APUSH CHPT 34 "America in World War II"
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
assigning a reading the day after winter break is kinda cruel but wtv
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
ABC-1 Agreement
Us and Germany agreed that if US joined WWII, we would coordinate military planning and protect GB. “getting Germany first'“
“active defence”
Pacific was put on ____.
National Unity
Pearl Harbor inspired massive _____.
Japanese
Racial group targeted during WWII
Executive Order No. 9066
Japanese were rounded up and sent to internment camps.
Internment camps
Where the Japanese were cruelly sent during WWII bc of fear during a Japanese invasion, they would help them and be saboteurs to the US.
Korematsu vs US
Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of Executive Order No. 9066
War Production Board (WPB)
American factories put out an avalanche of weaponry. Halted the manufacture of non-essential items & assigned priorities, for transportation and raw materials.
Henry Kaiser “Sir Launchalot”
Fastest ship builder
Office of Price Administration (OPA)
Helped bring down prices with extensive regulations
Rationing
Held down the consumption on critical goods.
National War Labor Board (NWLB)
Imposed ceilings on wage increases
United Mine Workers
Most prominent labor union group. (John L. Lewis)
Smith-Connally Anti-Strike Act
Authorized the federal government to seize and operate tied up industries
Most popular “women in arms”
Women’s Army Corps (WACs)
Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Services (WAVES) (navy)
U.S. Coast Guard Women’s Reserve (SPARs)
Bracero Program
helped w/ shortages. Mexican workers came to work on farms and railroads
“braceros”
Farmers from Mexico who came to work in farms b/c of Bracero Program
Rosie the Riveter
A former housewife turned war hero, Rosie emerged from the kitchen and built the machinery necessary to fight and win World War II. Posters emblazoned with her picture became a symbol of wartime courage and patriotism.

Baby Boomers
a person born in the years following World War II, when there was a temporary marked increase in the birth rate.
Men who were drafted (types)
Single men, Married men, Married w/ children
“Service Wives”
$50 monthly stipend from the government
“Latchkey” Children
Children left home alone by working moms
A. Phillip Randolph - “Negro March on Washington”
To demand equal opportunities in war jobs and military
Fair Emplyment Practices Commission (FEPC)
Banned racial discrimination in goverment and war production jobs
“Double V'“
Victory at home and abroad (for racial equality for blacks)
Congress of Racial Equality (CORE)
Established during WWII, pioneered key tactics of the modern civil rights movement, using sit-ins and other forms of civil disobedience to challenge segregation.
Cotton Picker
Rivaled the impact of Eli Whitney’s cotton gin, rid the South’s need of cheap labor. Allowed many BlackAmericans to move to urban areas (Second Great Migration)
Tuskegee Airmen
The Tuskegee Airmen were dedicated, determined young men who volunteered to become America's first Black military airmen.
Doris Miller
As a mess attendant second class in the United States Navy, Miller helped carry wounded sailors to safety during the attack on Pearl Harbor. He then manned an anti-aircraft gun and, despite no prior training in gunnery, shot down between four and six enemy planes.
“Code-Talkers”
Navajos who transmitted radio-transmissions in their native language which the Germans and Japanese couldn’t understand.
Detroit
Most serious race riot - 1943, 34 killed
“Zoot Suit” Riots
Tensions rose between white servicemen and Mexican youth.
Election of 1944
Democrats: FDR/Truman (much focus on VP)
Republicans: Thomas Dewey/John Bricker (liberal/more conservative, balance e/o. young and vibrant)
FDR won bc the war was going well and many trusted him to bring victory
FDR’s CLOSEST ELECTION
“wolfpacks”
Groups of German U-boats, disposed in long lines, would rally when one of them by radio signaled a sighting and overwhelm the convoy by weight of numbers. Made Germany dominate the Atlantic.
Sonar (radar)
Vital in the destruction on the German advantage and domination of the Atlantic. (technology)
Also “Engima” code-breakers were useful.
General Erwin (“Desert Fox”) Rommel
German General who led the Germans in North Africa (west of Egypt, Suez Canal, and oil fields of Middle East)
General Bernard Montgomery
Led GB and forced Germany to retreat at the Battle of El Alamein, lifting the danger to the Middle East (stopped Hitler’s land/air advances)
Operation Torch
The Allies, w/ the help of Ultra (Enigma decrypters), stopped the Nazis.
A compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to engage in the fight against Nazi Germany (through France-controlled North Africa) and Fascist Italy on a limited scale. Met in the middle and surrounded German troops in Tunisia.
