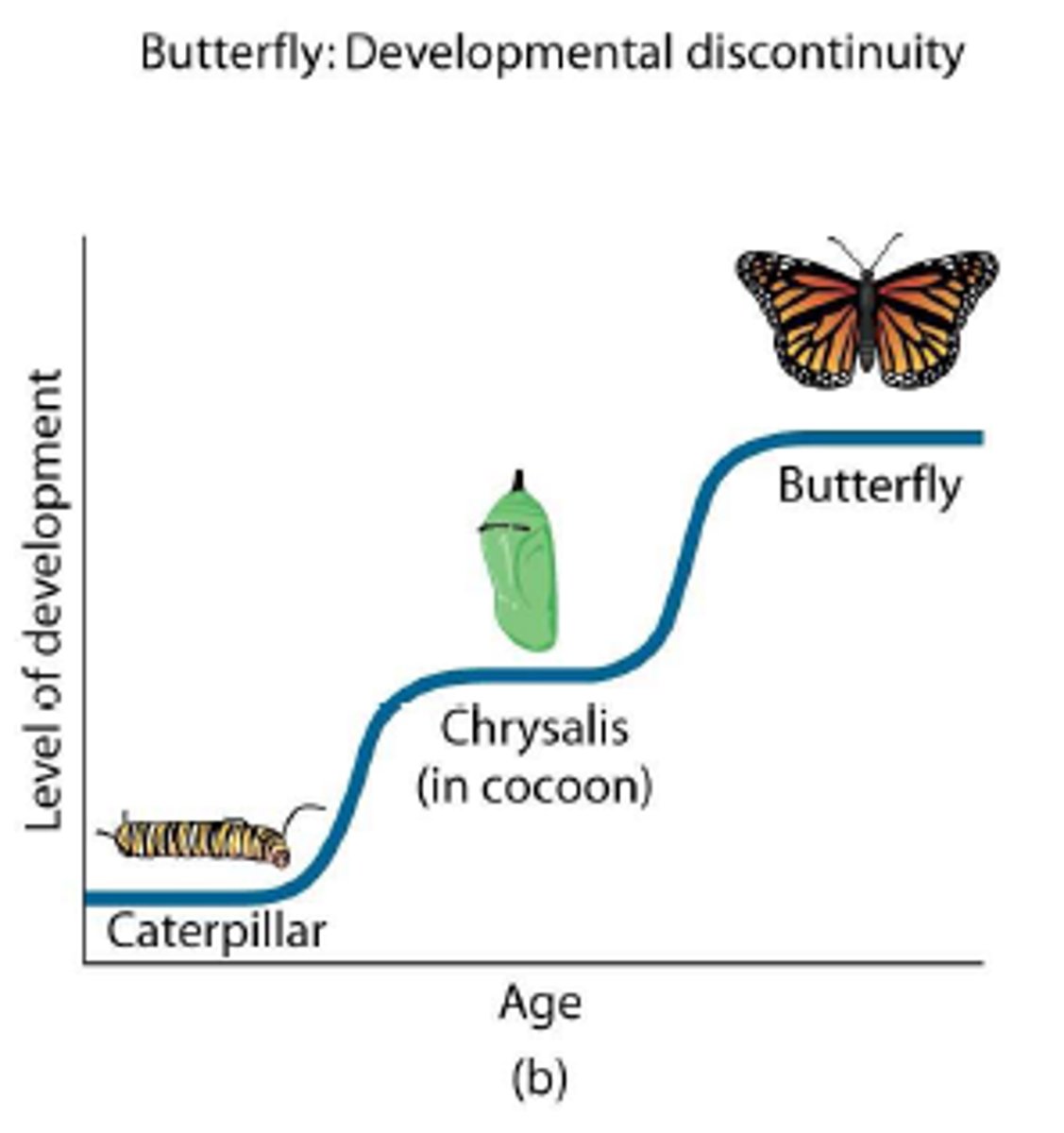
discontinuous development
development in stages - qualitative changes
case study
-in depth examination of a single person
-gather info from many sources
-however, not generalizable
correlational research
-Examine relationships among measured characteristics, behavior, and events
-cannot infer cause and effect
Valence
indicates direction of correlational relationship
Experimental research
examine relationship between dependent and independent variables, while holding related potential confounds constant
naturalistic observation
-observe and record in real world setting
-reactivity could be a problem
structured interview
same set of questions to each child, in the same way
unstructured interview
-no fixed set of questions and no systematic scoring procedure
-conversational style
survey
a self-report measured complied of a series of questions
questionnaire
used to collect data from large samples of people
cognitive, physical, social-emotional (psychosocial)
what are the three Domains of development?
