Ovaries
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Ovaries
produce gametes
estrogen and progesterone
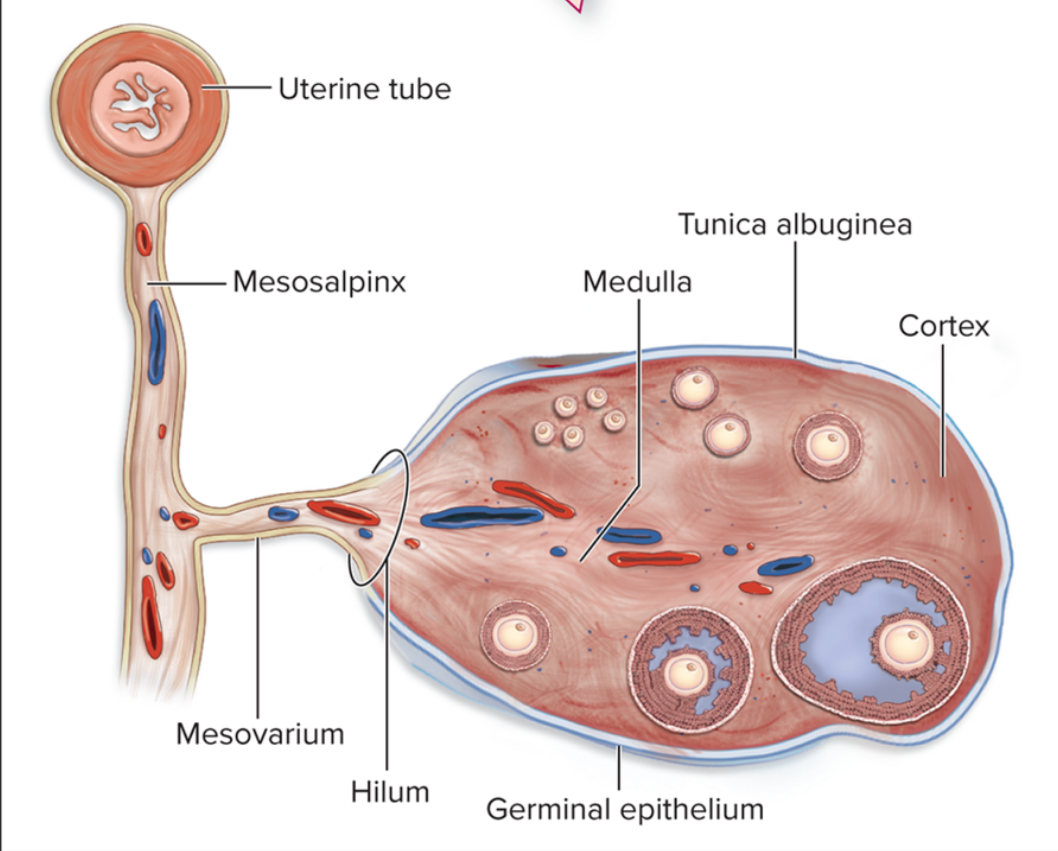
Germinal epithelium: a layer of simple cuboidal epithelium that covers the ovary is actually the ovary’s visceral peritoneum
tunica albuginea: the dense connective tissue layer just under the germinal epithelium
Cortex
the outer layer where the product and maturation of gametes occur
Medulla
the inner layer that carries the blood vessels
blood supply is through the various ovarian ligaments
