AP Biology - Community Ecology Chapter 54, AP Biology: Animal Behavior, AP Biology: Population Ecology
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
community
a group of populations of different species living close enough to interact
interspecific interaction
a relationship between individuals of two or more species in a community
interspecific competition
a -/- interaction that occurs when individuals of different species compete for a resource that limits their growth and survival
competitive exclusion
the concept that when populations of two similar species compete for the same limited resources, one population will use the resources more efficiently and have a reproductive advantage that will eventually lead to the elimination of the other population
ecological niche
the sum of a species' use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment
resource partitioning
the differentiation of niches that enables similar species to coexist in a community
predation
a +/- interaction between species in which one species kills and eats the other
cryptic coloration
camouflage such that a potential prey is difficult to spot against its background
aposematic coloration
the bright colors of animals with effective physical or chemical defenses that acts as a warning to predators
Batesian mimicry
a palatable or harmless species mimics an unpalatable or harmful model
Mullerian mimicry
two or more unpalatable species resemble each other
herbivory
a +/- interaction in which an organism eats parts of a plant or alga
symbiosis
a relationship where individuals of two or more species live in direct and intimate contact with one another
parasitism
a +/- symbiotic interaction in which one organism derives its nourishment from another organism which is harmed in the process
parasite
an organism that feeds on the cell contents, tissues, or body fluids of another species while in or on the host organism; often harm but usually do not kill their host
host
the larger participant in a symbiotic relationship, serving as home and food source for the smaller symbiont
mutualism
a +/+ symbiotic interaction that benefits both species
commensalism
a +/0 symbiotic interaction between species that benefits one of the species but neither harms nor helps the other
character displacement
tendency for characteristics to diverge more in sympatric populations than in allopatric populations of two species
disturbance
an event, such as a storm, fire, flood, drought, overgrazing, or human activity, that changes a community by removing organisms from it or by altering resource availability
ecological succesion
Change in an ecosystem that happens when one community replaces another community as a result of changing abiotic or biotic factors.
primary succession
an ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
secondary succession
succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
Ethology
study of animal behavior

Behavior
what an animal does and how it does it

Instinct (Innate) Behavior
behaviors that are inherited

Kinesis
random movement of animal in relation to stimulus; the stimulus causes an alteration in rate or direction of activity or movement.
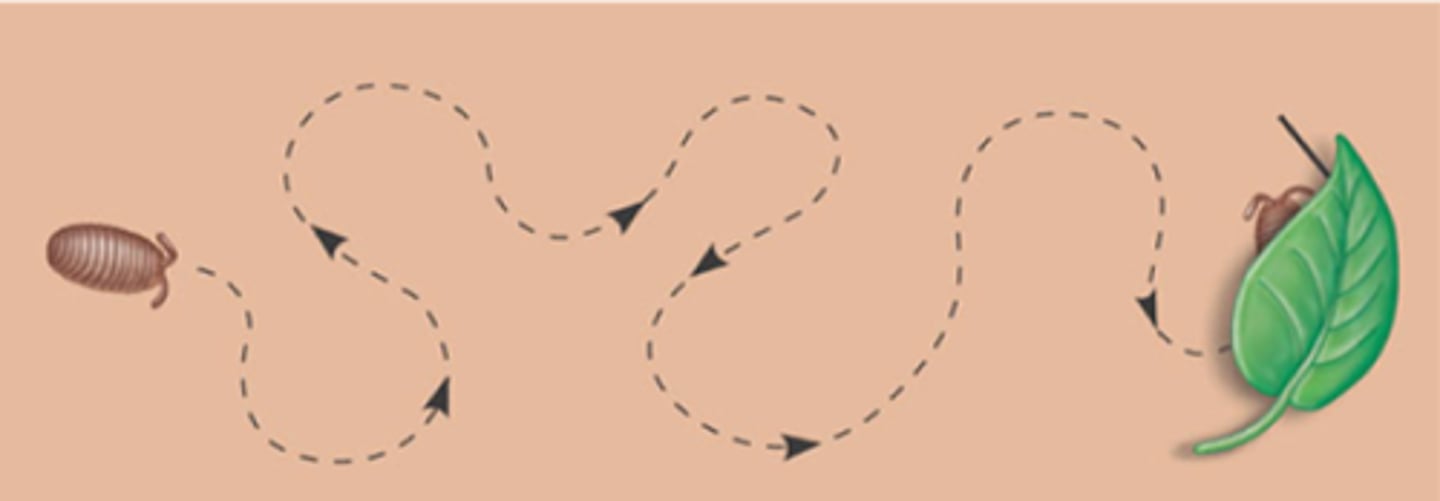
Fixed-action Patterns
sequence of unlearned acts that are unchangeable and usually continue until they are completed
Signal
stimulus that causes change in behavior
Learned Behaviors
Behaviors that are modified based on specific experiences
example: nest building

Associative Learning
ability to connect one stimulus with another

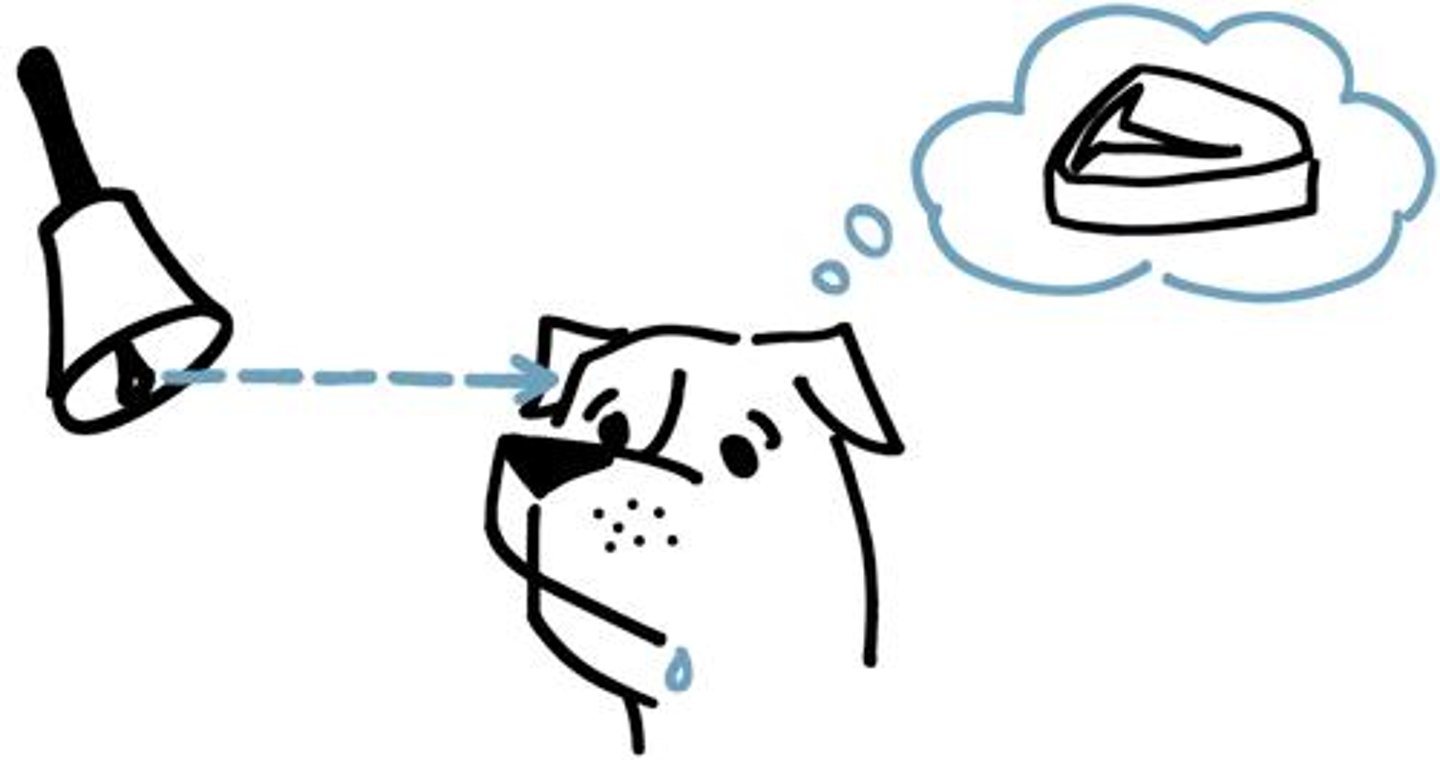
Classical Conditioning
arbitrary stimulus associated with particular outcome
example: training a dog
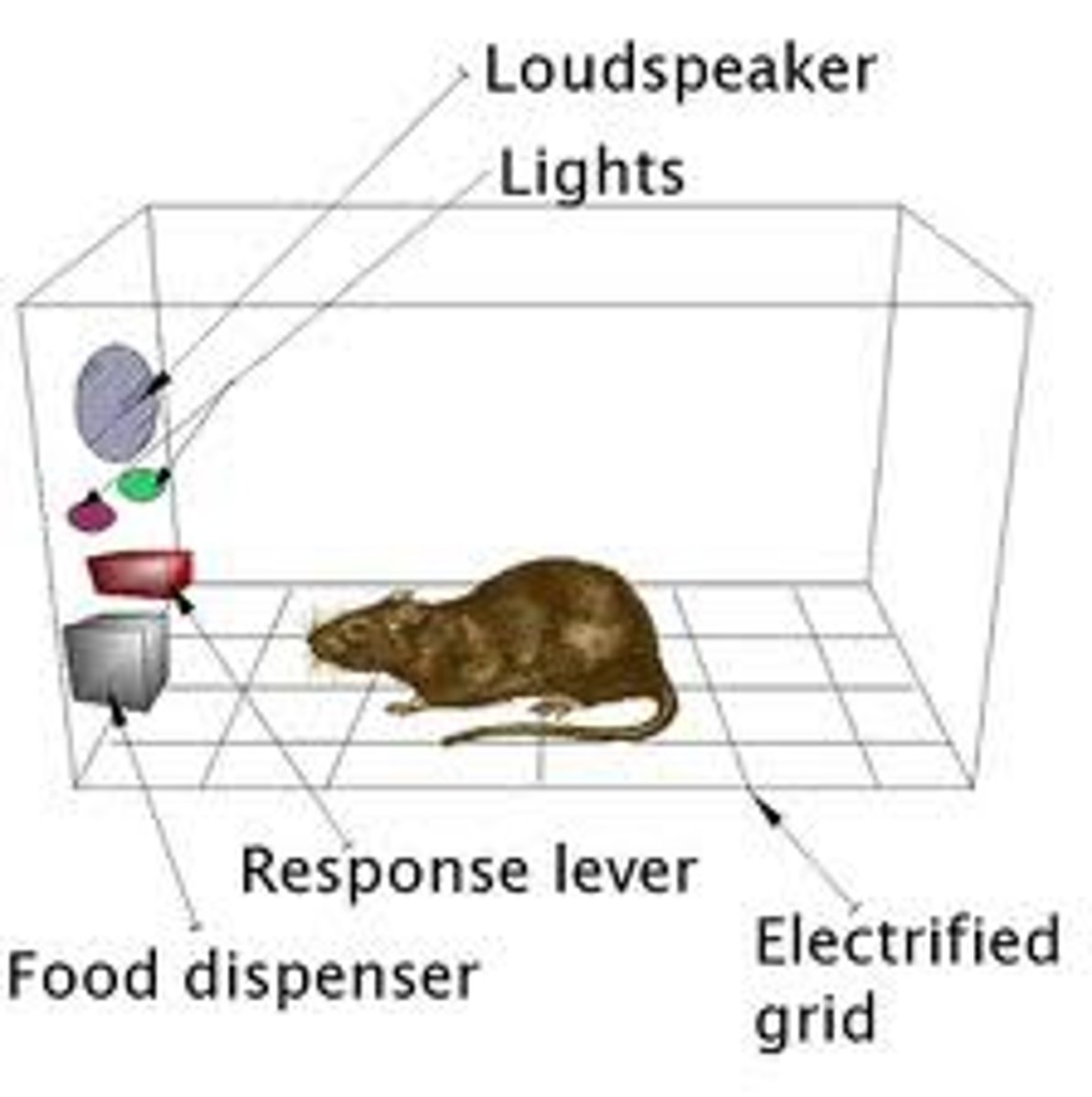
Operant Conditioning (trial and error)
when faced with two choices, an organism can learn to choose the option with the best reward.
example: students who study to improve their grades
Cognition
process of knowing that involves awareness, reasoning, recollection, and judgement

Social Learning
learning by observing others

Altruism
engaging in behavior that doesn't help you, but helps rest of population (selfless)

