BIO 201: Chapter 4.3 Peripheral Nervous System
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
31, fusion
each of the ___ pairs of spinal nerves form from the ____ of the anterior and posterior roots of the spinal cord
8
how many pairs of cervical spinal nerves?
12
how many pairs of thoracic spinal nerves?
5
how many pairs of lumbar spinal nerves?
5
how many pairs of sacral spinal nerves?
1
how many pairs of coccygeal spinal nerves?
motor, away
anterior roots carry ___ axons ___ from the spinal cord
sensory, to
posterior roots carry ___ axons ___ the spinal cord
posterior ramus
serve the skin, joints, and musculature of the posterior trunk
meningeal branches
reenter the vertebral canal to innervate spinal structures
anterior ramus
travel anteriorly to supply the muscles of the upper and lower limbs, anterior thorax and abdomen, and part of the back
intercostal nerves
anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves that travel between the ribs as 11 separate pairs of nerves that innervate the intercostal muscles, abdominal nerves, and the skin of the chest and abdomen
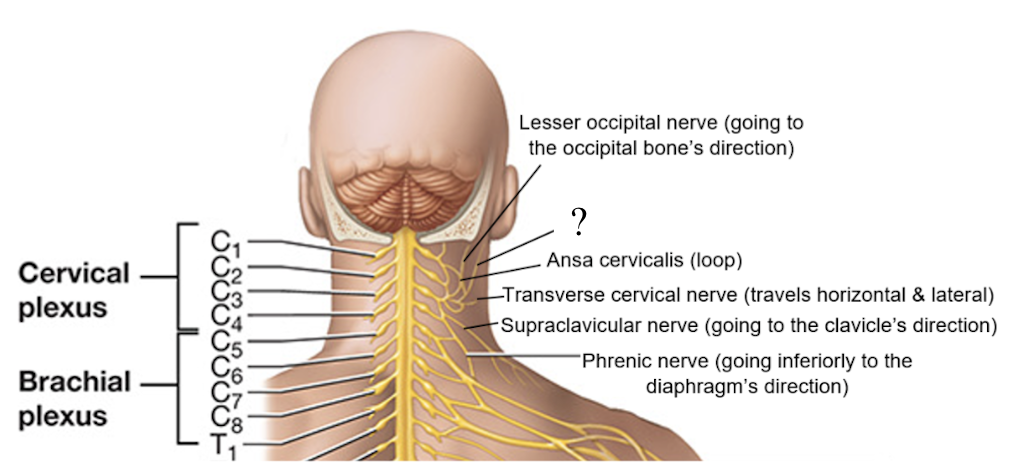
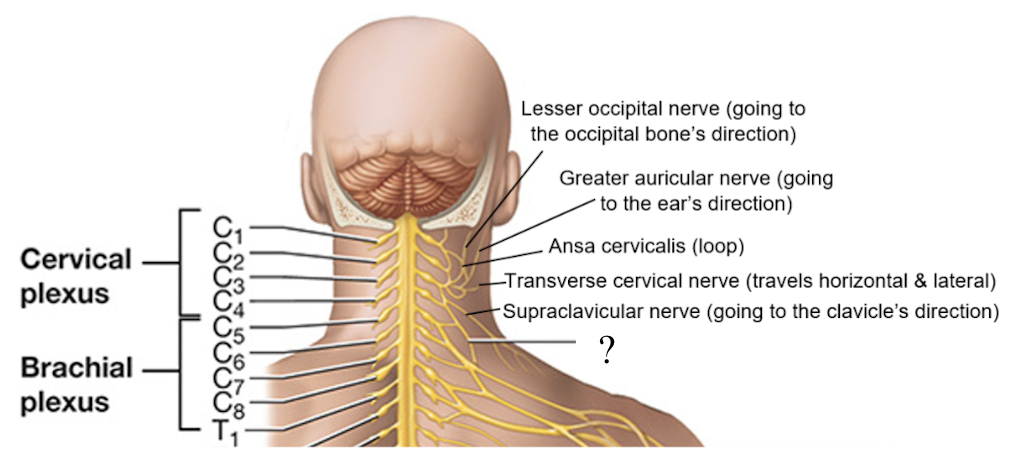
cervical plexus
consists of the anterior rami of C1-C4 spinal nerves with small contributions from C5 to serve the skin of the head and neck and some neck muscles
lesser occipital nerve
C2-C3, associated with cutaneous and sensory innervation of the external ear and nape (back of the neck), heads to the direction of the occipital bone
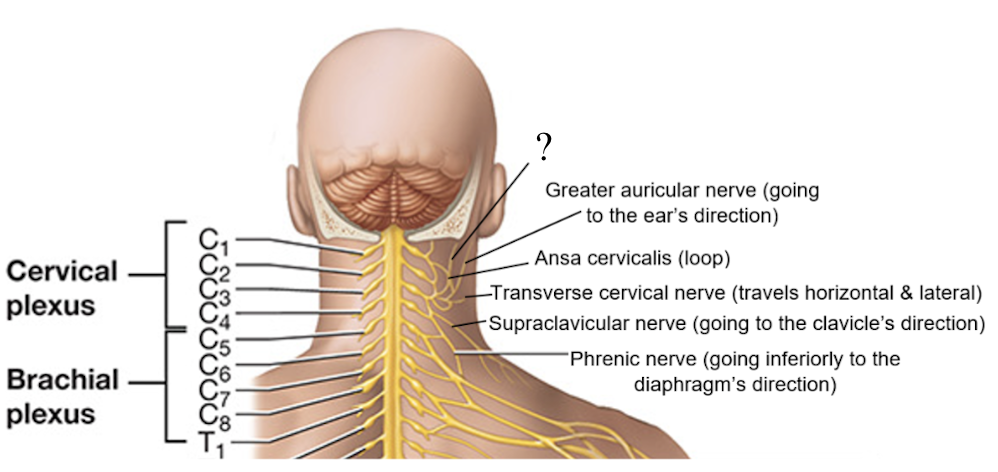
ansa cervicalis nerve
C1-C3, loop of nerves that innervate some neck muscles like the omohyoid, sternohyoid, and sternothyroid muscles
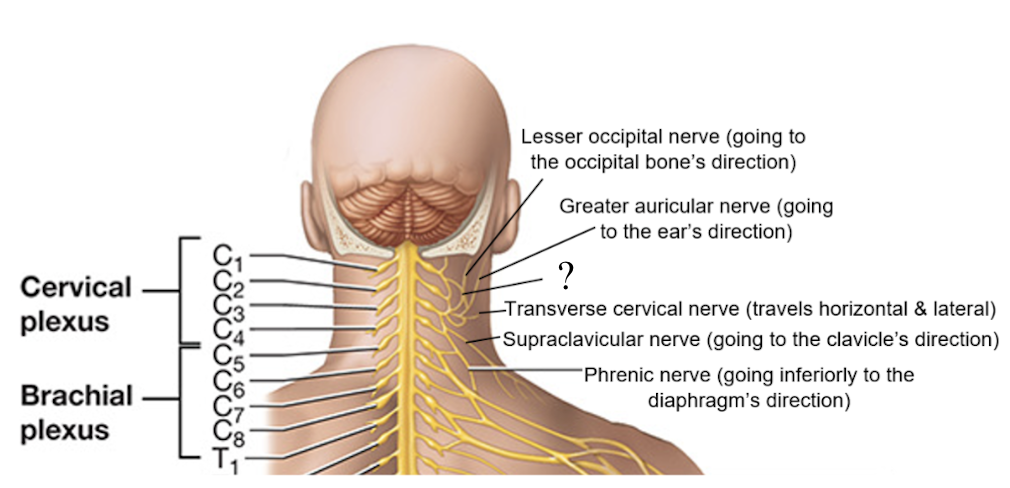
supraclavicular nerve
C3-C4, associated with the cutaneous and sensory innervation of the lower anterior and lateral neck, shoulder, and anterior chest, goes to the direction of the clavicle
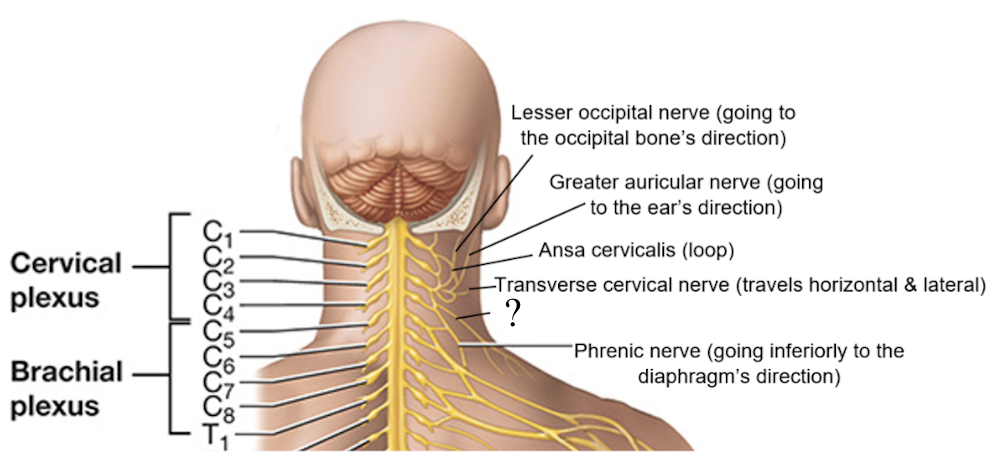