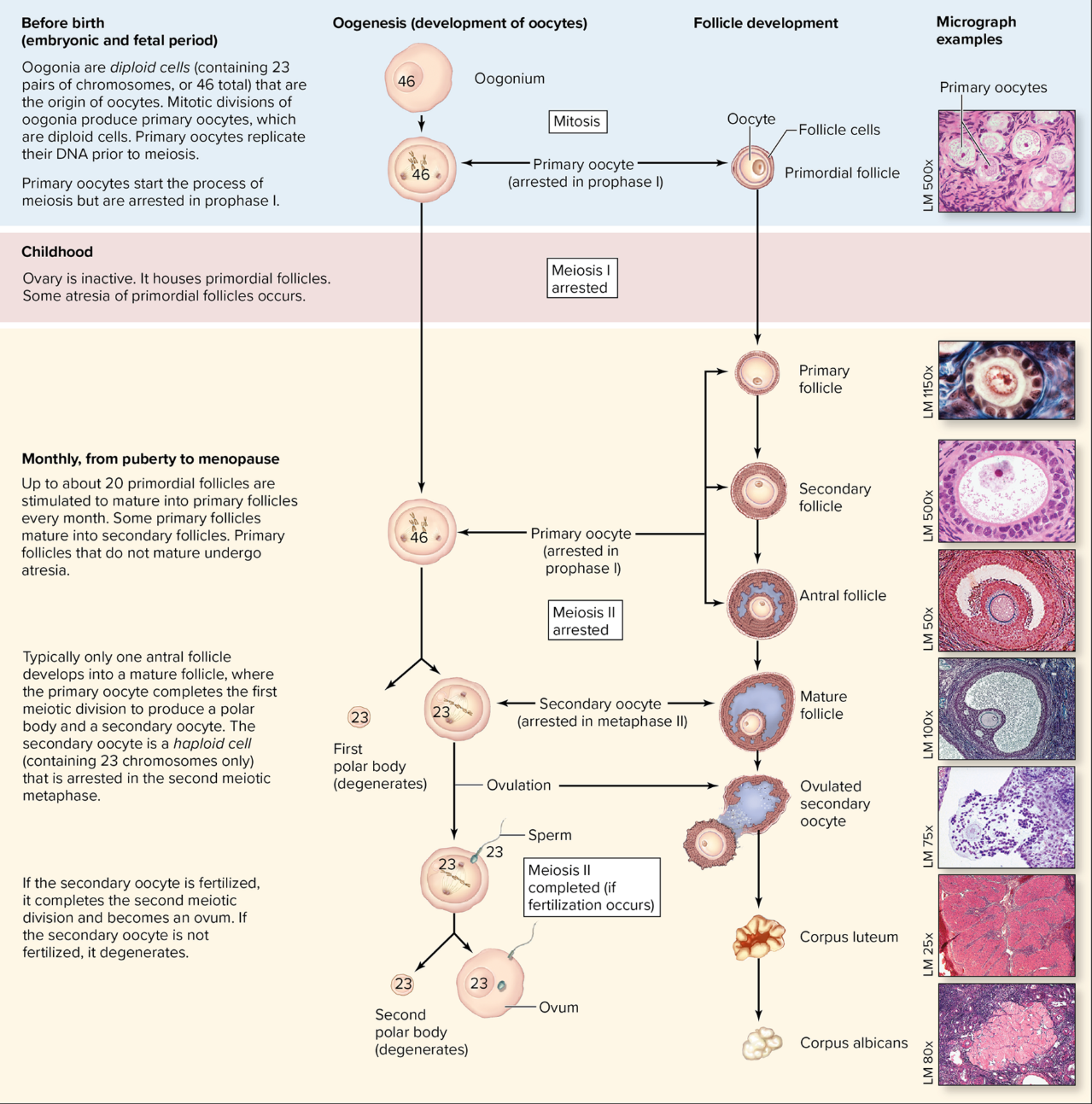
Oogenesis begins in…
utero
before birth, females have made all the oocytes they will ever make; mitosis of oogonia (female stem cells) cease
Millions of primordial follicles
Females stuck in Prophase I = primary oocytes
in utero = 7 million primary oocytes
at birth = 2 million primary oocytes
at onset of puberty = 300,000 - 400,000 primary oocytes
in a typical women’s entire reproductive life, only 400-500 gametes will finish meiosis I to become secondary oocytes arrested in metaphase II
Oogenesis
the primary oocyte remain stuck in prophase I until the onset of puberty