Inclusive Fitness
total effect of producing offspring and helping relatives
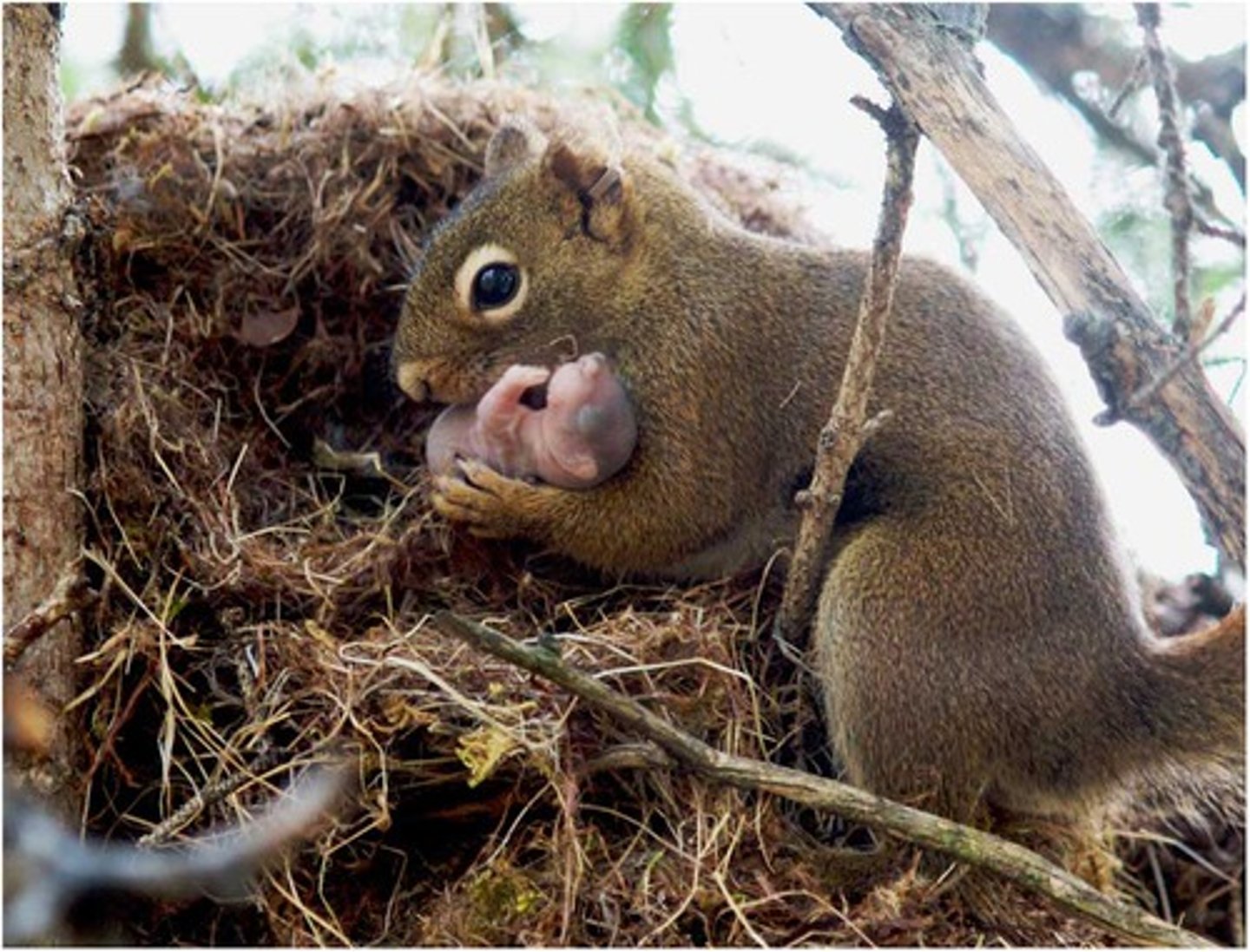

Foraging
food obtaining behavior
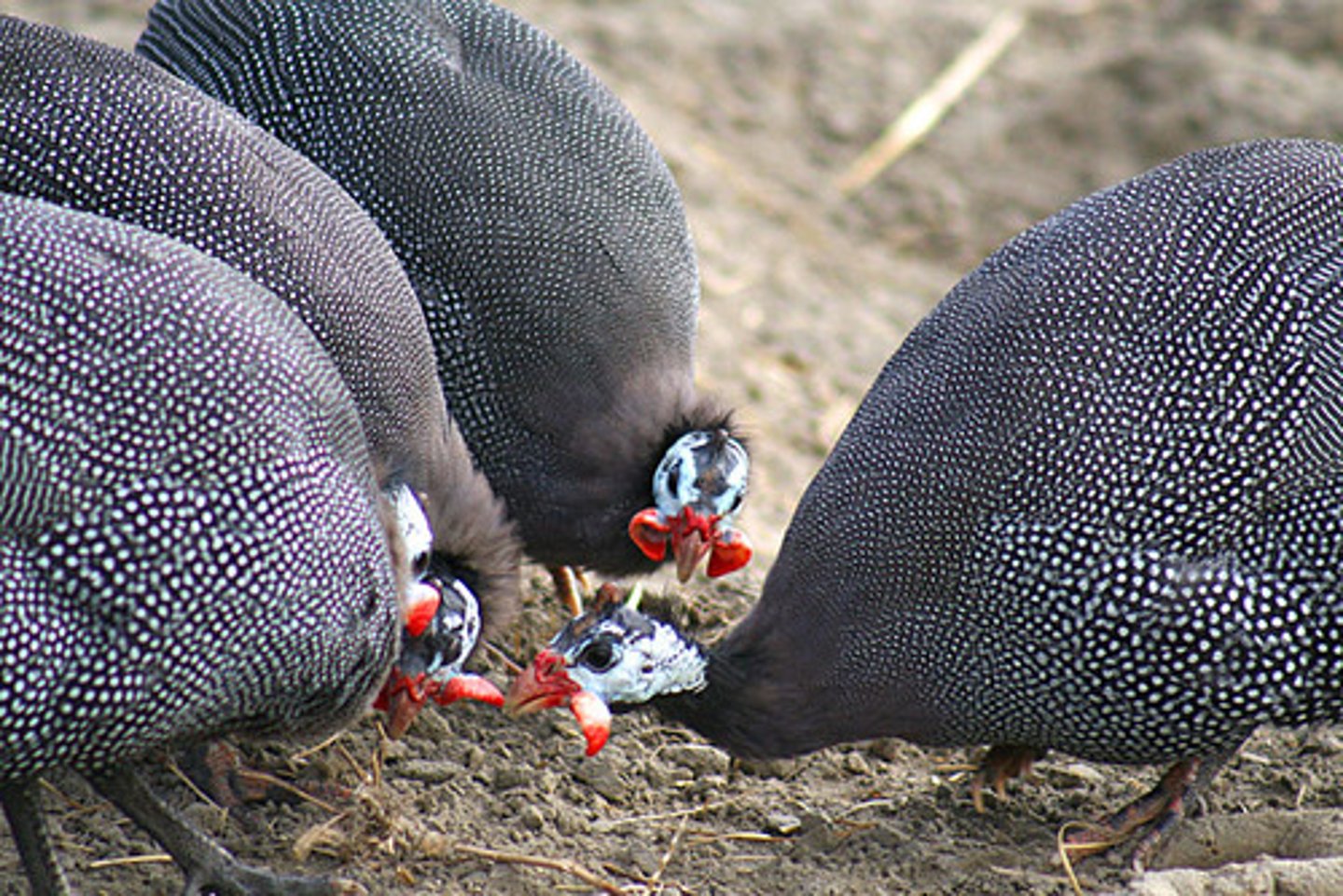

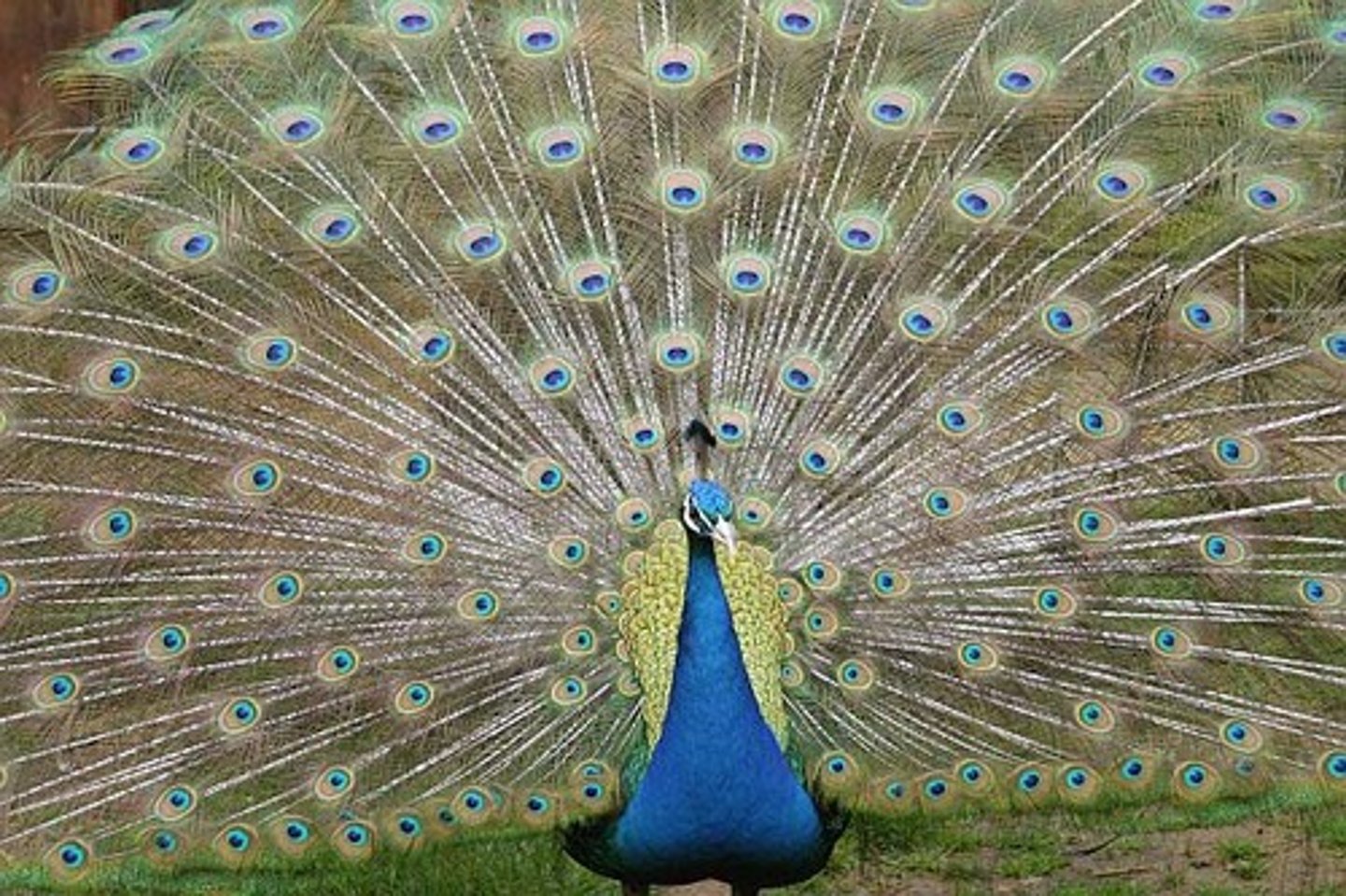
Sexual Selection
seeking and attracting mates/choosing and competing for males

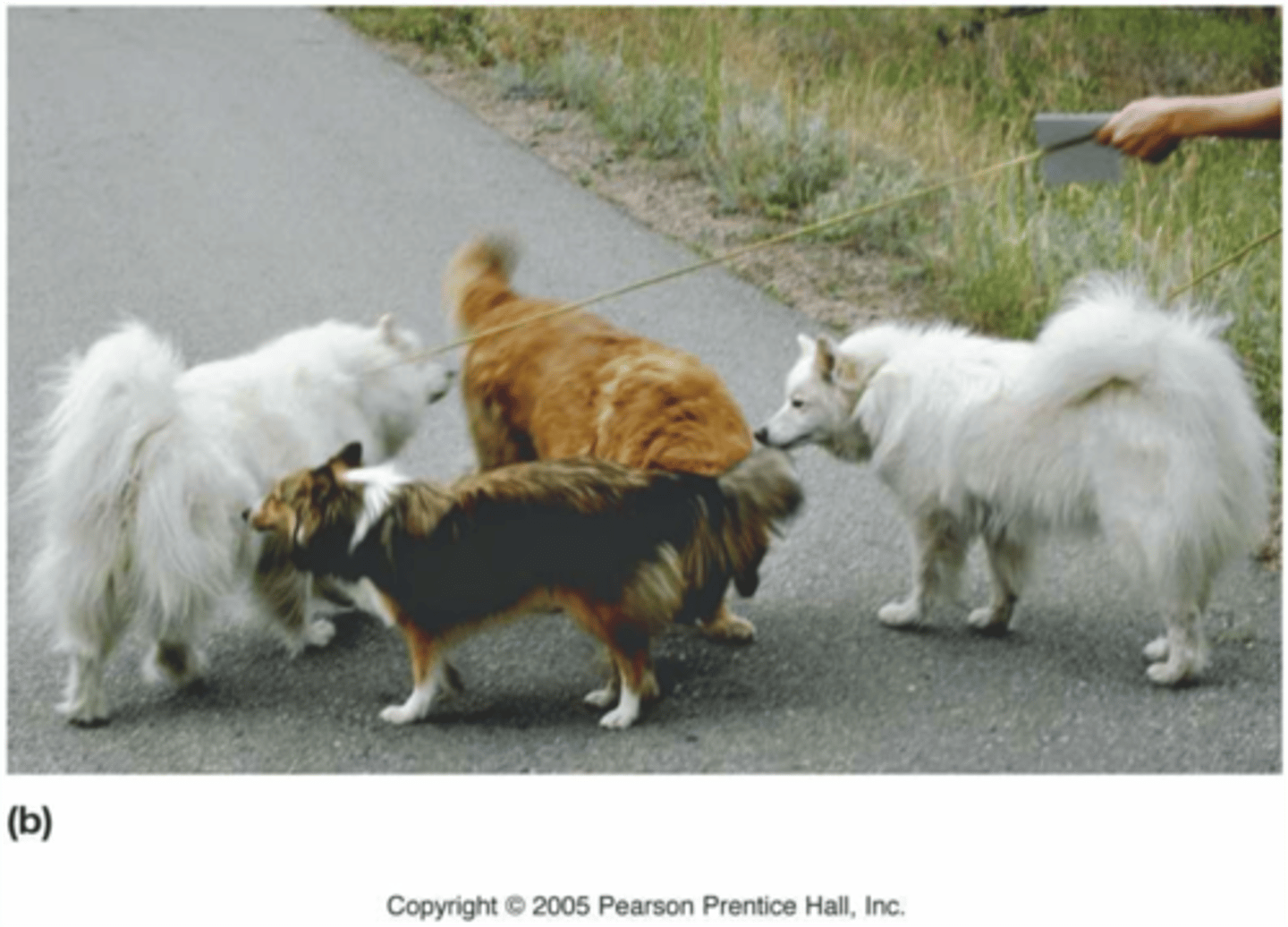
Pheromones
Chemical signals

Imprinting
Some baby bird species will follow the first moving object they see usually the mother.
example: ducks

Migration
organisms move from one place to another periodically, generally in response to temperature or food availability.
example: geese, monarch butterflies

