Hemoglobin Gene Organization And Hemoglobin Disorders (Lec 8)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
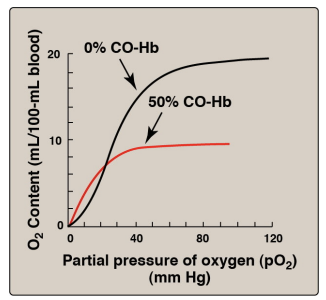
Effect of carbon monoxide (CO) on the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin
How does the CO (carbon monoxide) regulate
The carbon monoxide is so tiny it binds so slowly and stabilizes the R state
It is converted to myoglobin-like behavior
when the hyp
Carbon dioxide facilitates the R state
Carbon monoxide (CO) has 2 or 3 times more affinity to iron (Fe) than oxygen (O2)
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin belongs to a protein family
Hemoglobin is very similar and belongs to a protein family

have minor changes int he AA composition just the primary structure of the protein
The change in the AA can completely change the ability of being regurgitated
Divertion evolution: starts w. one protein and it is diverted into new proteins with diff functions, but the primary structure is kept the same
one or t2o AA changes can change the functions
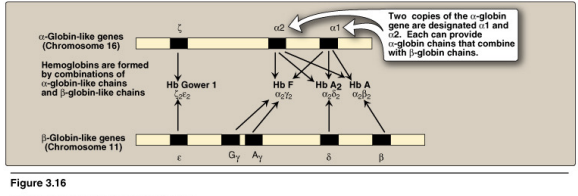
Globin gene clusters and expression during development
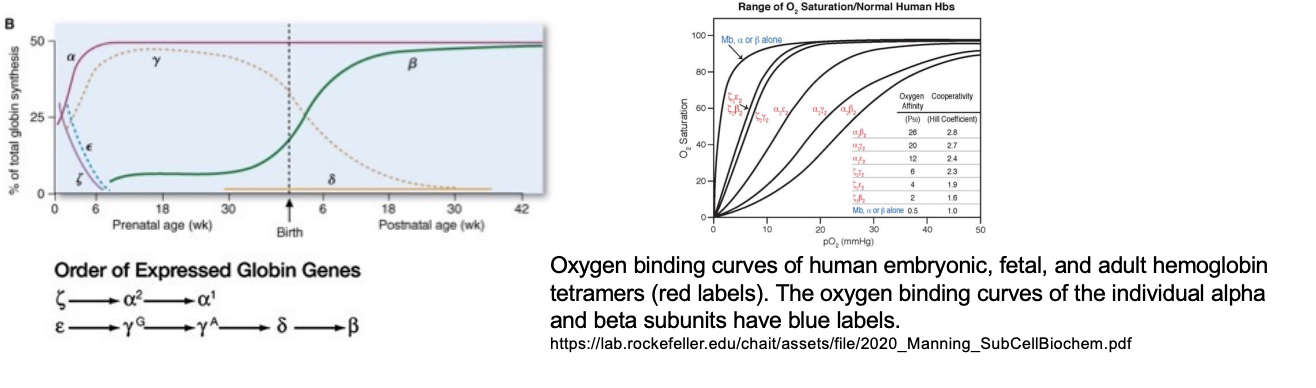
Multiple different versions of fetal hemoglobin w. different affinities towards O2
fetal hemoglobin does not have beta changes
both globin family of genes encodes these diff variations of the hemoglobin
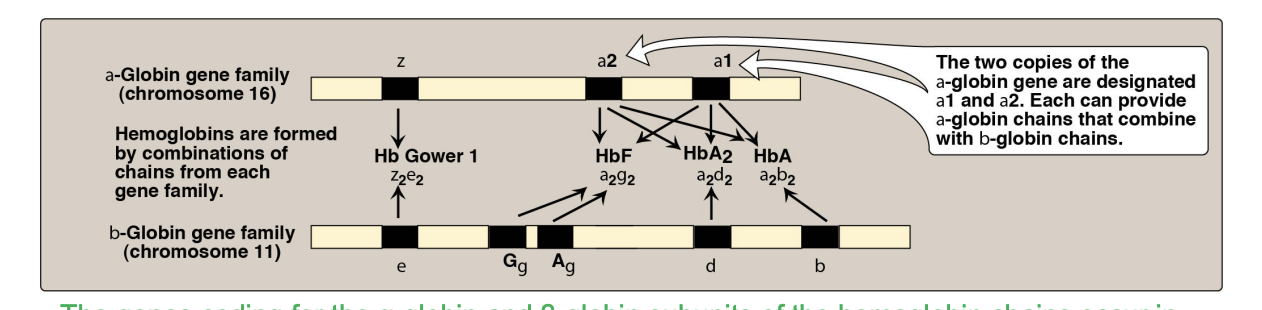
fetal hemoglobin is that alph beta, there are variaitons ot the alpha changes, and its afifnity of xogyen is regualted by its compositon of genes, and it is expressed in the hemoglobin structure throughg gene shuffling
Hemoglobinopathies
genetic disorders produced by strucutrally abnormal hemoglobin moelcule
Polymerization of deoxyhemoglobin S
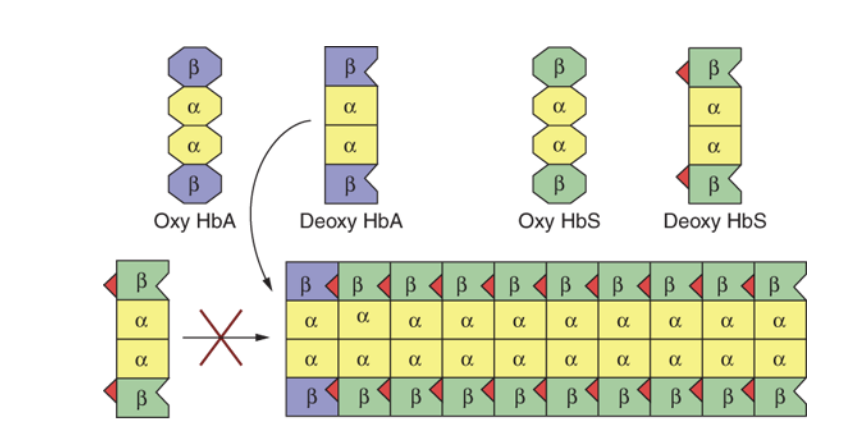
Hemoglobin just out of the blood cells by making a long hydrophibic interaction that polumerizzes hemoglobin