The hormones of puberty stimulate one (sometimes 2) 1 primary oocyte per month to complete meiosis I
This results in a secondary oocyte and a polar body (with most cytoplasm in the oocyte)
it is NOT an ovum, but a secondary oocyte that is ovulated! in other words, meiosis II has not yet been completed (stuck in metaphase II)
fusion of the sperm with the secondary oocyte stimulates the completion of meiosis II (a second polar body then results)
ovum exits for a very short time before it becomes a zygote
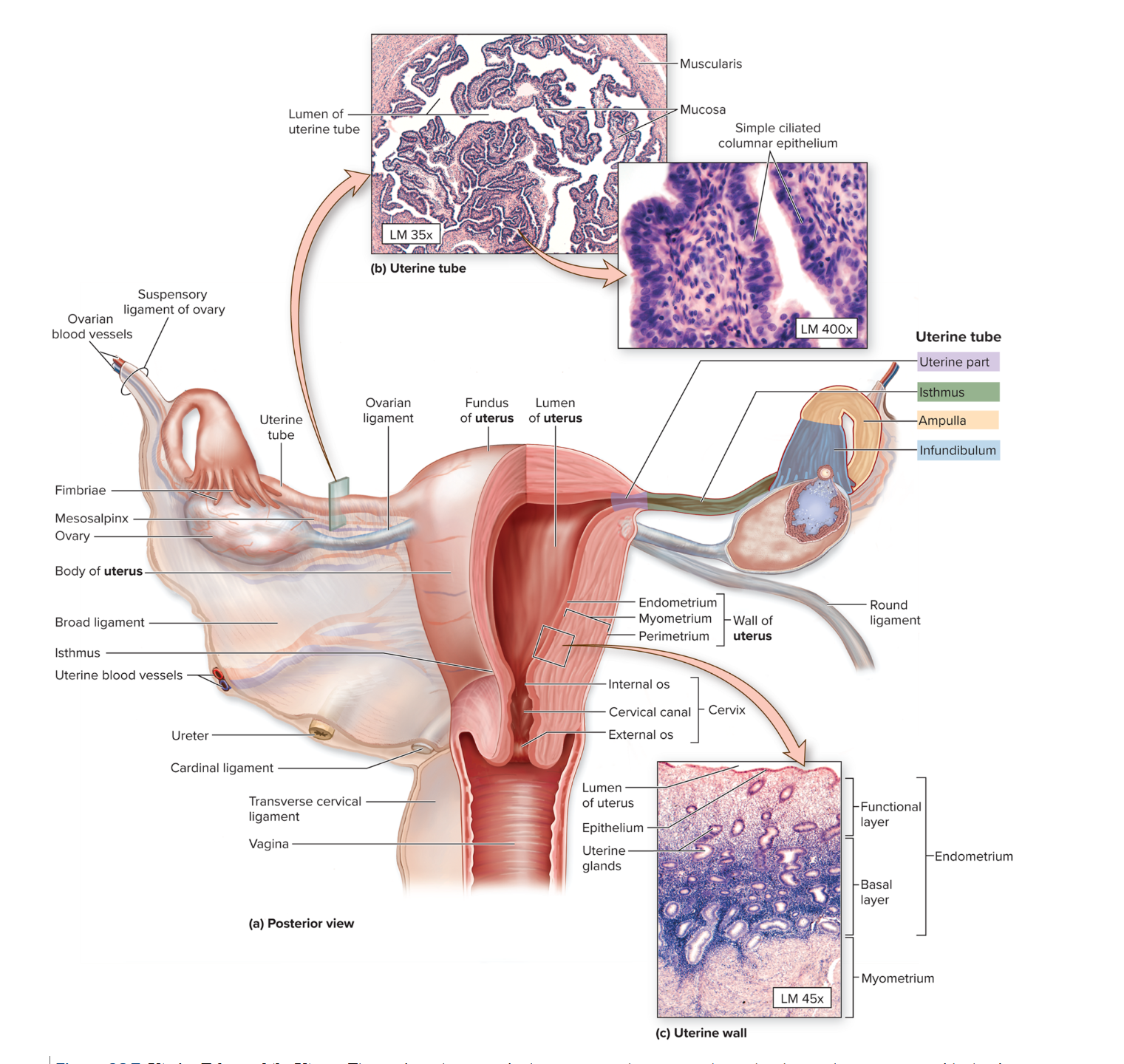
