Biology marking period one notes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
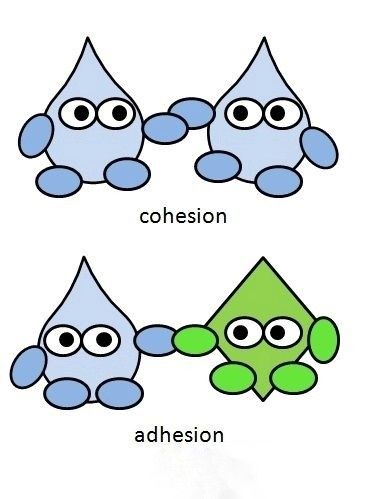
Cohesion
water interacting w/ other WATER molecules and forming hydrogen bonds
cohesion is what helps water move from the roots of a tree to the very top
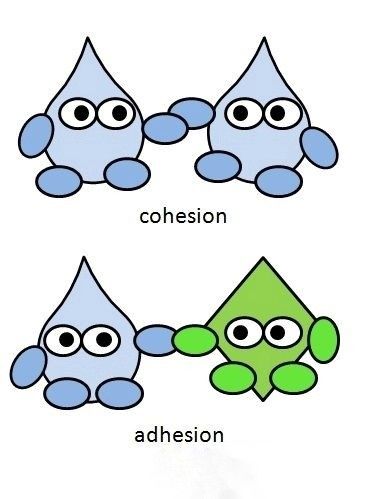
adhesion
water interacting w/ other POLAR molecules and forming hydrogen bonds
adhesion allows water to stick to the sides of a plant
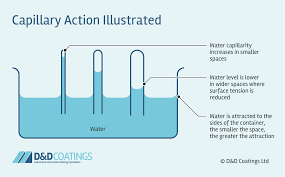
Capillary action
Used by plants to transfer water from their roots to their leaves
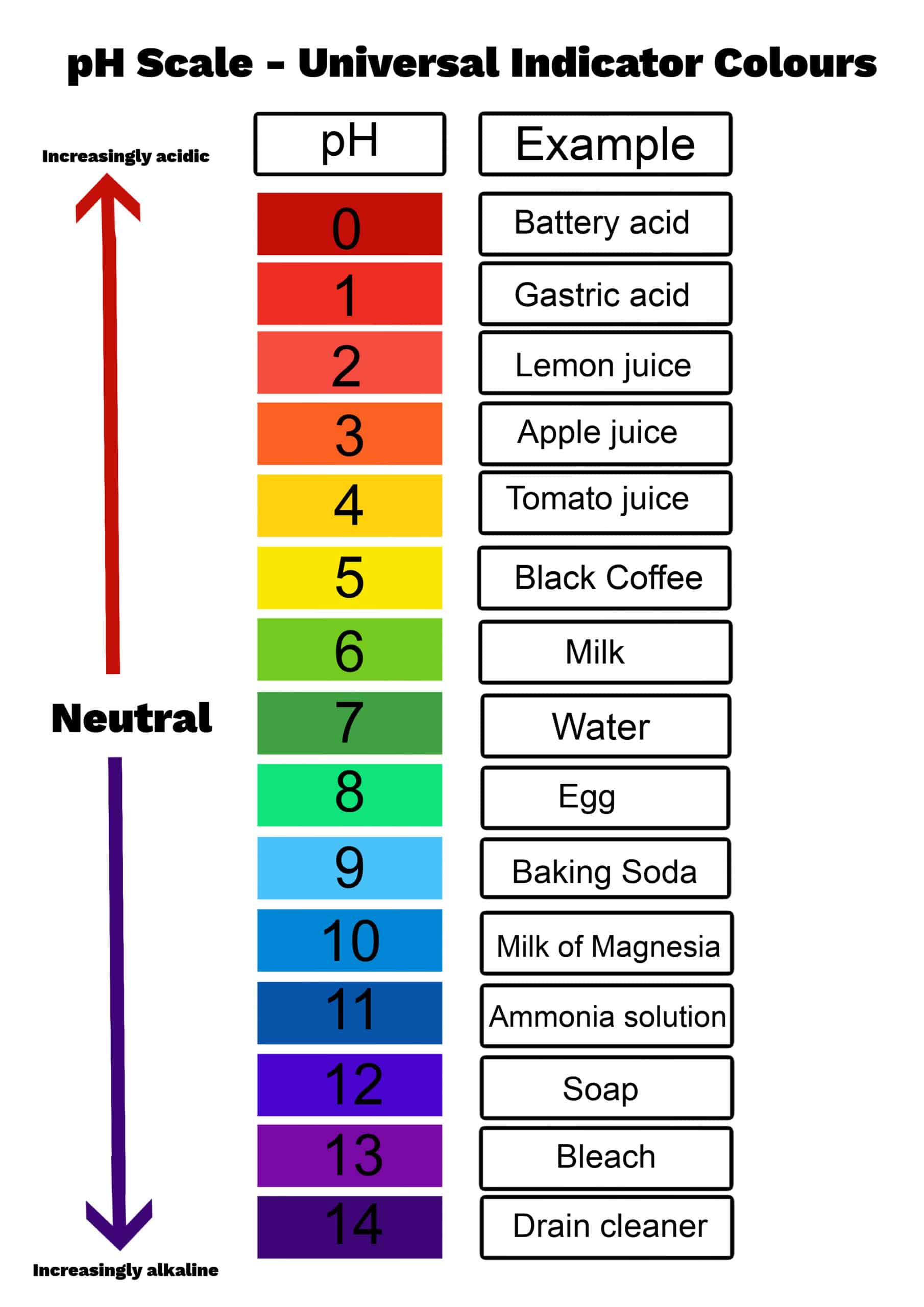
pH
0 is the most acidic, 14 is most basic/alkaline
Law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only converted into something else