cognitive development
Maturation of mental processes and tools individuals use to obtain knowledge, think, and solve problems.
physical development
Body maturation, including body size, proportion, appearance, health, and perceptual abilities.
social-emotional (psychosocial) development
changes in emotions, social abilities, self-understanding, and personal interpersonal relationships with family and friends
cross-sectional, longitudinal, cross-sequential
What are three methods used to study development?
cross-sectional study
compares groups of children of different ages at a single point in time
-cannot speak to how the change happened
longitudinal study
follows the same group of participants over many points in time
-problem of cohort effects
cross-sequential study
assesses multiple cohorts over a short period of time, allows differentiation between cohort and age effects
-cohort effect no longer a problem
Control Group
group that is not exposed to the independent variable
experimental group
the group in an experiment that receives the variable being tested
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
random sample
method of selecting from a population in which each person has an equal probability of being selected
sample
A relatively small proportion of people who are chosen to be representative of the whole.
quasi-experiments
-research that resembles experimental research but is not true experimental research
-Although the independent variable is manipulated, participants are not randomly assigned to conditions or orders of conditions
-the independent variable is manipulated before the dependent variable is measured
beneficence & non-maleficence, responsibility, integrity, respect for autonomy , and informed consent & child assent
What are the 5 ethics of research
beneficence & non-maleficence
dual responsibility to do good and avoid doing harm
responsibility
adhering to professional standards of conducts and clarifying obligations and roles to others
integrity
mindful of the promises made to participants.
justice
risks and benefits of research must be spread across individual groups
respect for autonomy
a person can make his or her own decisions about what to do and what to agree to
informed consent
legal voluntary agreement
child assent
voluntary agreement of the child after guardian provides legal agreement
Amniocentesis, Chorionic villus sampling (cvs), Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPI), Ultrasound, fetal MRI
What are some Prenatal Diagnostic Methods?
-when there is genetic abnormality
-Women older than 35
-Parents at risk for ethnicity linked genetic disorders
-Abnormal fetal development in ultrasound
when are prenatal diagnoses recommended?
Amniocentesis
-given at 14 wks
-A small sample of the amniotic fluid is extracted via needle, guided by ultrasound
-Small increase in miscarriage risk
Chorionic villus sampling (cvs)
-19-12 wks
-Samples genetic material from the chorion (membrane surrounding fetus)
-Higher risk of miscarriage than amnio
-Possible limb deformity
Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPI)
-10-22wks
-Screens mothers blood to detect chromosomal abnormality in cell-free fetal DNA
-Elevated alpha-fetoprotein protein in mom's blood
-Kidney disease, esophagus prob, spina bifida, missing parts of brain (anencephaly)
Ultrasound
-common
-High-frequency sound wave directed at the mothers abdomen provide clearish images of the womb
-Measure growth, gestational age, sex, number, physical abnormality
Fetal MRI
-Follow-up to image the fetus's body and diagnose malformation (including CNS)
genetic counseling and genetic screening
What are various reproductive options?
genetic counseling
-used to determine the risk that their children will inherit genetic defects and chromosomal abnormalities
-Pre-conception
-Develop a pedigree-family tree that estimates risk
genetic screening
-When disorder is common in family
-Personal decision
-May choose alt. method of reproduction if high risk found
artificial insemination
-a reproductive technology in which semen is collected from males, then used in fresh or frozen form to breed females
-70-80% effective
In-vitro fertilization
-A procedure in which gametes are fertilized in a dish in the laboratory, and the resulting zygote is implanted in the uterus for development
-Same sex sorter method to ensure female birth (avoid x-linked disorder)
-Surrogacy
-30% effective
-Early neglect, deprivation, and trauma
-Experience great stress before and after
-May affect academic attainment, psychological and adjustment issues, difficulty in emotion regulation
What are potential side effects of adoption?
Heritability
-the extent to which differences in a group of a characteristic is due to genetics, not environment
Range of Reaction
Wide range of potential expressions of a genetic trait, depending on environmental opportunities and constraints
Epigenetics
-means literally "above the gene"
Epigenisis
-development of the individual resulting from ongoing, bidirectional exchanges between heredity and all levels of the environment
Epigenome
-chemical modifications to DNA and histone proteins that alter gene expression
-Carries instructions for what each cell will be, which are carried out by turning a gene on and off
-can NOT be influenced by the environment before birth, but it can be passed from one generation to the next without changing the DNA itself.
