biolA 190 - ch 7
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
7.1
7.1
photosynthesis
captures light energy and uses this energy to synthesize carbohydrates
CO2 is
reduced
H2O is
oxidized
6CO2 + 12H2O + LIGHT ENERGY →
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
energy from light drives this
ENDERGONIC reaction
organisms can be categorized as
autotrophs or heterotrophs
life is primarily driven by
the photosynthetic activity of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria
chloroplasts are pr
organelles that carry out photosynthesis
they contain the pigment chlorophyll
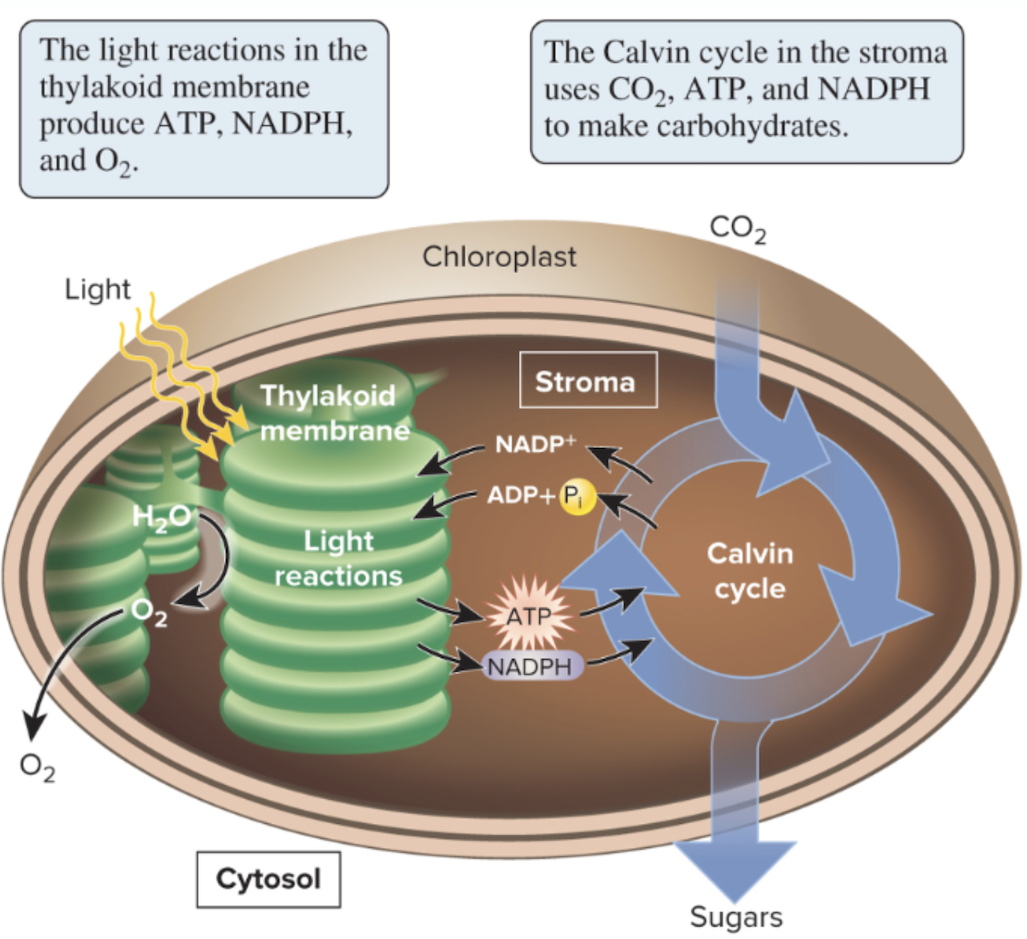
light reactions
involve a series of energy conversions
starting with light and ending with chemical energy
stored in ATP and NADPH
ATP and NADPH provide
the energy and electrons needed to make carbohydrates during the Calvin cycle
7.2
7.2
light is a type of
electromagnetic radiation
it consists of energy in the form of electric and magnetic fields
when light encounters a molecule
it may pass through the molecule
