organic chemistry - C10 + C11
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
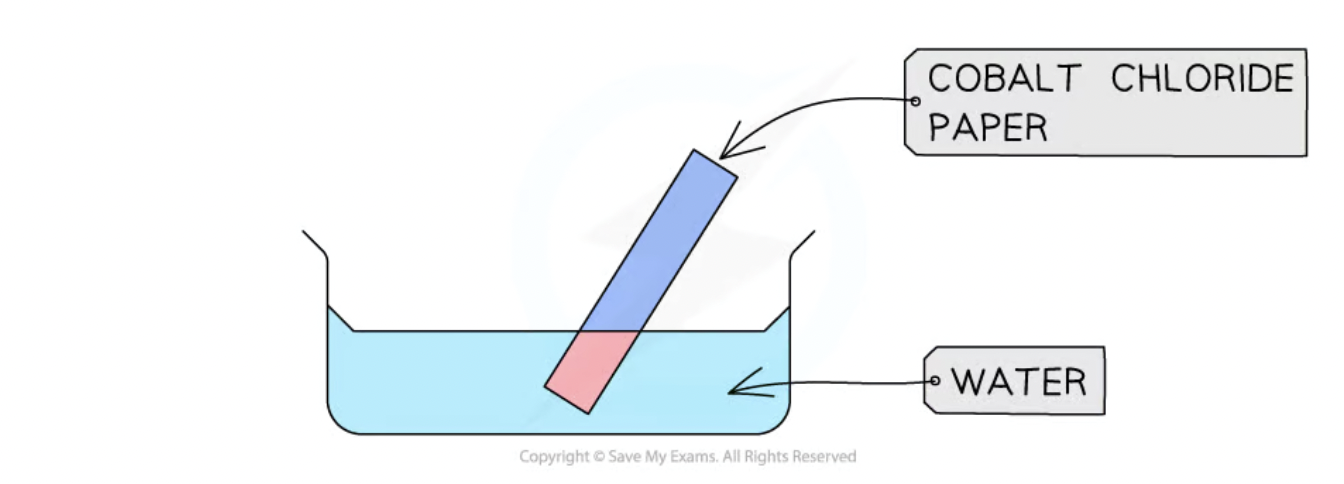
chemical test for the presence of water - cobalt (II) chloride
done with cobalt chloride paper
in the presence of water the paper turns from blue to pink
(Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride, CoCl2, is blue
Hydrated cobalt(II) chloride, CoCl2•6H2O is pink)
reversible
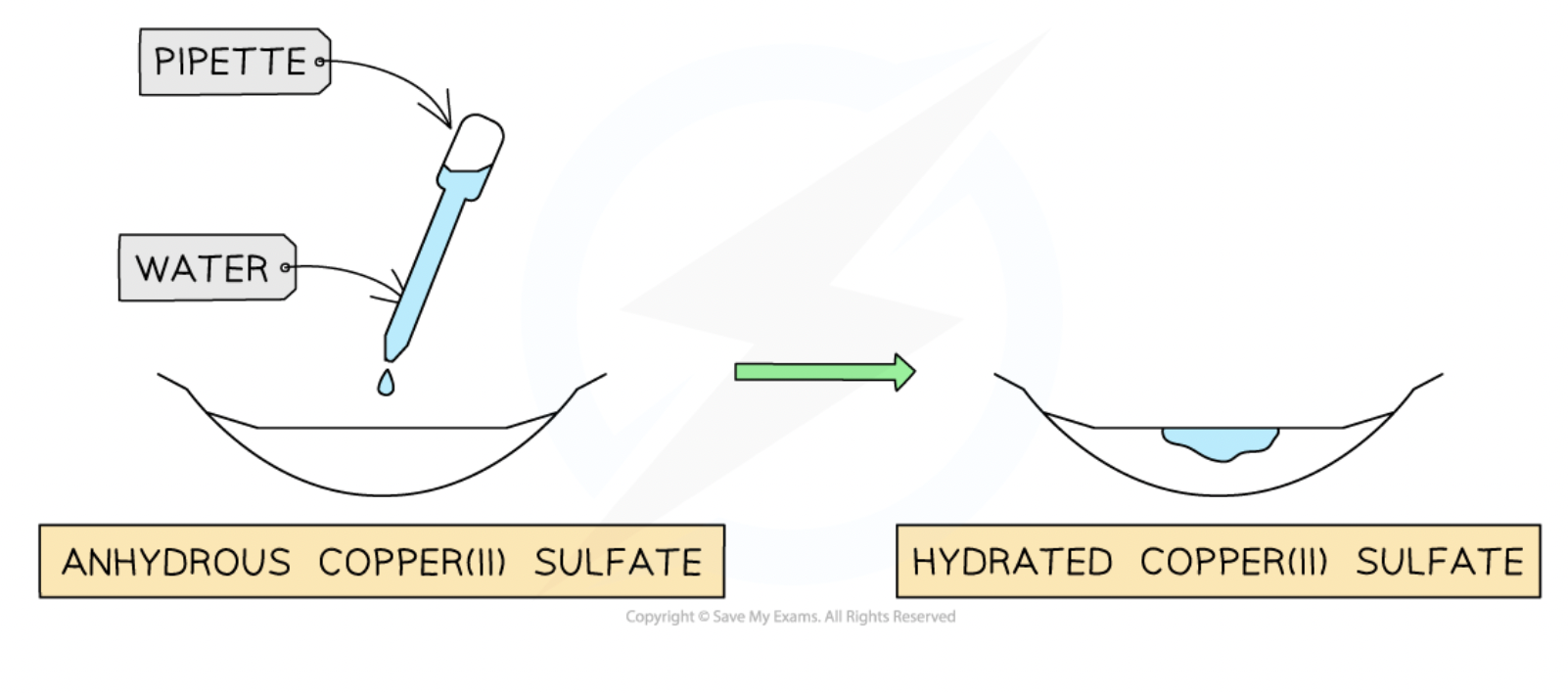
chemical test for the presence of water - copper(II) sulfate
in the presence of water copper(II) sulfate turns from white to blue
reversible
how to test for the purity of water
Impurities tend to increase the boiling point of water → impure water boils at temperatures above 100 oC
Impurities tend to decrease the melting point of water → impure water melts at temperatures below 0 oC
distilled water use
used in practical chemistry rather than tap water because it contains fewer chemical impurities
treatment of the water supply - stage 1
sedimentation -
Water is pumped into sedimentation tanks and allowed to stand for a few hours
Mud, sand and other particles will fall to the bottom of the tank due to gravity and form a layer of sediment
The water is then filtered through sand and gravel to remove smaller particles
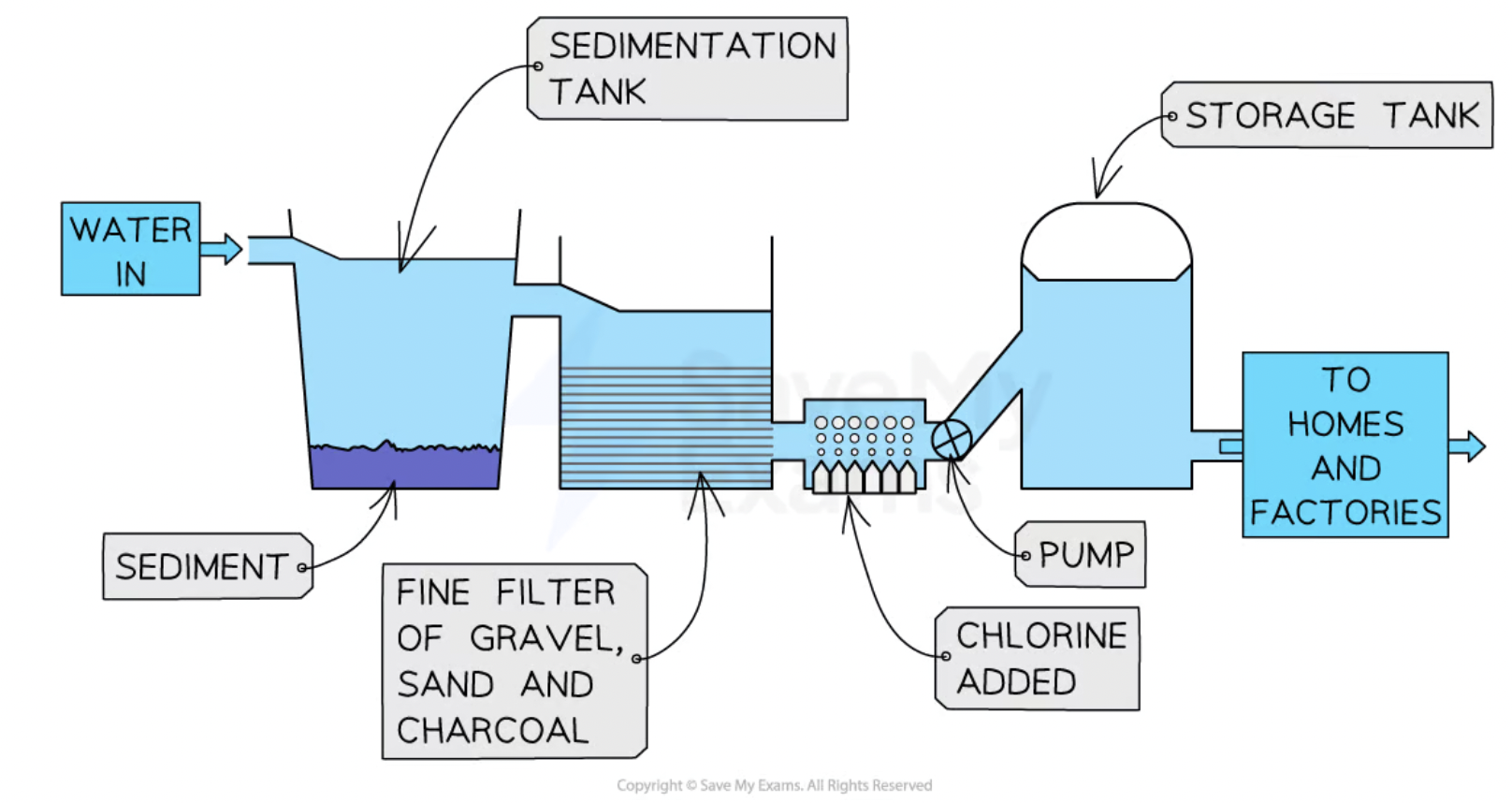
treatment of the water supply - stage 2
filtration - treatment with carbon(charcoal)
removes unpleasant tastes + odors
treatment of water supply - stage 3
chlorination
Bacteria and other microorganisms are too small to be trapped by the filters