Canalization
-Heredity narrows the range of development to few outcomes, thus ensuring species-typical skills
-Ex - motor development - we see variation between and within cultures but it generally happens in the same order with some variations
Niche-picking
-active gene-environment correlation
-Child seeks experiences that support a trait
-Ex. child actively seeks out experiences that support their musical ability
Gene-environment correlation
-the idea that heredity influences the environments to which individuals are exposed
-Many genetically influenced traits tend to be associated with environmental factors that promote their development.
-three kinds
1. active
2. passive
3. reactive
Conception
-Sperm travels through cervix to ovum
-Only 300 reach
-Chemical reaction upon merging (fertilization)
Zygote
-23 chromosome pairs
-First cleavage takes 30 hours
-by 3 days there are 16 cells
Cleavage
-30 hrs after conception
-zygote splits down the middle forming two identical cells
-following this continues at a rapid pace
blastocyte
-Fluid-filled sphere from which the embryo develops.
implantation
-blastocyte burrows into the wall of uterus
-happens around day 6, complete around day 11
-Occurs after blastocyte "hatches" from the zona pellucida
Amnionic sac
-Membrane holding amniotic fluid and the embryo. Provides temperature regulation, cushioning, and protection from shocks.
fallopian tubes
-tubes which carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and which provides the place where fertilization occurs
placenta
-new organ
-provides nutrient uptake, thermo-regulation, waste elimination, gas exchange; fights against internal infection; and produces hormones which support pregnancy.
-Protective barrier, preventing some toxins from entering the embryo's bloodstream.
-Keeps the mother and embryo's bloodstreams separate.
Neural tube
-Formed by ectoderm and folds after 22 days to develop into the nervous system.
indifferent gonads
-Develops into the male or female genitals.
Critical period
-extent to which exposure to teratogen disrupts prenatal development when exposure occurs
-period during prenatal development where developing organism is more susceptible to damage from exposure to teratogens
sleeper effects
-Effects of teratogen exposure appearing later in development
dilation
-cervix opens
-As labour nears, the cervix may start to thin or stretch (efface) and open. This prepares the cervix for the baby to pass through the birth canal (vagina). How fast the cervix thins and opens varies for each woman.
Germinal, Embryonic, Fetal
What are the stages of Prenatal Development?
Germinal Stage
-0-2 Weeks
-the period of the Zygote.
-Cell Differentiation and implantation begins
Cell Differentiation
Cell specialization in structure and function.
Embryonic stage
-3-8 WEEKS
-The developing organism begins the most rapid period of structural development
-chorion, amnion, and umbilical chord develop
chorion
outermost layer enclosing embryo, develops blood vessels that burrow into uterus
Ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm
what are the three layers of the embryonic disk?
fetal stage
-week 9 to birth
-combination of three trimesters
1st trimester
-conception to 12 wks
-part of fetal stage
-Organs, muscles, and nervous system organize.
-External genitals, limbs are are well-formed by 12th week
-.By the end, can move and respond to touch (reflexively)
2nd trimester
-13 to 27 wks
-part of fetal stage
-Mother can feel movements....17 to 20 weeks
-Lanugo (hair) and vernix caseosa (cheese-like substance provides infection protection)
-Glia cells & neuronal synapses form at a rapid pace.
-Sensitivity to sound and light emerges.
-Fetus reaches age of viability - b/w 22 and 26 weeks
-At 26 weeks, the lungs can breathe air.
3rd trimester
-Rapid gain in neural connectivity and organization continues. (@ 30wks coordinated neural networks)
-part of fetal stage
-Responsiveness to external stimulation increases.
-By wk 28, blinks to sound, 6 wks later can differentiate voices by tone & rhythm
-B/w 23 and 30 wks - connection b/w cerebral cortex and areas of pain sensitivity allow to experience pain
-30 Wks - differential response to old and new stimuli
-B/w 30 to 34 wk - has sleep-wake cycles
-8th month - gets antibodies from mom
-Extensive body growth occurs until last weeks
lanugo
hair
vernix caseosa
cheese-like substance provides infection protection
cephalic, breech, transverse
three kinds of fetal presentation during birth?
cephalic
-head first presentation for birth
-most ideal
breech
-buttocks-first presentation of the fetus at delivery
transverse
-more sideways position of delivery
Braxton Hicks contractions
-sign that delivery is coming
-not painful, no pattern, discomfort in abdomen
age of viability
-b/w 22 and 26 weeks
Placenta previa
-is a condition where the placenta lies low in the uterus and partially or completely covers the cervix. The placenta may separate from the uterine wall as the cervix begins to dilate (open) during labor.
Placenta abruptio
-is the separation of the placenta from the uterine lining. This condition usually occurs in the third trimester but can occur any time after the 20th week of pregnancy.