it may bounce off the molecule changing its path in a different direction
it may be absorbed by the molecule; pigments are molecules that can absorb light
pigments absorb some light energy and reflect others
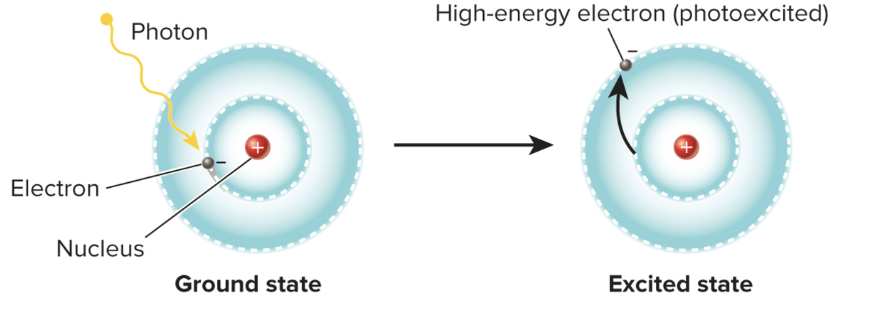
the wavelength of light that a pigment absorbs depends on the amount of energy needed to boost an electron to a higher orbital
after an electron absorbs energy
it is in an excited state, and it is usually unstable
excited electrons in pigments can be
transferred to another molecule or “captured“
two types of chlorophyll pigments
chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b
found in green plants and green algae
carotenoids are
another type of pigment
fruits and flowers
having different pigments allows plants to
absorb light at many different wavelengths
chlorophyll pigments absorb most strongly in
blue-violet and red parts of the visible spectrum
the thylakoid membranes contain 2 distinct complexes of proteins and pigment molecules called
PS II and PS I
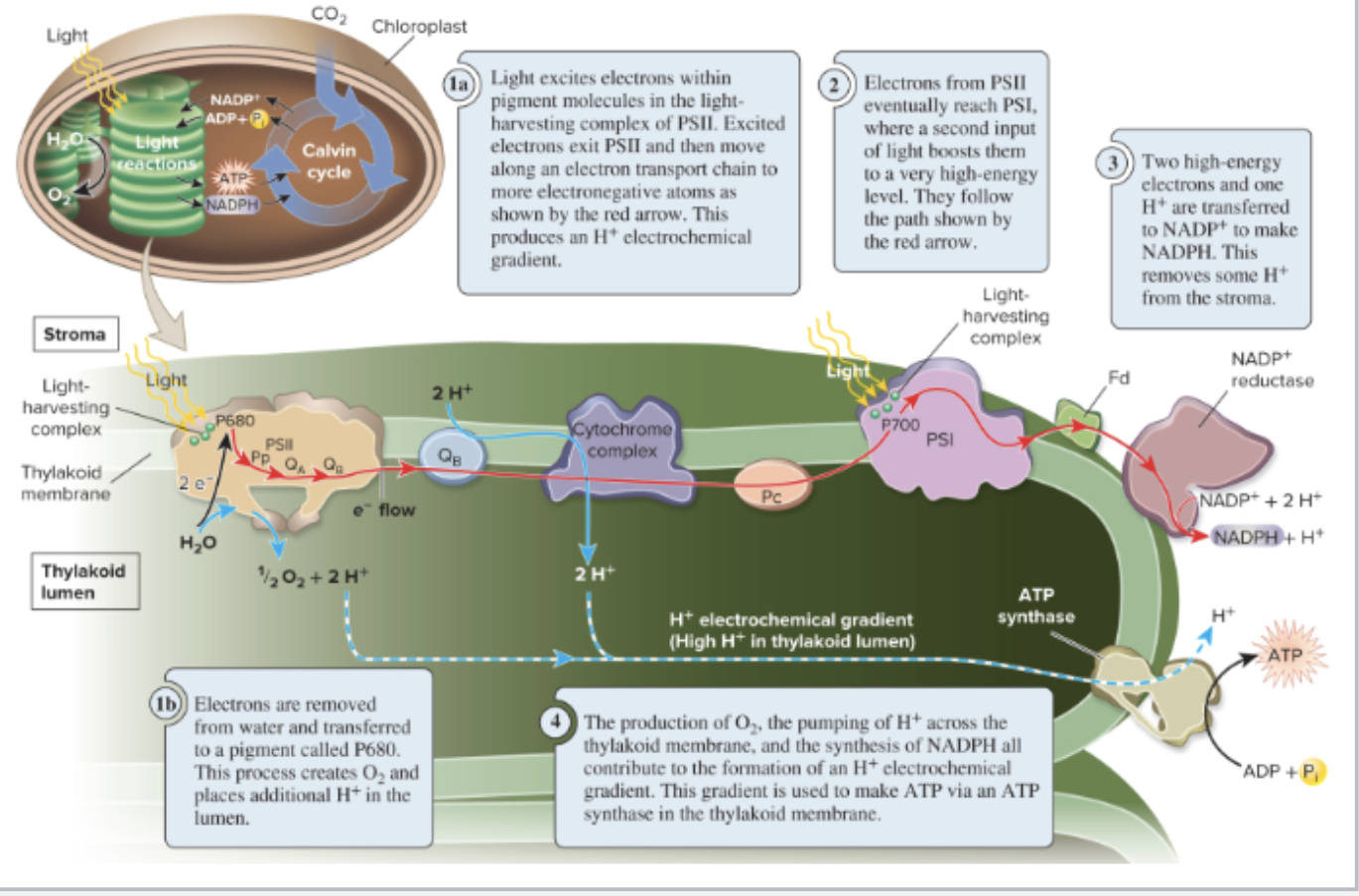
light excites pigment molecules in
