Paleolithic Era, Neolithic Rev., Mesopotamia, Judaism and Ancient Egypt, Indus River Valley Civilization (Harappan Civilization) and Hinduism Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
1
New cards
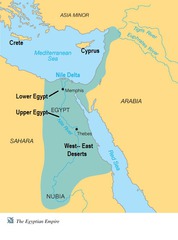
Nile River
The river the Ancient Egyptians settled around. It flows south to north into the Mediterranean Sea.
2
New cards
irrigation system
A way of supplying water to an area of land

3
New cards
natural barriers
deserts, mountains, or bodies of water that create barriers from invasion
4
New cards
mummification
embalmment and drying a dead body and wrapping it as a mummy

5
New cards
Gift of the Nile
Egypt was called this because it would not have existed without the Nile

6
New cards
The Nile flooding
was a predictable (annual) event that the Egyptians used to plan their farming and calendars.

7
New cards
hieroglyphics
An ancient Egyptian writing system in which pictures were used to represent ideas and sounds

8
New cards
Who was King Tut
Egyptian pharaoh, he died while still a young king. The discovery of his tomb in 1922 has taught archaeologists much about Egyptian culture.

9
New cards
polytheistic
Believing in many gods and goddesses

10
New cards
Silt
rich dirt left by the yearly flood of the Nile

11
New cards
Hieroglyphics
The Egyptian writing system that consisted of hundreds of picture symbols used to represent ideas and sounds

12
New cards
Papyrus
A reed plant that grew along the Nile and was used to make baskets, sandals, river rafts, and paper
13
New cards
Pyramids
Mountain-like tombs the size of several city blocks made for Egyptian pharaohs entirely out of stone; designed to protect the pharaoh's body from floods, wild animals, and grave robbers

14
New cards
polytheism
Belief in many gods

15
New cards
Egyptian contributions
Some examples include: pyramids, mummies, papyrus, math, science & medicine.
- mummification helped learn about anatomy of human body, diagnose illnesses, perform surgeries.
- calendar
- hieroglyphics, papyrus,
- Building and design of the temples, pyramids, monuments, statues etc. required knowledge of complex math
- mummification helped learn about anatomy of human body, diagnose illnesses, perform surgeries.
- calendar
- hieroglyphics, papyrus,
- Building and design of the temples, pyramids, monuments, statues etc. required knowledge of complex math