Hibernation
An organism goes dormant for a long period of time to escape cold temperatures
example: bears, chipmunks, frogs

population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
age structure
Percentage of the population (or number of people of each sex) at each age level in a population.
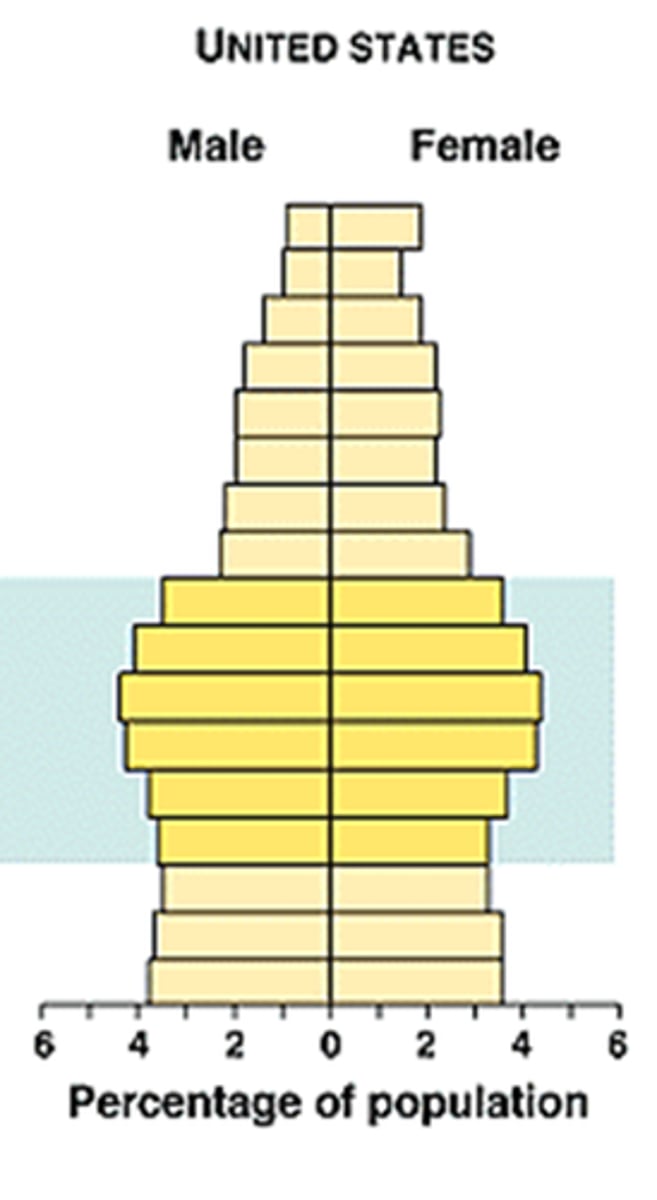
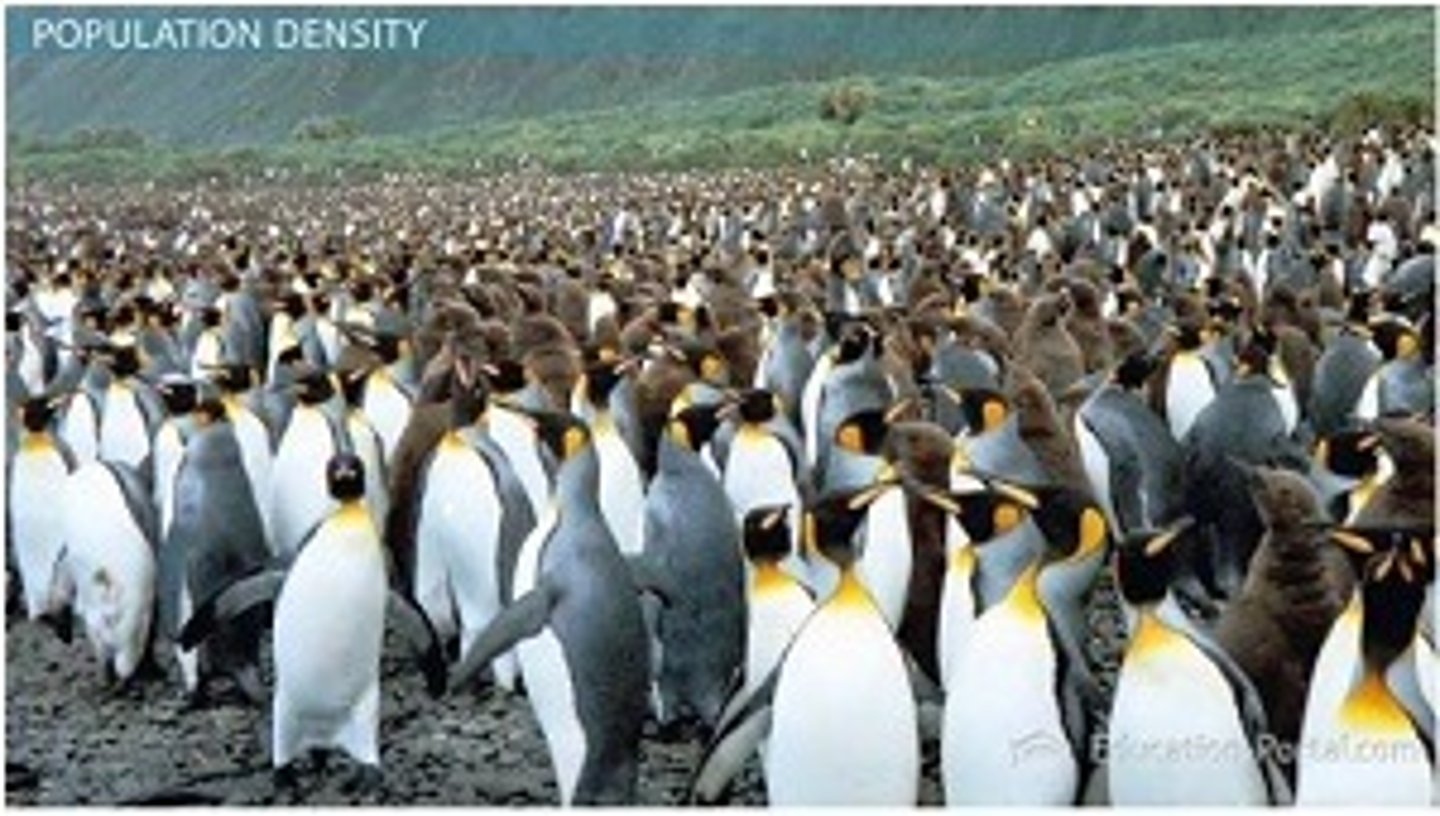
population density
Number of individuals per unit area
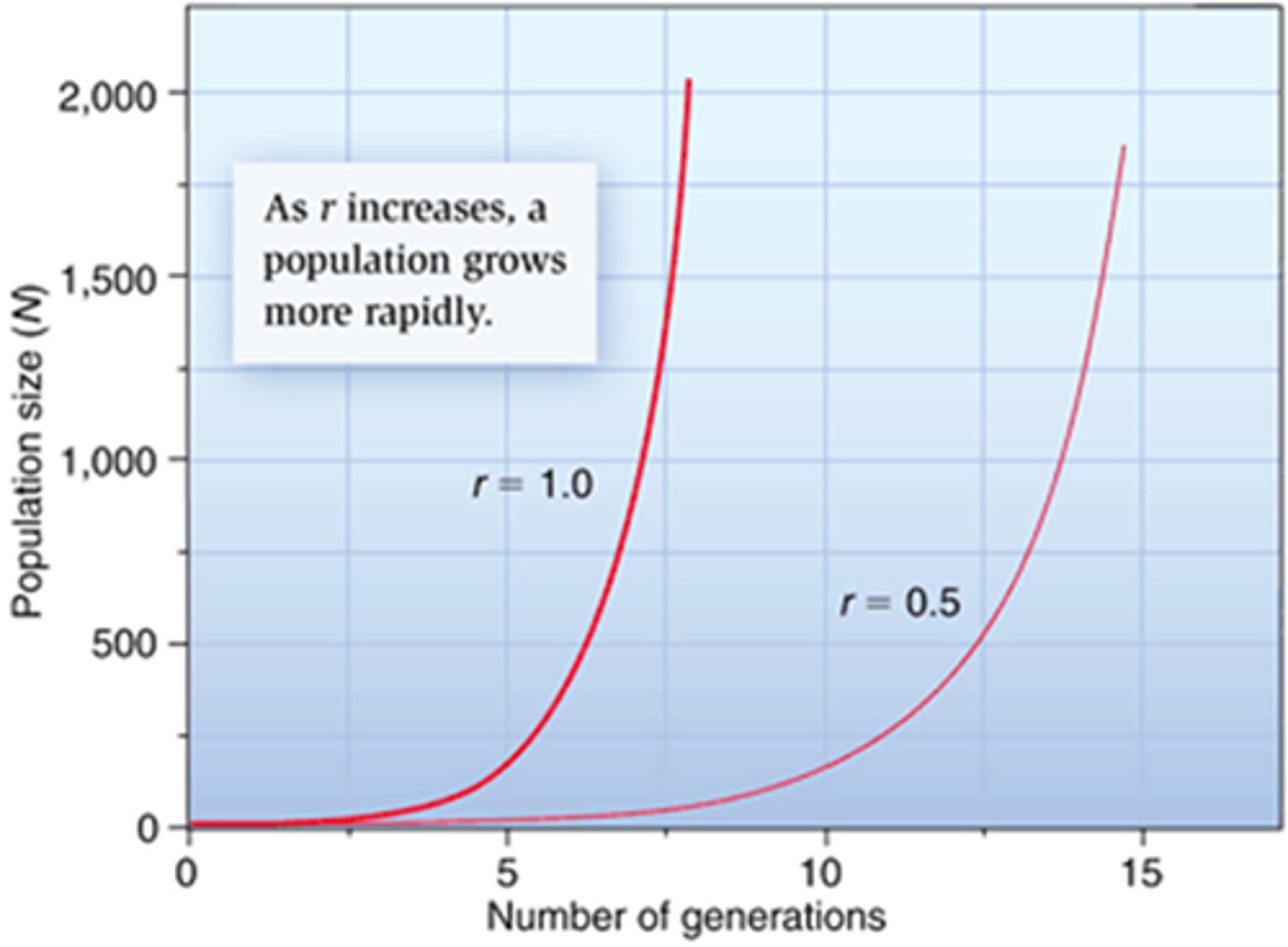
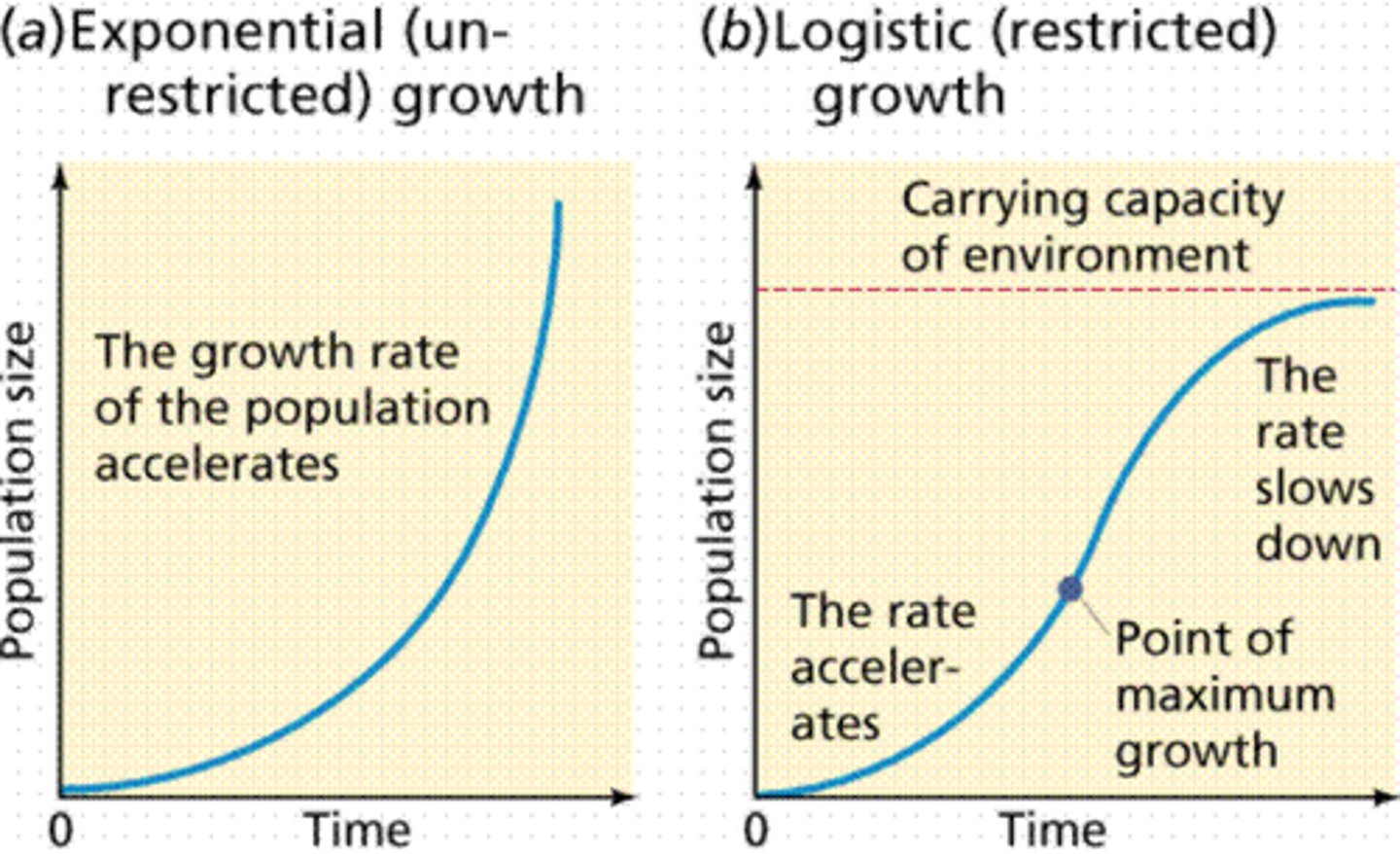
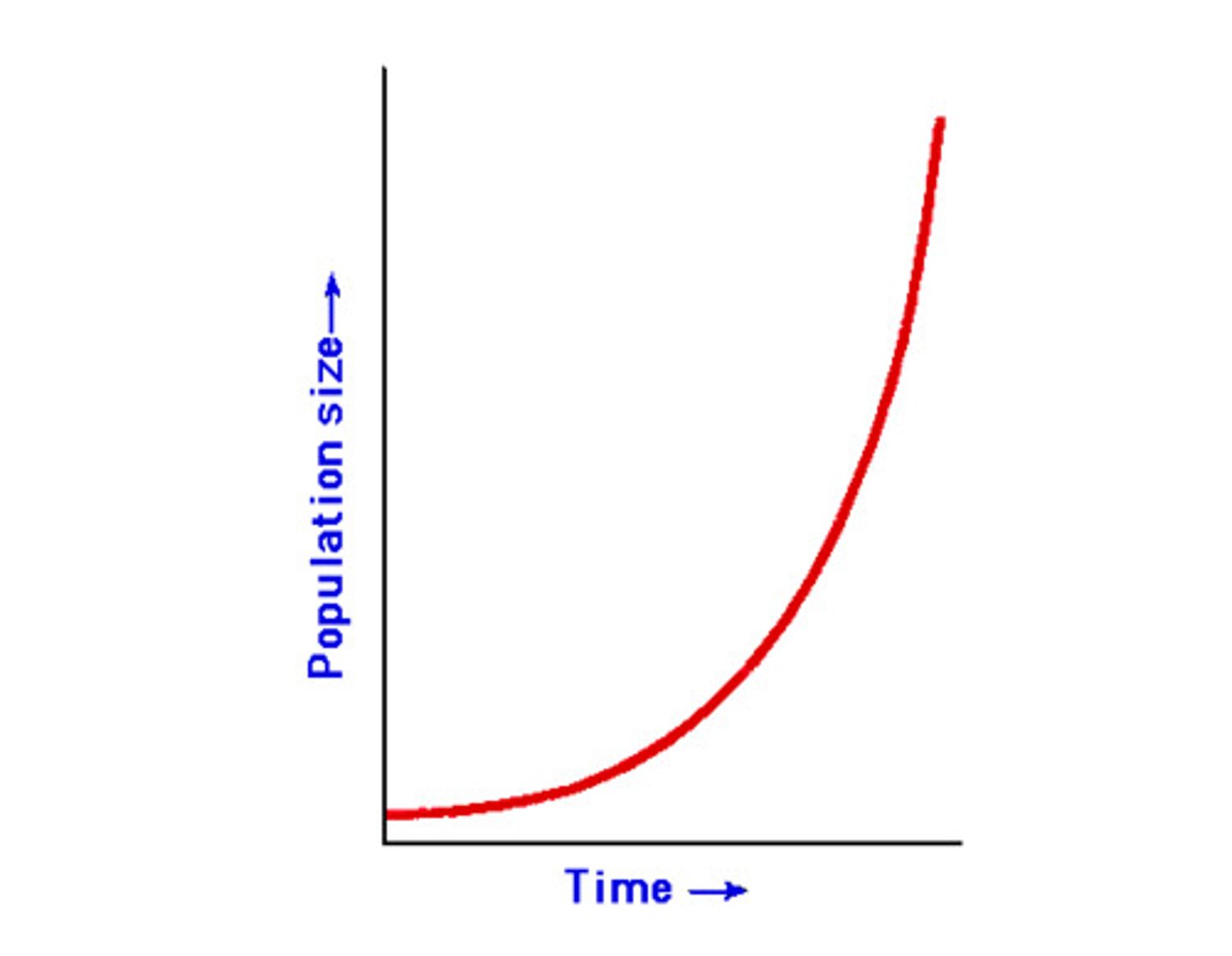
exponential growth
Growth of a population in an ideal, unlimited environment, represented by a J-shaped curve when population size is plotted over time.
