Large Animal Exam 2
1/426
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
427 Terms
Primary indigestion categories:
reticuloruminal motor disorders or diseases of rumen wall
reticuloruminal fermentive (microbial and biochemical) disorders
kinds of reticuloruminal motor disorders or diseases of rumen wall:
traumatic reticuloperitonitis
frothy bloat
free gas bloat
reticulitis/rumenitis
ruminal parakeratosis
obstructive indigestion
obstruction of cardia
obstruction of reticulo-omasal orifice
diaphragmatic hernia
kinds of reticuloruminal fermentive (microbial and biochemical) disorders:
inactivity of rumen microbial flora (caused by rumen impaction)
simple indigestion
acute ruminal lactic acidosis
rumen alkalosis
putrefaction of rumen ingesta
secondary indigestion is secondary due to…
systemic illness
secondary indigestion categories:
secondary reticuloruminal motor inactivity
secondary reticuloruminal microbiota inacativity
abomasal reflux
rumen fluid parameters:
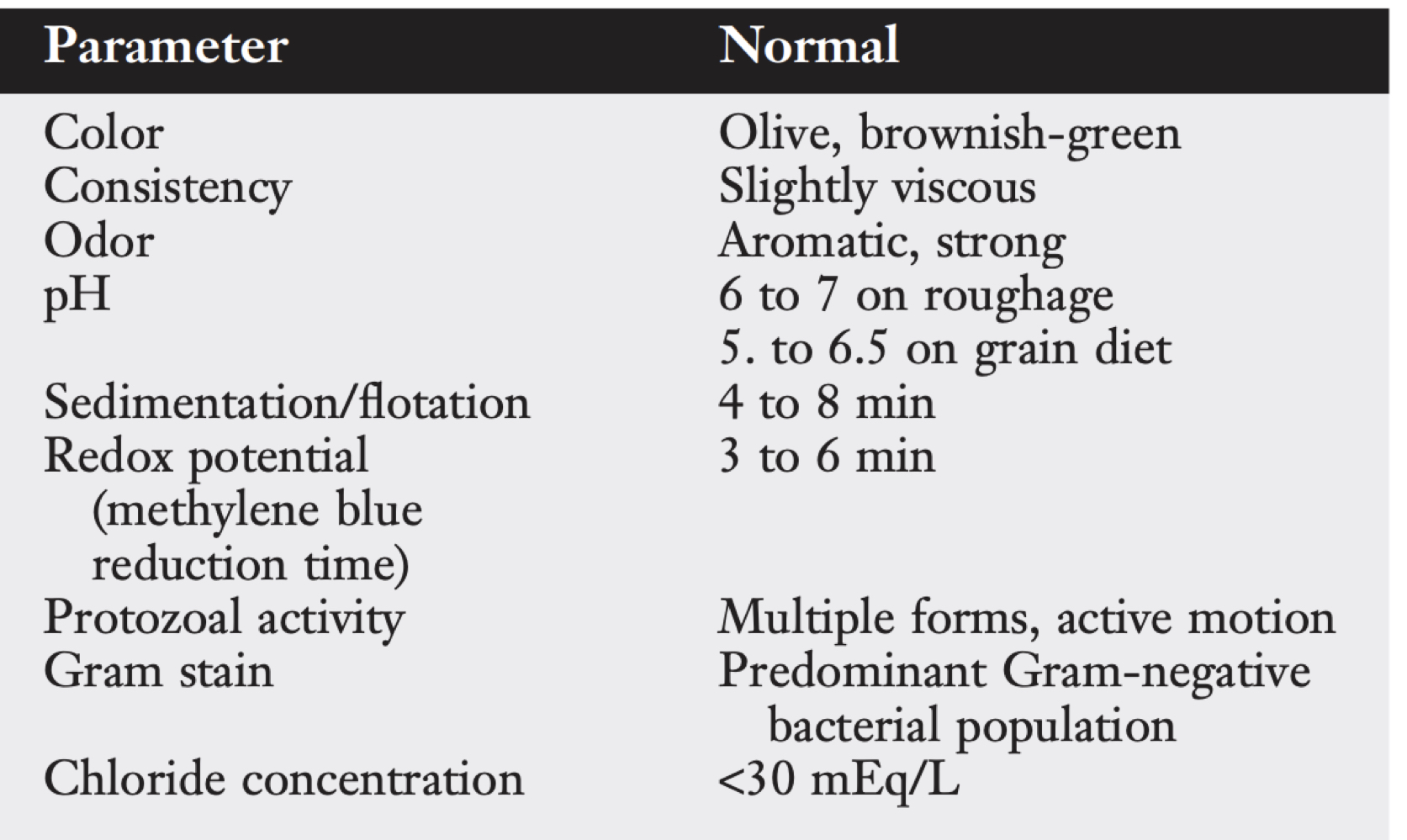
grain (low pH) + high protein diets (high pH) =
atony
indigestion clinical signs:
decreased appetite
reduced milk production
anorexia
dullness
no rumination
depressed or absent ruminal movements
enlarged rumen
tympany
firm, doughy rumen
reduced fecal output/dry feces
diarrhea
differential diagnoses for indigestion:
acetonemia
TRP
grain overload
LDA
right side dilation of abomasum
abomasal volvulus
vagal indigestion
phytobezoars
systemic disease
indigestion treatment:
rumen lavage
rumenatorics
parasympatheticomimetics
alkalinizing and acidifying agents
re-establish rumen microflora
obstructive indigestion syndrome
group of motor disturbances that hinder passage of ingesta out of reticulorumen or abomasum or both
causes of outflow disorders:
extraluminal
intraluminal
intramural
nerogenic
extraluminal causes of outflow disorders:
adhesions
abscesses
distortion of esophageal groove
intraluminal causes of outflow disorders:
foreign bodies
straw
intramural causes of outflow disorders:
neoplasia
inflammatory abscesses
granulomas
neurogenic causes of outflow disorders:
adhesions
lesions affecting tension receptors in medial wall of reticulum
anterior stenosis
no passage of ingesta from reticulorumen to omasum and abomasum
posterior stenosis
inhibition of abomasal flow resulting in impaction
anterior stenosis is caused by ______ vagal nerve branch injury
