visceral system
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
viscera
organs that regulate internal environment
occupy cavities of body: thorax, abdomen, pelvis. also neck and head
involved with secretion, excretion, digestion, absorption
can be hollow or solid
hollow viscera
Levels:
lumen
mucosa
muscularis
serosa (external layer) - minimises friction
muscle coats
wall: circular and longitudinal smooth muscle
provides motility and expansion
lumen of tubular (hollow) viscus
may have dilations and constrictions
constrictions - at end and beginning and also at specific sites
narrow where it approaches the wall of hollow viscus
sphincter
1) anatomical: localised muscle thickening around wall of tubular viscus - controls passage and prevents reflux of contents
can be voluntary (made of skeletal muscle, somatic NS) or involuntary (made of smooth muscles, autonomic NS)
2) functional: no localised muscular thickening
solid viscera
Glands: cluster of secretory cells
eg: pancreas, liver, thyroid gland
external capsule (protection) and serosa (reduces friction)
may have subdivisions: outer cortex, inner medulla
exocrine vs endocrine glands
exocrine glands:
glands that secrete into a duct or system of ducts
ducts emmerge from hilum of viscera
open into hollow viscera
eg: liver and bile duct
endocrine glands:
glands that secrete directly into blood stream
usually secrete hormones that act in other parts of body
rich blood supply
eg: adrenal glands
pancreas is both exocrine and endocrine
serous membrane
single membrane that lines a body cavity and contains a space within it
provides fluid which lubricates the cavity
lines body wall
covers or all of a viscus
subdivided into parietal and visceral layers
eg: pleura and pericardium in thoracic cavity
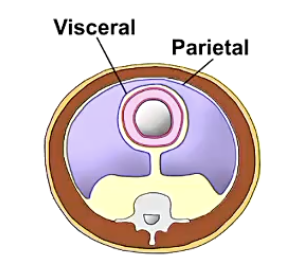
peritoneal cavity
a closed cavity in the abdomen lined by a serous membrane called the periotoneum
role of mesentrey
a mesentery provides viscus with:
1) a pathway for nerves and vessels
2) mobility
referred pain
is the perception of pain in areas other than the site of stimulation.
visceral pain is usually referred to somatic regions