transverse cervical nerve
C3, associated with the cutaneous and sensory innervation of the anterior and lateral neck and under the chin, travels laterally in a horizontal line
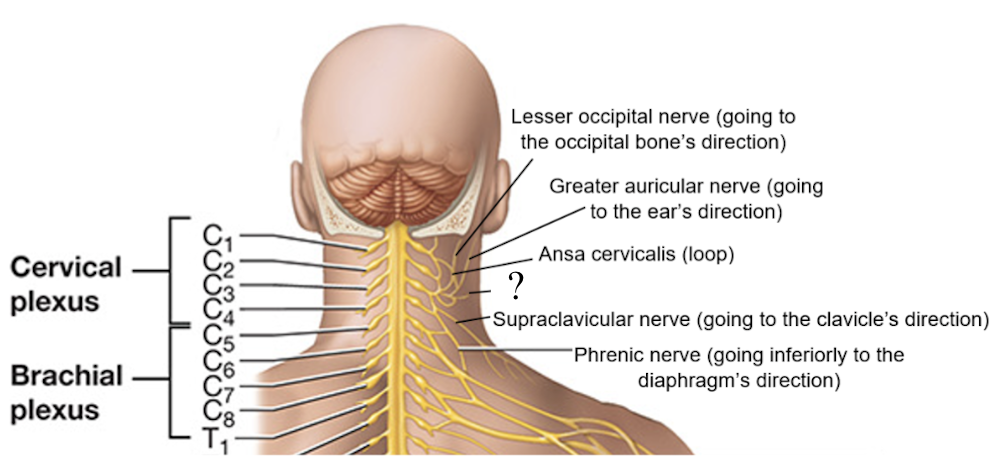
great auricular nerve
C3, associated with the cutaneous and sensory innervation of the external ear and mastoid area, travels toward the ear’s direction
phrenic nerve
C3-C5, travels superficially to the scalene muscles and internal jugular vein, goes inferiorly to the direction of the diaphragm
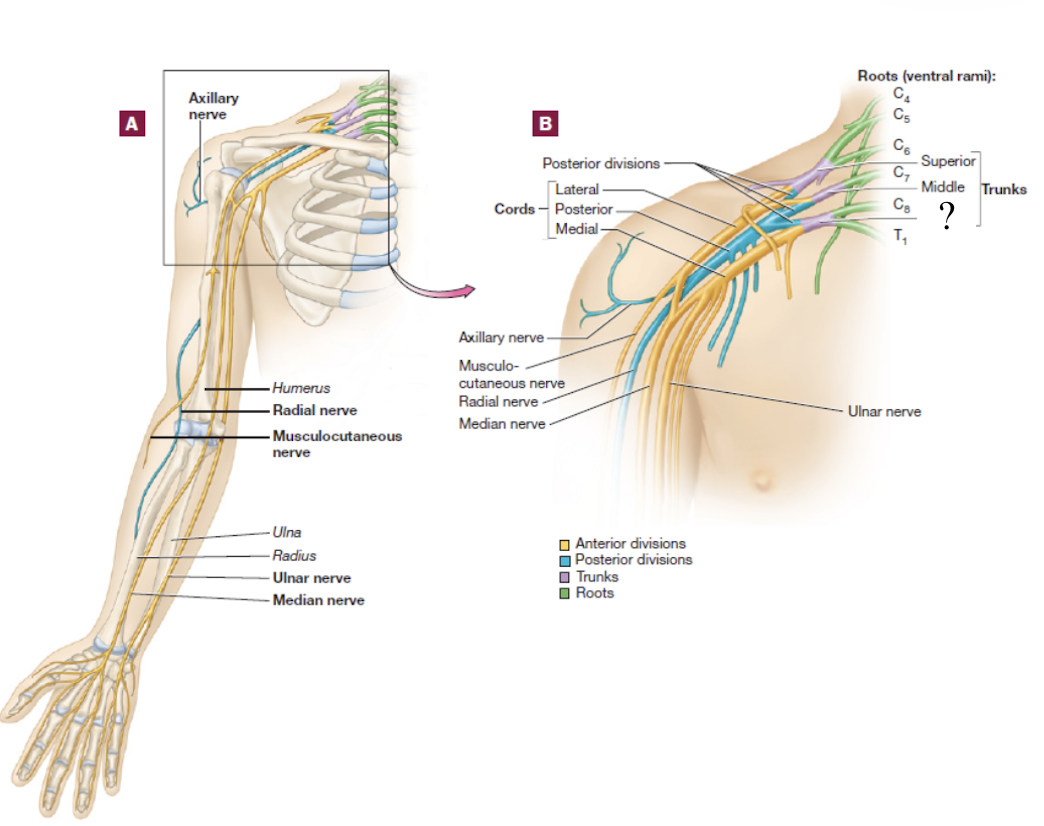
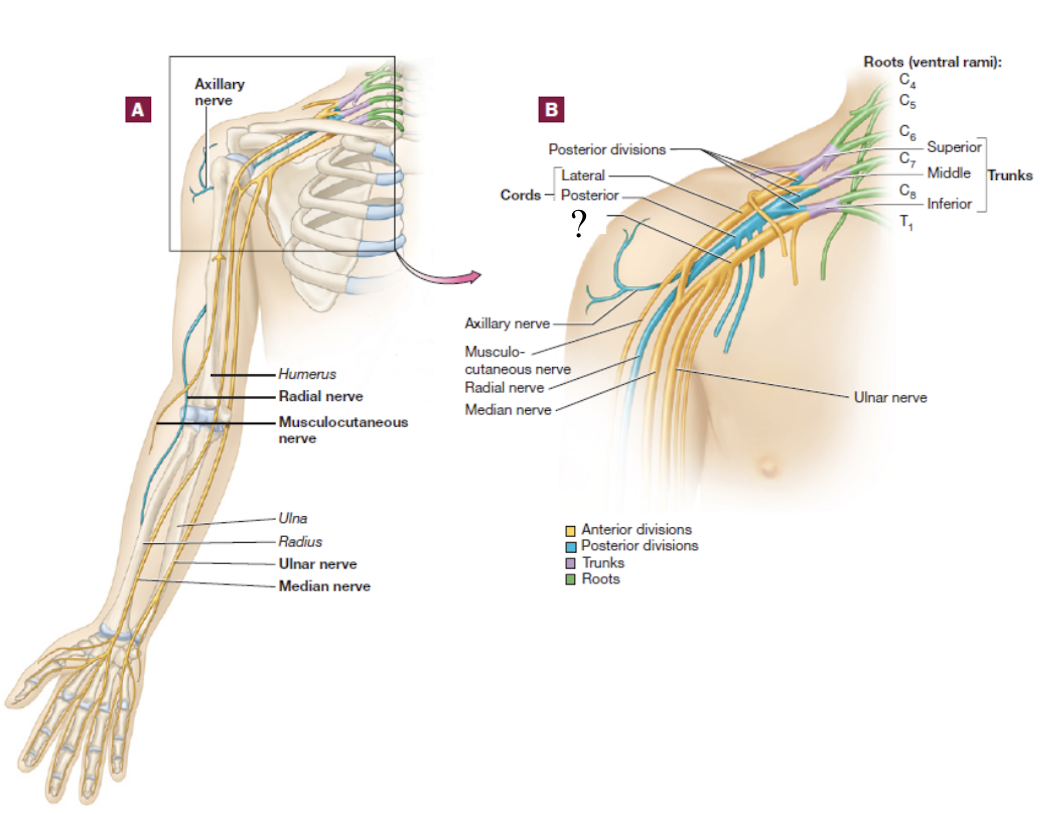
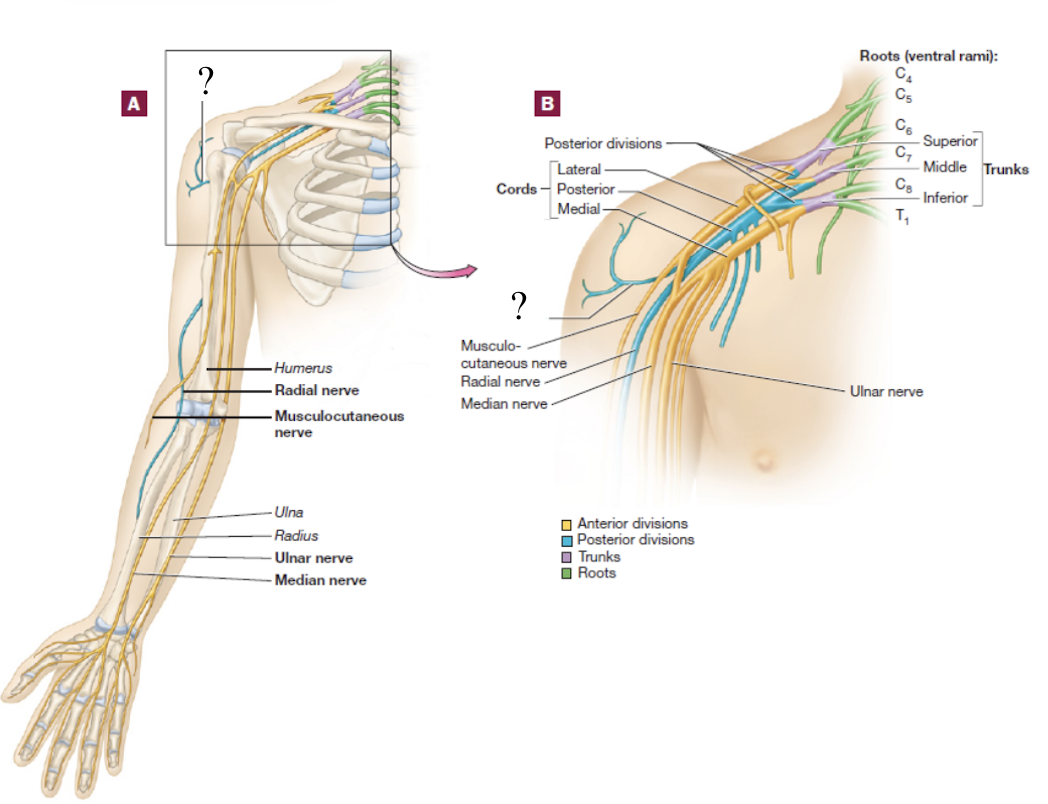
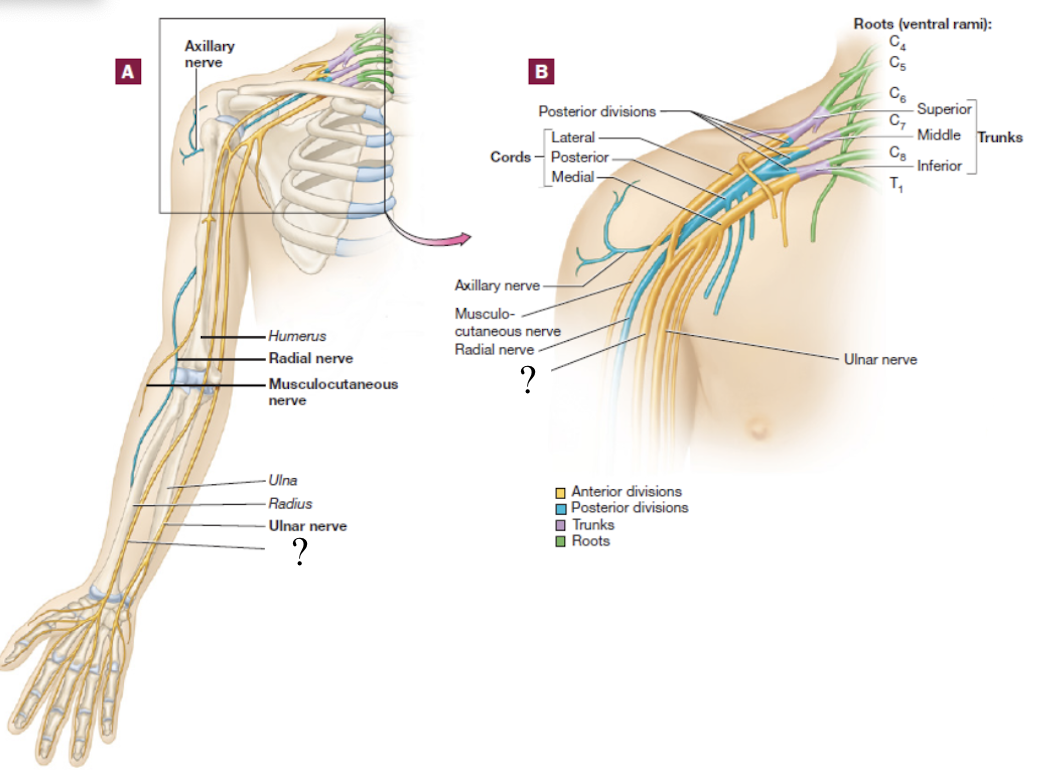
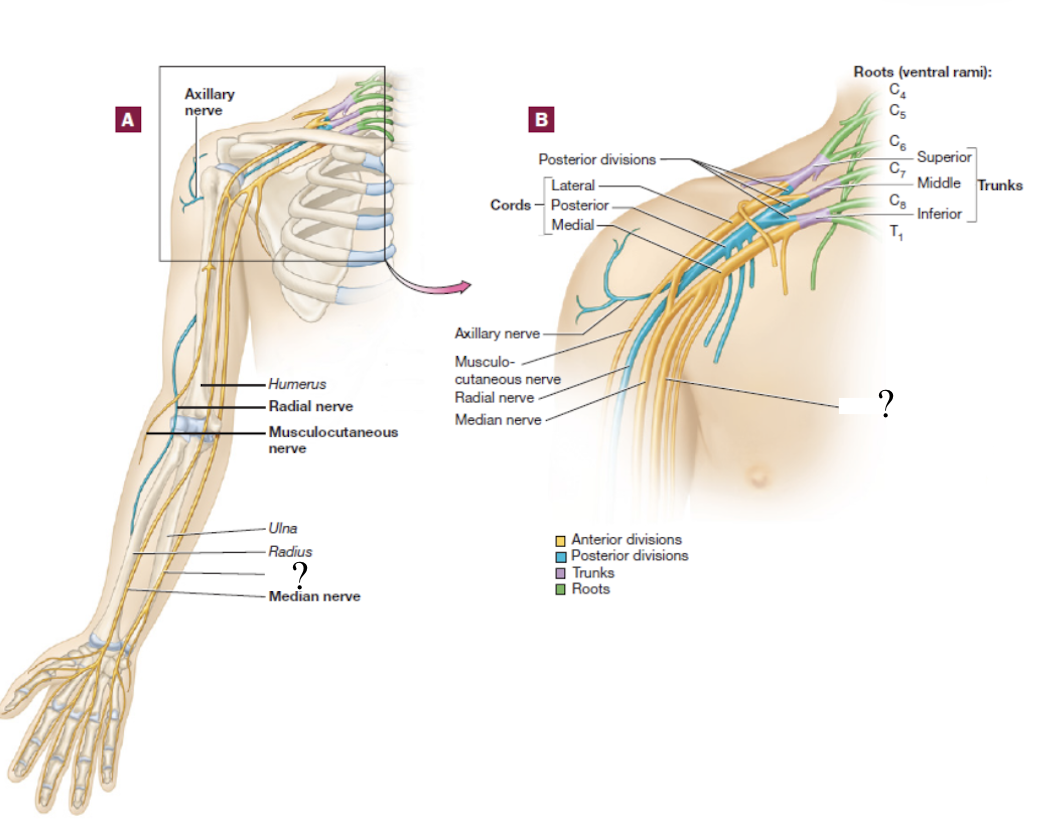
brachial plexus
consists of the anterior rami of C5-T1 spinal nerves
spinal nerve → 3 large trunks → 2 divisions → 3 cords → 5 nerve branches
superior trunk of brachial plexus
formed by the C5 and C6 spinal nerves
splits into anterior and posterior divisions