Monomer
Chemical subunits that combine to make polymers
Polymer
Macromolecule that is made up of many monomers
The four major classes of monomers
Amino acids (proteins), fatty acids (lipids), monosaccharides (polysaccharides), and nucleotides (DNA/RNA)
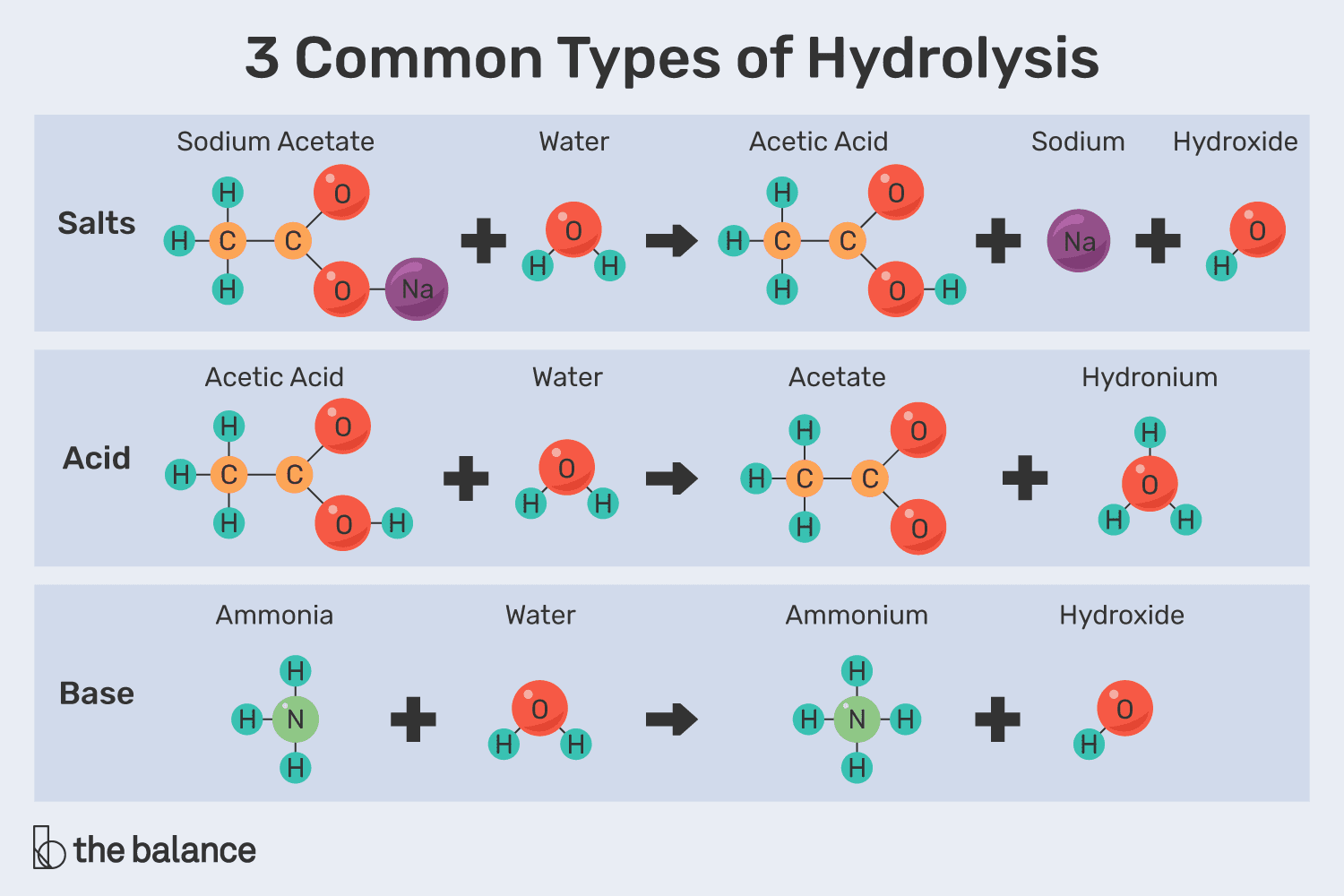
Hydrolysis
Reaction used to break polymers by adding water
Dehydration synthesis
Reaction used to build polymers by taking out water
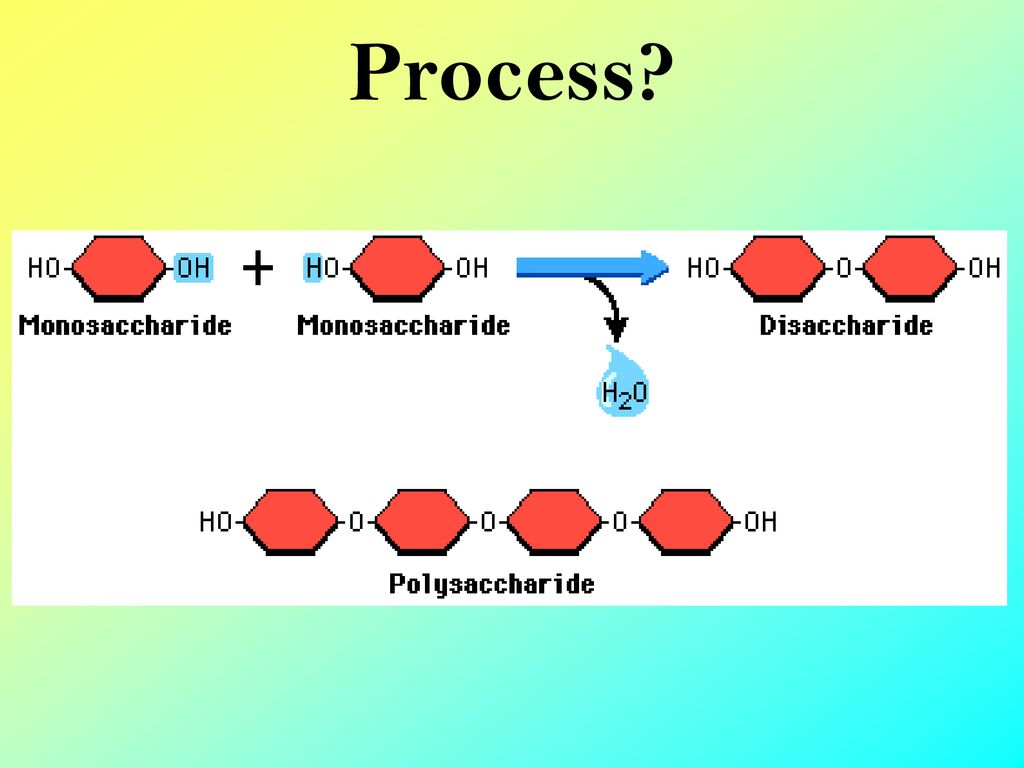
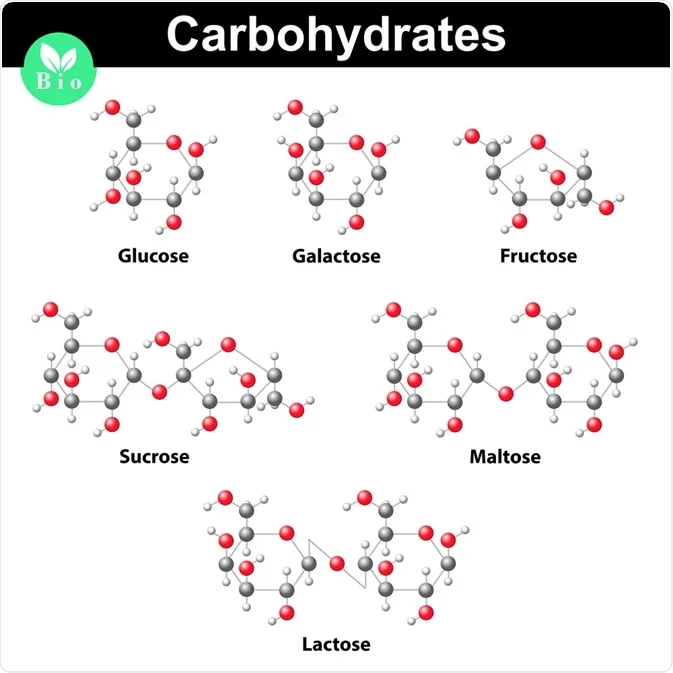
Carbohydrate
Monomer
Complex carbohydrates include cellulose, starch, glycogen, and chitin
CH2O
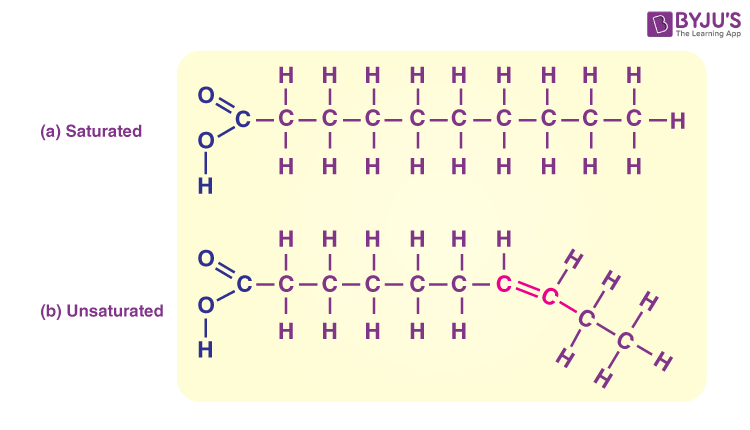
Lipids
Polymer
Lipids do not have a real monomer, but are composed of subunits. Subunits being fatty acid and glycerol.