BOTH PS II and PS I
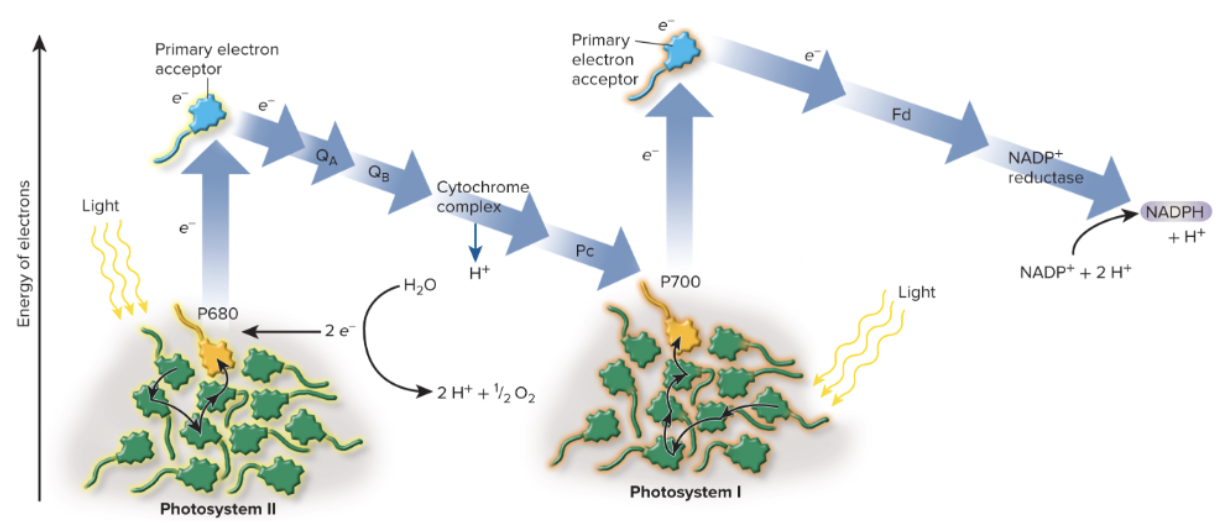
the combined action of PS II and PS I is termed
linear electron flow
produces O2, ATP, and NADPH
role of PS II in linear electron flow
oxidizes water
generating O2 and H+
role of PS I in linear electron flow
make NADPH
the process of ATP production in the chloroplast is called
photophosphorylation
linear electron flow produces ATP and NADPH in roughly equal amounts, however
the Calvin cycle uses more ATP than NADPH
cyclic electron flow
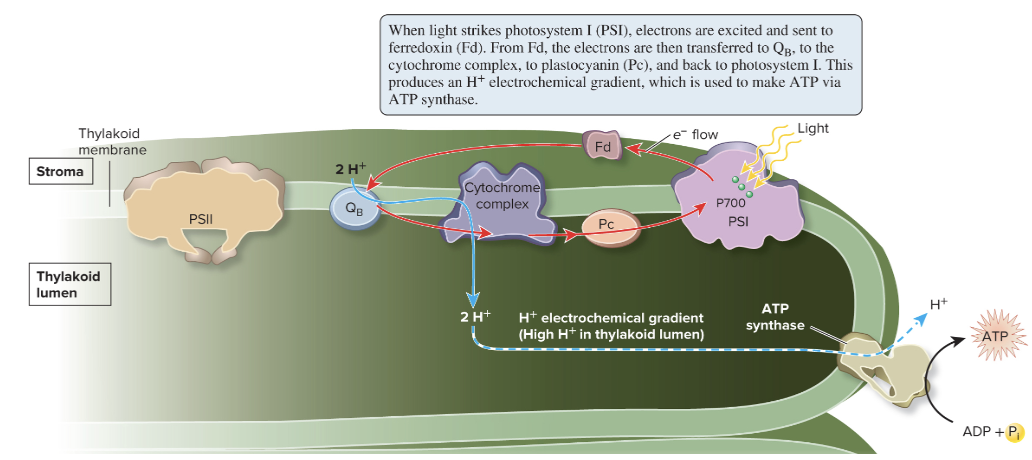
cyclic electron flow produces only
ATP
cyclic flow is favored when the level of NADP+ is low and
NADPH is high
also favored when ATP levels are low
7.3
7.3
PS II and PS I have 2 main components
a light-harvesting complex and a reaction center
light-harvesting complex
directly absorbs photons of light and transfers energy between pigments by a process of resonance energy tramsfer
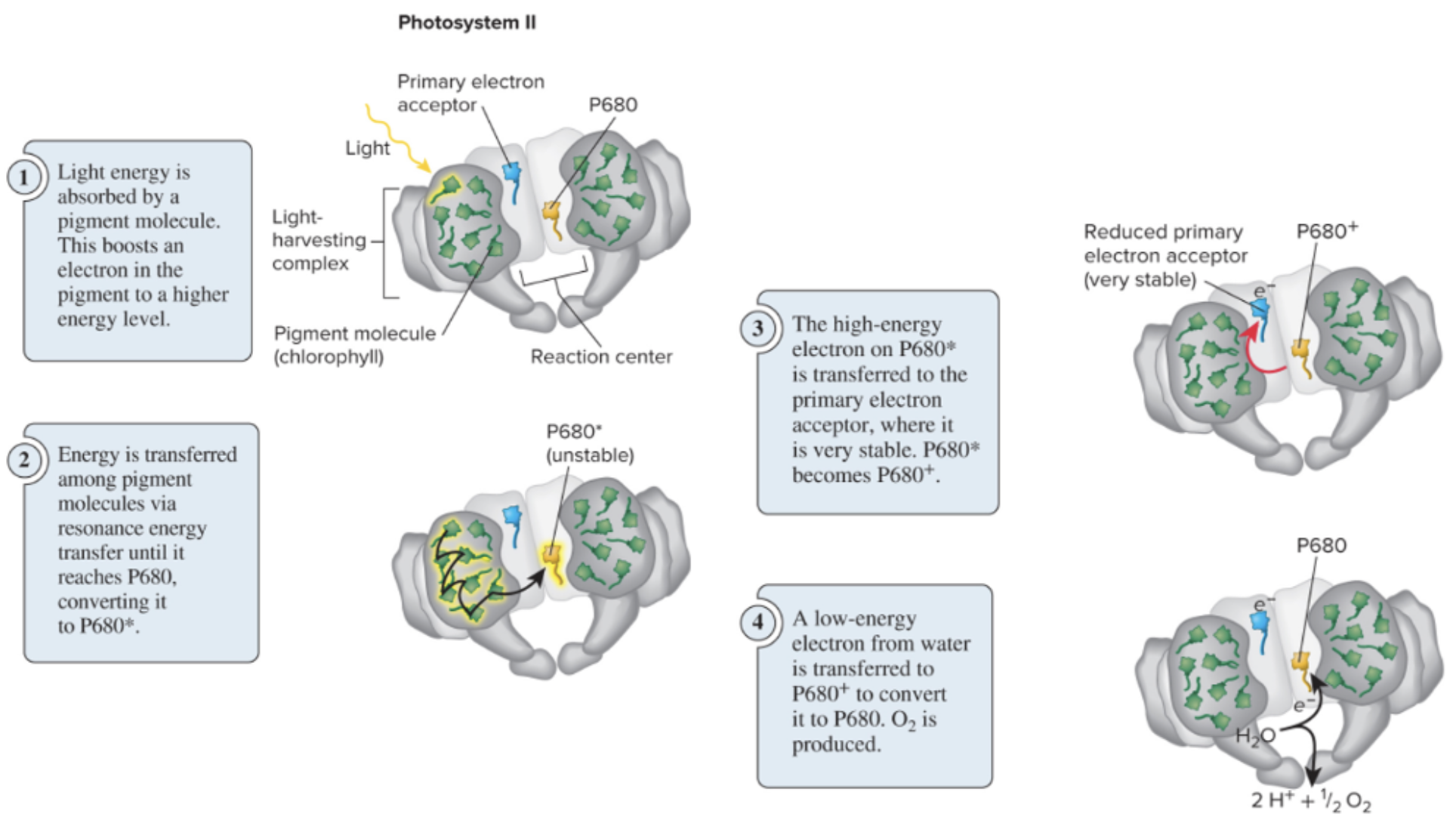
reaction center
where the redox reaction takes place
contains P680 (special pigment molecule)