dorsal
posterior stenosis is caused by ______ vagal nerve branch injury
ventral
reticular adhesions
mechanical impairment of reticular motility and esophageal groove dysfunction
what are causes of vagal indigestion that are believed to be secondary due to traumatic reticuloperitonitis?
vagal nerve injury
reticular adhesions
signs of omasal transport failure:
inappetence with distention of rumen
papple shape rumen
reduced fecal output
frothy bloat
how can vagal paralysis affect ingesta flow into omasum?
paralyzed or relaxed esophageal groove blocks flow into omasum
lack of pumping action of omasum to draw fluid through reticulo-omasal orifice
causes of carbohydrate engorgement in ruminants:
ingestion of highly fermentable feedstuffs in unaccustomed animals or in larger than normal amounts
which grains are most toxic?
wheat
barley
corn
which grains are least toxic?
oats
sorghum
pathogenesis of grain overload:
grain overload
increased volatile free fatty acids
decreased rumen pH and motility
increased lactic aacid
increased lactobacillus spp produce even more lactic acid
increased rumen osmolarity (400 mOsm/L)
grain overload in untreated animals has a mortality of ___%
90
signs of grain overload:
pain
dehydration
diarrhea
bloat
depression
lameness
scleral injection
initial pyrexia
tachycardia
elevated resp rate
rumen fluid parameters in grain overload:
pH < 5
sour odor
predominance of gram + bacteria
bloodwork abnormalities of grain overload:
metabolic acidosis
increased PCV and total protein
azotemia
increased AG
decreased calcium
lactic acid accumulation in rumen draws in water leading to ______ rumen
splashy
hepatic abscess due to grain overload pathogenesis:
lactic acidosis
rumenitis
bacterial access to systemic circulation
toxins that can increase in grain overload:
histamine
ethanol, methanol, tyramine, tryptamine (CNS depression)
thiaminase (polio)
endotoxins form death of gram - bacteria
grain overload treatment:
sodium bicarb IV
alkalinizing agents
fluids
rumenotomy
rumen lavage
antibiotics
antihistamines
causes of subacute rumen acidosis (SARA):
inadequate rumen buffering
inadequate adaptation to high carb diet
diets with excessively long forage particles
bloat
retention of gas from fermentation due to prevention of eructation
kinds of bloat:
foamy (primary)
free gas (secondary)
how many L of gas do cows burp a minute?