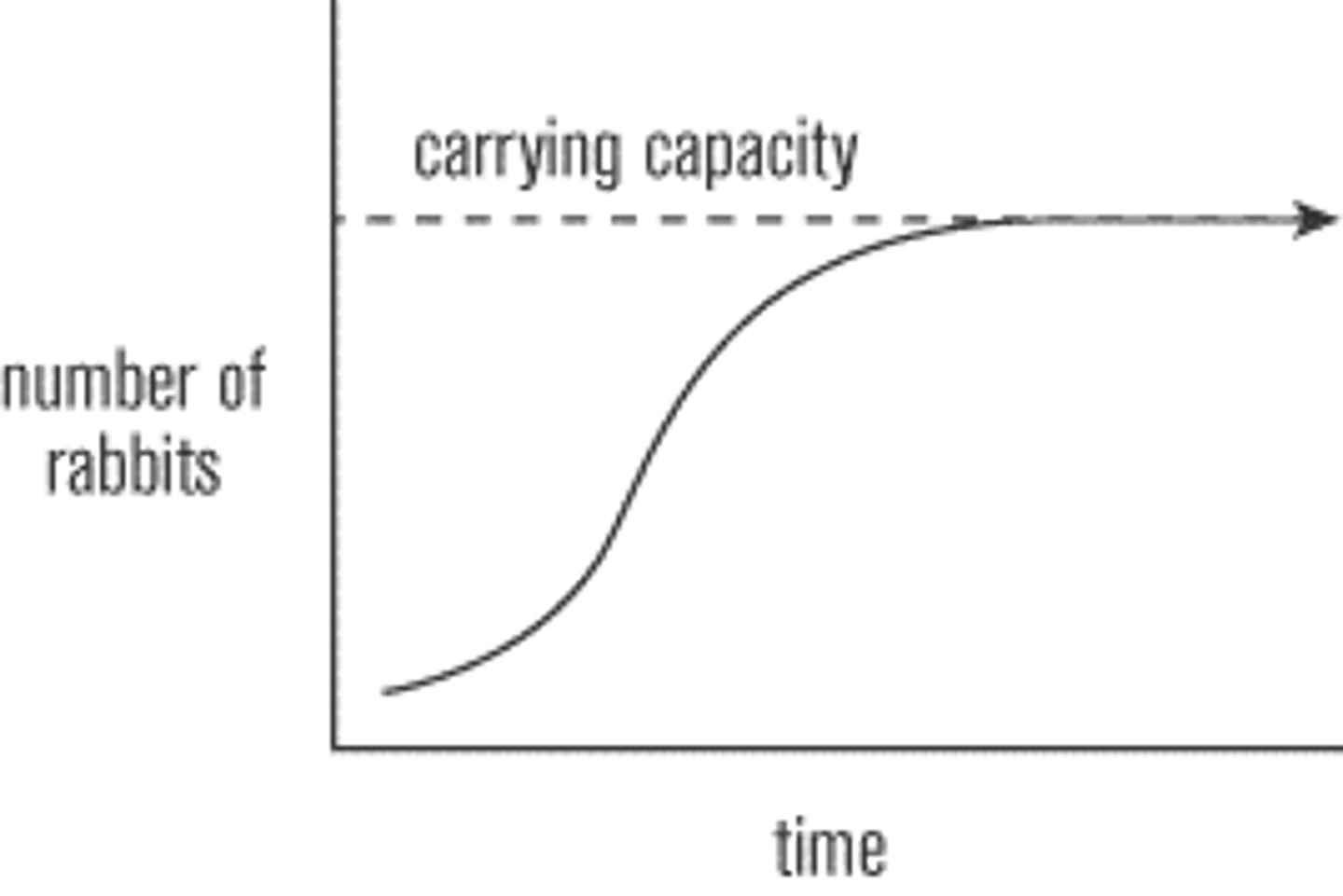
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
desnsity dependent factor
factor that limits population growth and has greater effect in dense populations than less dense populations
density independent factor
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size
limiting factor
Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms.
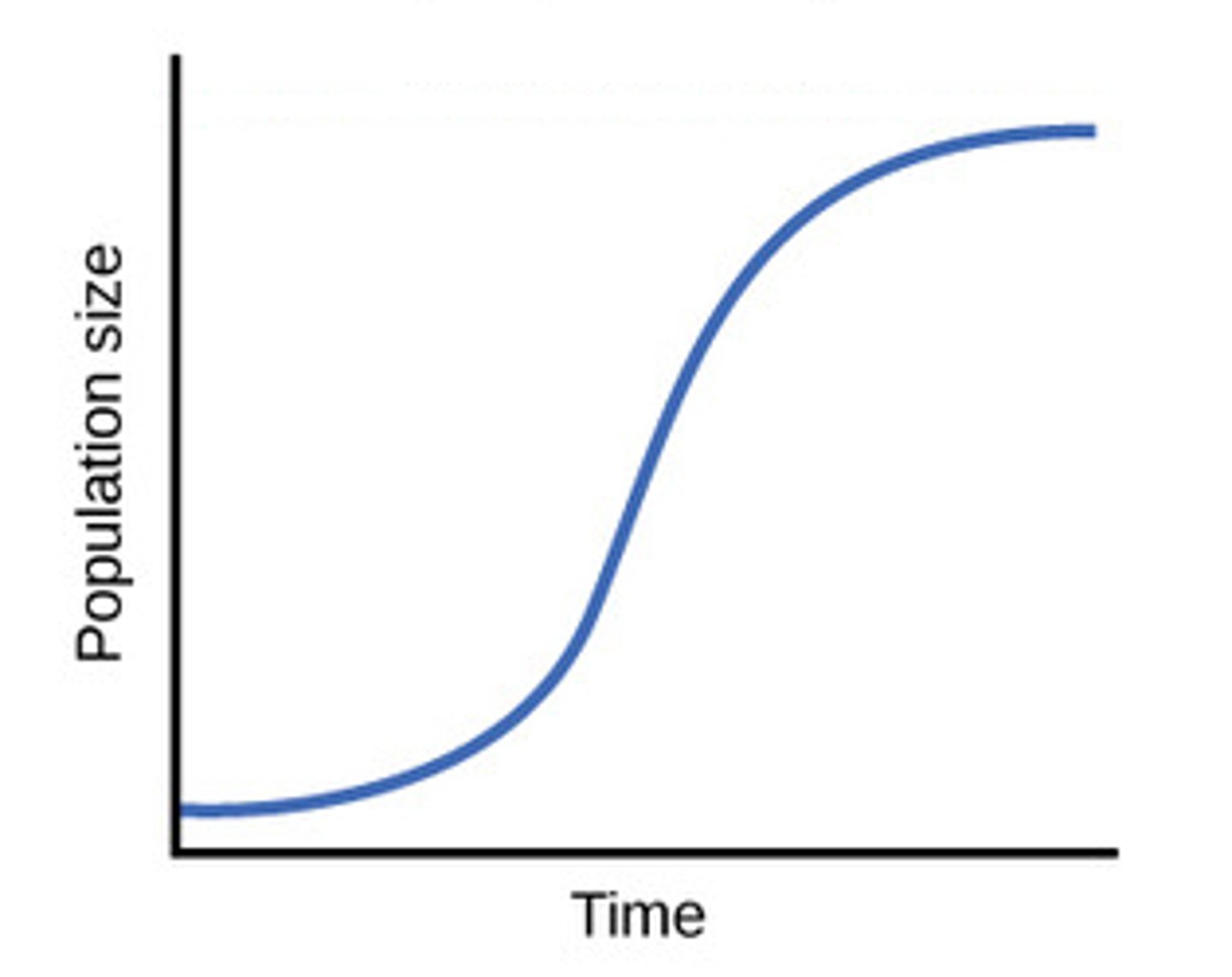
logistic growth
When limiting factors restrict size of population to the carrying capacity of the environment. Forms an S-shaped curve.
k-selected species
Species that produce a few, often fairly large offspring but invest a great deal of time and energy to ensure that most of those offspring reach reproductive age.