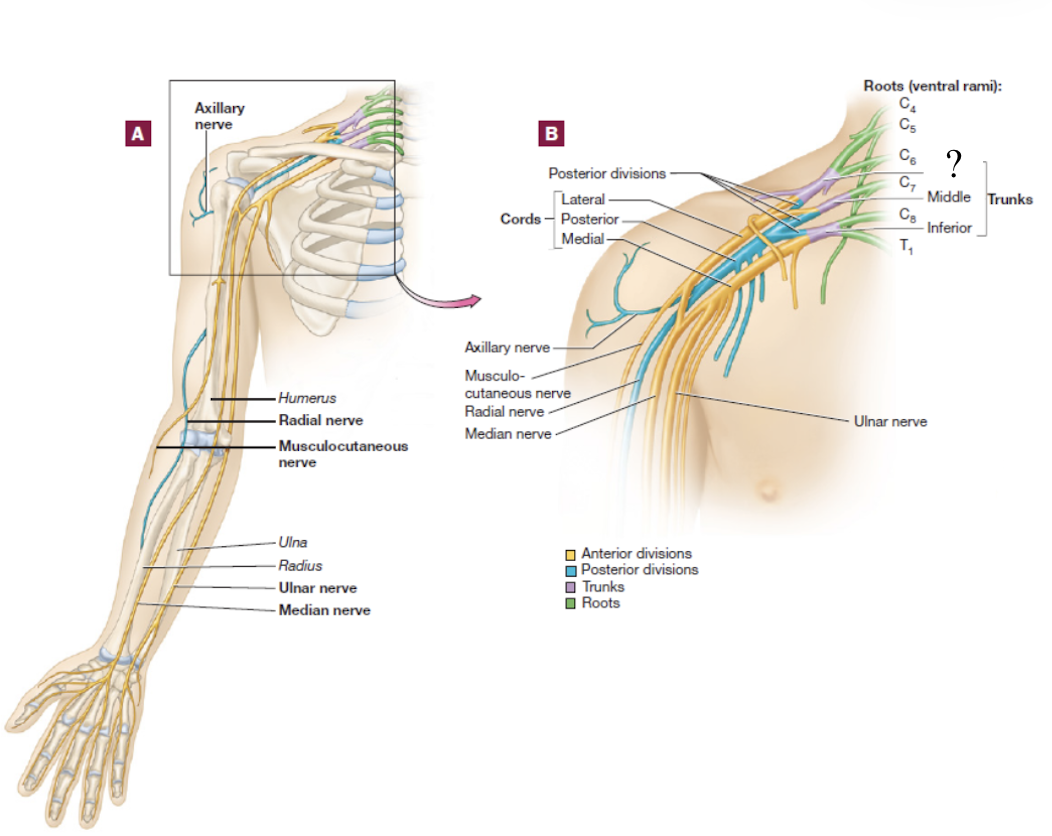
middle trunk of the brachial plexus
formed by the C7 spinal nerve
splits into anterior and posterior divisions
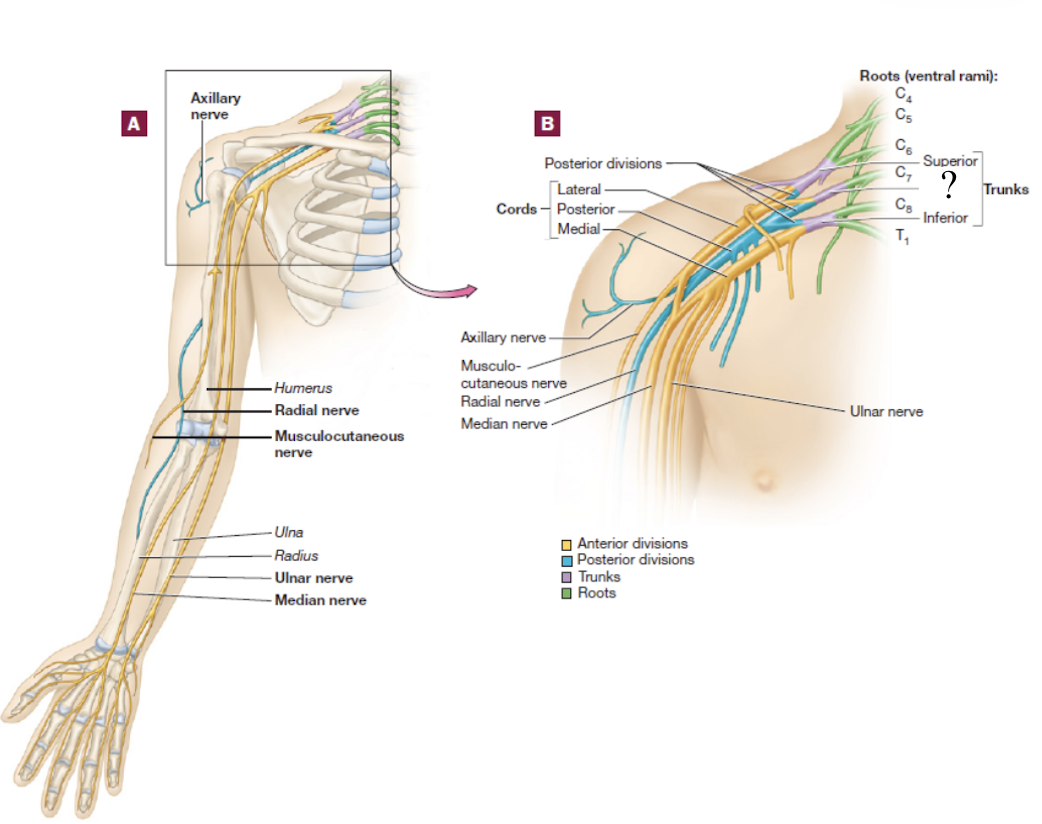
inferior trunk of the brachial plexus
formed by the C8 and T1 spinal nerves
splits into anterior and posterior divisions
medial cord
formed by contribution of the anterior division of the inferior trunk and descends in the medial arm
lateral cord
formed by the anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunks and descends in the lateral arm
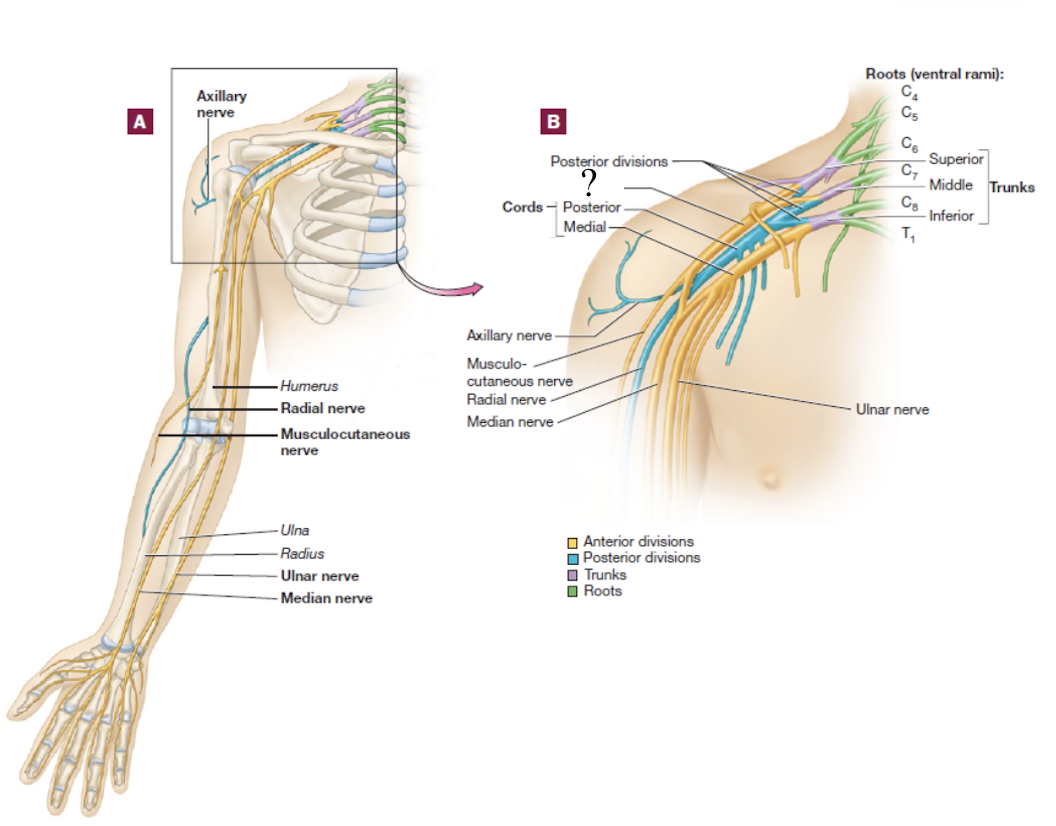
posterior cord
formed by the contribution of all posterior divisions of all 3 trunks and is located in the posterior arm
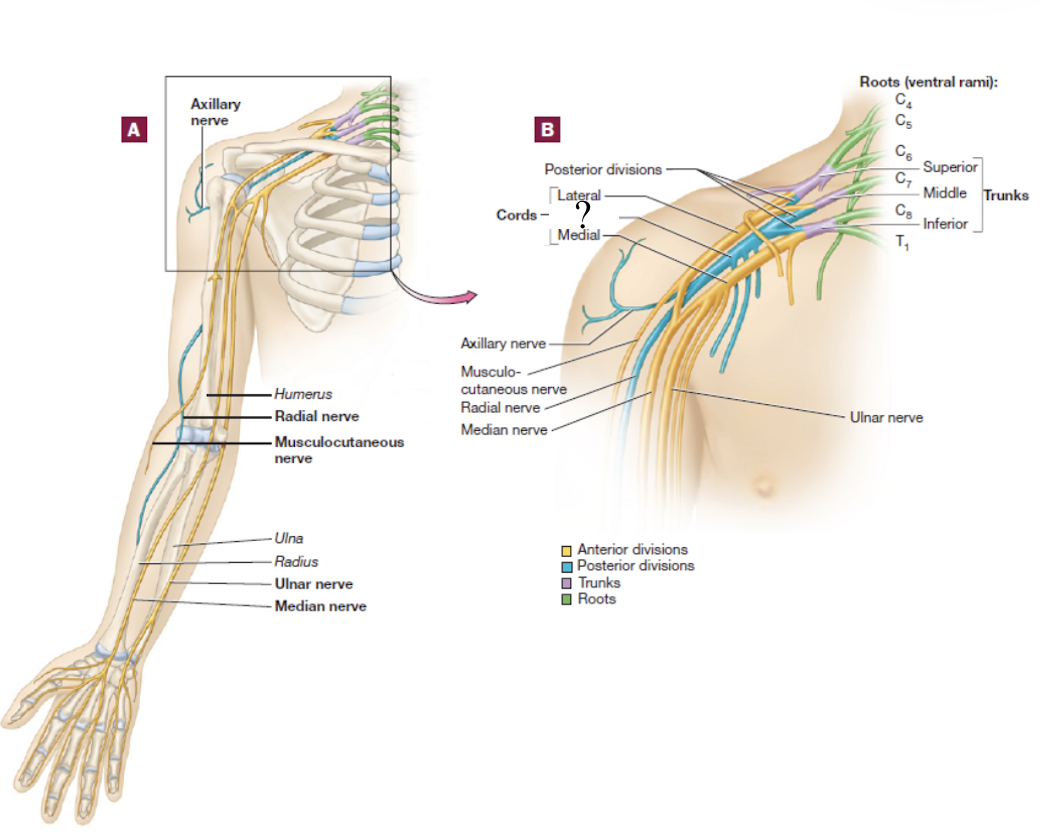
musculocutaneous nerve
distal continuation of the lateral cord, located in the lateral arm
serves the anterior arm muscles and skin
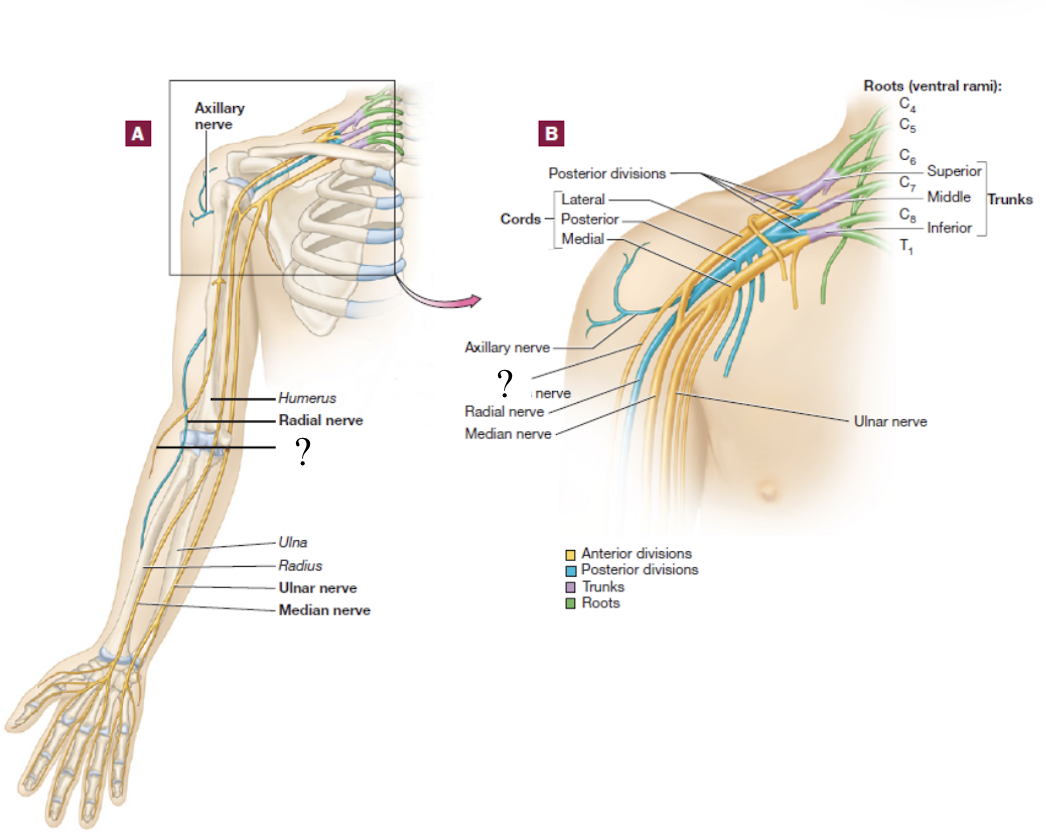
axillary nerve
short branch of the posterior cord