2
causes of frothy bloat:
lush pasture
finely ground feedlot grains
what forages cause bloat?
alfalfa
red clover
white clover
sweet clover and alsike clover
cereal crops, cabbage, peas, bean, young grass
foamy bloat pathogenesis:
production of stable proteinaceous foam
foam traps gas and prevents coalescence of small gas bubbles
gas remains trapped in lumen that cannot be eructated
distension→increased pressure on veins→reduced venous return and increased blood pressure
frothy bloat signs:
distended left paralumbar fossa
pain
open mouth breathing
anorexia
salivation
anxious
depressed
death
free gas bloat therapy:
stomach tube
sternal recumbancy
exercise
calcium
rumen stimulants
rumen trocharization or rumenotomy
stomach tube is not effective in ______ bloat
frothy
frothy bloat treatment:
antifoaming agents
what are different antifoaming agents?
alfasure, polaxalene
alcohol ethoxylate detergent
peanut oil
mineral oil
dioctyl sodium sulfanate
bloat prevention:
avoid grazing legumes in the morning
graze on mixed grass/legumes
mature pastures
feed roughages
causes of abomasal ulcers:
primary: unknown
secondary
lymphoma
BVDV
rinderpest
MCF
types of abomasal ulcers:
nonperforating
ulcer causing severe blood loss
perforating ulcer with acute local peritonitis
perforating ulcer with diffuse peritonitis