All lipids are nonpolar
The three important types of lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids
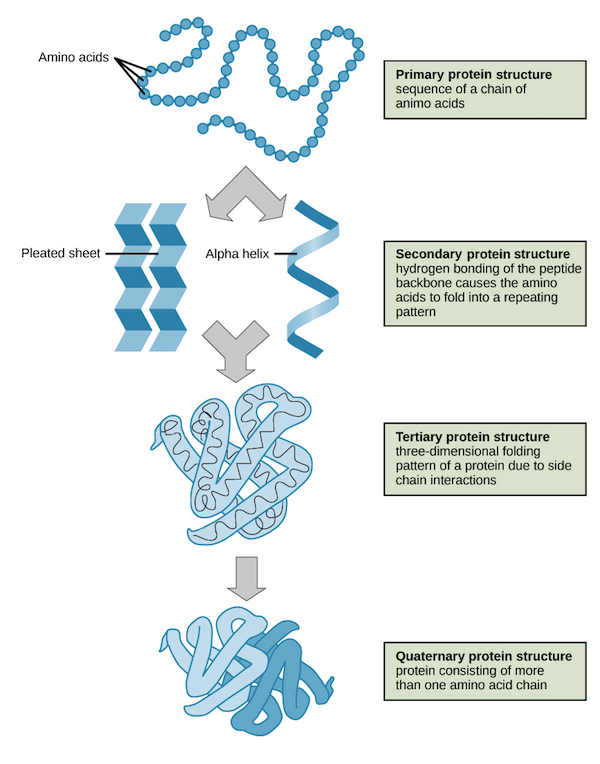
Proteins
Polymer, add up of amino acids, has peptide bonds between the amino acids
Four sub components of proteins are amino, groups, carbon groups, hydrogen, and R groups
Proteins carry out most jobs in the cell
All enzymes are proteins but not all proteins are enzymes
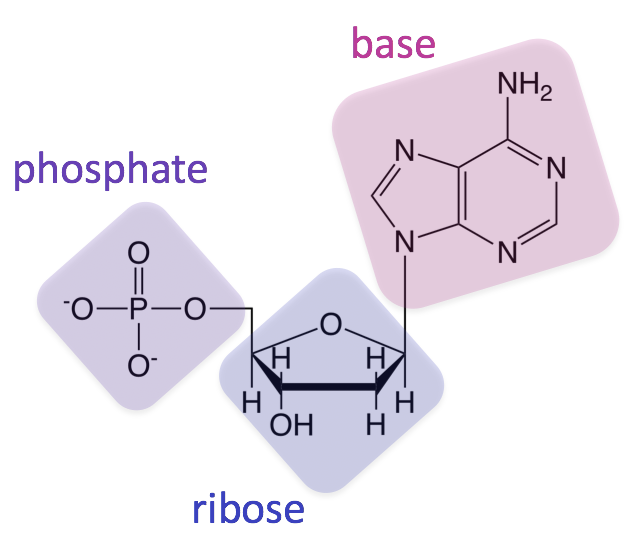
Nucleic acids
Polymer
Three sub components of nucleic acids being one five carbon sugar, one phosphate group, and one nitrogenous base.
Stores genetic information
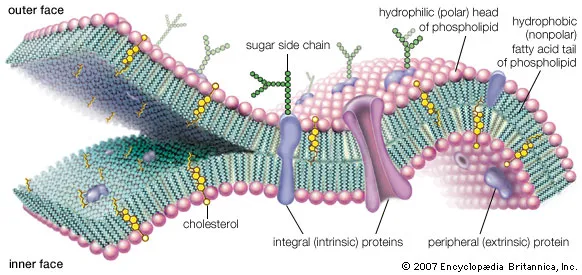
cell membrane
Outer membrane of the cell
Controls the movement in and out of the cell
Cell wall
found in plant cells (Rarely bacteria)
Supports and protects cells
Cell wall is made up of cellulose in PLANT CELLS.
Cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan in BACTERIA CELLS
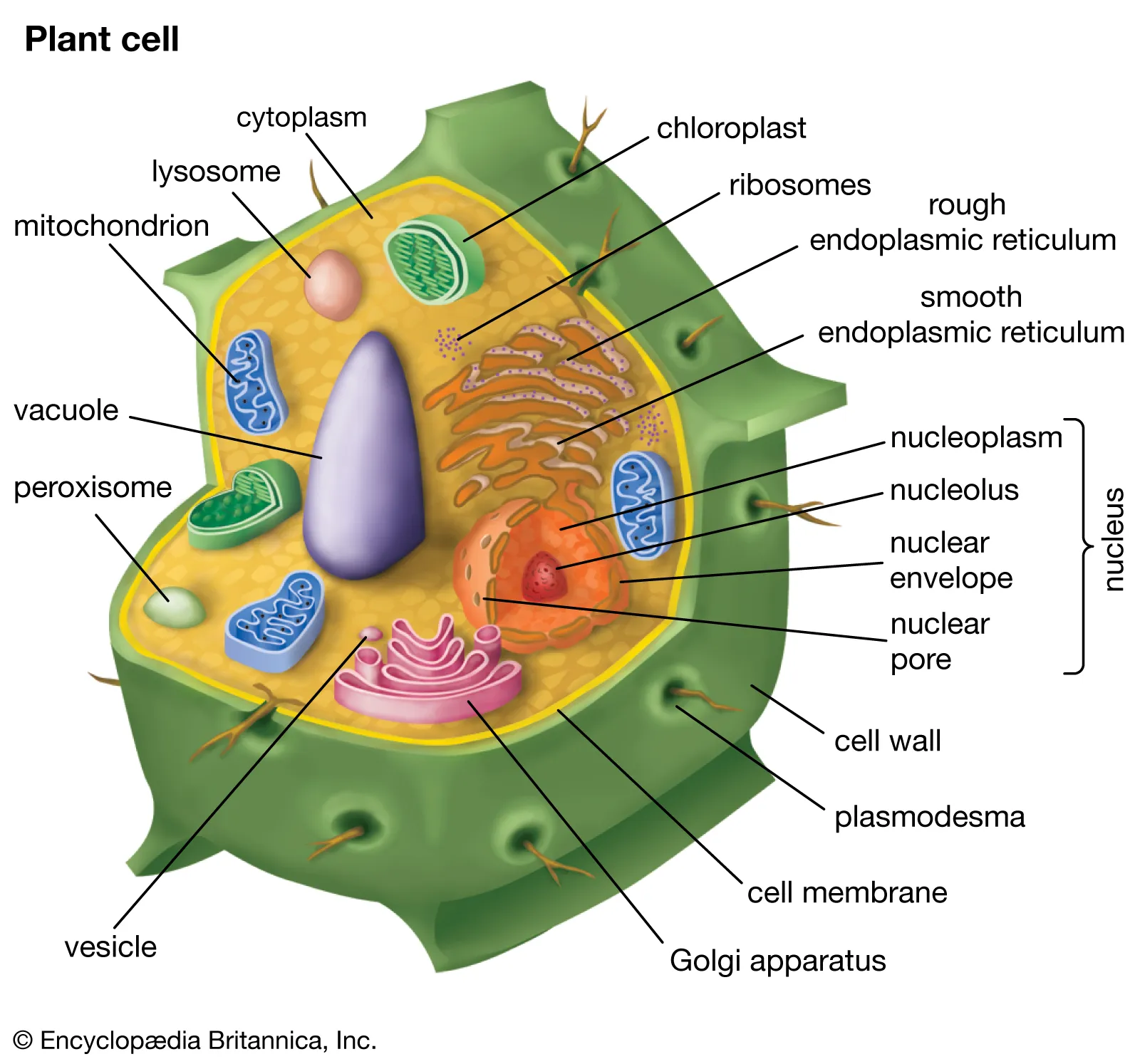
Nucleus
Directs cell activity
Contains genetic material
Separated from the cytoplasm by nuclear membrane
Control center for the cell. Contains all the instructions (DNA)
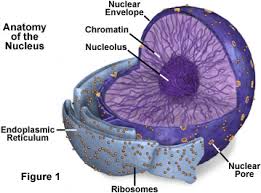
Nuclear membrane
Surrounds membrane
Made of two layers
Allow material to enter and leave the nucleus
Chromosomes
In the nucleus
Made of DNA
Contains instructions for traits and characteristics
Nuceolus
Inside the nucleus
Contains RNA to build proteins
Cytoplasm
Gel-like mixture surrounded by a cell membrane
Contains hereditary material
endoplasmic reticulum
Moves material around cell
Two types
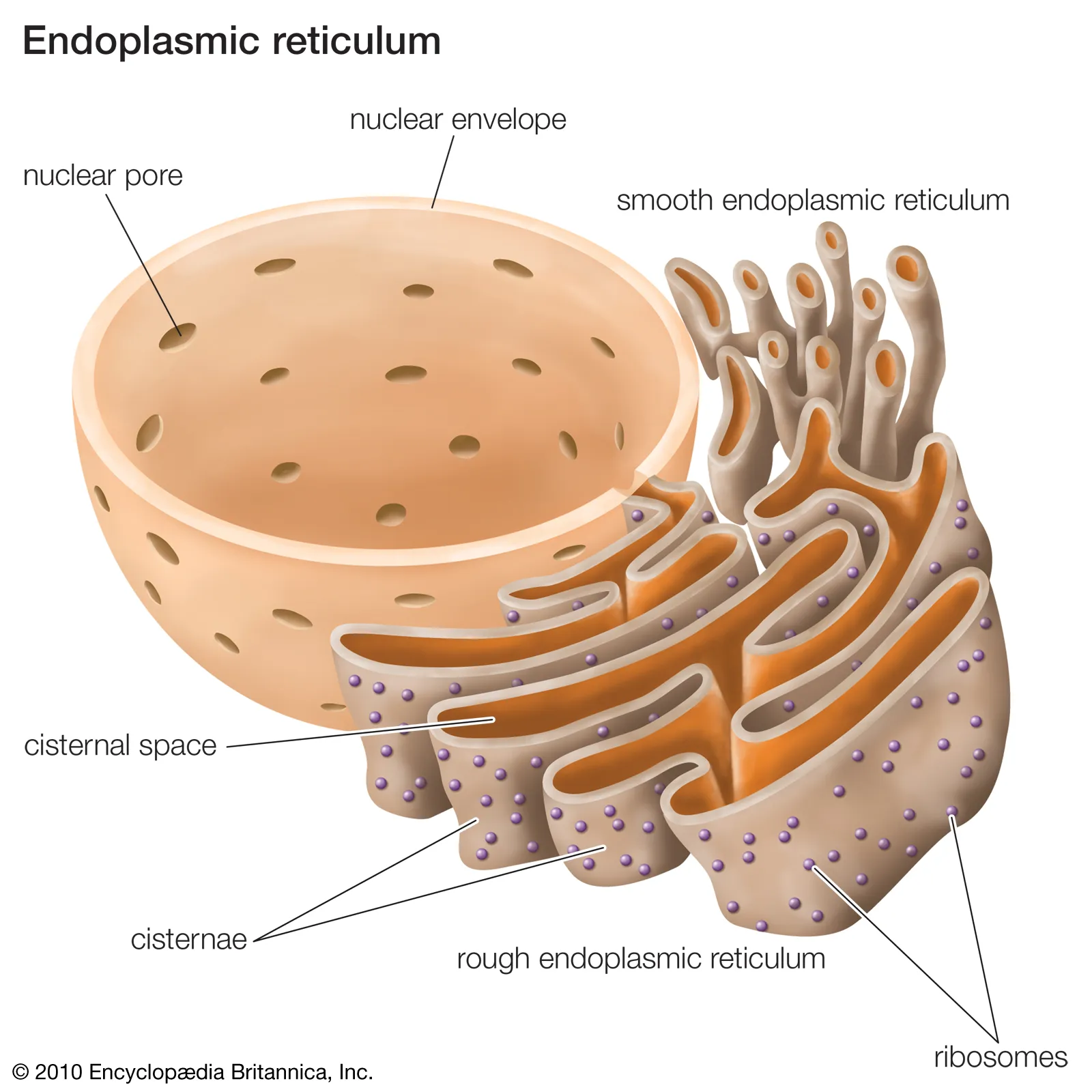
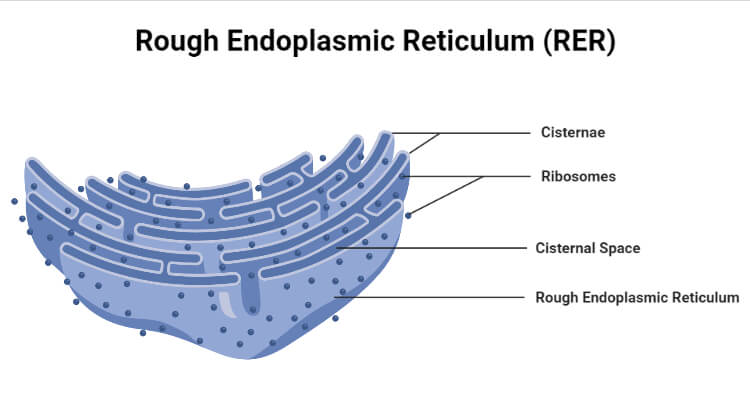
rough ER
Contains ribosomes on the surface (Provides rough texture)
compartmentalizes the cell
Packages new proteins made by the ribosomes
Focuses on aiding metabolic (digesting) activities.