Fallopian tubes
also called oviduct or uterine tube; hollow muscular tubes ~5 in long
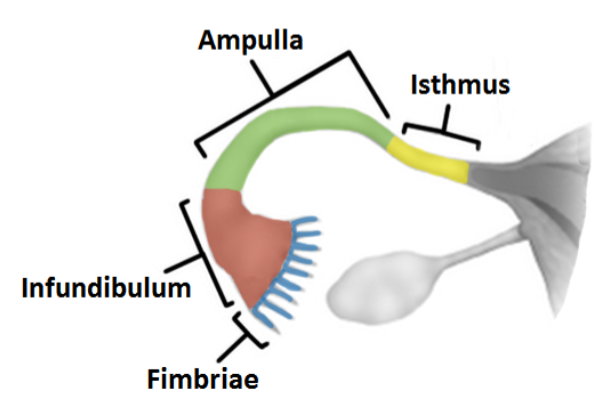
Infundibulum
an expanded funnel contains many finger like projections called fimbriae lined with cilia
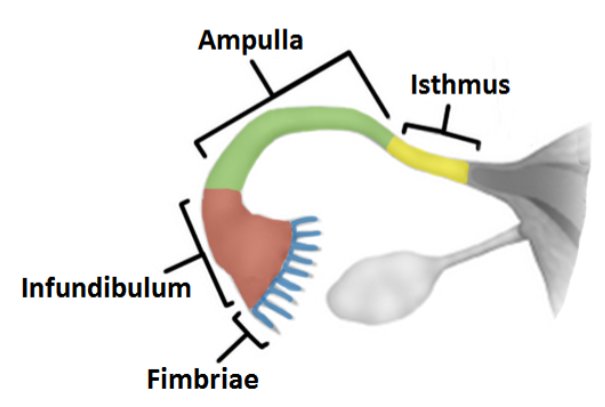
Ampulla
most of the middle portion of the tube; the site of fertilization
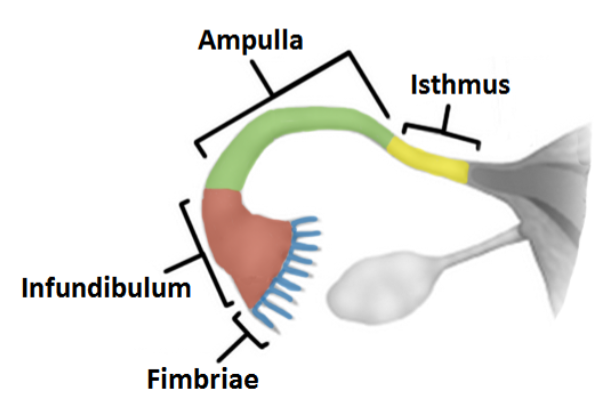
Isthmus
short segment adjacent to the uterine wall
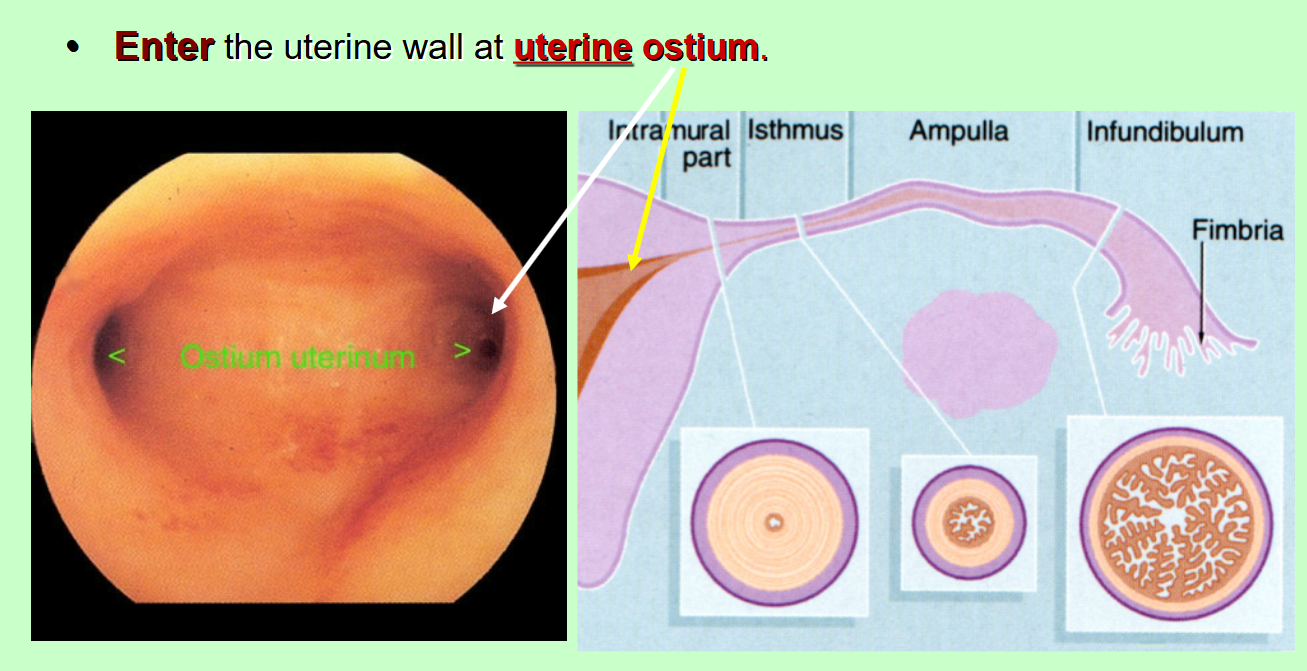
The fallopian tube enters…
the uterine wall at the uterine ostium