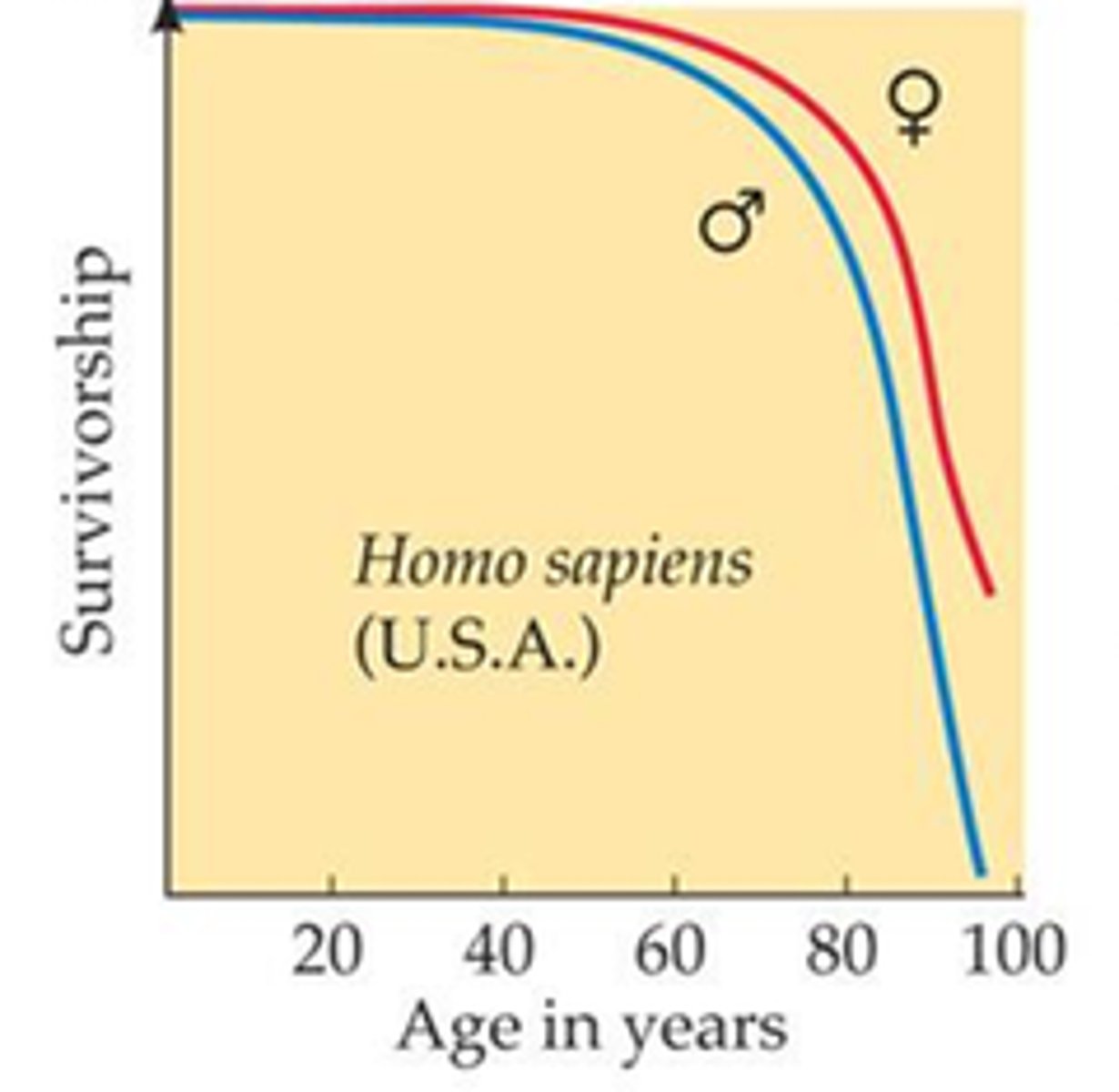
r-selected species
Life history traits maximize reproductive success in uncrowded environments. Many small offspring that mature quickly, little if any parental care.
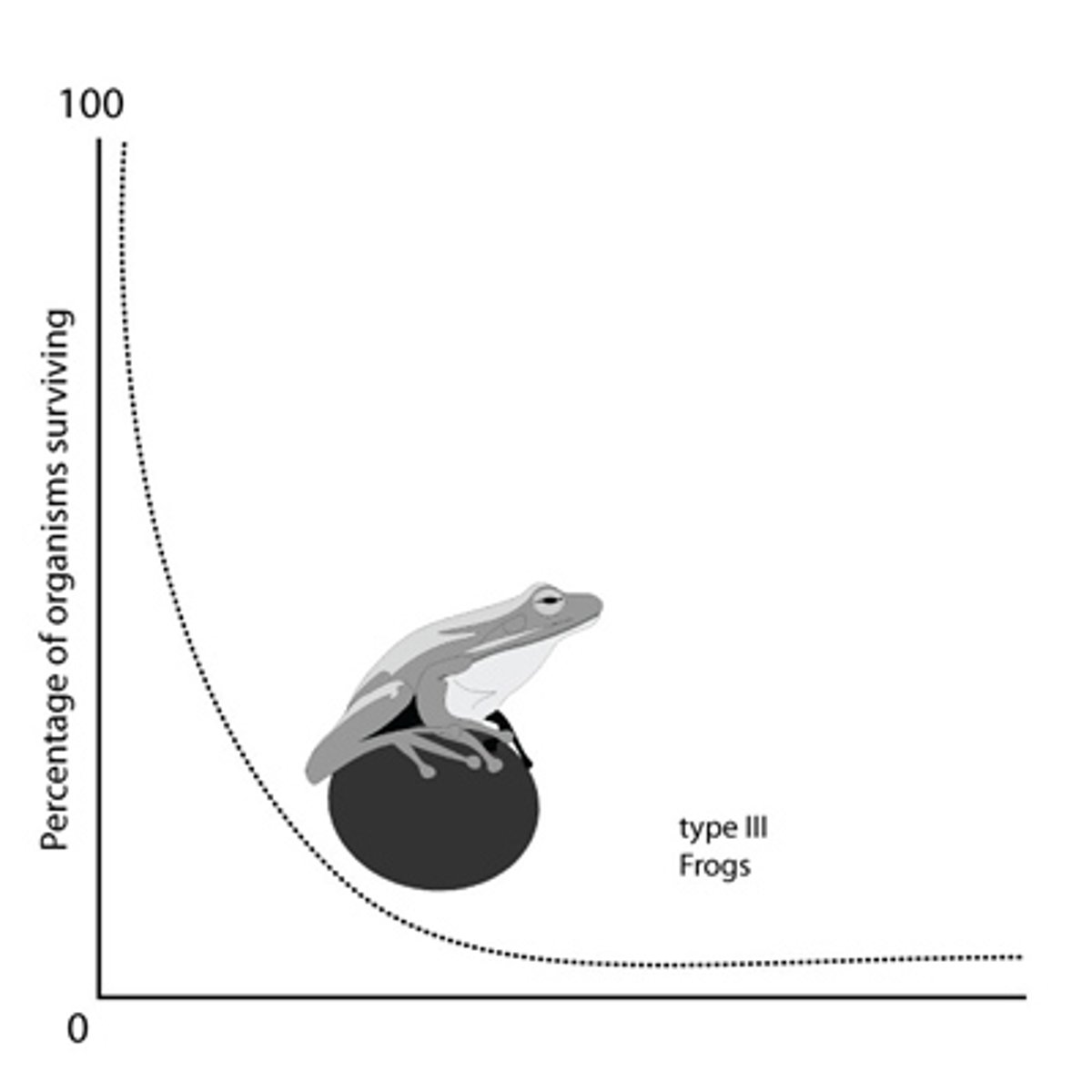
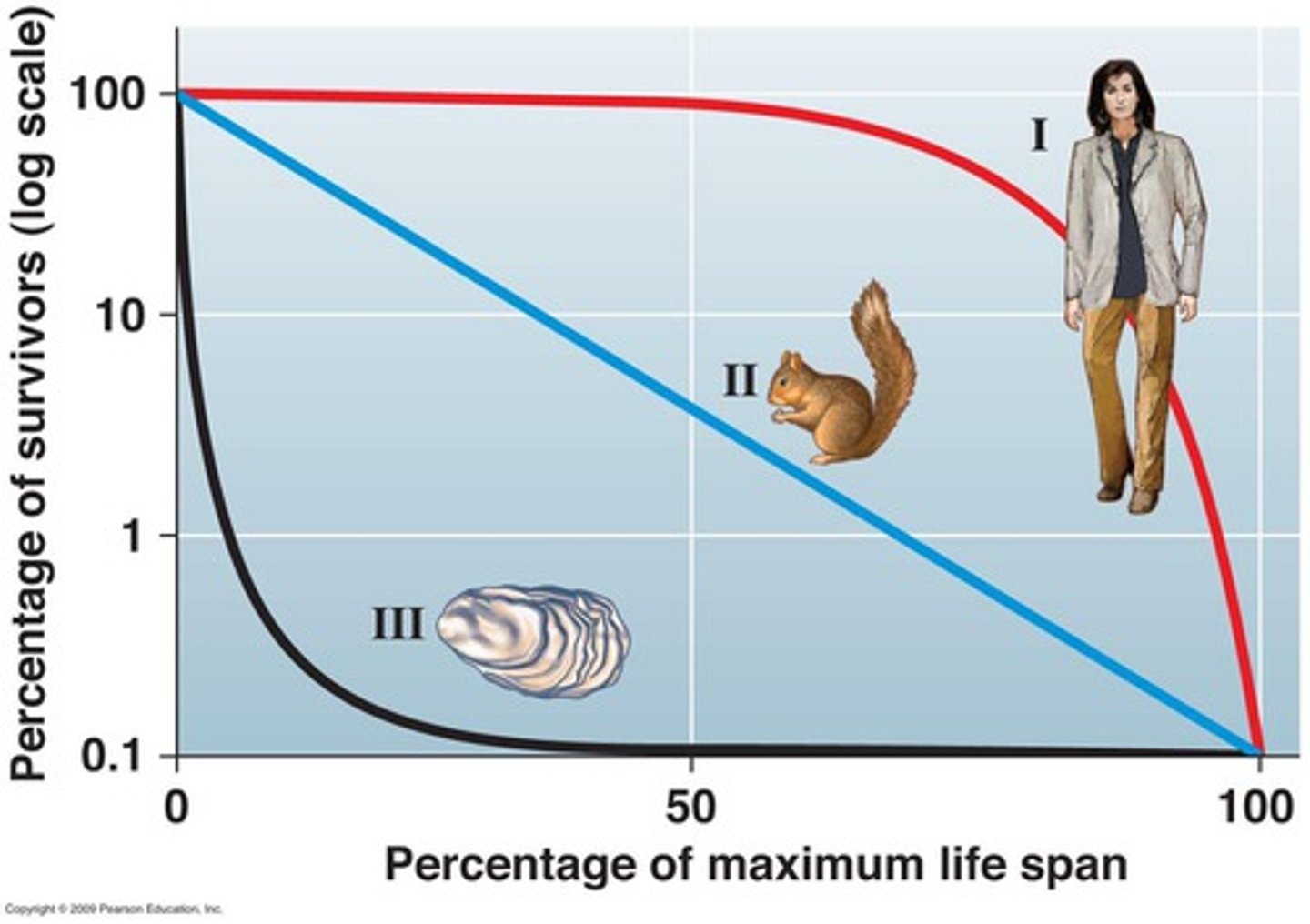
survivorship curve
a graph showing the decline in numbers of a cohort over time
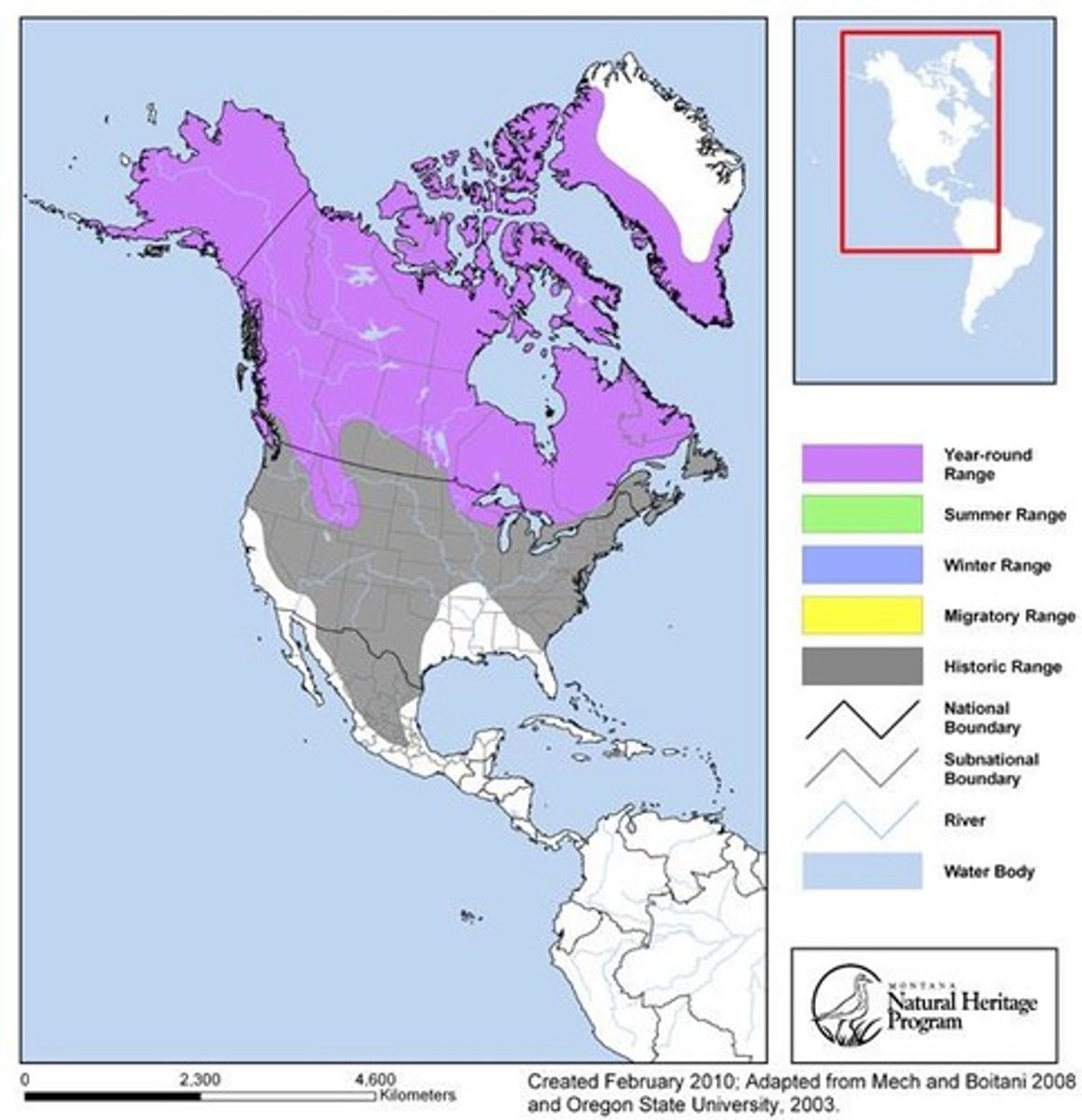
Geographic Range
The area inhabited by a population.
Population Density
For Example: Wildebeest live in densely populated herds.
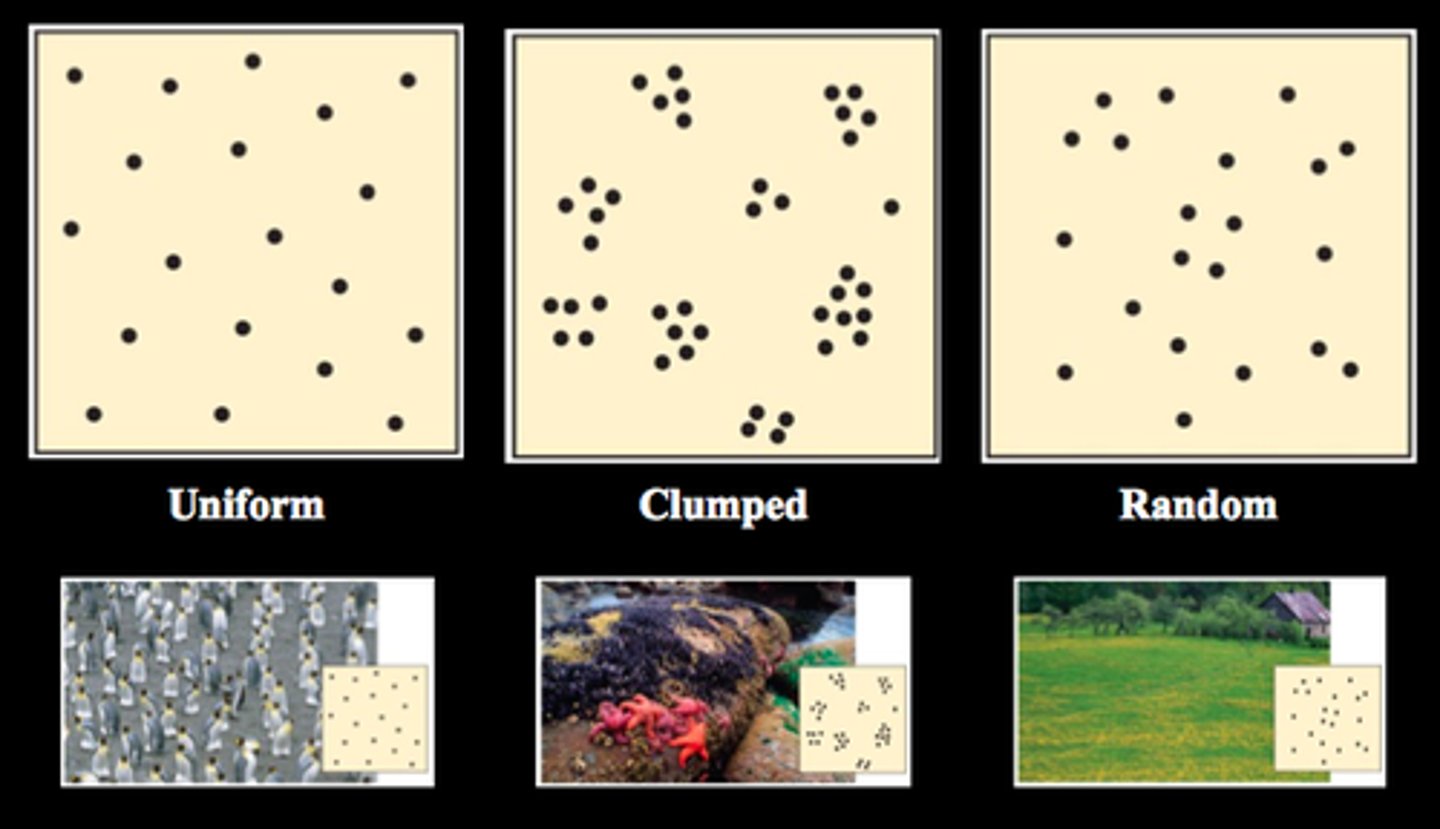
How individuals in a population are spaced out across the range. Clumped (most common), uniform, random (plants).