serves structures near the axilla and skin around this region
radial nerve
distal continuation of the posterior cord and is located in the posterior upper limb
serves the muscles that extend the forearm and skin in the lateral hand
travels on the radial groove on the posterior side of the humerus
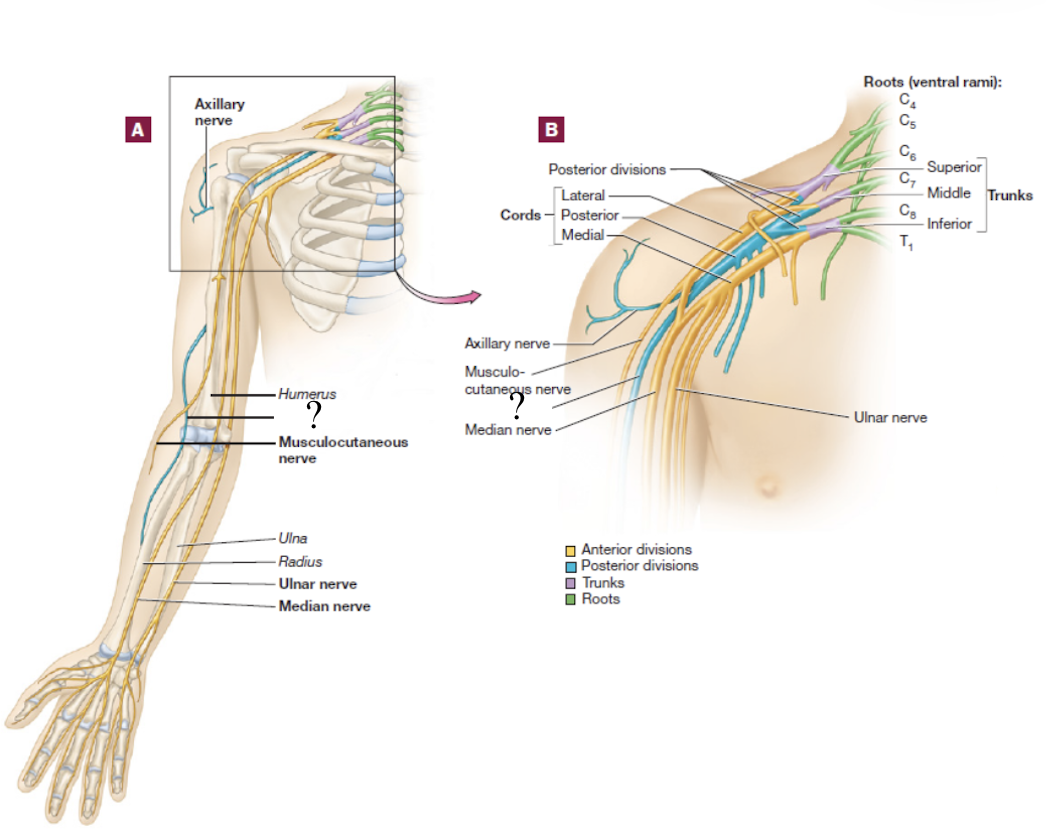
median nerve
formed by the fusion of both the medial and lateral cords, travels down the middle arm and forearm
supplies most of the muscles of the forearm that flex and skin over the anterior and lateral hand
travels under the flexor retinaculum as it enters the wrist
carpal tunnel syndrome
results from the median nerve becoming trapped and inflamed under the flexor retinaculum
ulnar nerve
distal continuation of the medial cord
supplies certain muscles in the forearm that flex and skin over the medial hand
“funny bone nerve”
lumbar plexus
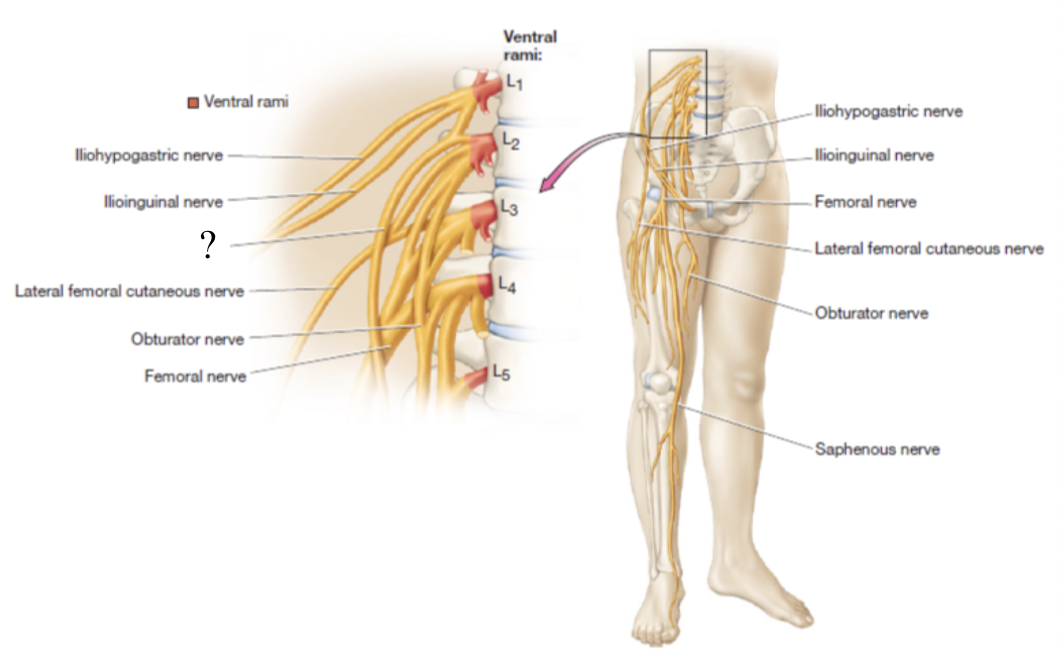
consists of the anterior rami of L1-L4 with a small contribution from T12 spinal nerves