16
New cards
Rosetta Stone
A stone discovered that enabled historians to decode hieroglyphics.

17
New cards
Mesopotamia is located in this area (the _________ __________) which describes it's shape and its ability to easily grow crops.
Fertile Crescent
18
New cards
Mesopotamia is located between which two rivers?
Tigris and Euphrates
19
New cards
irrigation
Supplying land with water through a network of canals
20
New cards
city-state
A city with political and economic control over itself and the surrounding countryside
21
New cards
Ziggurat
massive pyramidal stepped tower made of mudbricks. It is associated with religion in ancient Mesopotamian cities
22
New cards
What were contributions of the Sumerians?
writing (cuneiform), technology (wheel), mathematics (calendar)
23
New cards
Cuneiform
A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge shaped stylus and clay tablets.
24
New cards
scribe
a person who writes things down
25
New cards
Empire
A large territory or a group of territories controlled by one ruler
26
New cards
Hammurabi's Code
first written code/set of laws that all were expected to obey.
27
New cards
the largest building in every city state was the
ziggurat
28
New cards
city walls
Sumerians built strong, thick walls around their cities for protection.
29
New cards
How did Mesopotamians water their crops during droughts?
irrigation systems
30
New cards
Hammurabi
He designed a legal code in early Babylon that gave punishment based on crime and social status.
31
New cards
Paleolithic Age
(750,000 BCE - 10,000 B.C.E.) Old Stone Age. A period of time in human history characterized by the use of stone tools and the use of hunting and gathering as a food source.
32
New cards
Prehistory
Period of time before writing.
33
New cards
Culture
The shared beliefs, customs, practices, and social behavior of a particular nation or people.
34
New cards
Archaeologist
A social scientist who studies the past by looking at artifacts people have left behind.
35
New cards
Artifact
Any item, made by humans, that represents a material aspect of culture.
36
New cards
Nomads
Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals.
37
New cards
Arable
Farmable land. Very fertile land
38
New cards
Neolithic Revolution
(10,000 - 8,000 BCE) The development of agriculture and the domestication of animals as a food source. This led to the development of permanent settlements and the start of civilization.
39
New cards
Civilization
A complex society that has language, religion, a division of labor, and a social hierarchy. There is also a food supply and a political system.
40
New cards
Cradle of Civilization
Mesopotamia is called this because the earliest people and cultures were located here
41
New cards
Agriculture
The cultivating of land, producing of crops, and raising of livestock for human consumption.
42
New cards
Domestication of Animals
the taming of animals for human use.
43
New cards
Food surplus
extra food creation that allows people to engage in activities besides farming
44
New cards
River valleys
first civilizations are all located near these (Nile, Tigris & Euphrates, Indus and Hwang He)
45
New cards
Components of a Civilization
Centralized Government, Infrastructure (roads, bridges, and cities), Organized Religion, Social Class system, Job Specialization, Written language
46
New cards
Agriculture + Domestication of Animals
= Food Surplus
47
New cards
Cultural diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another
48
New cards
History
any period of time after writing
49
New cards
Fertile Crescent
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates
50
New cards
Specialized Workers
People who have 1 job to do and they get really good/efficient at that job
51
New cards
Artisans
skilled workers who make goods by hand
52
New cards
Great Rift Valley of East Africa
home to the earliest people
53
New cards
Monotheism
belief in one God
54
New cards
Abraham
Founder of Judaism
55
New cards
Jew
Someone who believes in Judaism
56
New cards
Rabbi
A Jewish teacher who usually teaches laws from the Torah
57
New cards
Yahweh
God of Judaism
58
New cards
Judaism
Oldest monotheistic religion
59
New cards
Synagogue
The center of Judaism public worship
60
New cards
Persecute
Treat someone poorly and not very nicely due to their religion, usually involving some violence and abuse
61
New cards
Torah
Most important part of the Jewish holy book
62
New cards
Kosher
prepared according to Jewish laws and traditions and most commonly used to refer to food
63
New cards
Exodus
"Departure." Tells how the Israelites were enslaved in Egypt and freed by Moses when he parted the Red Sea. Recounts the wandering in the desert for 40 years.
64
New cards
Covenant
Agreement with God. Jewish people were the chosen ones
65
New cards
Diaspora
any group migration or flight from a country or region; dispersion. Particularly used in relation to Jews scattered by Romans in 70 CE.
66
New cards
Passover
Jewish holiday celebrating the Jews exodus from Egypt.
67
New cards
10 Commandments
Moral and Ethical code of Judaism and Christianity
68
New cards
Jerusalem
Holy city for all three monotheistic religions
69
New cards
Moses
Led the Exodus of the Hebrews from Egypt; received the 10 commandments
70
New cards
Harappan Civilization/Indus River Valley Civilization
They developed a civilization in the river valley because of the fertile soil and protection from outside invaders that the physical features provided them. This civilization is known for advanced cities of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa. They had organized urban planning (grid patterned cities), indoor plumbing/bathrooms and sewers to distribute waste outside the city walls. They used symmetrical sun-dried bricks to build their cities.
71
New cards
Hinduism
An eastern religion which evolved from an ancient Aryan religion in which followers strive to free their soul from reincarnation until the soul is finally freed. This religion is practiced primarily in India.
72
New cards
Religious majority in India
Hinduism
73
New cards
Atman
Hindu's soul
74
New cards
Aryans
Nomadic Central Asian group that took over the Indus River Valley and brought the Vedas and Caste System.
75
New cards
Cultural Diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another
76
New cards
No Founder
Hinduism was created through the process of cultural diffusion. The Aryans conquered the Indus River Valley and mixed with the remnants of the Harappa's to create Hinduism.
77
New cards
Vedas
A Hindu holy book which is a collection of Aryan hymns that were transmitted orally before being written down in the 6th century BCE.
78
New cards
Upanishads
A major book in Hinduism that is often in the form of dialogues that explored the Vedas and the religious issues that they raised.
79
New cards
Reincarnation
In Hinduism and Buddhism, the process by which a soul is reborn continuously until it achieves perfect understanding
80
New cards
Karma
(Hinduism and Buddhism) the effects of a person's actions that determine his destiny in his next life
81
New cards
Dharma
In Hindu belief, a person's religious and moral duties
82
New cards
Caste System
Rigid/Strict social class system rooted in the religion of Hinduism. No social mobility. Born into the system and cannot move up or down in your lifetime.
83
New cards
Brahmin
A priest or member of the priestly caste in Hinduism
84
New cards
Kshatriya
Hindu caste of warriors and nobles.
85
New cards
Vaisya
third level of the varnas in the Hindu caste system; Skilled laborers
86
New cards
Sudra
4th social class in the caste system very little rights. Servants; unskilled laborers
87
New cards
Untouchables
LOWEST LEVEL OF INDIAN SOCIETY; not considered a real part of the caste system; often given degrading jobs; their life was extremely difficult (Dalit or Pariahs); cleaned toilets and bathrooms, sewers, street sweepers and cremated bodies of the dead.
88
New cards
Brahma
A single spiritual power that Hindus believe lives in everything. The Creator God of Hinduism.
89
New cards
Vishnu
God of Preservation or Preserver God
90
New cards
Shiva
Destroyer God
91
New cards
Moksha
Becoming liberated from the cycle of reincarnation in Hinduism. The ultimate goal for all Hindus. To become one with the creator God Brahman Negruna.
92
New cards
Holy Cow
Hindus believe the cow is a sacred animal; do not eat
93
New cards
Varna
A caste in the Hindu caste system
94
New cards
Ahimsa
Hindu belief in nonviolence and reverence for all life
95
New cards
Ganges River
Holy River of Hinduism
96
New cards
The caste system still exists strongly in ___________________ areas of India
Rural
97
New cards
Monsoons in India
Wet monsoon (summer)(Southwest Monsoons)- Air traveling across oceans and gathering water; farmers in India wait for these monsoons to create fertile land for another period of time to grow different types of crops.
Dry monsoon (winter)- Cold dry air from the Himalayas; The Himalayas block the cold air and leave India dry and moderate temperatures.
Dry monsoon (winter)- Cold dry air from the Himalayas; The Himalayas block the cold air and leave India dry and moderate temperatures.
98
New cards
The caste system breaks down in ________________ areas of India
Urban
99
New cards
The caste system still exists strongly in ___________________ areas of India
Rural