what are the splits of abomasal ulcer types in adult cows:
1/3 type 2
1/3 type 3
1/3 type 4
abomasal ulcer signs:
pain
tympany
anemia (shock in severe cases)
tarry, black feces
pale MM
tachypnea and tachycardia
fever
bruxism
dehydration
abomasal ulcer treatment:
dietary changes
rumen transfaunation
decrease stress
avoid steroids and NSAIDs
treat concurrent problems
blood transfusions
antibiotics
GI protectants
H2 antagonists
what are the 2 layers of the peritoneum?
subserosa: CT
mesothelial squamous cells
stomata
lymph channels between mesothelial cells
peritoneal fluid parameters:
1 mL/kg BW
1.016 density
< 3 g/dL total protein
< 10,000 cells
peritonitis
inflammatory process of peritoneal cavity and its serosal surface
what are causes of chronic local peritonitis?
acute localized peritonitis
abomasal ulcer perforation
post surgical
penetrating wound
what are causes of acute diffuse peritonitis?
traumatic reticuloperitonitis
abomasal ulceration
metritis→ruptured uterus
rumenitis
rectal perforation
ruptured abdominal abscess
peritonitis signs:
death
abdominal rigidity, tenderness, distension
scleral injection, fever, anorexia
rumen atony and intestinal ileus
chronic localized peritonitis signs:
decreased appetite
decreased milk
pain
acute diffuse peritonitis signs:
constipation
distended abdomen
