Discrete Mathematics 2
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Probability
It is a measure of how likely an event is to occur. It quantifies the uncertainty of events and is expressed as a number between 0 and 1.
0
It indicates that the event is impossible.
1
It indicates that the event is certain.
Experiment
It is an action or process that produces a result. In probability, this result is uncertain.
Outcome
It is a possible result of an experiment.
Sample space
It is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
Event
It is a specific outcome or set of outcomes that we are interested in. It is a subset of the sample space.
Random Variables
It is a variable whose values are determined by the outcome of a random event. These are fundamental concepts in probability and statistics.
Discrete Random Variable
It can only take a finite number of distinct values. The values are exact and can be represented by nonnegative whole numbers.
Continuous Random Variable
It can assume an infinite number of values in an interval between two specific values.
Conditional Probability
It is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It's denoted as P(A∣B).
Independence
The probability of both events happening is the product of their individual probabilities.
Steps for solving probability problems
1.Identify the experiment
2.List the sample space
3.Identify the event
4.Use the classical probability formula
Steps on how to find the value of the random variable on any events or experiments
1.Assign letters that will represent each outcome.
2.Determine the sample space.
3.Count the number of the random variable.
The formula for conditional probability is:
Where:
•P(A∩B) is the probability that both events A and B occur.
•P(B) is the probability of event B occurring (and it must be greater than 0).
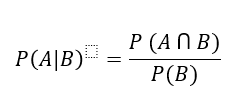
The mathematical condition for independence is:
P(A∣B)=P(A)
This means that if event B has occurred, it does not change the probability of A.