found by the iliopsoas muscle group and quadratus lumborum muscle
iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves
both supply motor innervation to the transverse abdominis and internal oblique muscles and sensory to the pelvic area
iliohypogastric nerve is superior to ilioinguinal nerve
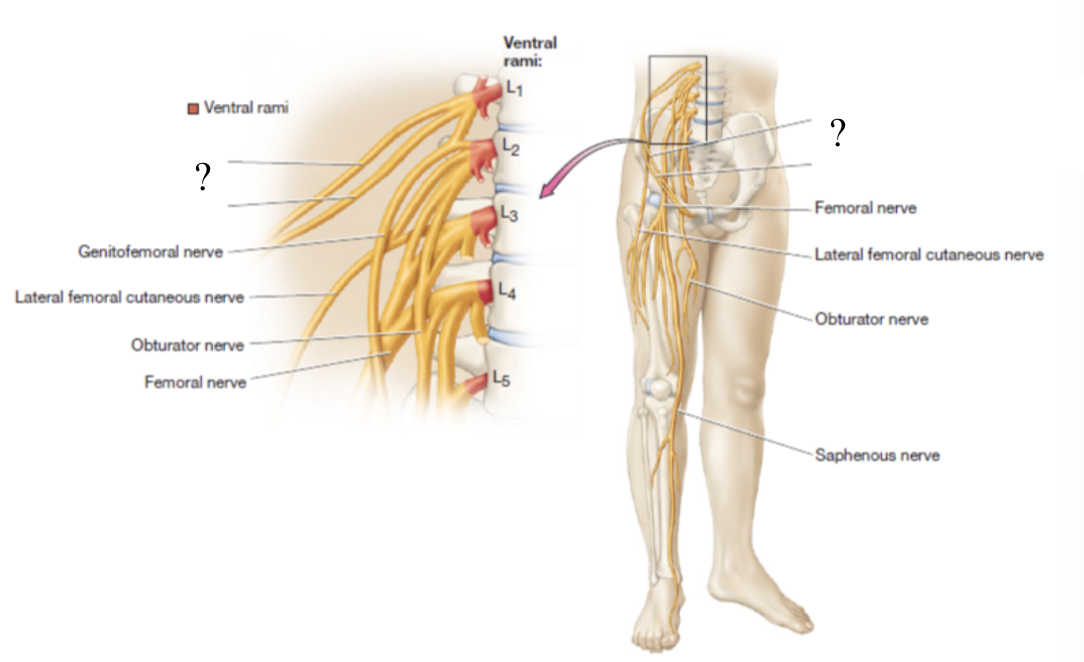
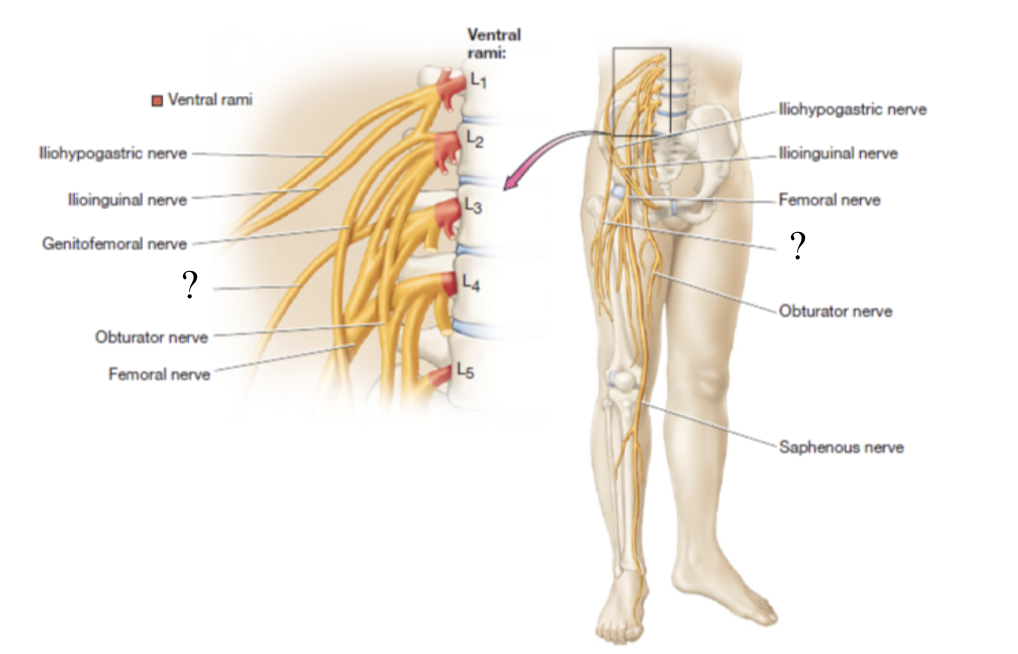
genitofemoral nerve
curves around medially to supply the cremaster muscle in males and the skin around the anteromedial thigh and genitals in both sexes
only nerve that pierces the psoas major muscle
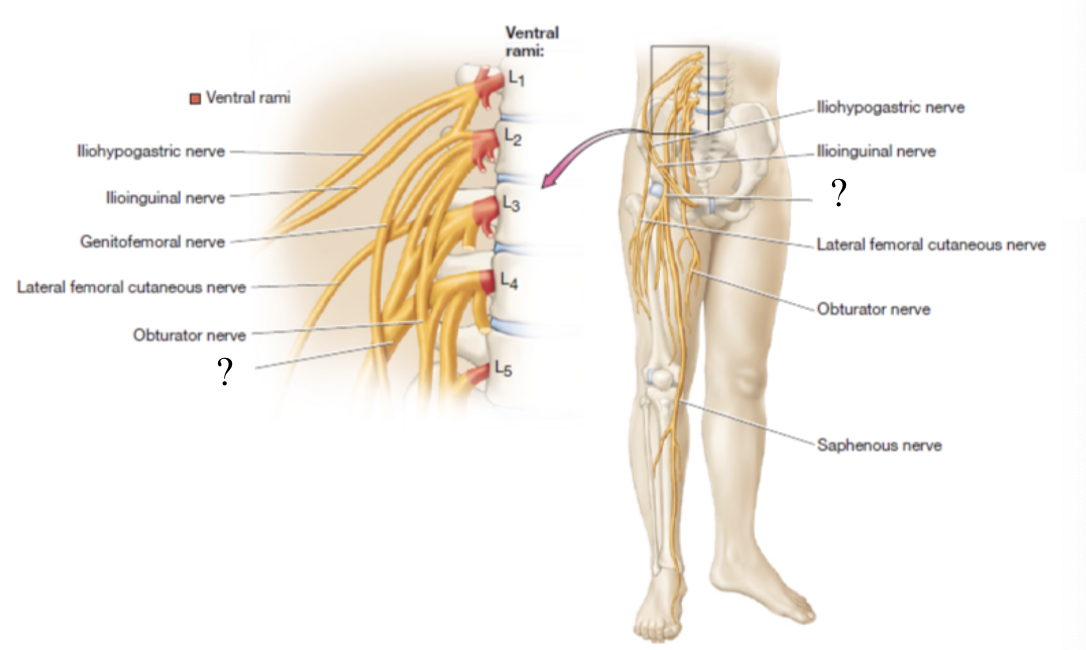
obturator nerve
located in the medial thigh to supply the medial thigh muscles and skin
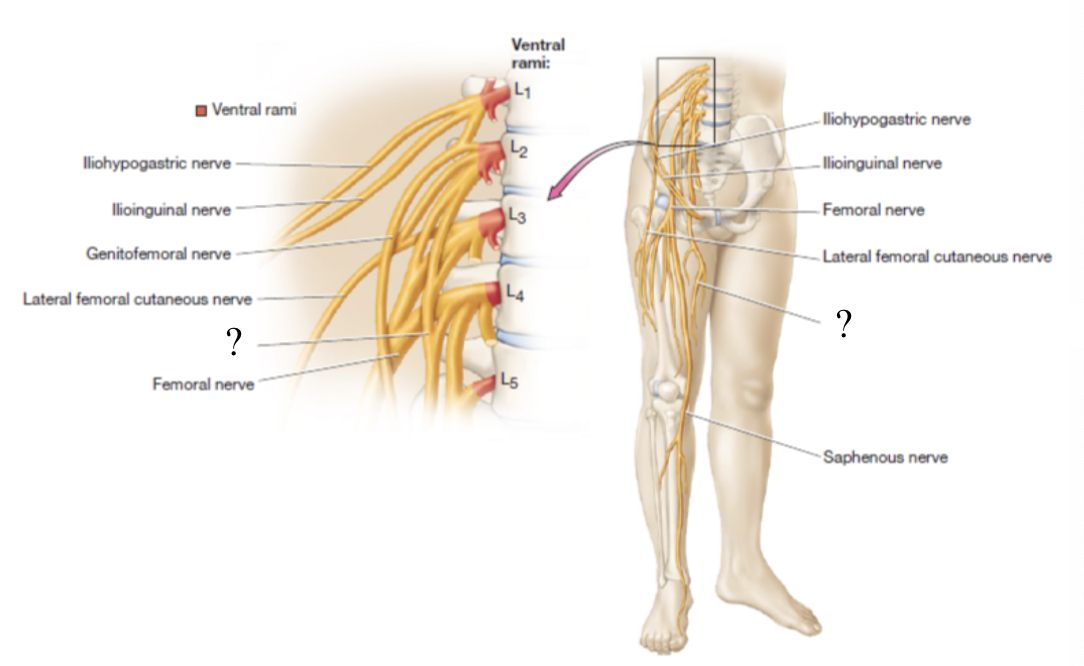
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
provides sensory innervation to the skin of the anterolateral thigh
femoral nerve
largest nerve of the lumbar plexus, provides motor innervation to anterior thigh muscles and sensory innervation to skin of anterior and medial thigh