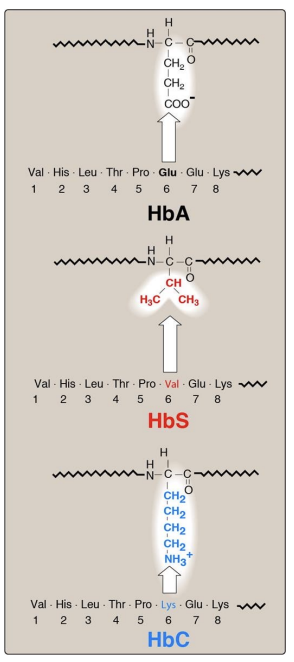
Hemoglobinopathies: Sickle cell anemia (HbS)
Sickle cell is found in various areas of the world
The assumption is that sickle cell is a genetic adaption of how to restrain malaria in these populations (Africa)
in regions where malaria is very common in the world, the ppl hjave these types of traits as a genetic adaption for resiting the malaria disease
Hemoglobinopathies: Hemoglobin C disease
Hemoglobin C —> it is amutation
this mutation has 2 effects
active transport
has a normal conc. of hemoglobin in the cells
when there is a high conc. in a very confined area → they percipiatate becauses of the excess
Percipiataiton of hemologbin in the cells → when perciipiated there is no use for it
Hemoglobinopathies: Methemoglobinemia (HbM
The Fe+3 state does not have any affinity for oxygen
certain molecule has to be kept in a certain oxidation state
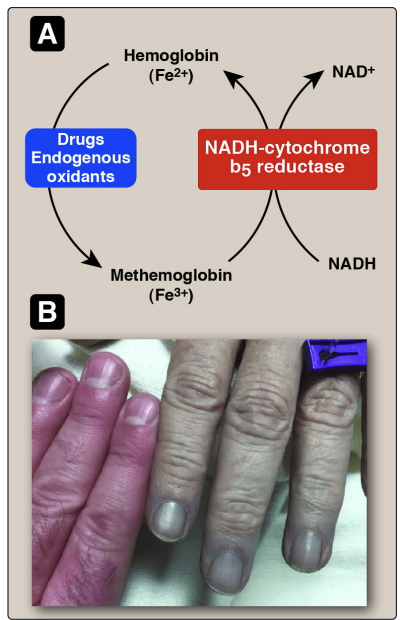
Hemoglobin Fe+2 becomes methmoglobin Fe+3
it is oxidized and Fe3+ cant bind to oxygen
caused by rare mutations sin the a or b globin chain
Blue coloration of the skin is indiation of deoxy hemologbin
Hemoglobinopathies: Thalassemias
Every one caries 2 alpha and 2 beta chains —> any chainges to these ratios leads to an inability of carrying the function it is suppsoed to carry
A-thalasemia: where the aplha chain is silent not produced engough
does not have an alpha chain
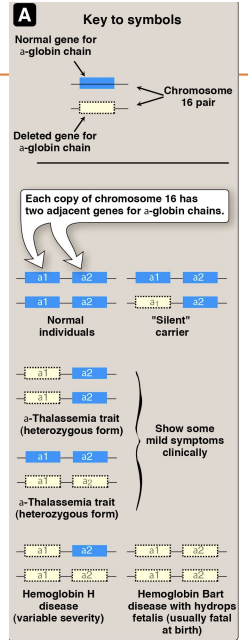
B-thaalsemia: does not have a beta chain
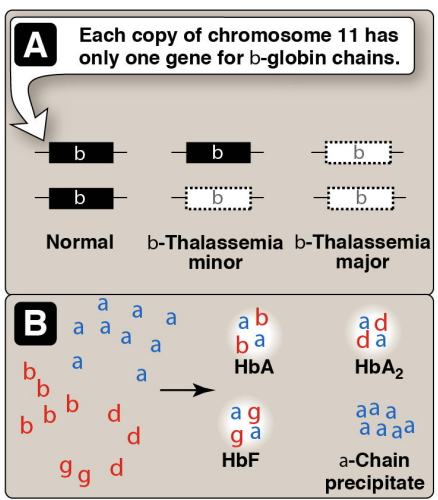
Changes in the structure results in perciptating and loss of RBCs can lead to aneia
GLYCATED HEMOGLOBIN (HbA1c)
A1c levels show glucose fluctuation in blood
high
normal glucose levels of 5 MM concentration
Glucose can attach to the hemoglobin and store it/ have it circulating for many weeks