bilateral, pear shaped abdomen
abdominal paracentesis
reluctant to move
sepsis
tachycardia
weak pulse
cold
dehydration
peritonitis diagnosis:
abdominocentesis
ultrasound
peritonitis treatment:
stabilize patient
identify and correct primary causer
treat infection by medical or surgical procedures
traumatic reticuloperitonitis
accidental swallowing of metal foreign object that penetrates reticulum leading to peritonitis
traumatic reticuloperitonitis signs:
sudden ruminoreticuar atony and sharp fall in milk production
decreased fecal output
mildly increased rectal temp
normal or slightly increased HR
shallow and rapid resp
pain
kyphosis
arched back and uneasy gait
pleurtis or pericarditis signs:
depressed, tachycardic, pyrexic
shallow resp and muffled lung sounds
gas and fluid splashing sounds on auscultation
jugular vein distension
congestive heart failure
pleurtis or pericarditis diagnosis:
grunt when pressure is applied to xiphoid
pleurtis or pericarditis due to traumatic reticuloperitonitis diagnosis:
antibiotics
magnet
confinement
rumenotomy
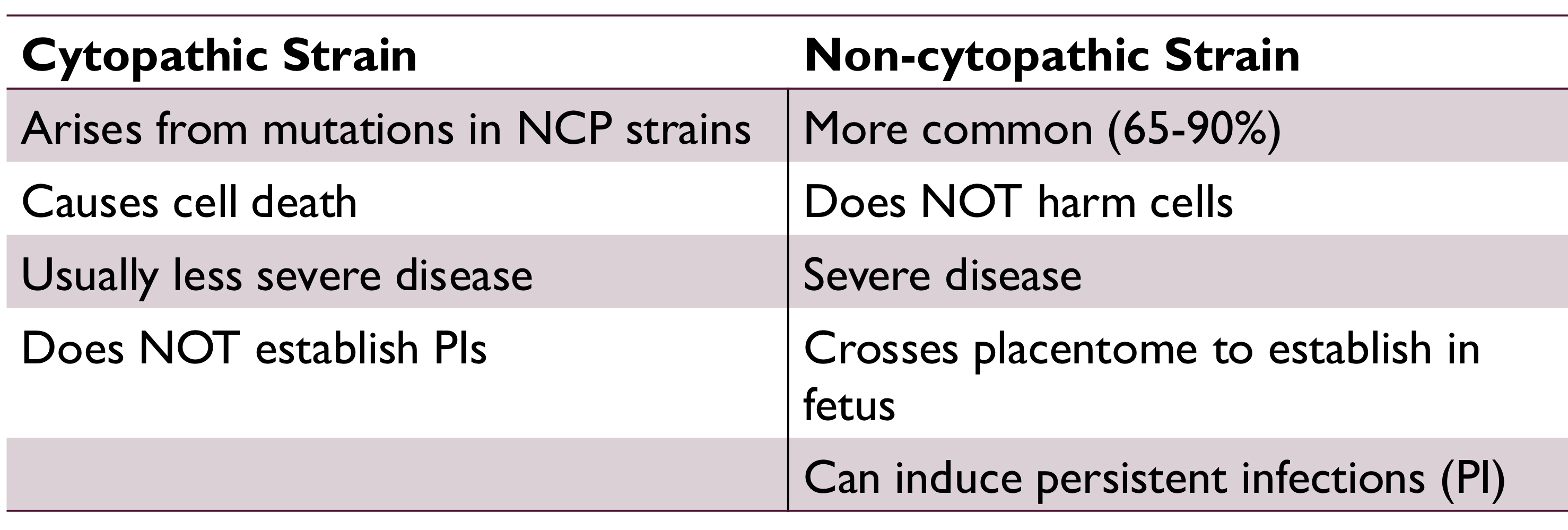
what are the 2 BVDV genotypes?
BVDV-1: used in vaccines
BVDV-2: more virulent, hemorrhagic syndrome, death
what are the 2 BVDV strains?
BVDV has topism for acutley dividing cells such as…
repro tissues
fetal tissues