Smooth ER
No attached ribosomes (ergo smooth surface)
Detoxifies the cell & synthesizes lipids
Lipids allow for encasing of the SER until it is to be placed in a new hydrophobic environment
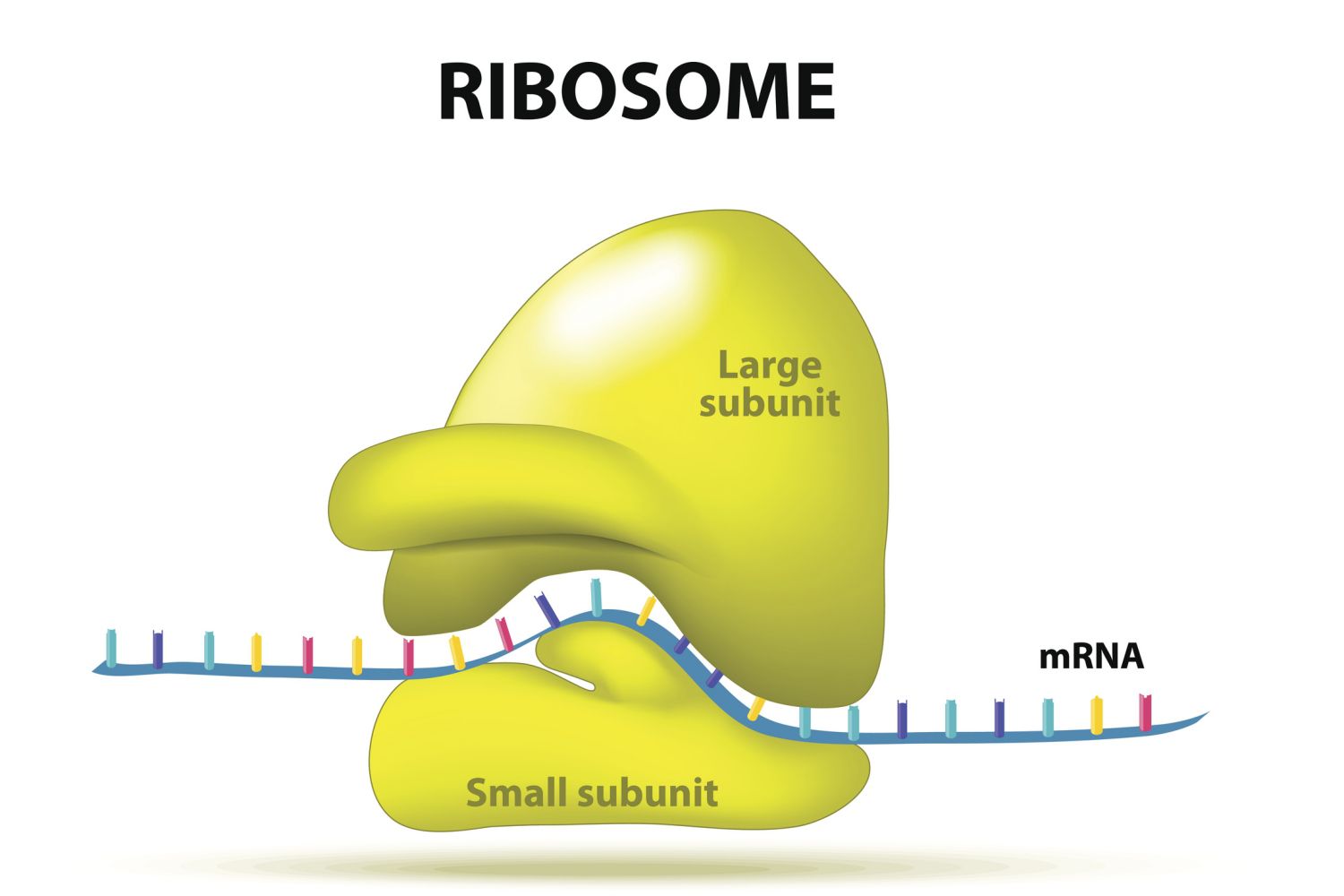
Ribosomes
In every cell
Made up of RNA and proteins, they SYNTHESIZE proteins
Found floating through the cell
Made up of 2 subunits, LARGE ribosomal unit and SMALL ribosomal unit
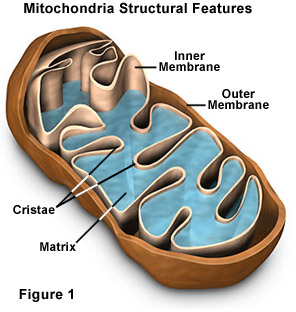
Mitochondria
Power house of the cell
Produces ATP through chemical reactions
Breaks down fats & carbohydrates, Controls levels of water and other material in the cell, Recycles & decomposes proteins, fats, & carbs.