Population Distribution
How individuals in a population are spaced out across the range. Clumped (most common), uniform, random (plants).

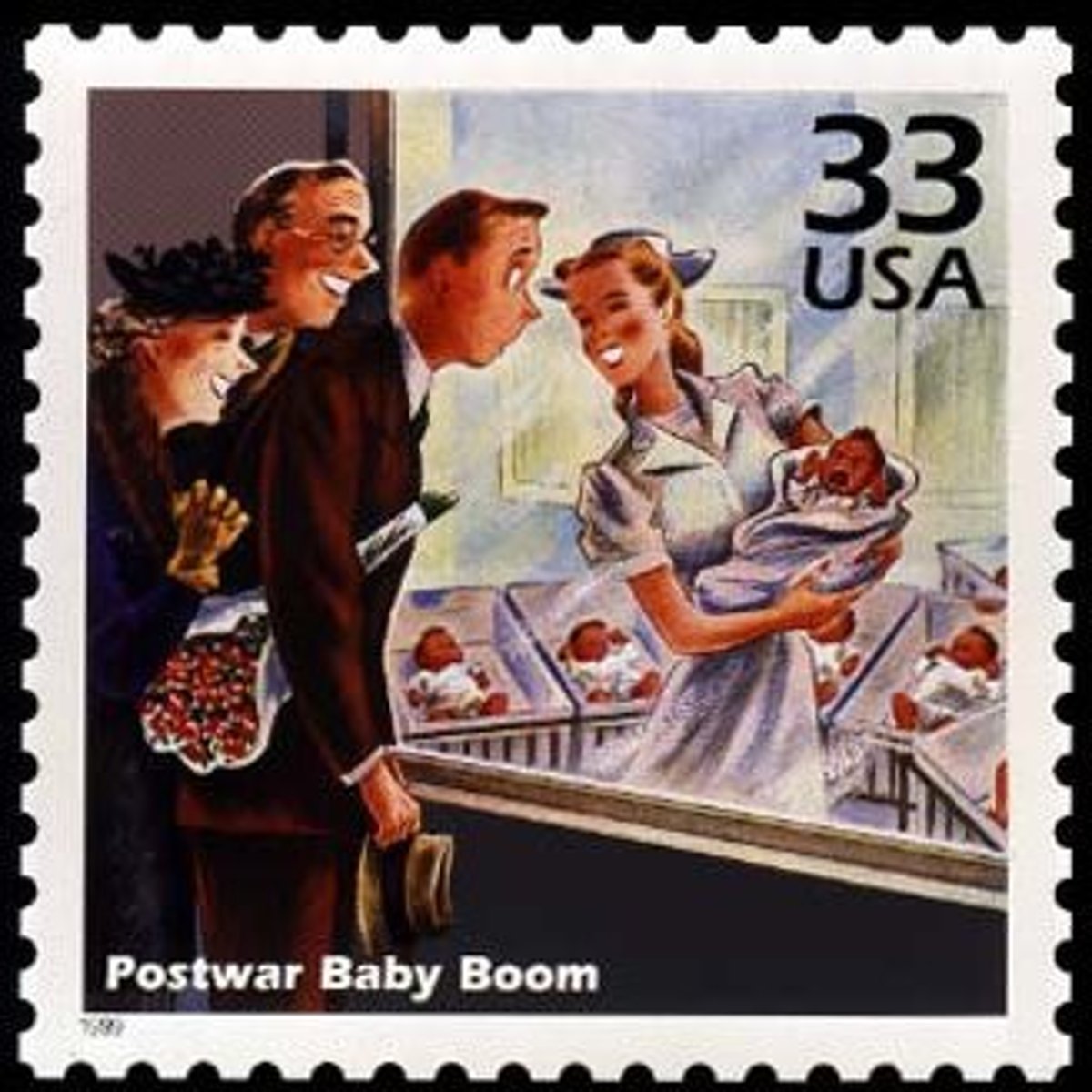
Growth Rate
This determines whether the size of the population increases, decreases, or stays the same.
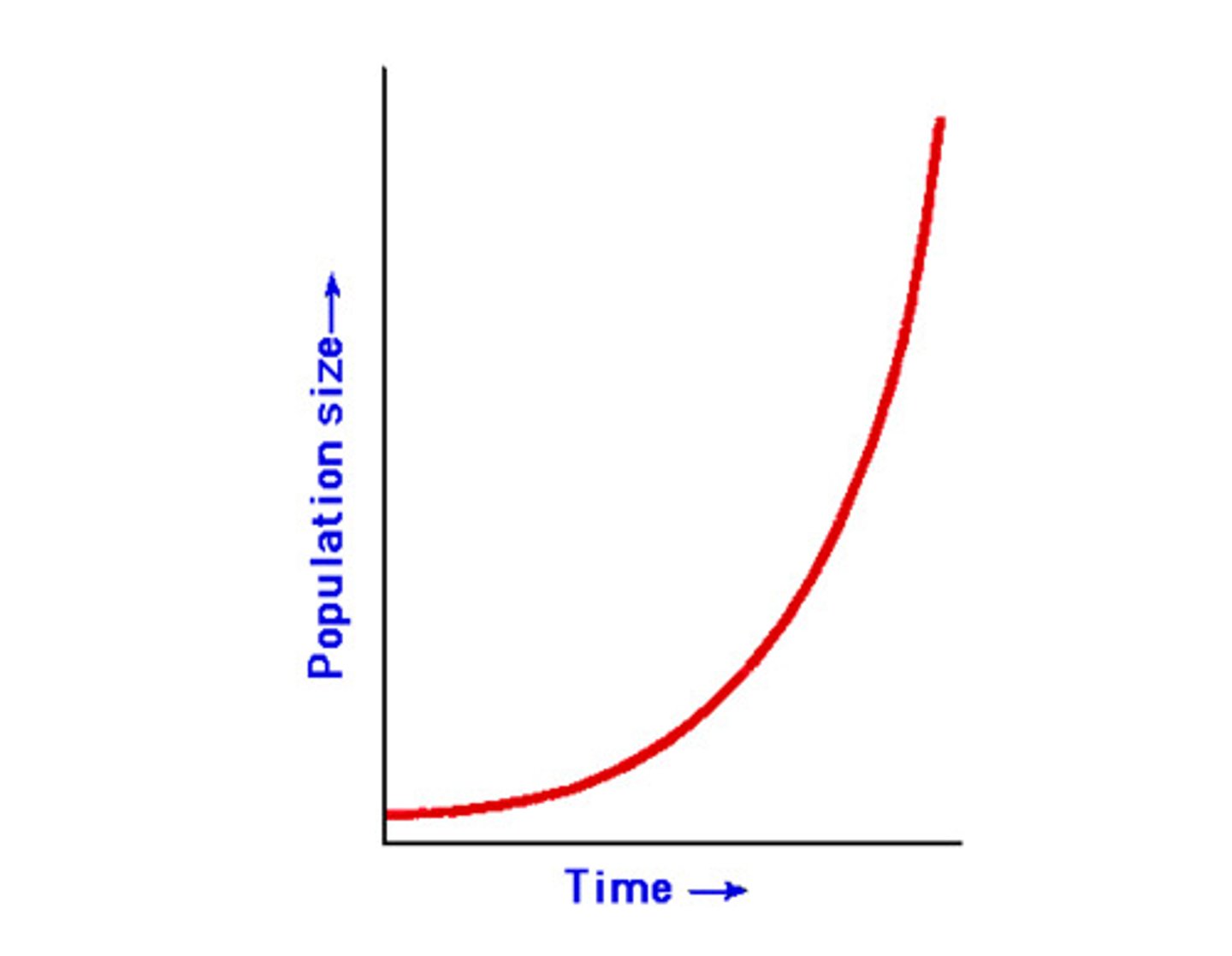
Why is Age Structure important?
Determines how many individuals are likely to reproduce in a population.

1) Birth Rate
2) Death Rate
3) Immigration
4) Emigration
4 Factors that Affect Population Growth?

Birth Rate
The rate at which individuals in a population are born.
Death Rate
The rate at which individuals in a population die.

The birth rate must be higher than the death rate.
In order for populations to grow, what has to happen to the birth rate and the death rate?