unlike other pigments, P680 releases
its high energy electron and is oxidized
P680* → P680^+ + e-
water is oxidized to replace the
electrons on P680^+
PS II is the only known protein complex that can
oxidize water
resulting in the release of O2
Z scheme
a model developed in 1960 that proposed that photosynthesis involved 2 events of light absorption
7.4
7.4
the ATP and NADPH generated during the light reactions are used during
the Calvin cycle to make carbohydrates
the reactions of the calvin cycle require
a massive input of energy
for every 6 CO2 incorporated
18 ATP and 12 NADPH must be used
the product of the calvin cycle is
G3P
a carbohydrate with 3 carbon atoms that can be used in the synthesis of glucose and other organic molecules
carbon fixation
CO2 is incorporated into RuBP, 5-carbon sugar
enzyme rubisco catalyzes this reaction
6 carbon intermediate splits into 2 3-carbon molecules
reduction and carbohydrate production
ATP is used as a source of energy
NADPH is used as a source of high energy electrons
G3P is produced
regeneration of RuBP
most of G3P is used to regenerate RuBP to continue the cycle
7.5
7.5
Environmental conditions can alter the operation of the calvin cycle
temperature
water availability
light intensity
most plants are called C3 plants because
the first molecule that CO2 is incorporated into is a 3-carbon molecule
photorespiration occurs when
rubisco adds O2
as intermediates are processed
a molecule of CO2 is released
if C3 plants are subjected to hot and dry environments
as much as 25%-50% of their photosynthetic work is reserved by photorespiration
C4 plants mace oxaloacetate (4-carbon molecule) in
the first steps of carbon fixation
mesophyll cells capture CO2 into oxaloacetate using
an enzyme that only binds to CO2
then transports the captured carbon to the bundle-sheath cells, where the Calvin cycle happens
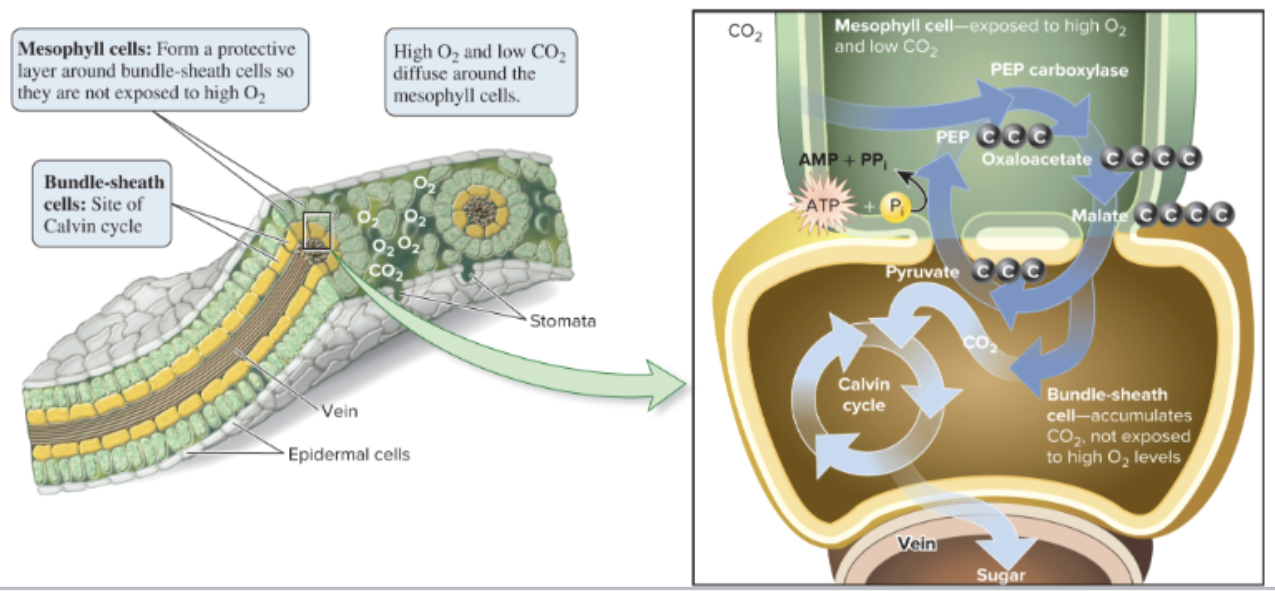
CAM plants open their stomata at
night
CO2 is captures and stored
which is better — C3 or C4?
depends on environment
C4 and CAM plant adaptations evolved to help plants living in hot and dry environments to
conserve water and minimize photorespiration