Both inner and outer membranes are smooth
Responsible for cellular respiration; electron transport chain, reaction happens at the membrane
Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
Cristae: the folding of the inner membrane (increases surface area)
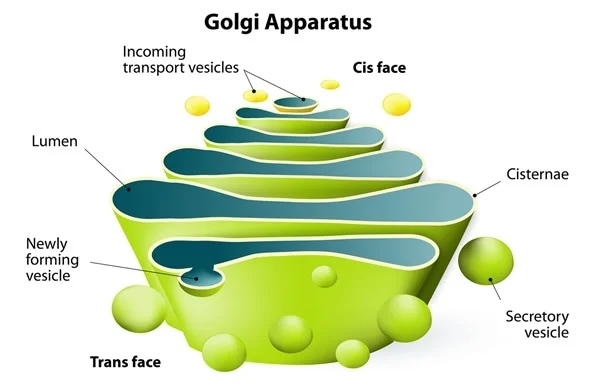
Golgi bodies
Proteins packing plant
Moves materials WITHIN the cell
Moves materials OUT of the cell
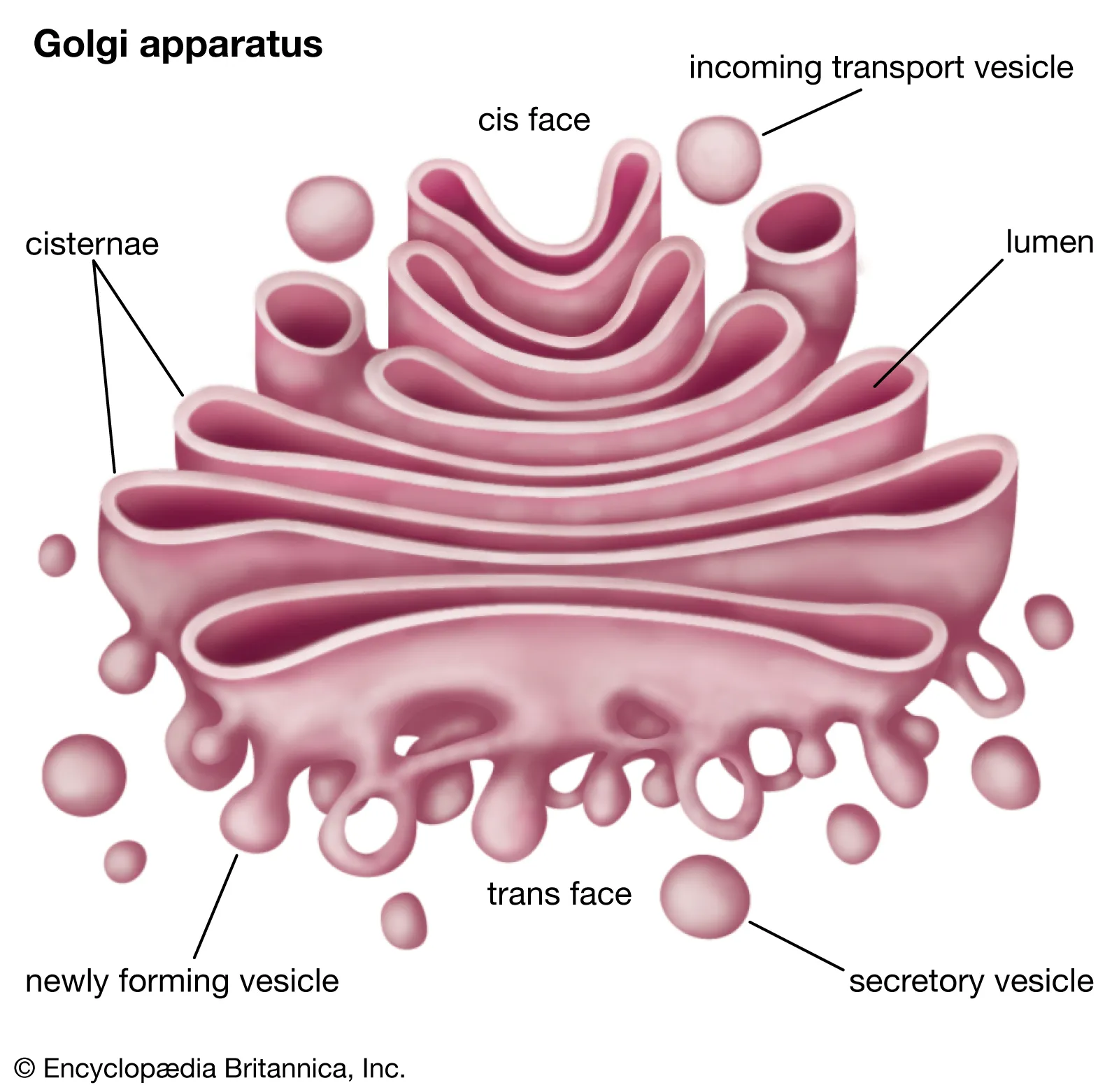
Golgi complex (apparatus)
All eukaryotic cells
Involved w proper folding and modification of new proteins & packing and trafficking them within and out the cell Believed
Focused on preparation and distribution of compounds
Lysosomes
DIGESTIVE plant for proteins, fats, & carbs
Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal
Digest damaged and degraded cell parts or macromolecules
Contains hydrolic enzymes for digestion
The cell will break down if the lysosome explodes
Vacuoles
Membrane bound sack for storage
Stores water or other macromolecules for later use
Will store and eventually release waste products
Digestion and waste removal
Contains water solution helps plants maintain shape
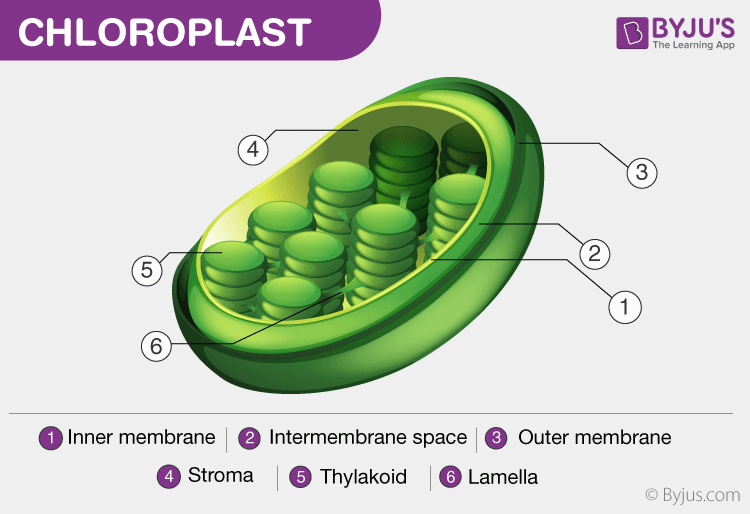
Chloroplast
ONLY in plant cells and autotrophic algae
Contains chlorophyll
Where photosynthesis takes place in plant cells; designed for capturing light energy; main function is to utilize light energy (photons), and CO2 to make glucose
2 main structures; thylakoid and grana
Thylakoid; highly folded membrane compartments that are organized in stacks. (Contain chlorophyll pigments that compromise the photosystems and electron transport proteins
Grana; stacks of discs made of thylakoid