weak peristalsis occurs in smooth muscle in the days around ovulation; oocyte takes 3-4 days to make the trip
Ectopic pregnancy
development outside of the uterus
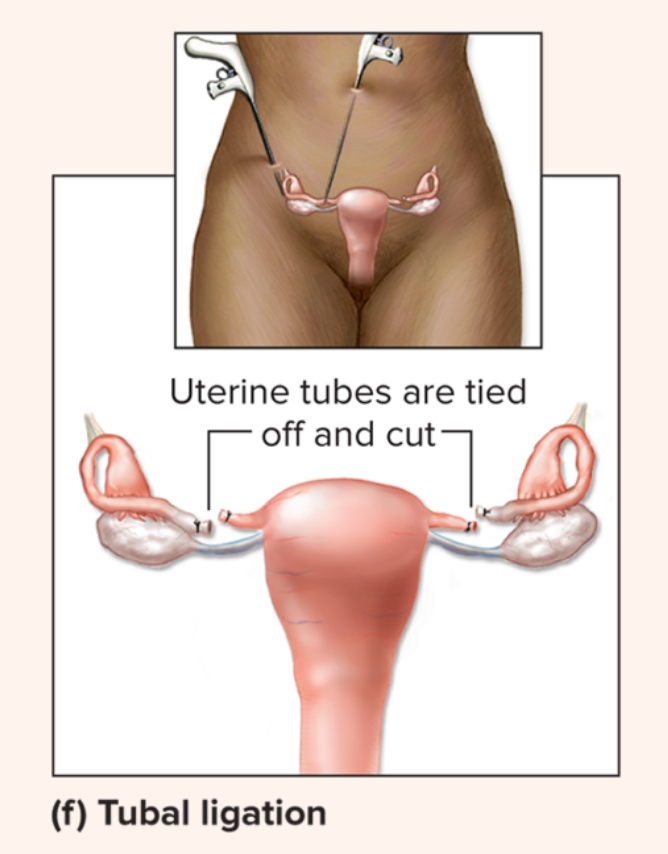
Tubal ligation
is a surgical hospital procedure (requiring anesthesia) whereby the uterine tubes are cut, and the ends are tied off or cauterized shut to prevent both sperm from reaching the oocyte and the oocyte from reaching the uterus
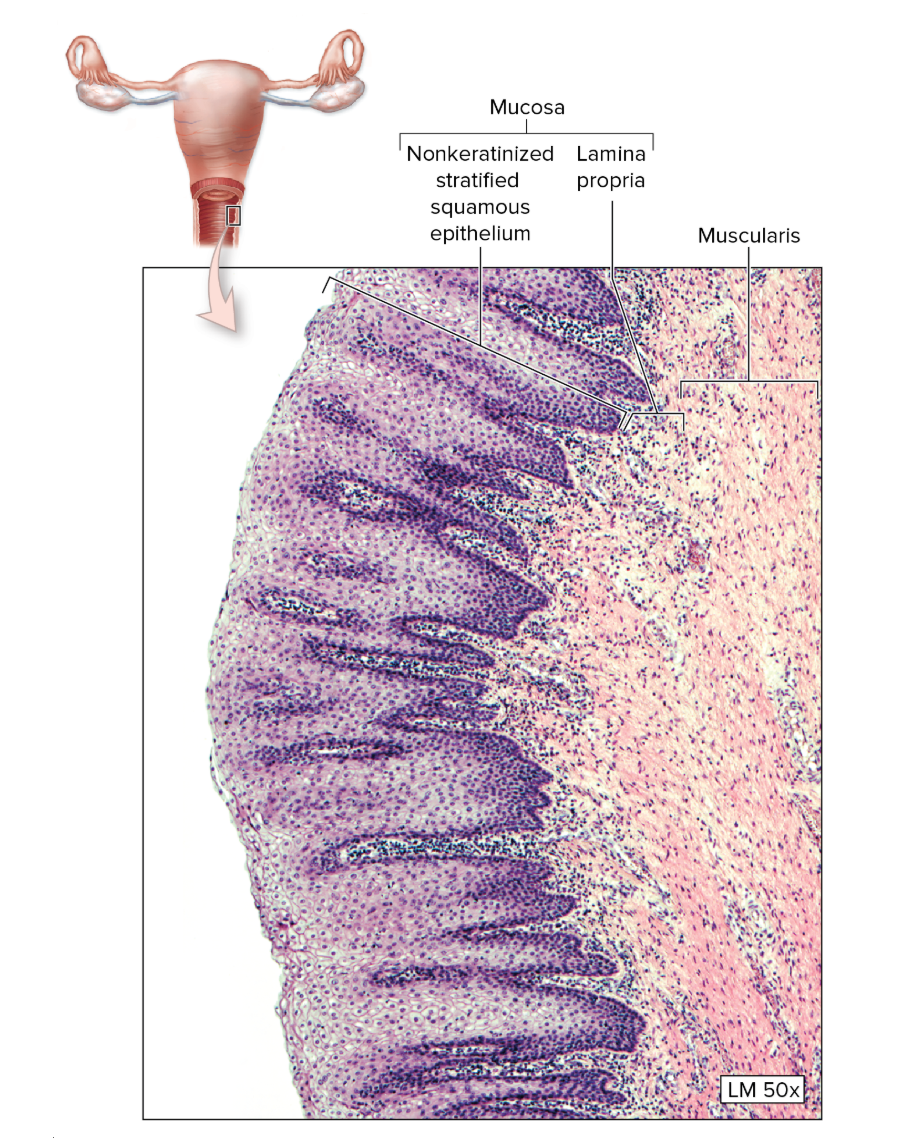
Vagina
for sexual intercourse as well as birth canal
nonkeratinized stratified squamous and rugae
