The Working memory model
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What is the WMM
The working memory model (Baddeley and Hitch 1974) is an explanation of how STM is organised and how it functions
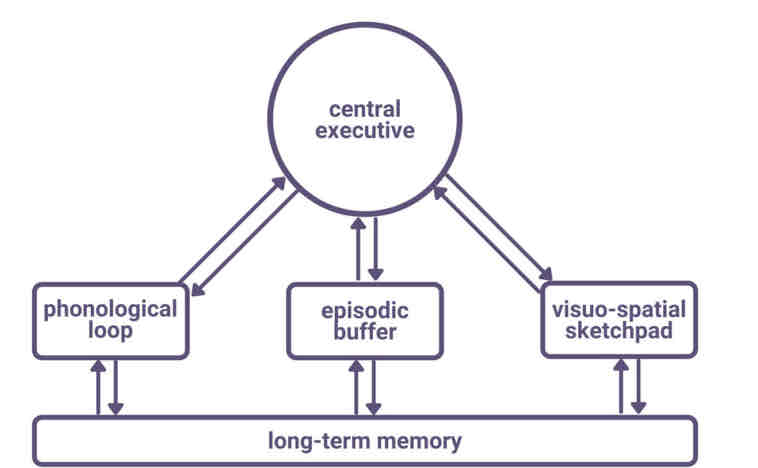
Central executive
The central executive monitors incoming information , focuses and divides our limited attention and allocates subsystems to tasks
The Central executive has very limited processing capacity and does not store information
Phonological loop
the phonological loop (PL) deals with auditory information (codes acoustically)
-The PL is subdivided into :
the phonological store- stored the words you hear
The articulatory store- allows maintenance rehearsal
Visio-spatial sketch pad
the Visuo-spatial sketch pad (VSS) stores visual and/or spatial information (codes visually)
It has a limited capacity of about 3 or 4 chunks according to Baddeley
-Logie 1995 subdivided the VSS into:
The visual cache- stores visual data
The inner scribe- records arrangements of objects in the visual field
Episodic buffer
the episodic buffer(EB) is a temporary store for information
It integrates the visual, spatial and verbal information that has been processed by other stores whilst also maintaining a sense of time sequencing
It is also a storage component for the central executive and has a limited capacity of about 4 chunks
The EB links memory to LTM and wider cognitive processes such as perception
Evaluation
one strength is that there is clinical evidence and support from the case study of KF . after his brain injury, KF had poor STM ability for auditory information but could process visual information normally . His phonological loop was damaged but his visuo-spatial sketch pad was intact
One limitation is that that’s there is a lack of clarity over the nature of the central executive. The CE needs to be more clearly explained than just being simply ‘attention’. For example , some psychologists believe the CE may consist of separate sub components