stroma; fluid between the inner chloroplast membrane and outside the thylakoids
Plasma membrane
Found in ALL cells
Separated extra cellular and intercellular environments
Controls all materials that enter and exit the cell
Believed that all membrane bound organelles are just extensions of the cell membrane
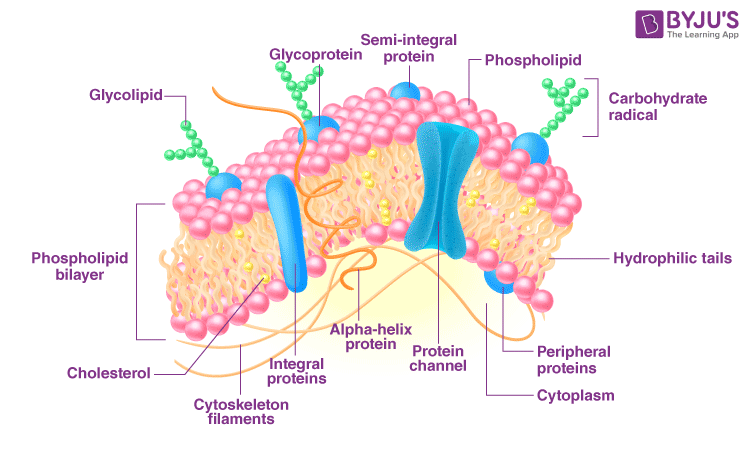
Cytoskeleton
Eukaryotic cells (Not usually plant cells)
Consists of three fibers, microtubles, micro filaments, intermediate filament
microtubles; used for separation of cells and DNA in mitosis and meiosis. Also important for cilia and flagella movements
Microfilaments; major role in muscle contraction
Intermediate filament; reinforce shape and strength
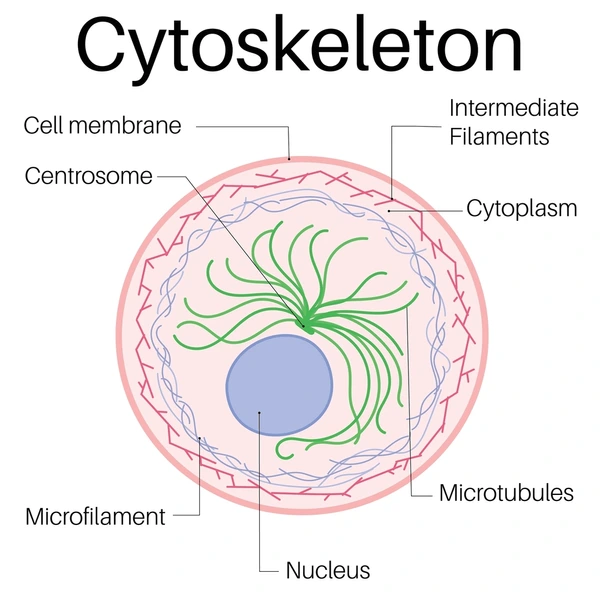
Centrioles
Animal cells
Always in pairs
Aid cell division(meiosis and mitosis) by organizing microtubles
Help determine the reaction of all the organelles in an animal cell
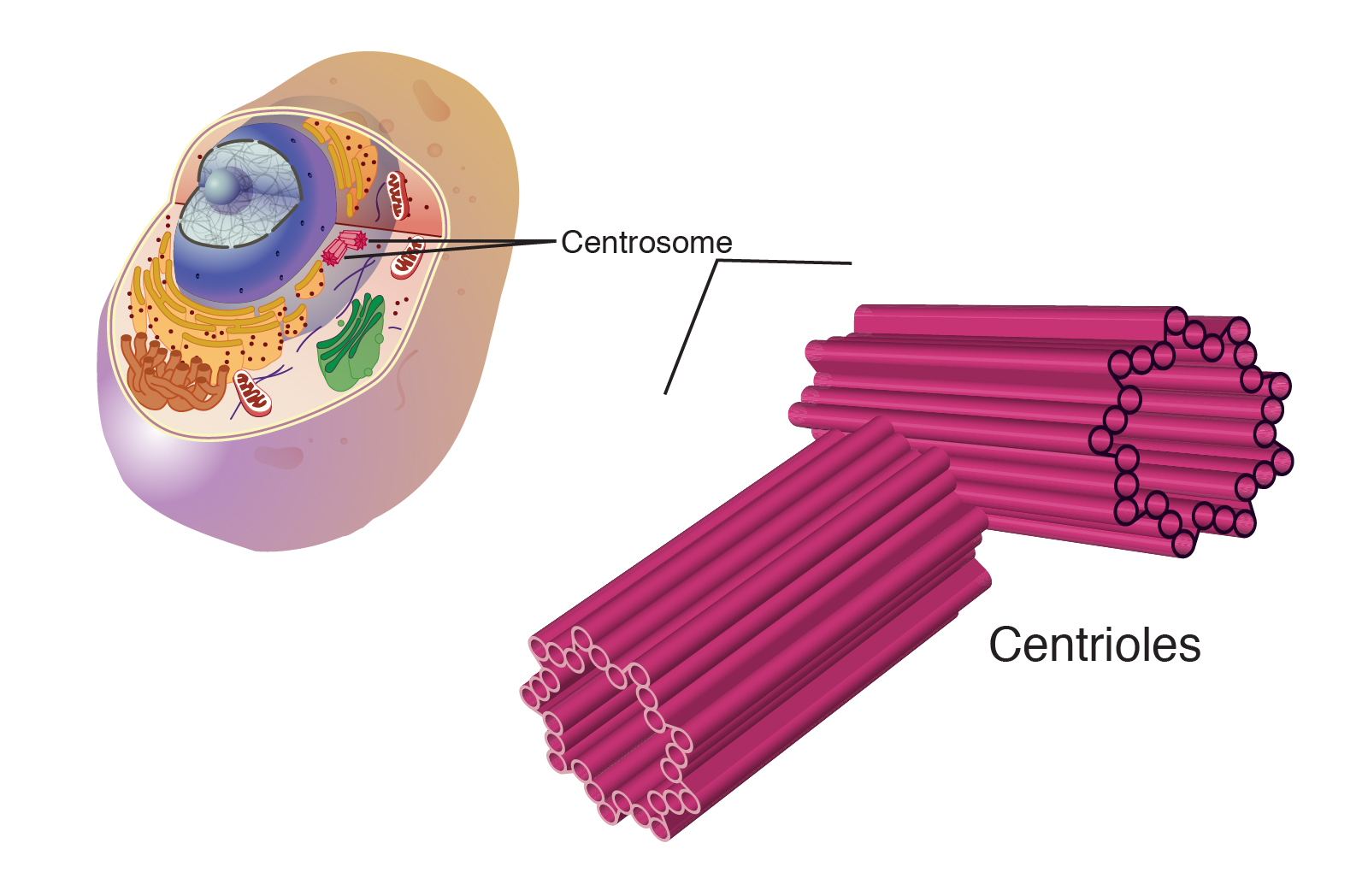
Peroxisomes
In all eukaryotic cells, surrounded by membrane
Contains enzymes to to ease function, oxidize unwanted materials (useless/damaged fatty acids and amino acids)
differ from lysosomes b/c lysosomes DIGEST, peroxisomes OXIDIZE
they prevent oxygen peroxide (H2O2) byproducts from accumulating in the cell
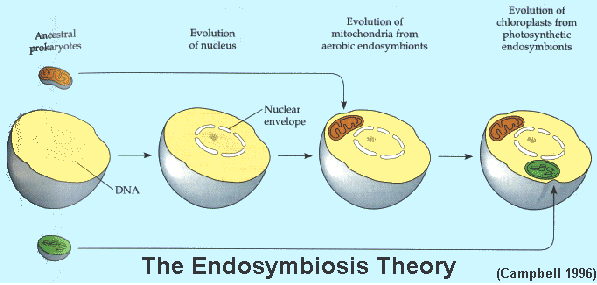
Endosymbiosis
A theory that states primitive prokaryotes engulfed primitive plastids (mitochondria & chloroplasts) and instead of destroying them, created and endosymbiotic relationship and evolved to rely on one another
Facts that support this theory; double membrane, each plastid has their own DNA, plastid DNA is circular unlike bacteria, they have microscopic ribosomes, and they divide in a fission like process.
