Topic 6
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is epidemiology?
A method used to find the causes of health outcomes and disease in populations.
What are the five components of the definition of epidemiology?
Population, Distribution, Determinants, Outcome, Control Health Problems.
Who is considered the Father of Epidemiology?
Dr. John Snow.
What was Dr. John Snow's significant contribution to epidemiology?
He conducted studies of cholera outbreaks in London to discover the cause and prevent reoccurrence.
What types of diseases does epidemiology study?
Communicable diseases, non-communicable diseases, environmental exposures, and injuries.
What is the goal of epidemiology?
To promote health and reduce disease in populations.
What is the difference between prevalence and incidence?
Prevalence refers to the total number of existing cases in a population, while incidence refers to the number of new cases during a specific time period.
What is morbidity?
The occurrence of illness in a population.
What is mortality?
The occurrence of death in a population.
What are determinants in epidemiology?
Causes or factors that influence disease occurrence and health-related events in a population.
What is primary prevention?
Actions taken before disease occurs, such as immunization.
What is secondary prevention?
Actions taken during early stages of disease to limit progression, such as cancer screening.
What is tertiary prevention?
Actions aimed at restoring optimal functioning after disease has occurred, such as rehabilitation.
What role does distribution play in epidemiology?
It refers to the frequency and pattern of health events by time, place, and person.
What is the significance of control in epidemiology?
It involves using health data to inform policy, allocate resources, and promote health.
What was the outcome of Dr. John Snow's intervention during the cholera outbreak?
He removed the handle of the Broad Street Pump to control the outbreak.
What types of questions can epidemiological research answer?
Questions about safety of food, health outcomes associated with substances, mortality rates, mental health promotion, and cancer risk.
What is the importance of calculating ratios, proportions, and percentages in epidemiology?
They are essential for interpreting health data and understanding the frequency of health events.
What is the role of environmental exposures in epidemiology?
They are studied as potential risk factors for various health outcomes.
How does epidemiology apply to public health?
It provides data and insights necessary for health promotion and disease prevention strategies.
What is the primary question addressed in epidemiology regarding health problems?