GI tract mucosa
intestinal crypts
peripheral lymphoid tissue
bone marrow
______% of BVDV infections occur without clinical signs
70-90
transient acute vs severe acute BVDV infection:
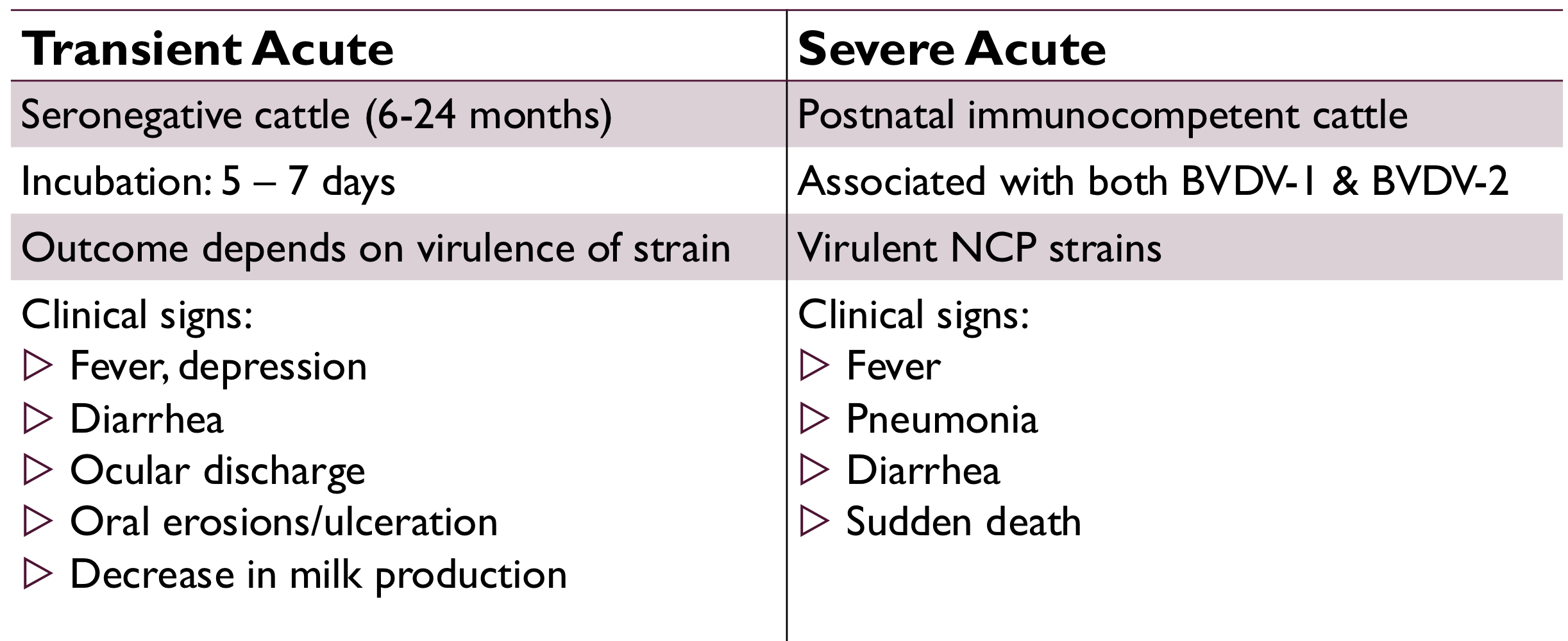
hemorrhagic syndrome is associated with __________ BVDV-2 severe acute infection
noncytopathic
hemorrhagic syndrome signs:
thrombocytopenia
bloody diarrhea
epistaxis
mucosal hemorrhage
hyphema
pyrexia
BVDV forms synergistic infections with…
mannheimia hemolytica and mycoplasma bovis
how does BVDV cause immunosuppression?
lymphopenia: reduced helper and cytotoxic T cells, B cells, and neutrophils
reduces ability to stimulate T cell responses
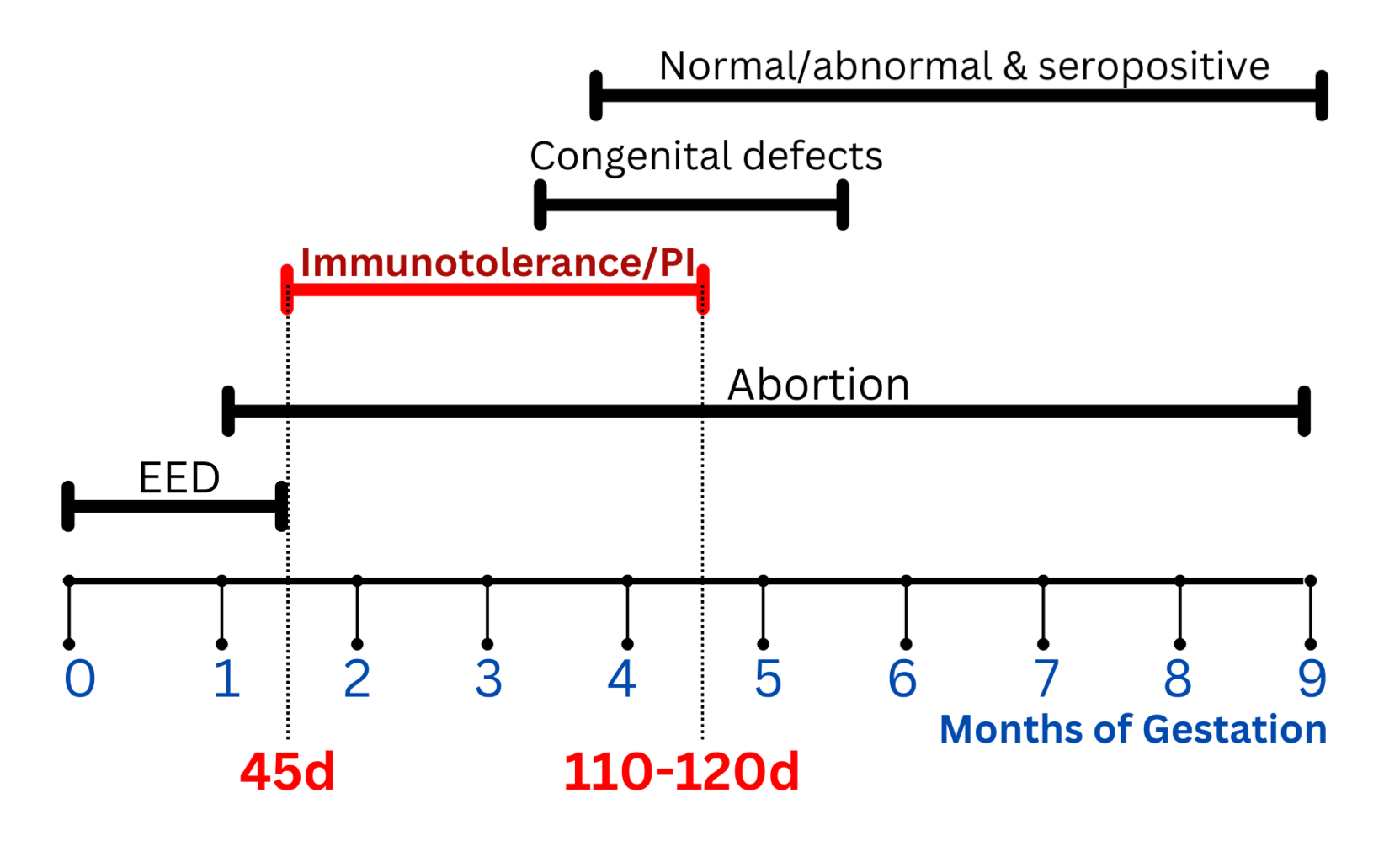
BVDV repro signs:
fertilization failure
embryonic death
abortion
persistent infections
congenital defects
outcomes of fetal BVDV
BVDV congenital neuro defects:
cerebellar hypolasia
hydrananecephaly (absent cerebral hemispheres)
hydrocephalus
hypomyelinogenesis (inadequate myelin)
BVDV congenital ocular defects:
retinal atrophy and dysplasia
cataracts
microphthalmia
hypoplasia of optic tract
BVDV congenital immune system defects:
thymic hypoplasia
BVDV congenital skin defects:
hypotrichosis
alopecia
BVDV congenital musculoskeletal defects:
growth retardation
brachygnathism
persistently infected cow prevalence