Enzymes
Belong to the protein family of macromolecules
Biological catalysts meaning they are made of organic material and are made by living organisms
In order for an enzyme to work it’s tertiary and quaternary's structure must be intact (this is to ensure the active site has its proper structure)
Every enzyme has an active site specific to its substrate.
Law of thermodynamics at a glance
Law 1: energy cannot be created nor destroyed, can only change forms. For AP bio only two basic forms of energy are needed to know
Kinetic energy associated with/ movement & potential energy stored based on position height etc
Chemical energy still exists in chemical bonds (it is considered stored energy) therefore a type of potential energy.
Enzyme function theories
Lock and key - emphasizes that enzymes have specificity/works w only specific shapes that a substrate have (one lock fits only one key)
hand and glove theory (also called induced fit) essentially same as lock and key.
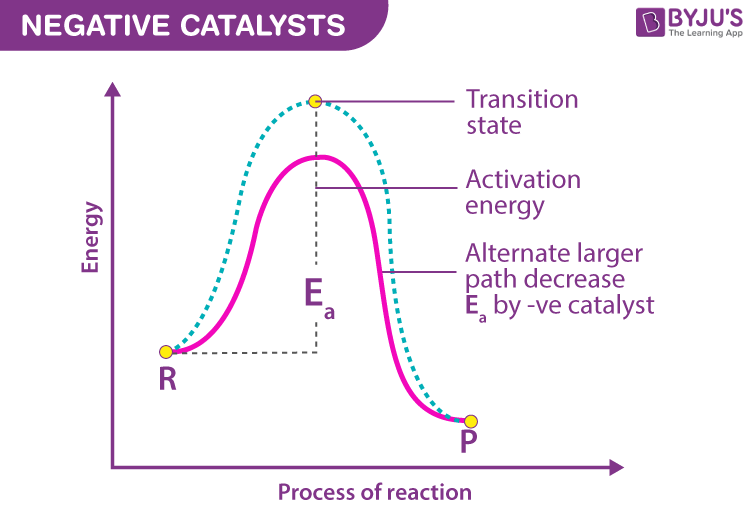
CATALYSTS!!!
Substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction w/out itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. Catalysts do this by decreasing the needed activation energy for any given reaction
Enzymes are not included in this reaction but they assist.
2 types of catalysts
ENZYMES: catalysts made up of proteins (most catalysts are enzymes)
RIBOENZYMES: catalysts made of RNA (involved W/ the creation and destruction of proteins)
Reactants & products
A reactant is the “before” and a product is the “after” of a reaction
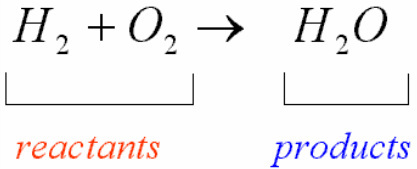
Activation energy
Energy needed for for a reaction to go forward (the distance between the reactants and the peak of the graph)
CO2 + H2O >< H2CO3 (carbonic acid)
Active site
The active site is the location on the enzyme where the substrate bonds
The active site is what must be specific to the enzyme, and compatible w the substrate
Changing properties of the active site; charges, size, shape, or other chemical properties
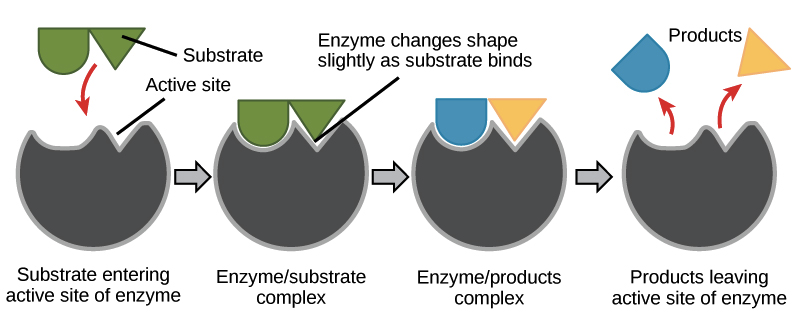
Substrate
The substrate is the molecule(s) that are being hydrolyzed or synthesized
Hydrolyzed: breaking bonds by adding water
Synthesized: building bonds by removing water
Naming enzymes
Enzymes bus ALWAYS end w the suffix -ase
Enzyme prefixes usually identify what reaction the enzyme is involved in
LipASE, sucrASE, proteASE
Two kinds of respiration
AEROBIC respiration; requires O2
ANAEROBIC respiration; does not require O2
Two kinds of fermentation
ALCOHOLIC fermentation; makes alcohol, occurs in bacteria/yeast cells, human use = brewing/distilling
LACTIC ACID fermentation; making lactic acid, humans do this in their muscles w/ NO O2, human effect = muscle fatigue (the burning feeling in muscles)
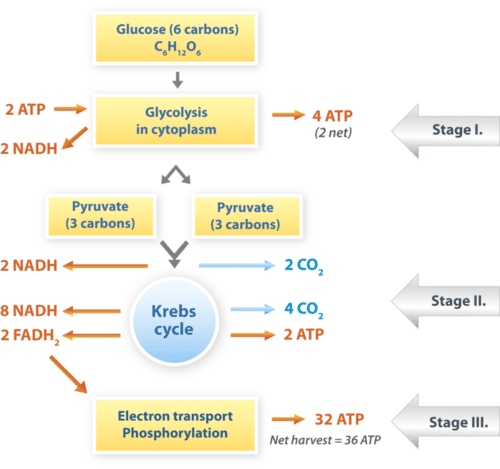
Aerobic respiration 3 steps
Glycolysis; occurs in cytoplasm, splits glucose into 2 Pyruvic acid, produces 2 ATP
The Krebs cycle; pyruvic acid is changed into 2 ATP, occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria
The electron transport chain; hydrogen ions from pyruvic acid are bounced around in mitochondria (the inner membrane), 32 ATP are produced in the end
TOTAL OF 36 ATP IS PRODUCED THROUGH AEROBIC RESPIRATION
Net reaction: C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + 36 ATP
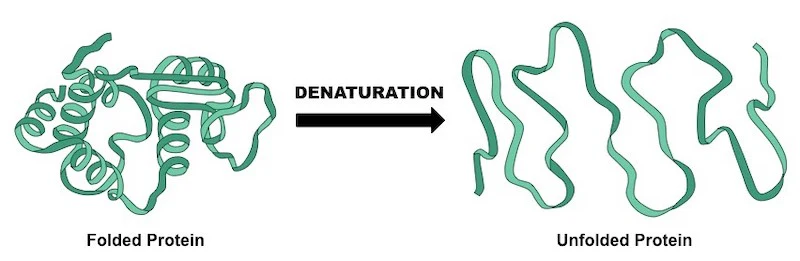
Protein denaturing
The process of breaking the bonds and forces that hold a proteins structure together causing it to unfold or unravel.