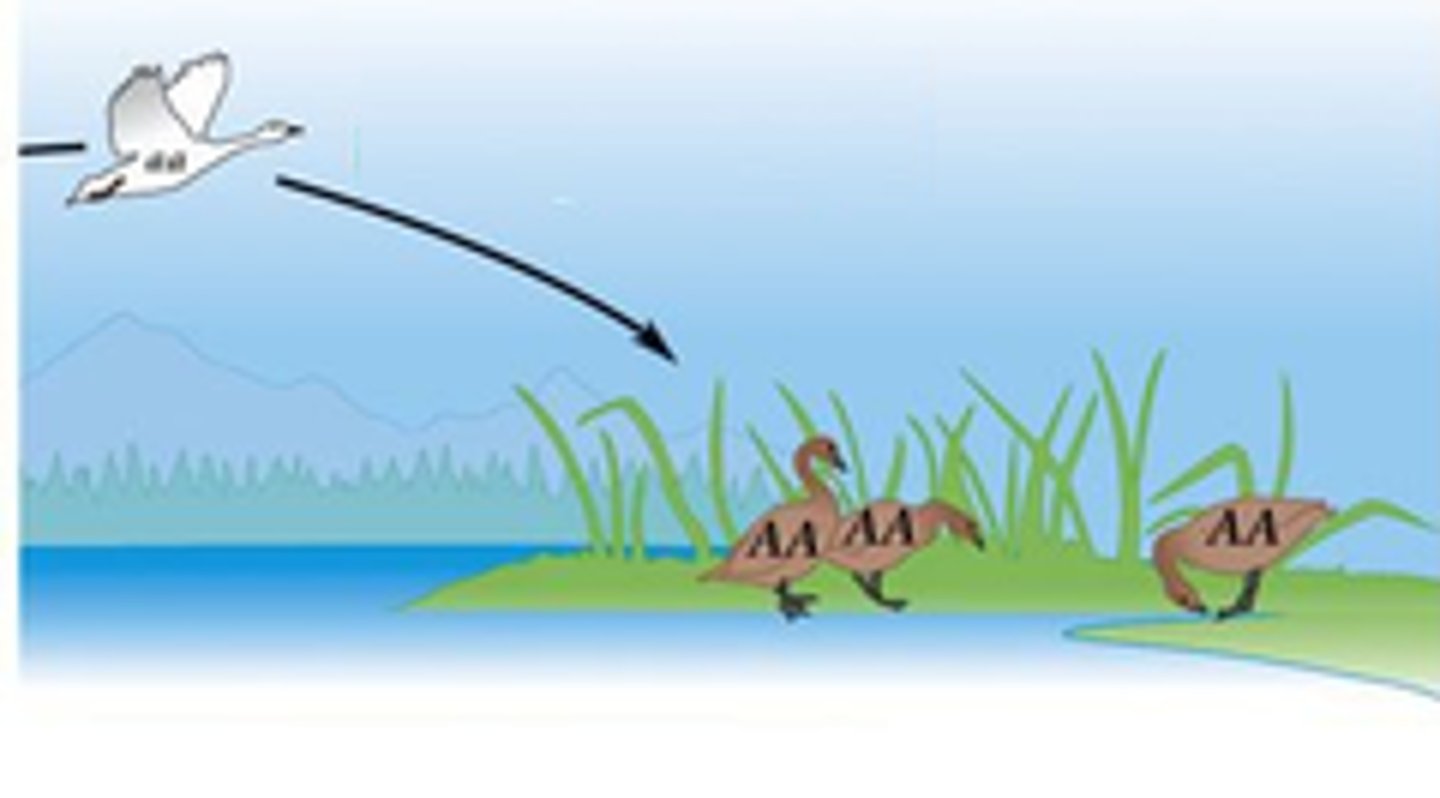
Immigration
The movement of individuals INTO an area. This can cause a population to grow.
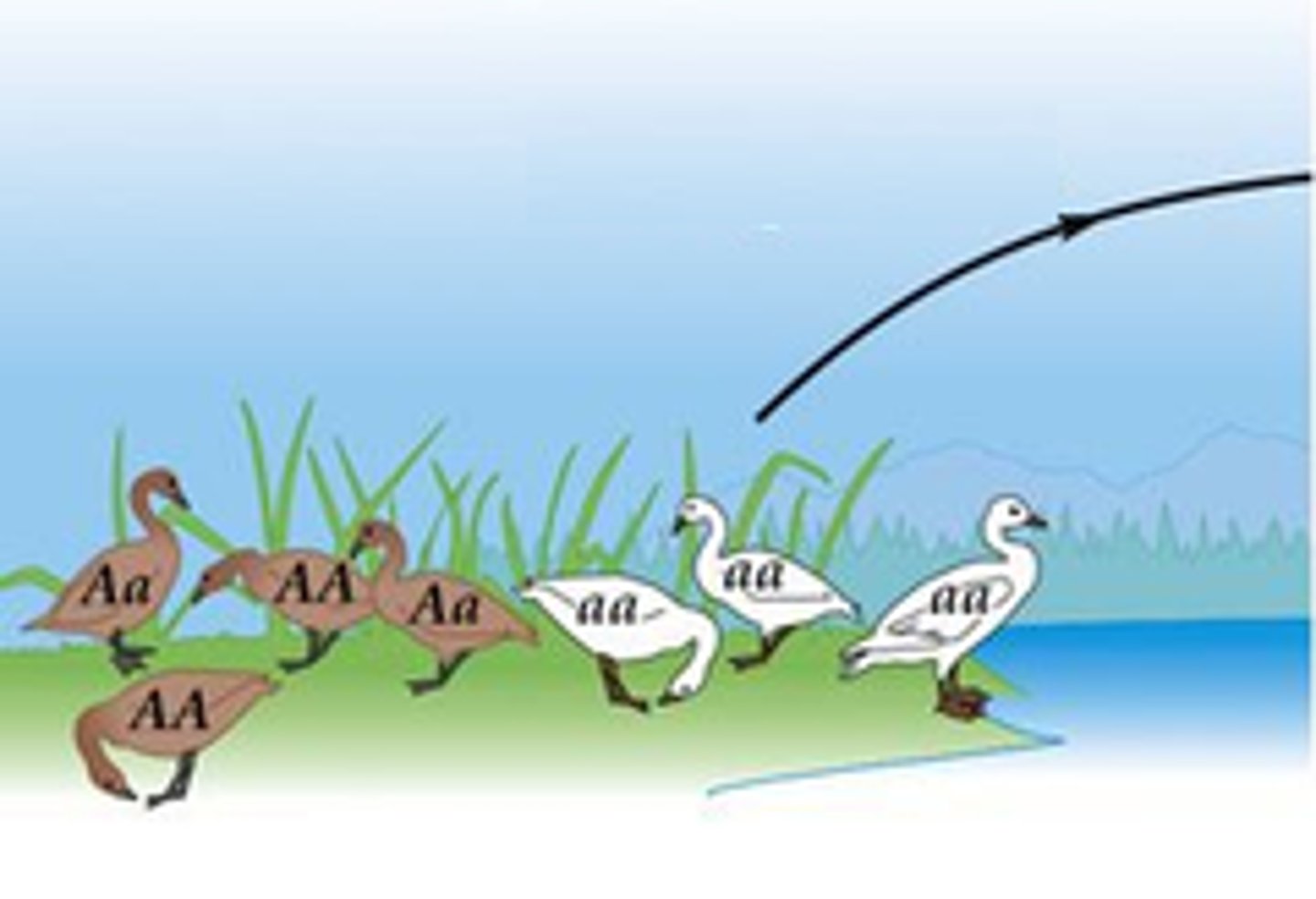
Emigration
The movement of individuals OUT of an area. This can cause a population to decrease in size.
1) Exponential Growth
2) Logistic Growth
The two different types of Population Growth
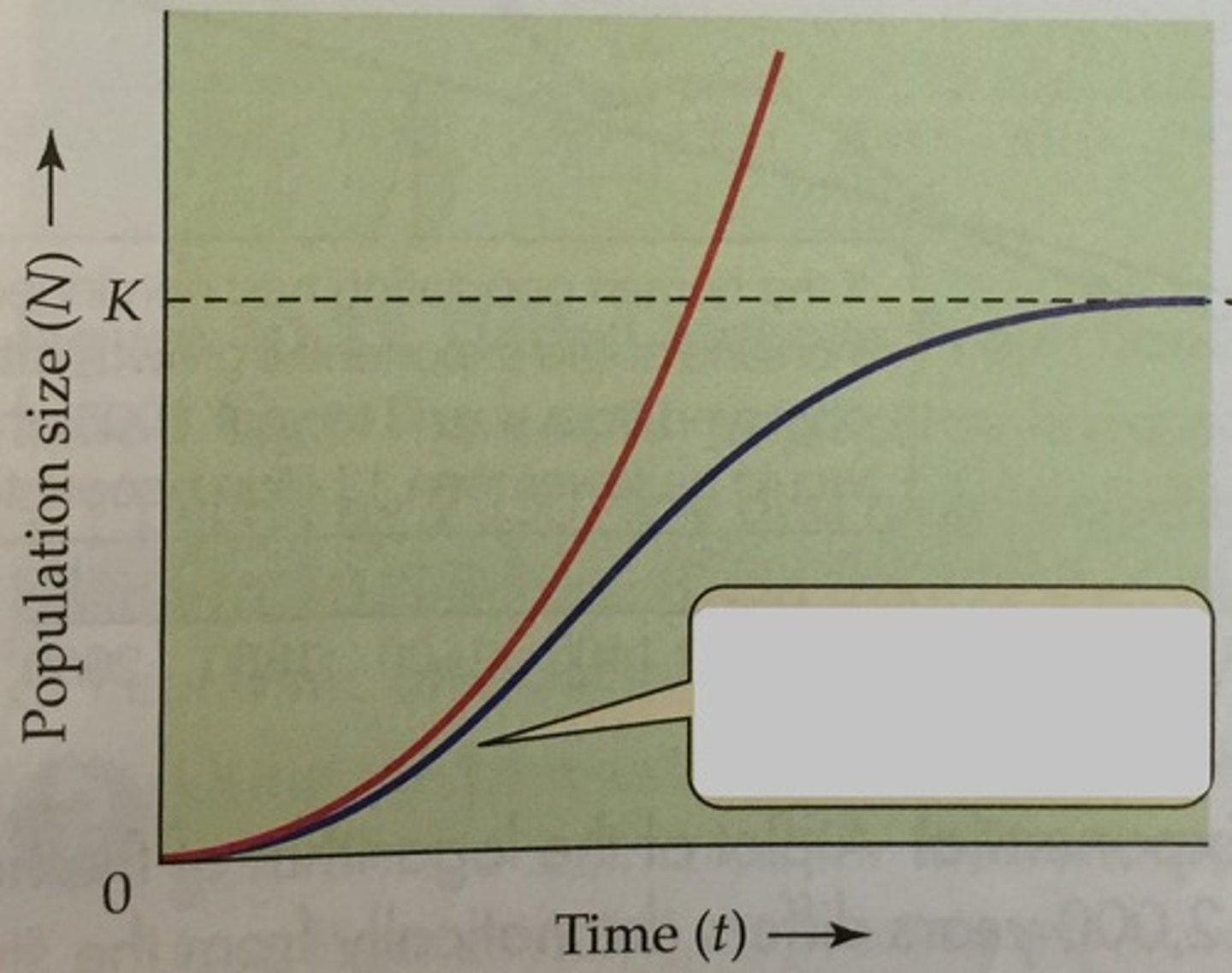
Exponential Growth
Individuals reproduce at a constant rate. The larger he population, the faster it grows. Not affected by density dependent limiting factors.
Logistic Growth
Population Growth slows or stops following a period of exponential growth. The population has reached carrying capacity and IS affected by density dependent limiting factors.
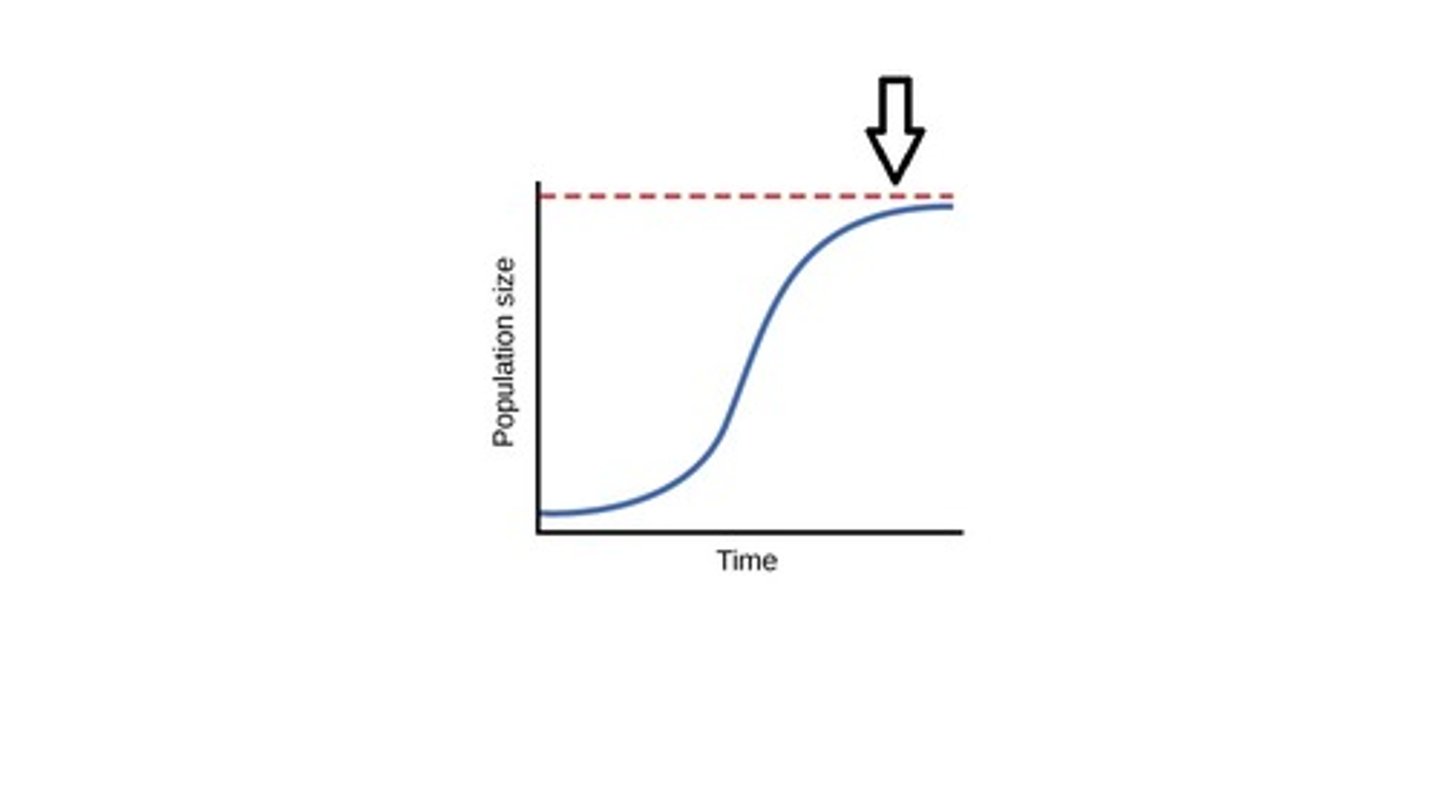
Limiting Factor
Resource/Something that can cause population growth to decrease; controls the growth of a population.

Carrying Capacity
Limiting Factors determine the _____________ of an environment for a species. (How many individuals the environment can support.)
1) Competition
2) Predation
3) Parasitism and Disease
4) Stress from Overcrowding
5) Unusual Weather
6) Natural Disaster
6 things that can limit population Density (Size).