chlorine is added to the water supply to kill bacteria and other microorganisms (pathogens)
e.g Cholera and typhoid →bacterial diseases that come from untreated water
composition of air
78% nitrogen (N2)
21% oxygen (O2)
1% - noble gases and carbon dioxide
sources of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide + particulates
carbon dioxide - complete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
carbon monoxide + particulates - incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
sources of methane
decomposition of vegetation
waste gases from digestion in animals
sources of oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
oxides of nitrogen - car engines
sulfur dioxide - combustion of fossil fuels which contain sulfur compounds
effects of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide
carbon dioxide - increased global warming → climate change
carbon monoxide - toxic gas
effects of particulates and methane
Particulates - increased risk of respiratory problems
Methane - increased global warming → climate change
Effects of oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
oxides of nitrogen - acid rain + respiratory problems
Sulfur dioxide - acid rain
How to reduce carbon dioxide emissions
hydrogen and renewable energy supplies (e.g solar or wind energy)
more fuel-efficient vehicles, (e.g. electric and hybrid cars)
Reducing the number of vehicles on the road ( e.g. public transport)
Recycling or reusing products made from crude oil
Reducing household energy consumption ( e.g. turning lights out, using more efficient appliances)
Reducing deforestation and / or re-forestation
Planting more trees, can help reduce the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide through photosynthesis
How to reduce methane emissions
Reduce the amount of livestock farming
(Methane is produced during digestion in animals)
How to reduce acid rain
Acid rain is caused by oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
Catalytic convertors in vehicles can be used to remove oxides of nitrogen
How to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions
Using fuels which contain low levels of sulfur
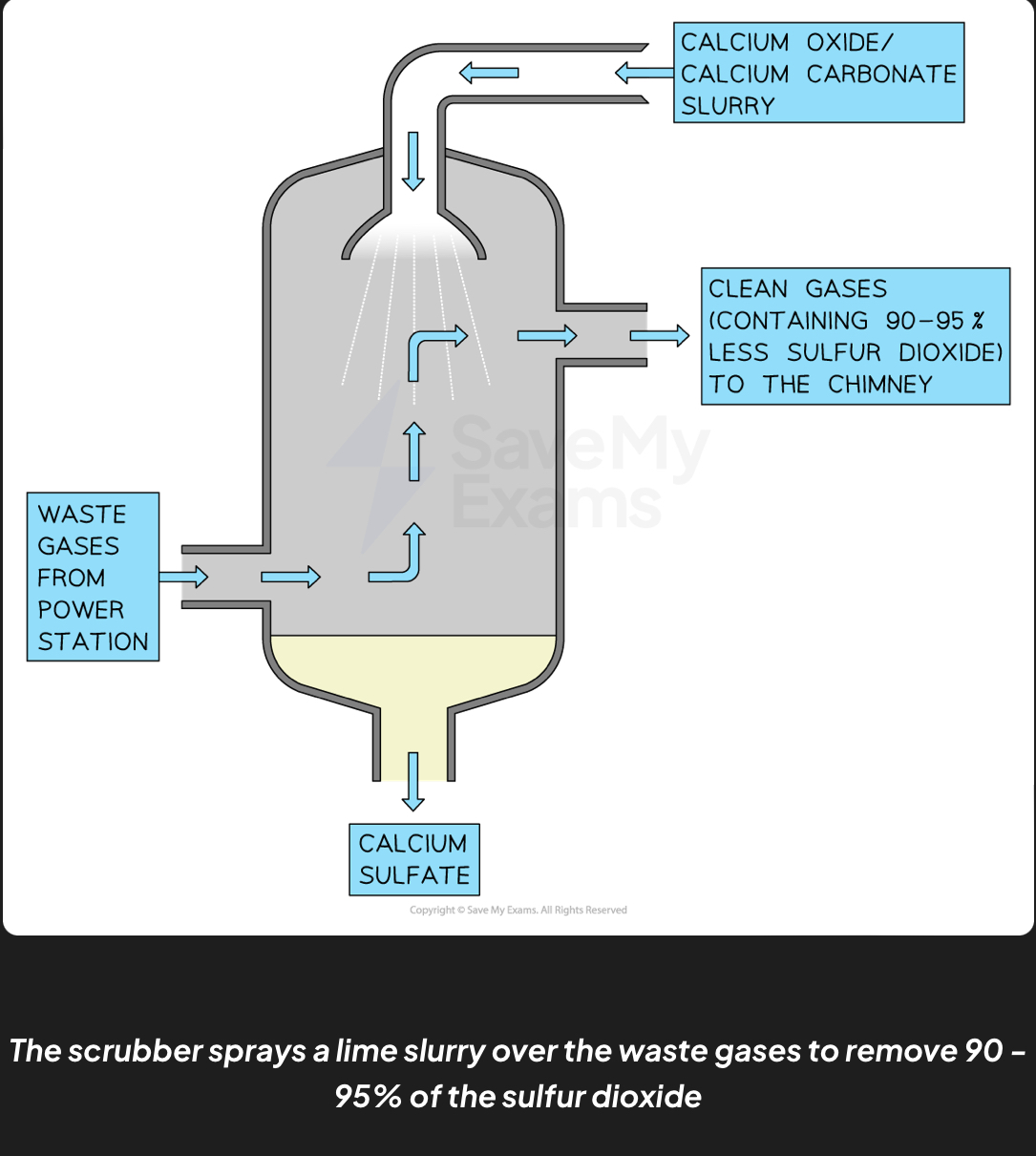
Flue gas desulfurization
main way to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions
Waste gases from coal fired power stations are passed into a scrubbing chamber
They are sprayed with a wet slurry of calcium oxide and calcium carbonate
The calcium compounds react with sulfur dioxide to produce calcium sulfate
How do carbondioxide and methane cause global warming
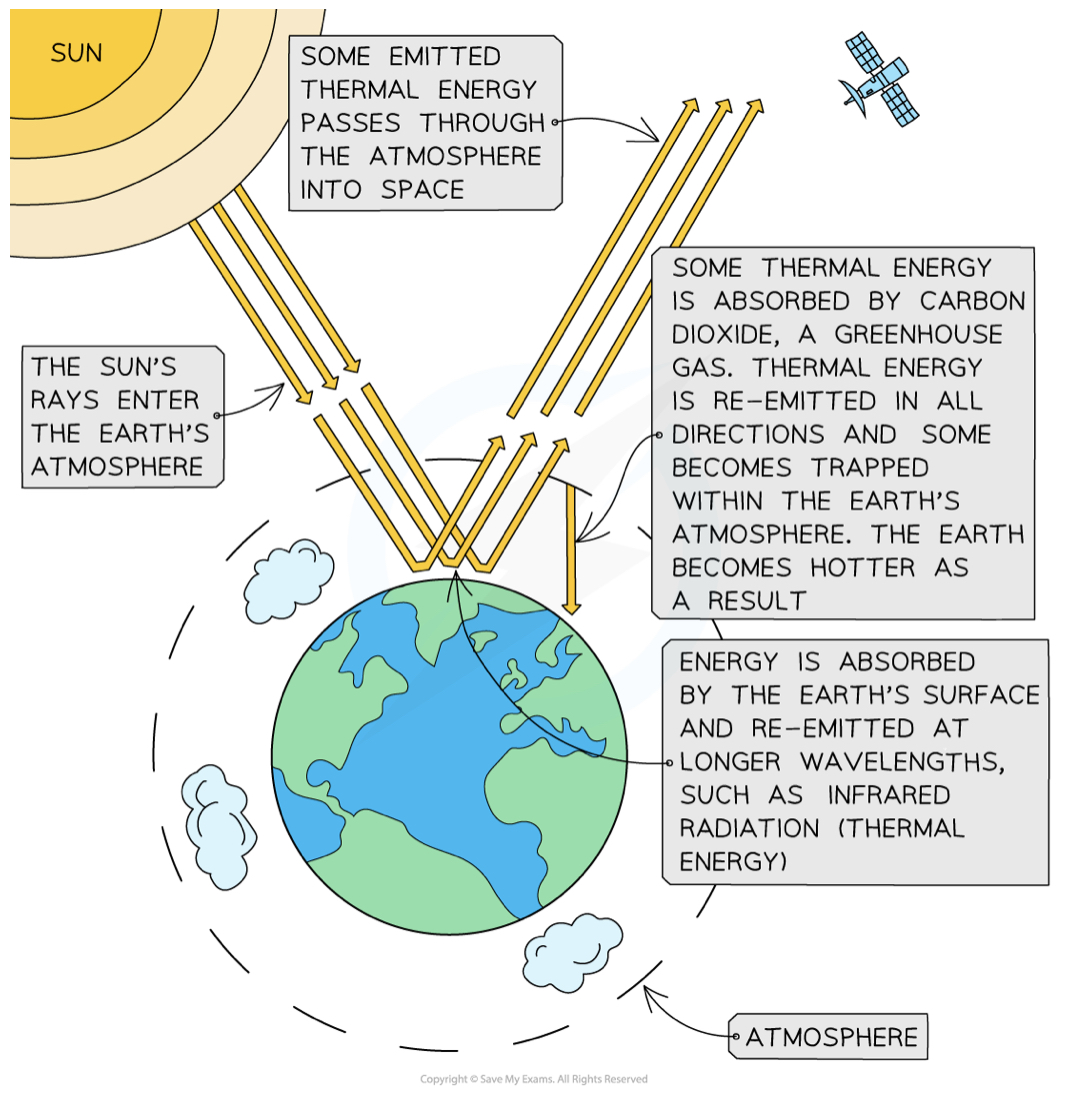
Green house effect
some thermal energy is absorbed by greenhouse gases(e.g carbon dioxide and methane) and is re-emitted in all directions
This reduces the thermal energy lost into space and traps it within the Earth’s atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm
How do oxides of nitrogen form in car engines
nitrogen and oxygen react in the high pressure and temperature conditions of internal combustion engines and blast furnaces
How to catalytic converters work ?