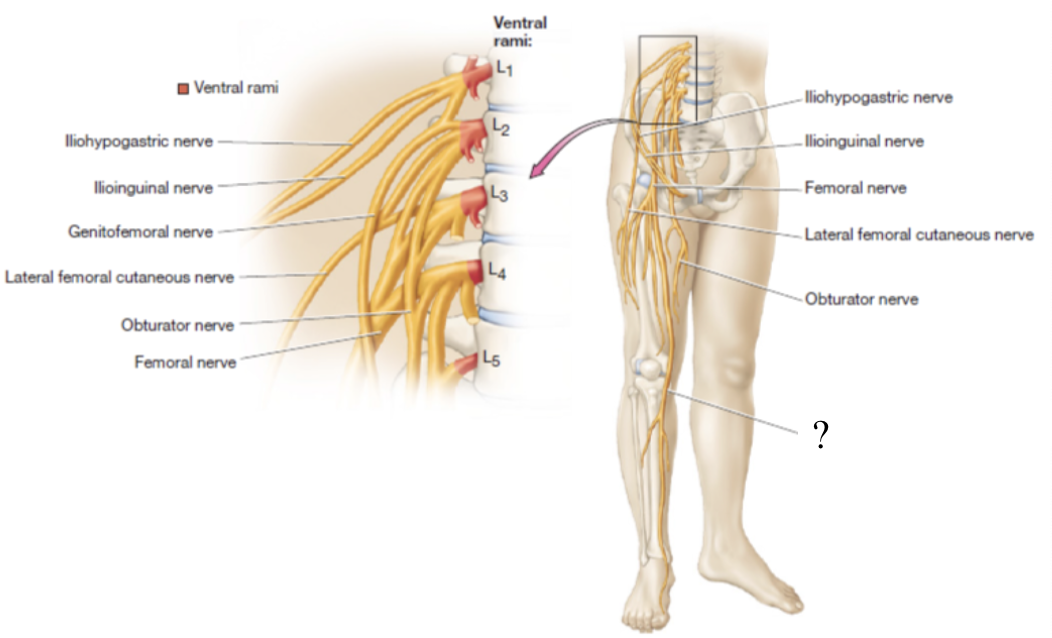
saphenous nerve
once the femoral nerve passes the medial side of the knee, it becomes the _____ which supplies the knee joint, medial leg, and foot
sacral plexus
forms from the anterior rami of L4-S4 spinal nerves
superior gluteal nerve
supplies the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fascia lata muscles
located superficial to the gluteus minimus muscle and deep to the gluteus medius muscle
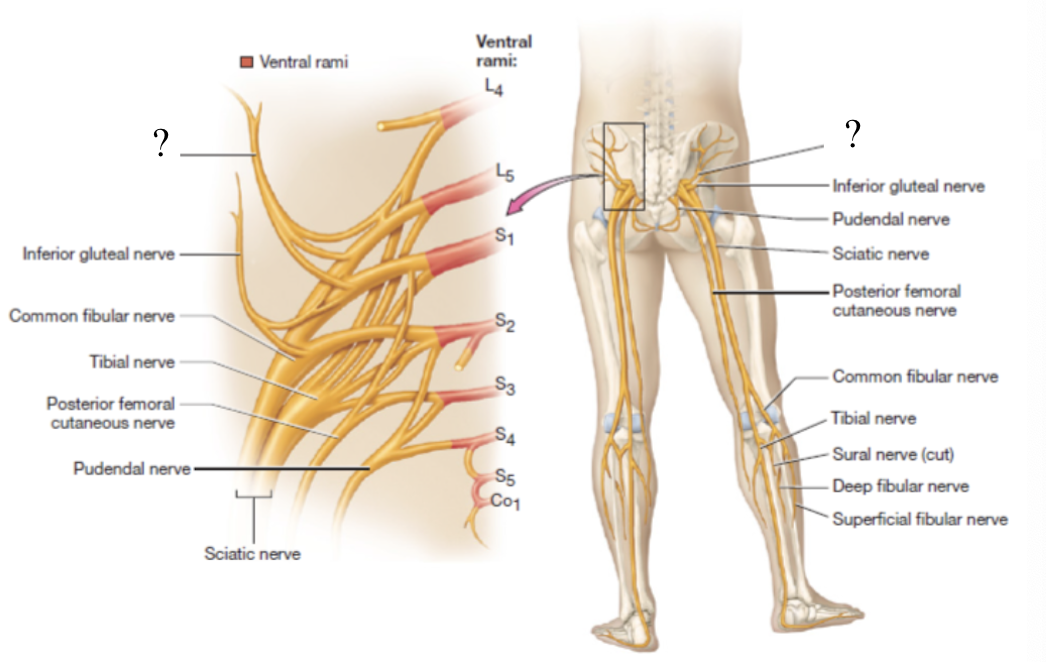
inferior gluteal nerve
supplies the gluteus maximus muscle
located by the piriformis muscle
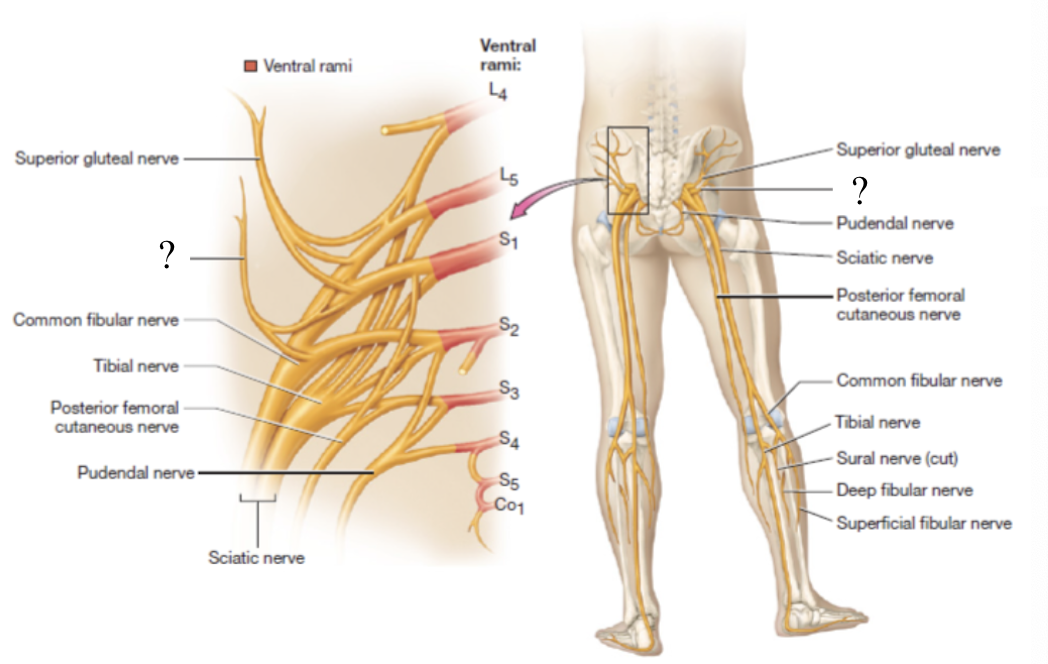
pudendal nerve
innervates the muscle of the pelvic floor, anogenital sphincters, and provides sensory innervation to the genitalia
located traveling medially towards the anus and genitals
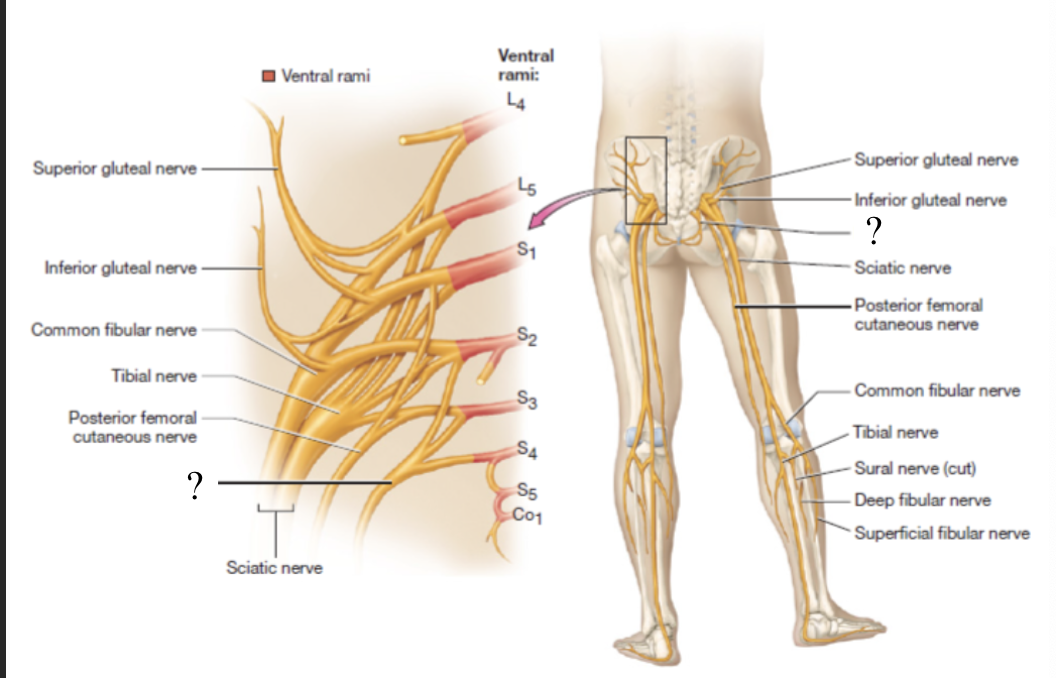
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