Density dependent factor definition
A limiting factor that depends on population size.
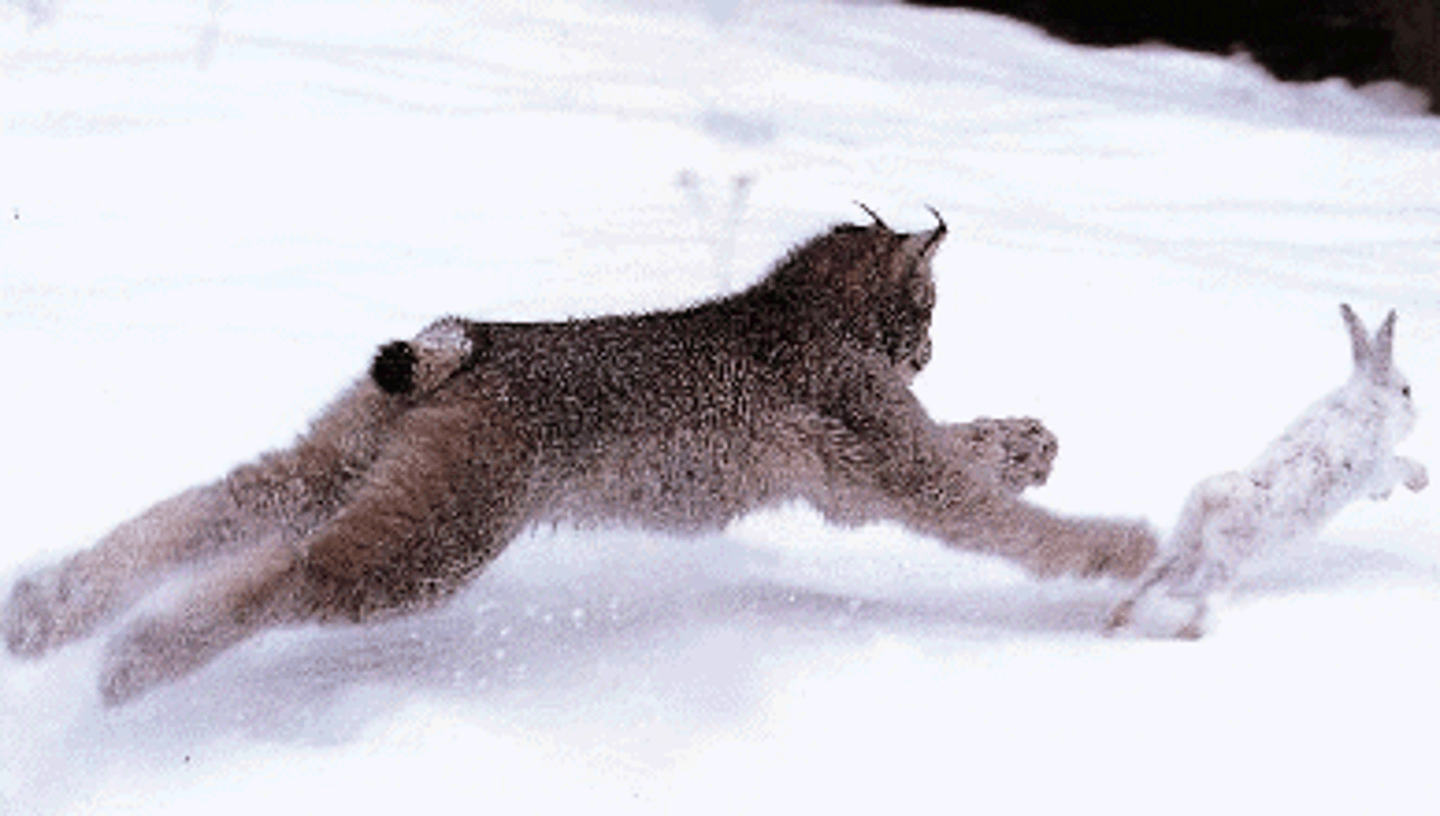

Density dependent factor examples
1) Competition
2) Predation
3) Parasitism and Disease
4) Stress from overcrowding
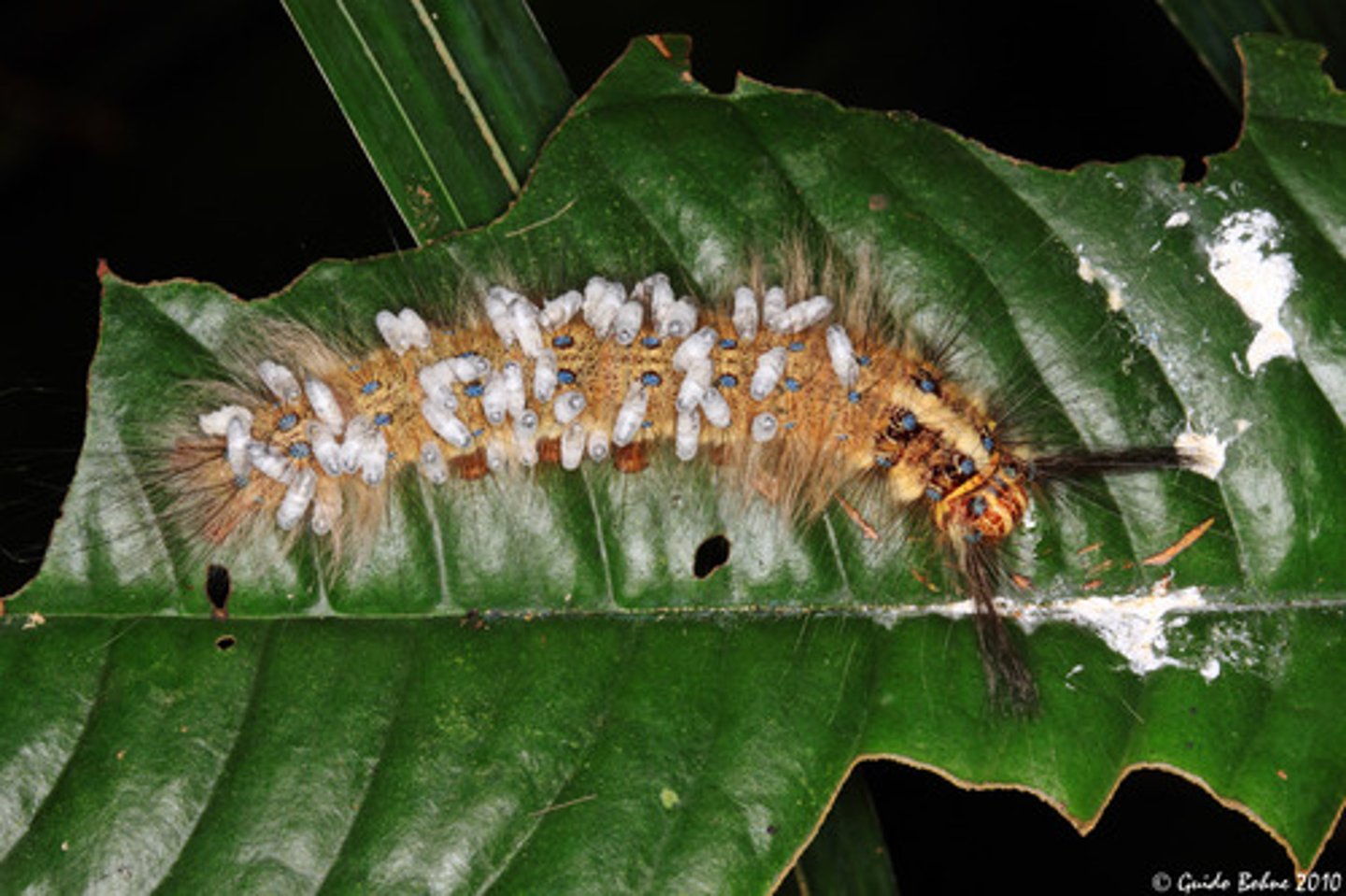

competition
Organisms fight for water, space, sunlight, and other resources. Increases as population size increases.
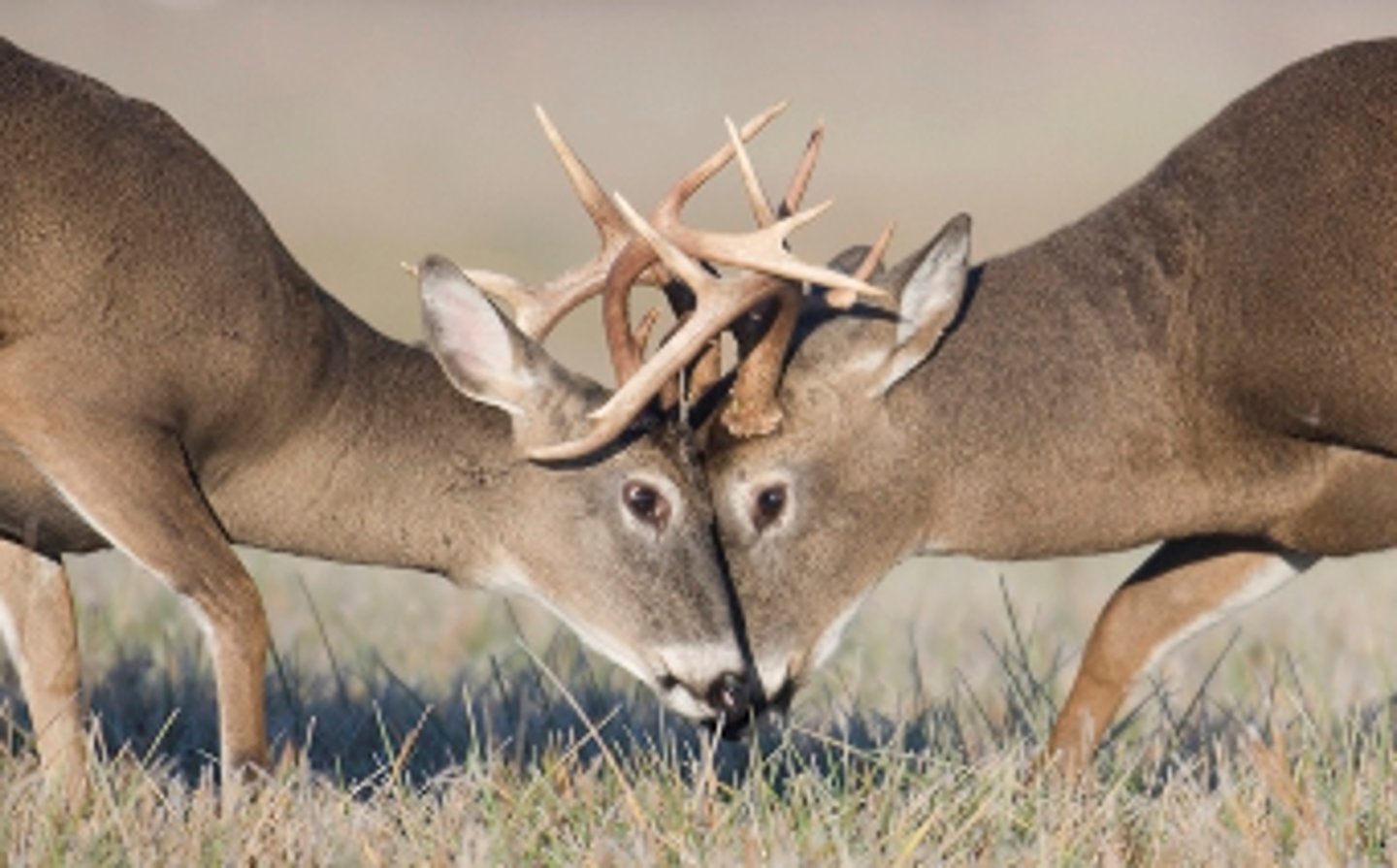

density independent limiting factor definition
Limiting factor that affects ALL populations regardless of size.
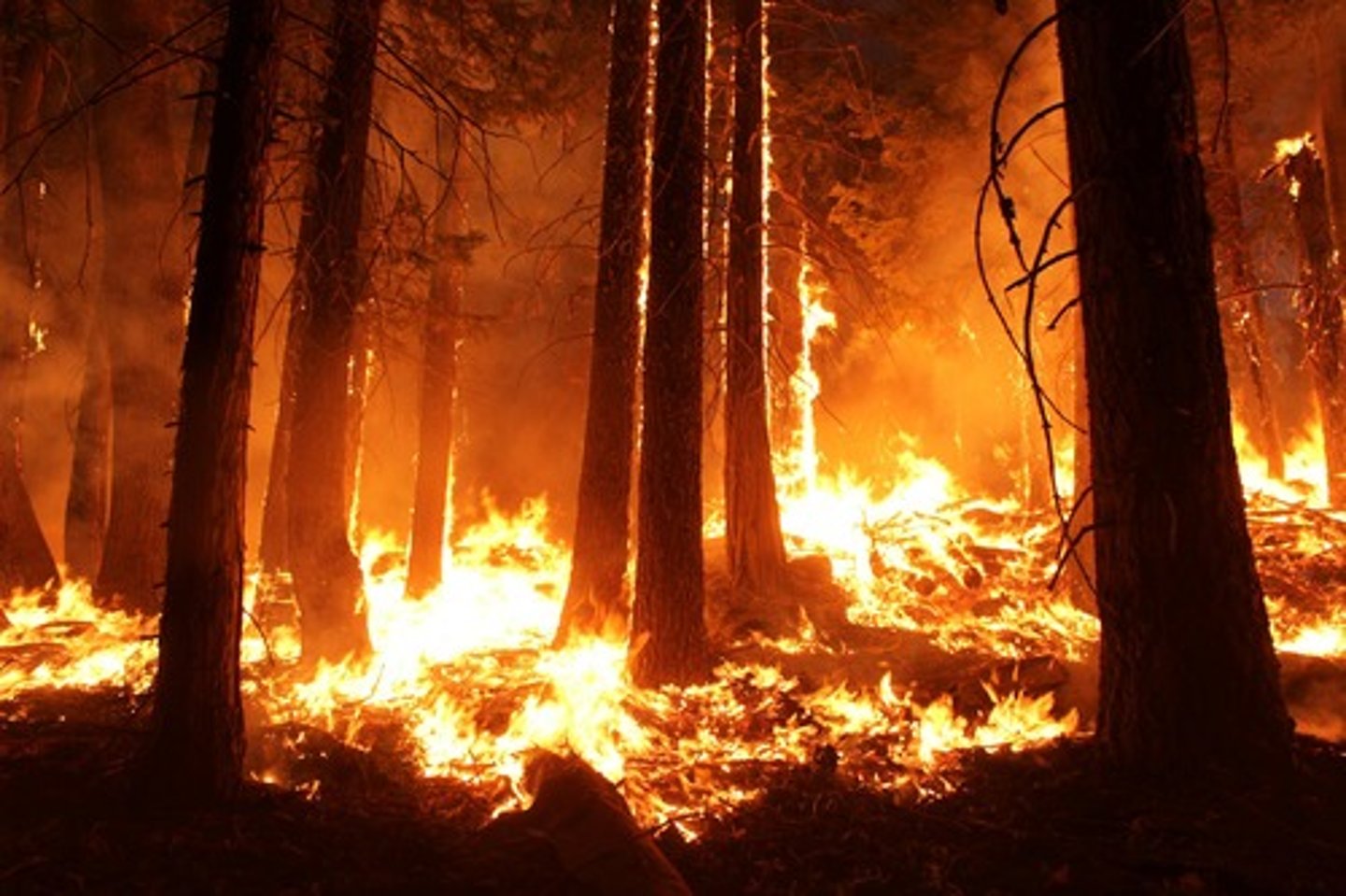

Density independent limiting factor examples
1) Weather
2) Natural Disaster
3) Seasons
4) Human Activities