<1%
how does mucosal disease occur?
immunotolerant PI infected with cytopathic strain
what are the 3 clinical presentations of mucosal disease?
acute MD
chronic MD
MD with recovery
acute MD occurs if the cytopathic strain a cow is infected with has close antigenic homology to the _________________ strain
PI noncytopathic
acute MD signs:
near 100% mortality
fever
anorexia
bloody, fibrinous diarrhea
blunted papilla
ulcers of tongue, palate, buccal surface, pharynx
chronic MD occurs if the cytopathic strain a cow is infected with is ____________ to the PI noncytopathic strain
heterologous
chronic MD signs:
anorexia, weight loss
diarrhea
bloat
alopecia
erosions of mouth and skin
lameness
BVDV diagnosis:
virus isolation
PCR
antigen detection
BVDV treatment:
supportive care
prevent secondary infection
BVDV prevention:
eliminate PI animals
vaccinate
biosecurity
when to vaccinate against BVDV:
after 6 months of age
prior to breeding
pros and cons of inactivated BVDV vaccines:
contain type 1 and 2
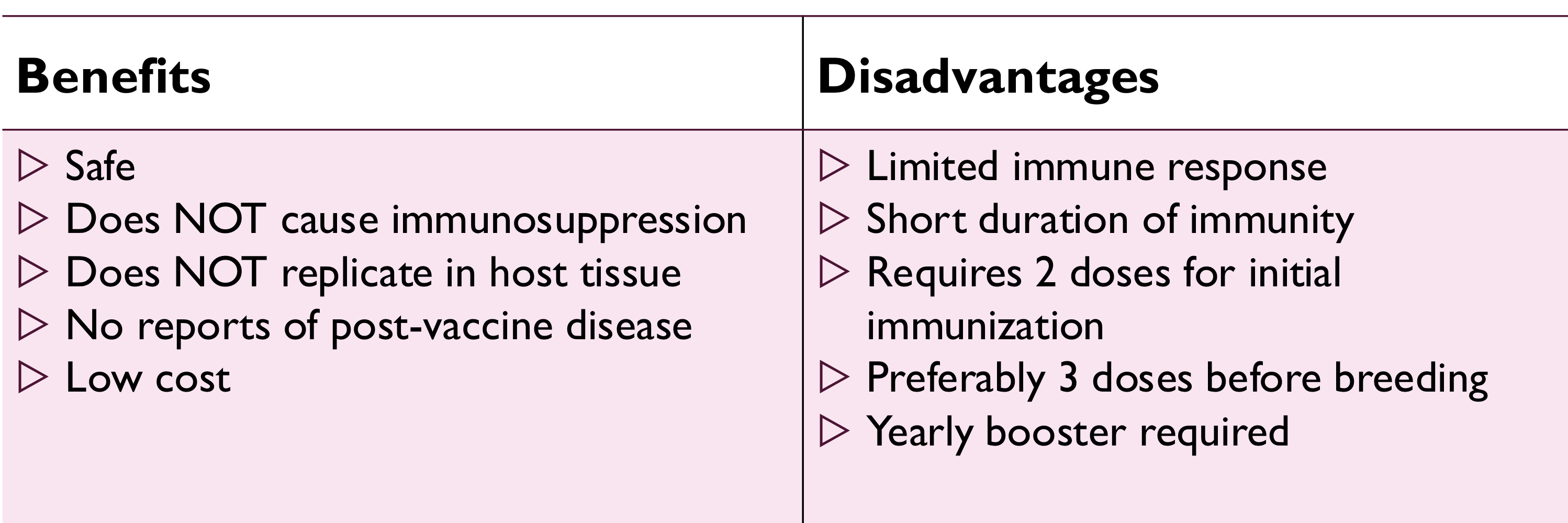
pros and cons of modified live BVDV vaccines:
contain type 1 cytopathic strain
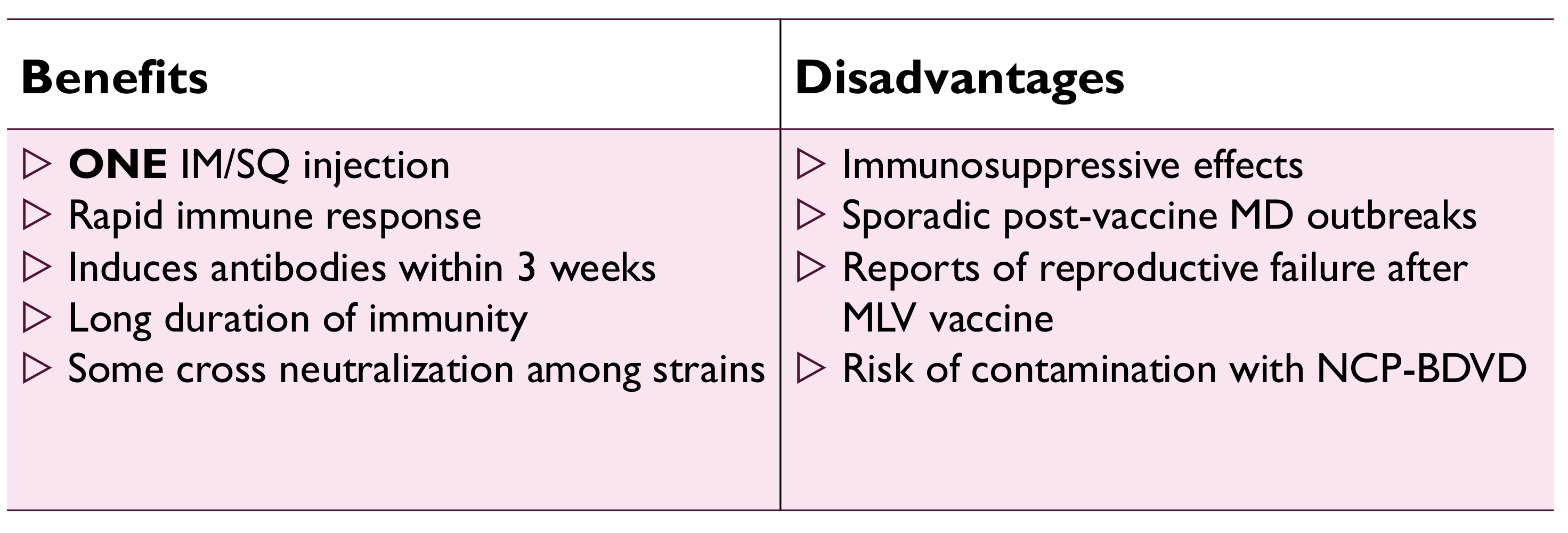
bovine neonatal pancytopenia
calves born to cows vaccinated with pregsure BVD vaccine receive alloantibodies via passive transfer that damage bone marrow