When and why does the health problem happen in the population?
What health issues are associated with vaping?
Vaping-associated lung illness, nicotine-related mental health issues, and oral health and cancer from nicotine pouches.
What is a count in epidemiology?
The number of people in a studied group who have a disease or characteristic of interest.
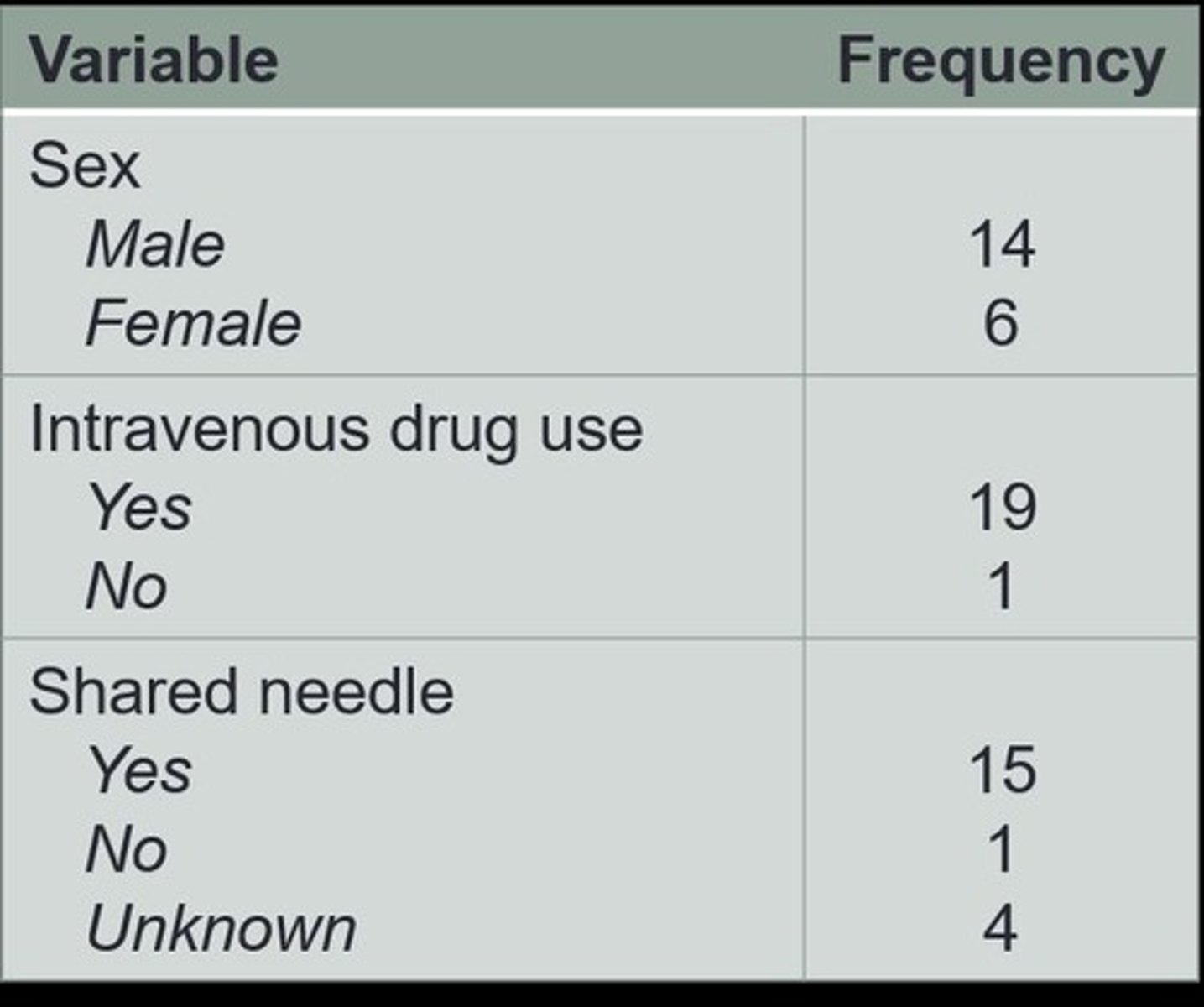
Why can counts be misleading in epidemiology?
Counts lack a denominator, providing no context about the importance of cases relative to population size.
In what situations can counts be informative?
Counts can highlight the need for prevention efforts or healthcare resource allocation.
What is a ratio in epidemiology?
An expression of the relationship between two numbers, expressed as X:Y or X to Y.
What is the formula for calculating proportion?
Proportion = A / (A + B)
What is the formula for calculating percentage?
Percentage = (A / (A + B)) * 100
What does prevalence measure?
The number of existing cases in a population relative to the population size.
How is prevalence expressed?
As a rate per 100 or per 1000 of the population.
What is the prevalence of arthritis if 310 people in a population of 2477 have it?
125.15 per 1000 people.
What does incidence measure?
The number of new cases that occur during a specific period relative to a population.
What is the formula for incidence proportion?
Incidence Proportion = # new cases / # persons at risk.
What does incidence proportion describe?
How quickly disease occurs in a population, also known as 'risk'.
In a study of 500 male smokers, if 74 were diagnosed with lung cancer, what is the risk per 100 people?
14.8 per 100 people.
What is the risk of developing lung cancer for 500 male smokers expressed per 1000 people?
1.48 per 1000 people.
What is the significance of proportions and percentages in epidemiology?
They indicate how important a health outcome is relative to the size of the group at risk.
What is the difference between incidence proportion and incidence rate?
Incidence proportion focuses on the number of new cases relative to the population at risk, while incidence rate considers the time period of observation.
What are some examples of descriptive measures in epidemiology?
Male-to-female ratio, death-to-case ratio.
What is the importance of calculating prevalence and incidence in public health?
They help assess the burden of disease and inform healthcare resource allocation and prevention strategies.
What is an example of how counts can be misleading?
Comparing the number of STD cases in two residences without considering the population size of each residence.