2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2
contain a series of transition metal catalysts in a honeycomb shape + converter to increase the surface area for reaction
A series of redox reactions occurs which neutralizes the greenhouse gases
Saturated vs unsaturated compound
saturated - molecules in which all carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds
Unsaturated - molecules in which one or more carbon-carbon bonds are not single bonds
Homologous series definition
A family of similar compounds with similar chemical properties
General characteristics of a homologous series
have the same general formula
Display a trend in physical properties
Fossil fuels
Coal, natural gas, petroleum
Describe methane, hydrocarbons,petroleum
methane - the main constituent of natural gas
Hydrocarbons - compounds that contains hydrogen and carbon only
Petroleum/crude oil - a mixture of hydrocarbons, not useful by itself as a mixture
Why does fractional distillation of crude oil work?
The molecules in each fraction have similar properties and boiling points, which depend on the number of carbon atoms in the chain
size of molecule is directly related to how many carbon and hydrogen atoms the molecule contains
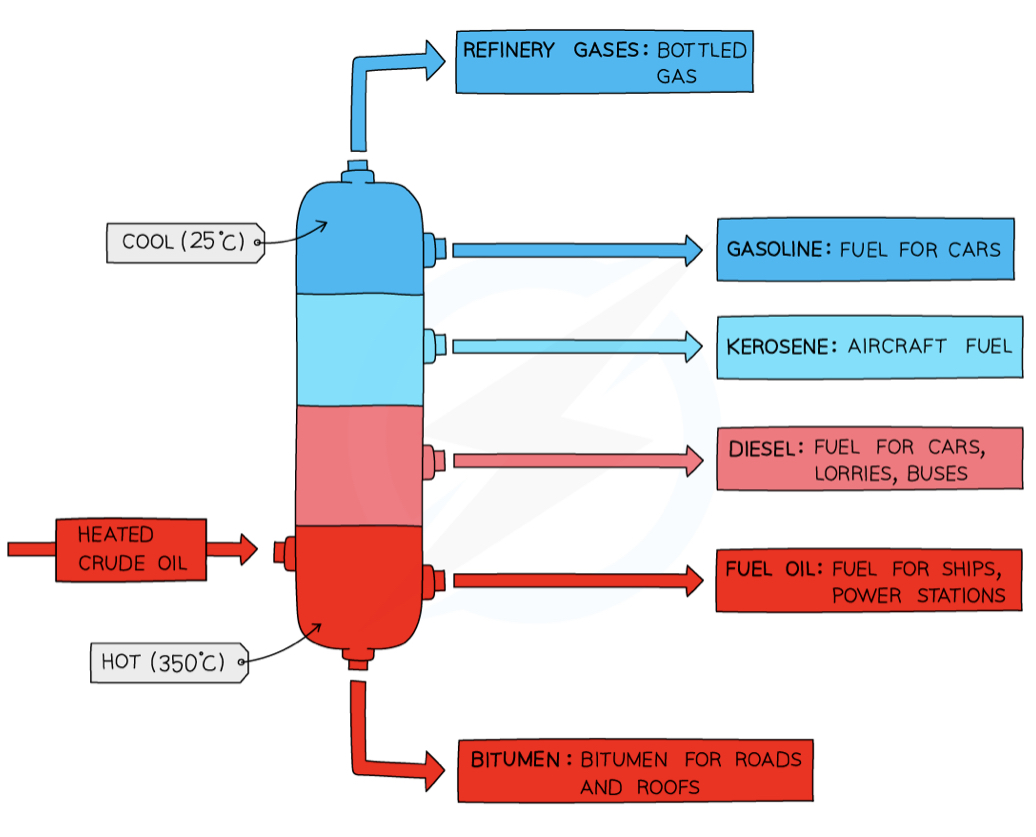
The separation of petroleum by fractional distillation
Carried out in a fractionating column - very hot at bottom and cooler at the top - temperature gradient
crude oil is heated → vaporizes
vapors of hydrocarbons enter column
Vapors of hydrocarbons with high boiling points condense at the bottom of the column
Vapors of hydrocarbons with lower boiling points rise up the column and condense at the top
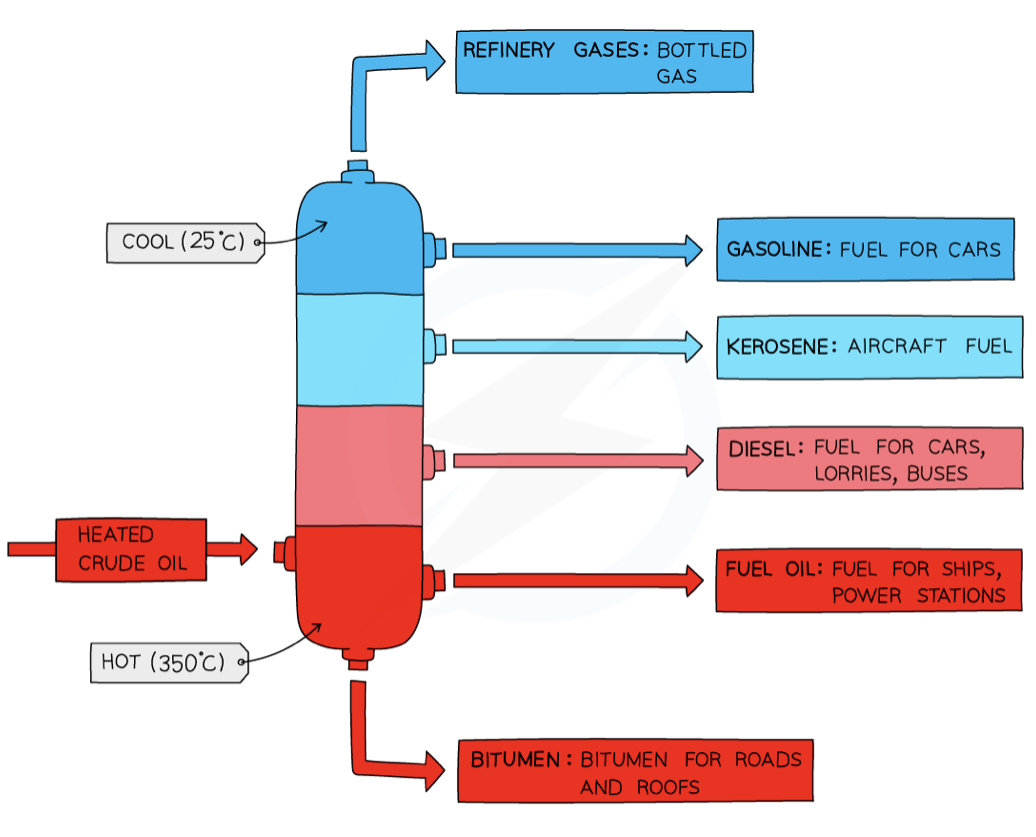
Uses of fractions - refinery gas fraction + gasoline/petrol fraction
refinery gas - used in heating + cooking
Gasoline/petrol - for fuels used in cars