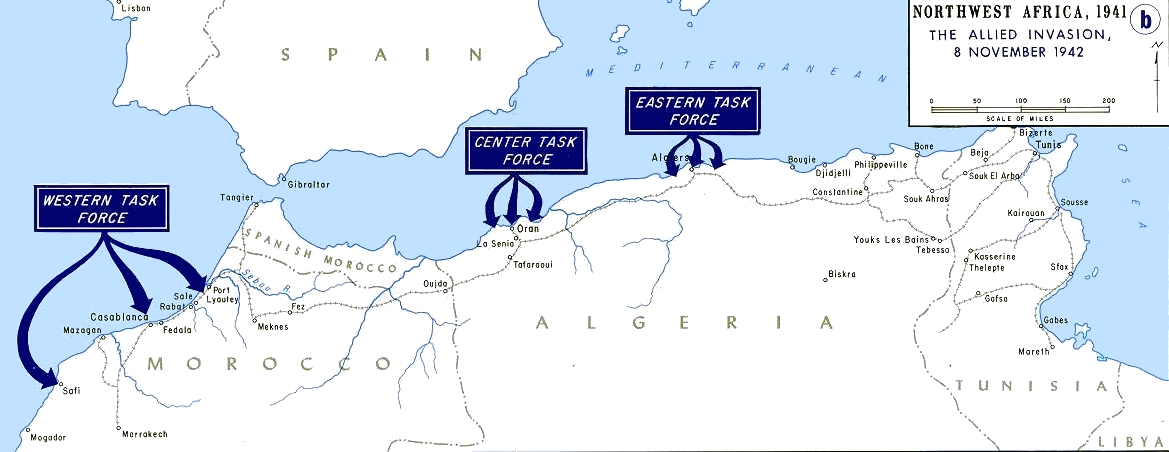
Dwight D. “Ike” Eisenhower
Gen. Omar Bradley
Gen. George Patton
Led Operation Torch
Casablanca
Jan. 1943 - FDR & Churchill met, decided on Italy next, & to just soften France (UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER)
Unconditional Surrender
The Allies chose this tactic of surrender of the Axis powers, would leave Germany demoralized and left with nothing. Affects post war reconstruction.
Tehran
Nov. 1943 - FDR, Churchill, and Stalin discussed strategy. Committed to invade France, but not when. Broad plans. Operation Overload
Operation Overload
Code name for the Battle of Normandy
Battle of Stalingrad
Soviet troops were ordered to defend at all costs, and they did. Lasted into the winter where the USSR had the advantage and Germany surrendered in this battle (first time they had done so).
Battle of Kursk
A revived Soviet army marched West w/ 13 million. The battle tied up 1 million men on each side and left germany capable of a fighting retreat, but too weak to have any hope of winning the war.
Operation Overload (Battle of Normandy) LED BY EISENHOWER
Allies launched a bold plan to cross the English Channel into France.
Battle of the Bulge
Germans last desperate attempt to break Ally lines. Created a “bulge” in army lines, but eventually, bc of the 101st Airborne Division, the “bulge” was pinched off and Germany was forced back.
V-E Day
Victory in Europe Day (May 8th)
Bushido Code
Japanese were taught to believe that their emperor was god, and it was honor to die in battle
Kamikaze Attacks
Suicide missions
General Doolittle
Led the Raid on Tokyo
Raid on Tokyo
Did little damage to Japan, but lifted US morale
Gen McArthur and Admiral Nimitz
In charge of the Pacific Theater
Battle of Coral Sea
US stopped Japan’s expansion and forced them to recall their invasion of Australia. Confirmed US Navy could fight effectively. Showed how aircraft carriers had changed the war.
Magic
Japanese code
Enigma
German code
Battle of Midway
US was ready and waiting thanks to Magic. Ended Japanese efforst to expand in the Pacific. Japan’s first great naval defeat and shifted the balance of pwer to the US. Pivotal victory.
Battle of Guadalcanal
Battle that finally stopped the advance on the Pacific.
Island Hopping
US bypassed some of the most heavily fortified Japanese posts, to instead capture smaller nearby islands, set up airfields on them, and attack the enemy bases through heavy bombing.
Bataan Death March
60,000-80,000 US & Filipino POW’s killed en route to the POW camp
Battle of Leyte Gulf
US began retaking the Phillippenes. Japanese navy was destroyed and the last Japanese offensive was destroyed. US got Luzon, Manila, and the Phillippines.
Manhattan Project
supervised by R. Oppenheimer. Us was building an atomic bomb (bc of german actions and also germany had started to too)
Potsdam Conference
US and UK warned Japan of a “prompt and utter destruction”
Little Boy, Hiroshima
first atomic bomb dropped by Enola Gay on ___.
Fat Man, Nagasaki
Second atomic bomb dropped on ____.
V-J Day
Victory in Japan Day
USS Missouri
Japan formally surrendered aboard the ______.