located in the posterior thigh to provide sensory innervation to the skin
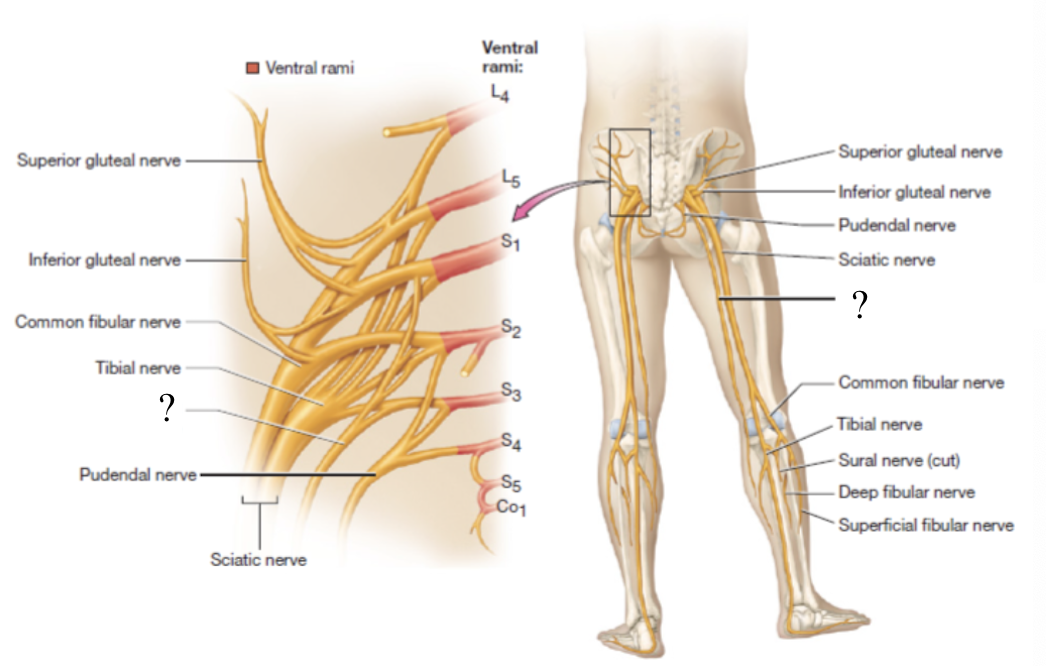
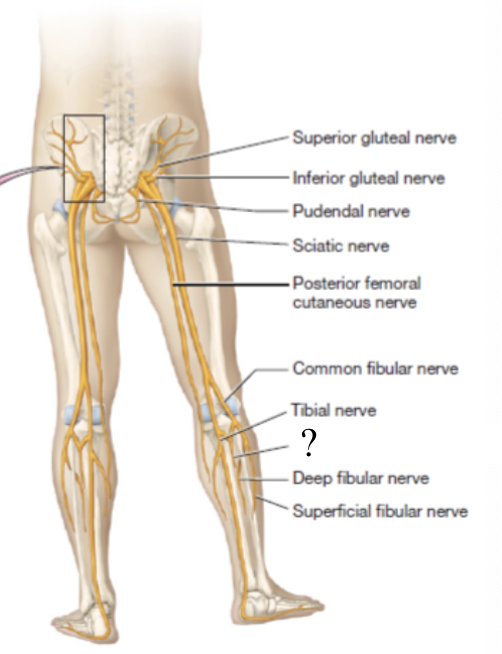
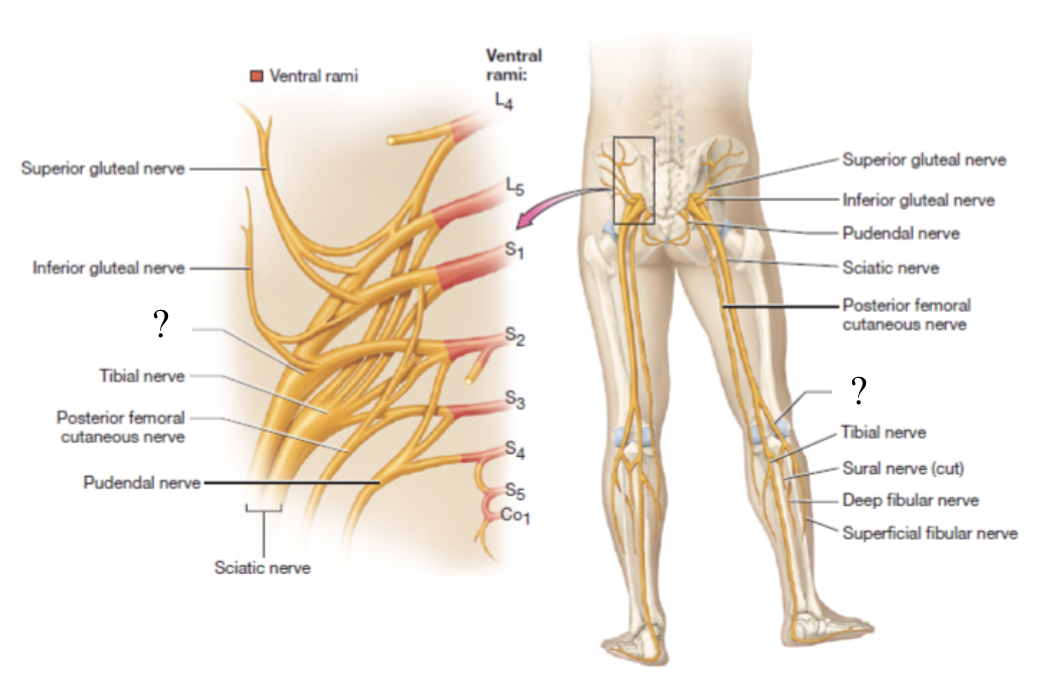
sciatic nerve
largest nerve of the sacral plexus and in the body
travels in the posterior thigh where it splits into two branches: tibial and common fibular nerves
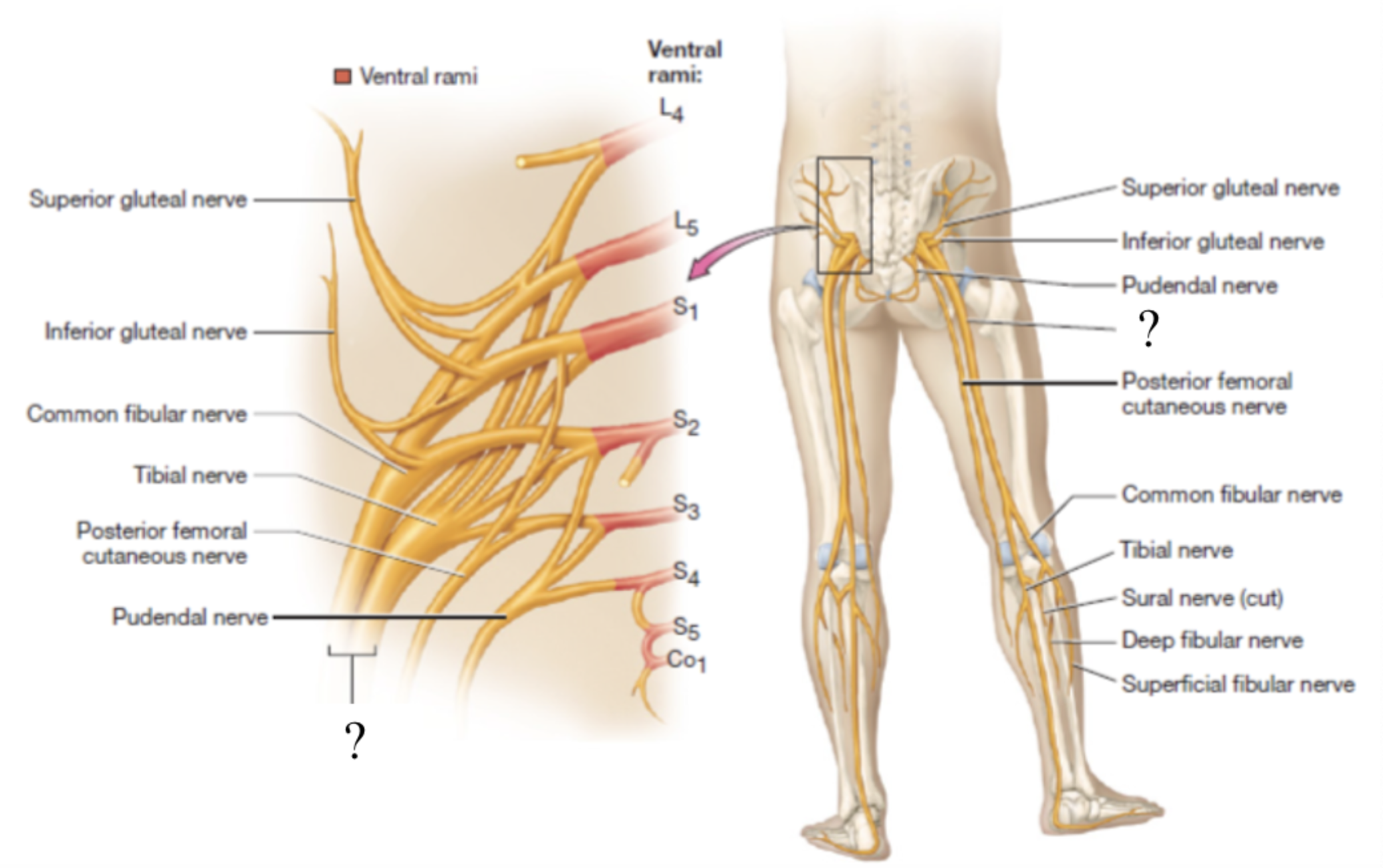
tibial nerve
provides motor innervation to posterior muscles of thigh, posterior leg, and foot
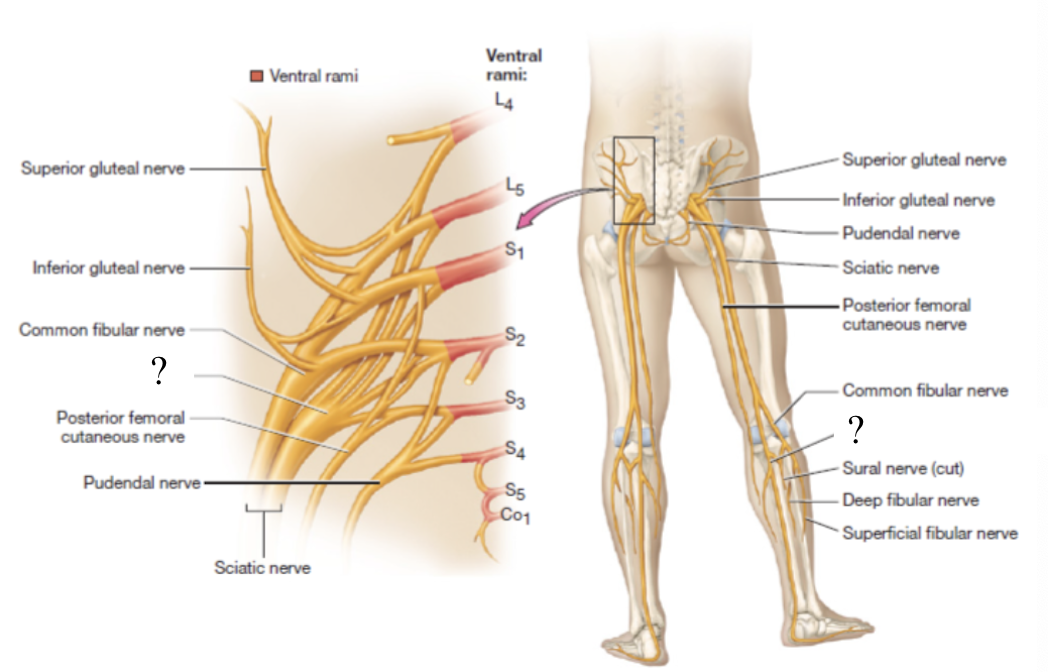
common fibular nerve
divided into superficial and deep fibular nerves
superficial fibular nerve
provides motor innervation to the lateral leg
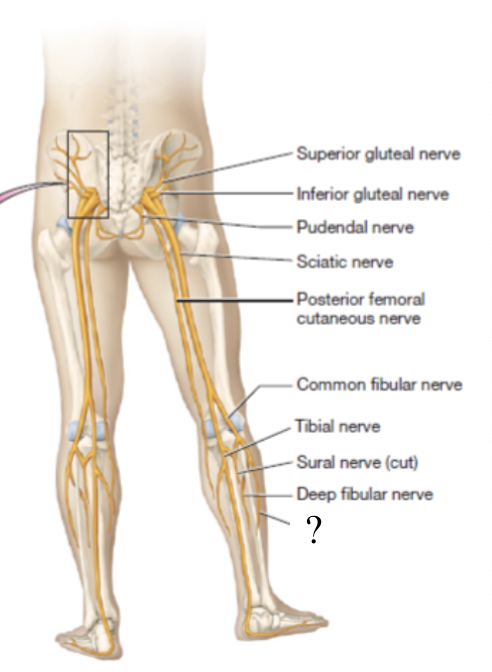
deep fibular nerve
supplies the anterior muscles of the leg that dorsiflex the foot and intrinsic foot muscles
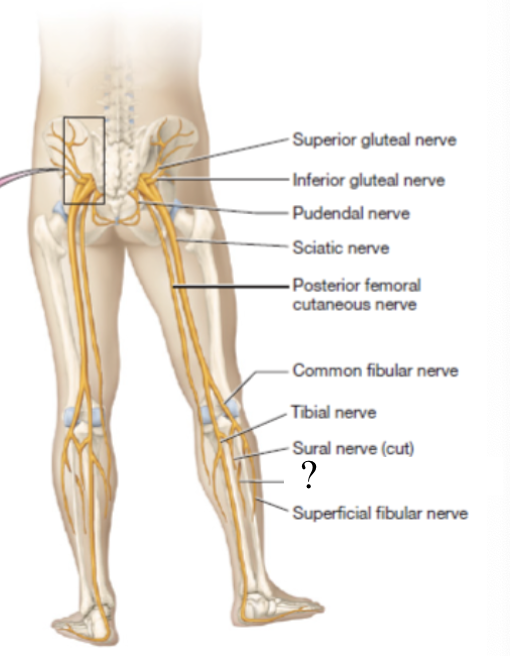
sural nerve
small superficial sensory branch that supplies the skin of the posterior leg and foot
formed by both the tibial and common fibular nerves