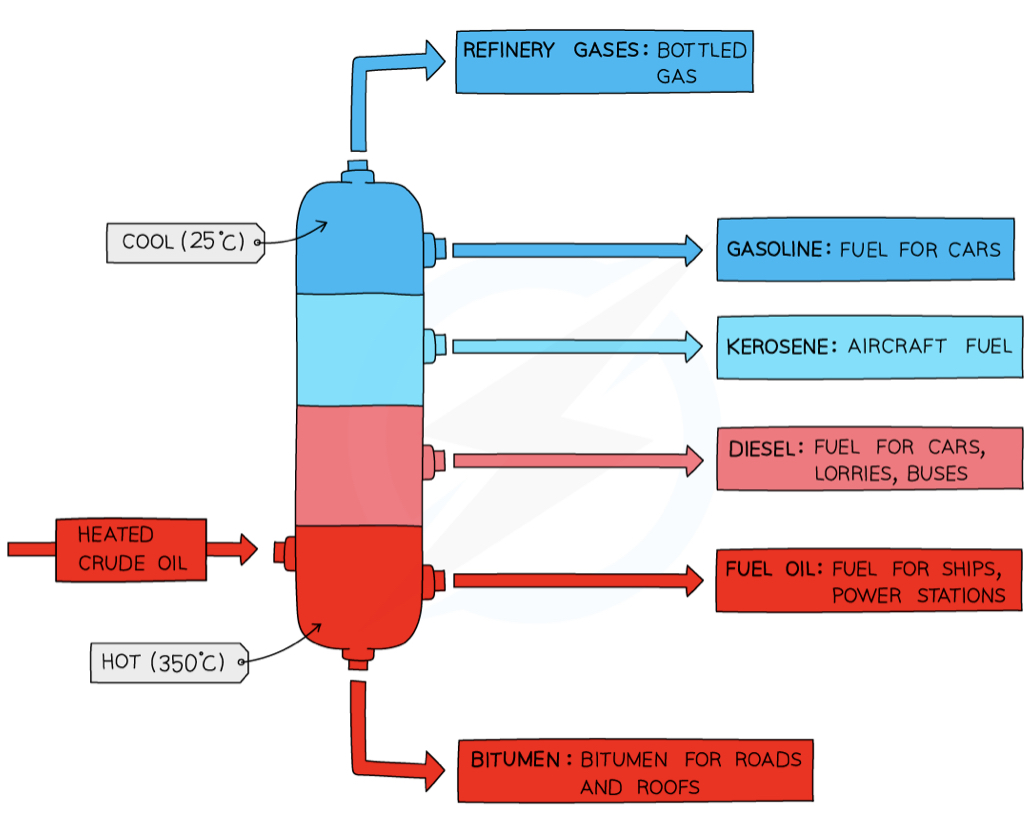
Uses of fractions - naphtha fraction + diesel/gas oil fraction + bitumen
naphtha - chemical feedstock
Diesel/gas oil - fuel used in diesel engines
Bitumen - making roads
Alkanes
saturated hydrocarbons - single covalent bonds only
Properties
un reactive except for combustion reactions
Bonding in Alkenes
Includes a double carbon-carbon covalent bond
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
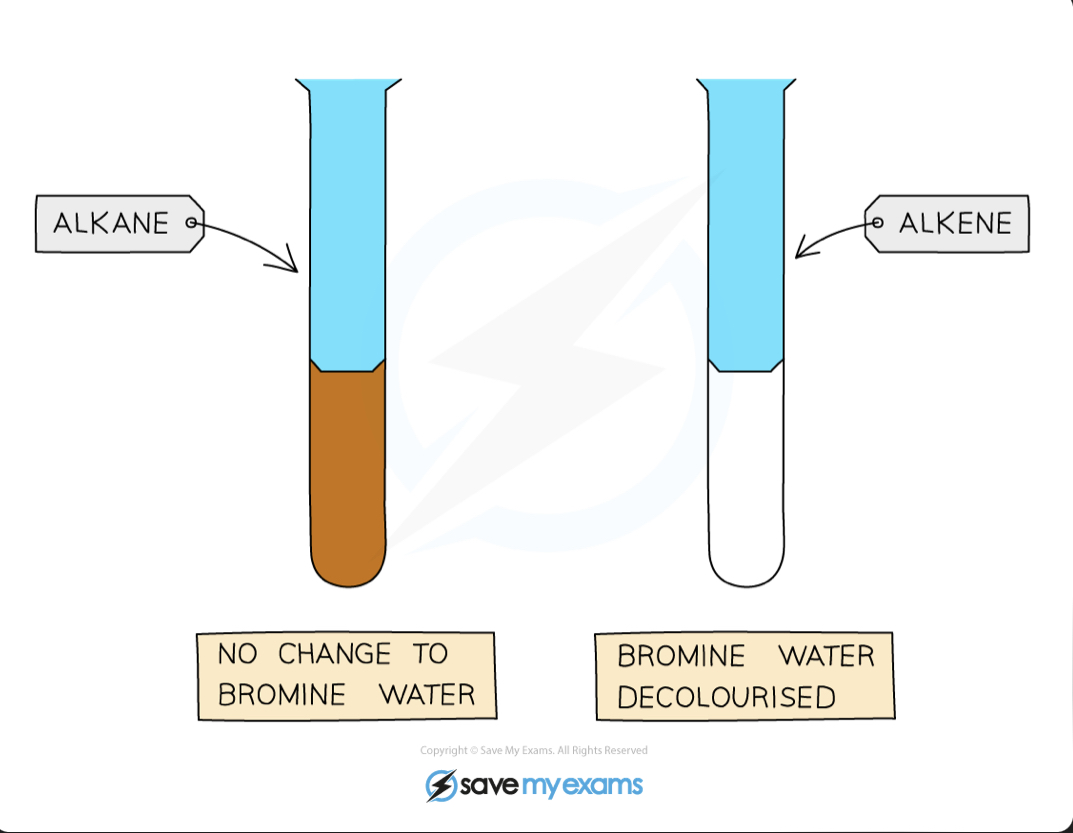
How to tell the difference between alkanes and alkenes experiment
See their reaction with aqueous bromine
Alkane - no change to bromine water
Alkene - will cause bromine water to become discolored
Alkene + Alkane + alcohol general formula
Alkene - CnH2n
Alkane -CnH2n+2
alcohol - CnH2n+1OH
Manufacturing of alkenes and hydrogen - cracking
Cracking involves heating the hydrocarbon molecules to around 600 – 700°C to vaporise them
vapors pass over a hot powdered catalyst of alumina or silica
Vapors come in contact with catalyst → breaks covalent bonds into molecules → thermal decomposition reactions
produces an alkene + another hydrocarbon
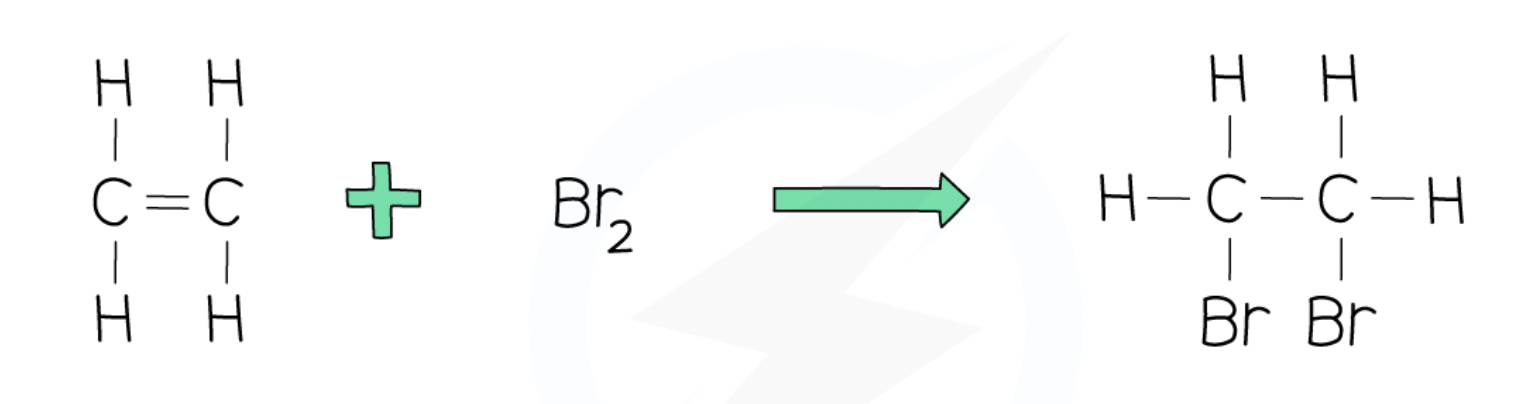
Addition reaction - alkene + bromine
ethene + bromine → dibromoethane
C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
decolorises bromine
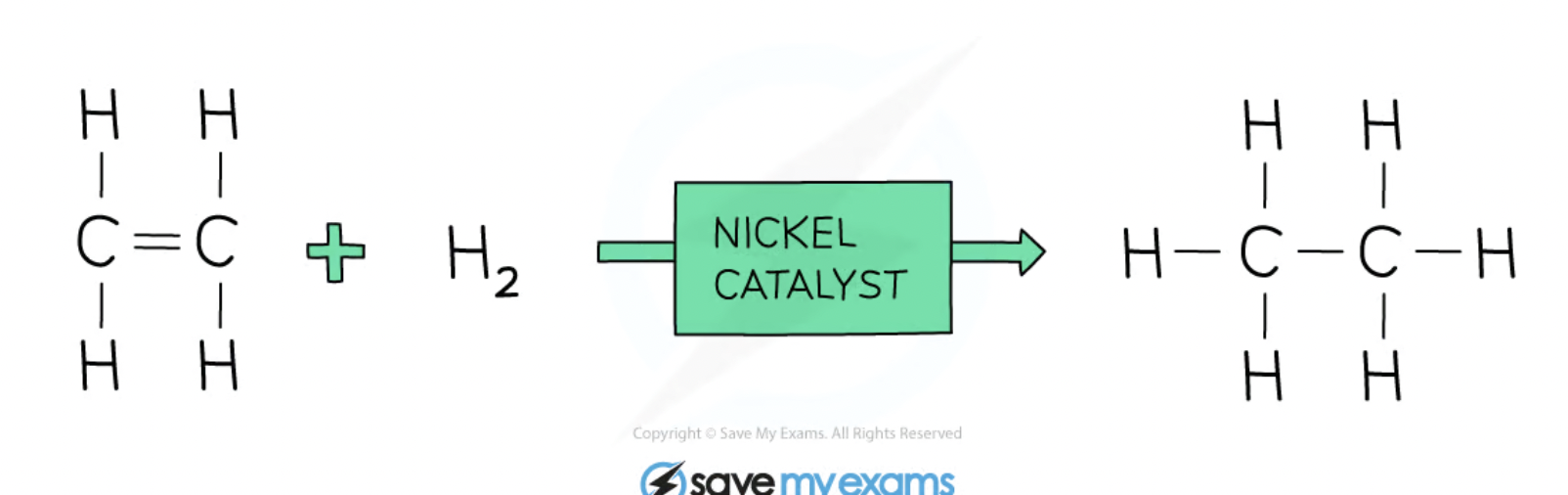
Addition reaction - alkene + hydrogen
make an alkane
e.g ethene + H2 → ethane, propene + H2 → propane (has to be in presence in nickel catalyst)
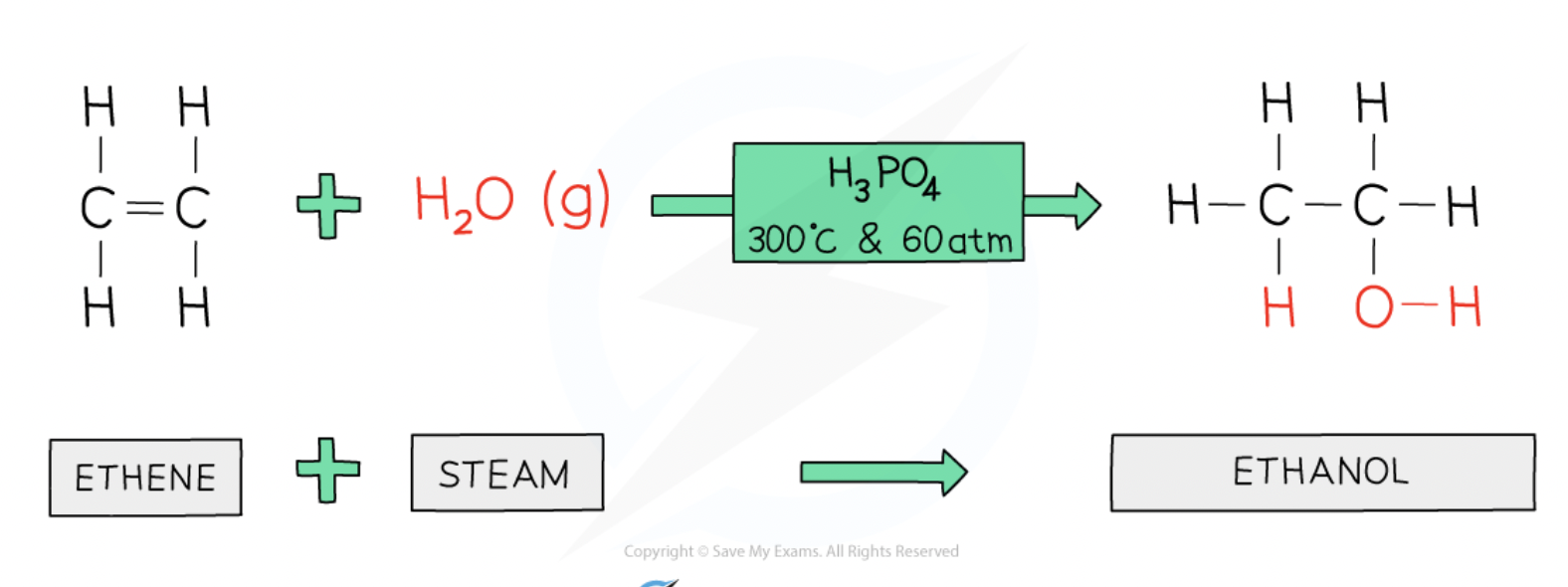
Addition reactions - alkene + steam
make an alcohol
requires acid catalyst
e.g ethene + steam → ethanol
combustion of ethanol
produces carbon dioxide and water
this is because it burns excess oxygen
C2H5OH (l) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l)
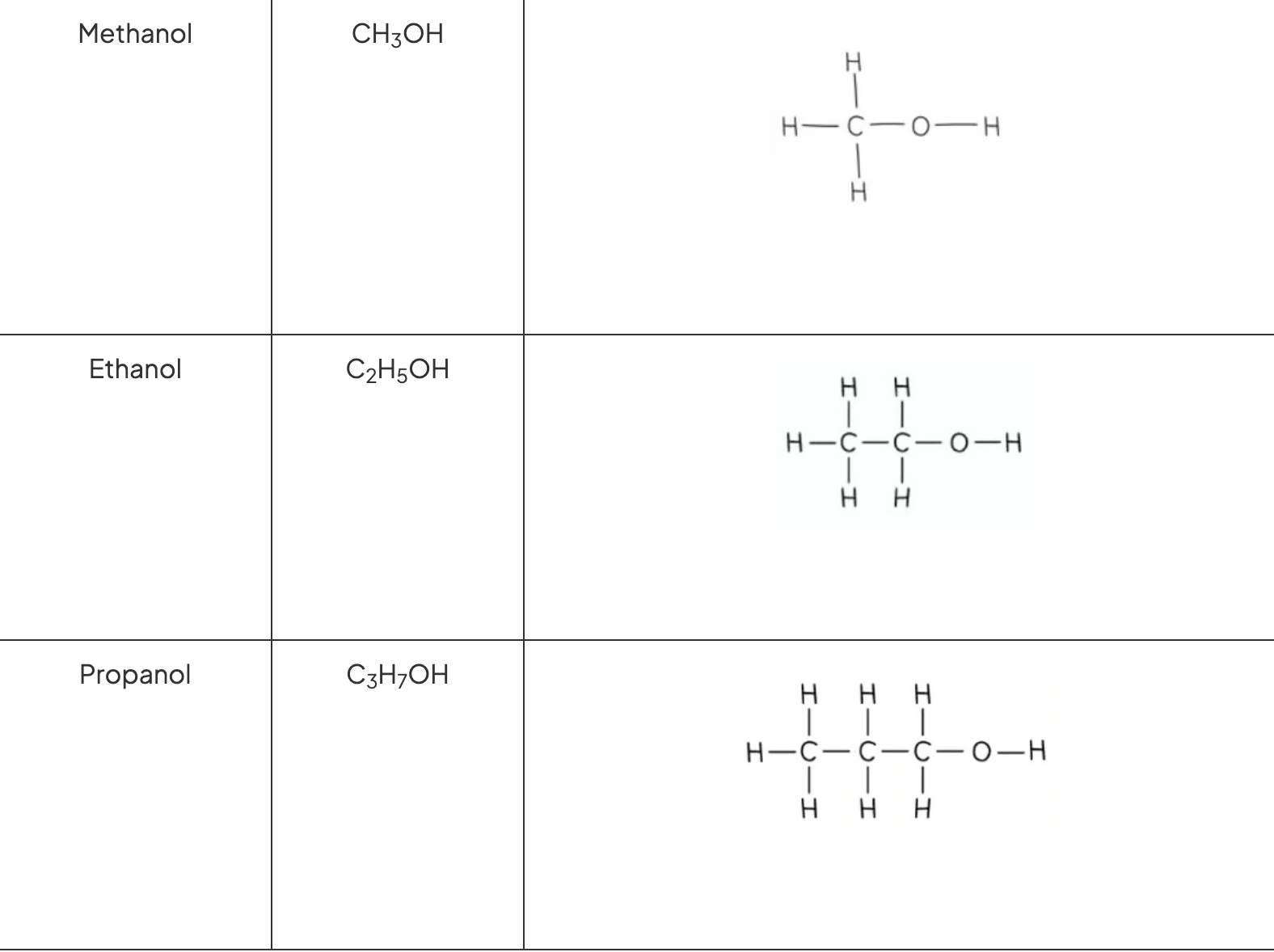
Ethanol, Methanol and Propanol formula
ethanol - C2H5OH
methanol - CH3OH
propanol - C3H7OH
ethanol uses
solvent
fuel in cars
polymers definition
large molecules built up from many smaller molecules called monomers
formation of polyethene
addition polymerisation using ethene monomers
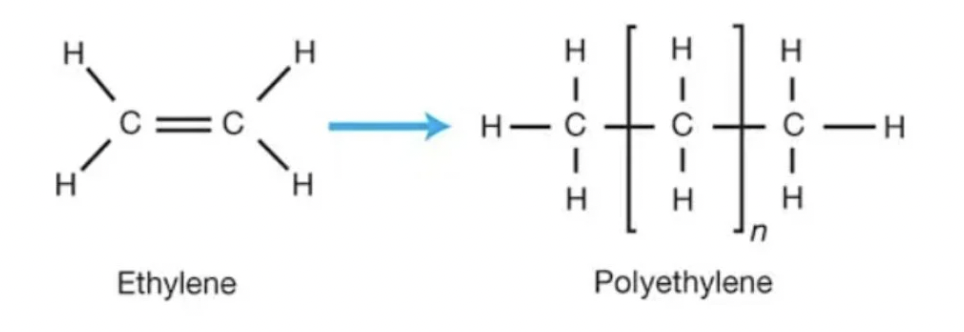
addition polymerisation
joining same alkene monomers
double bond breaks
polymer formed → only single bonds
forms only polymer
condensation polymerisation
2 different monomers linked together with the removal of a small molecule (usually H2O)
forms polymer + 1 water molecule per linkage
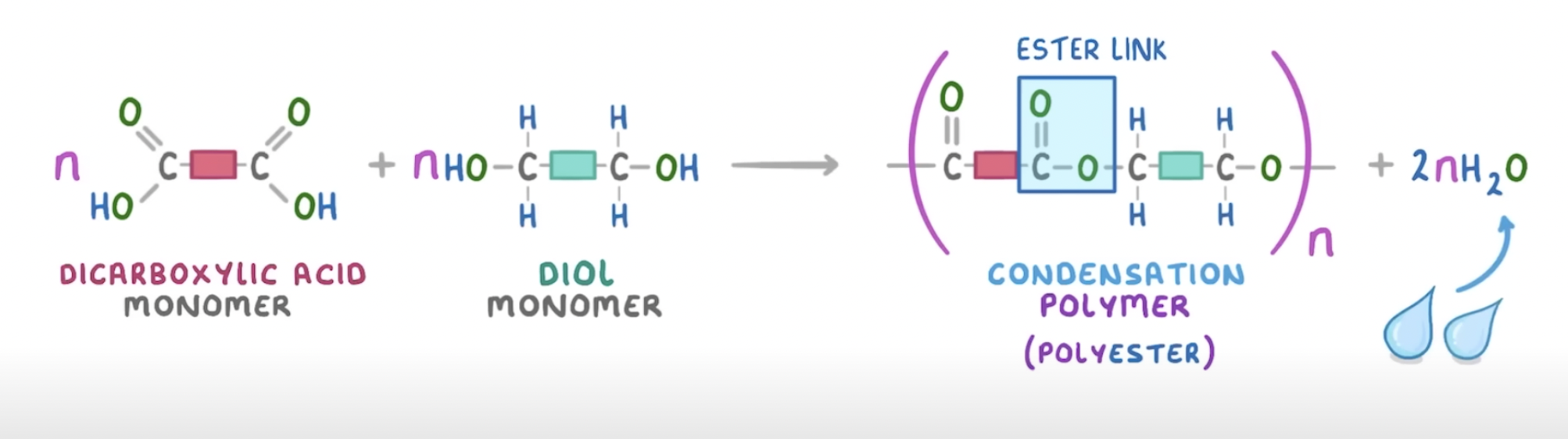
forming Nylon
a polyamide is formed from a dicarboxylic acid and a diamine
condensation polymerisation
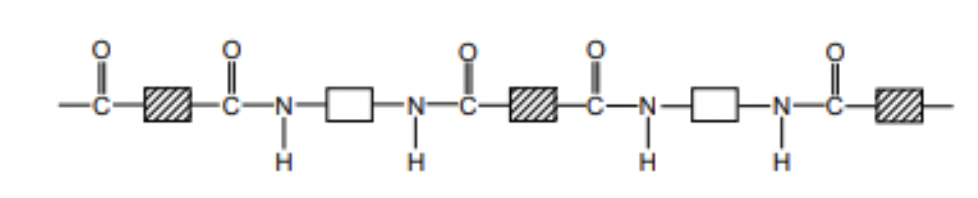
polymer vs polyester
polyester - condensation polymer, biodegradable
polymer - addition polymer, not biodegradable