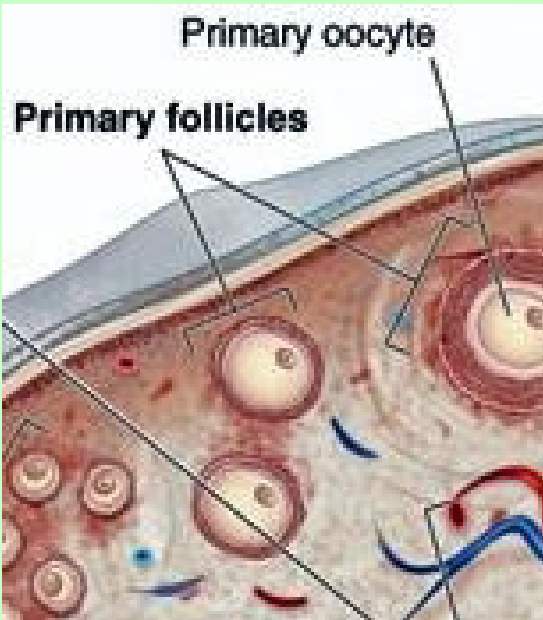
Ovarian cycle
million’s of primordial follicles are present at birth
contain primary oocyte
Primordial follicles
primary oocyte
millions before birth
contains primary oocyte; stopped in prophase I
Primary follicle
primary oocyte covered by stratified cuboidal epithelium
about 20/month
Secondary follicle
has antrum (a few develop)
still primary oocyte
Vesicular follicle
mature (one develops)
secondary oocyte continues to metaphase II
ovulation
secondary oocyte
fertilization (finishes meiosis)
egg/zygote
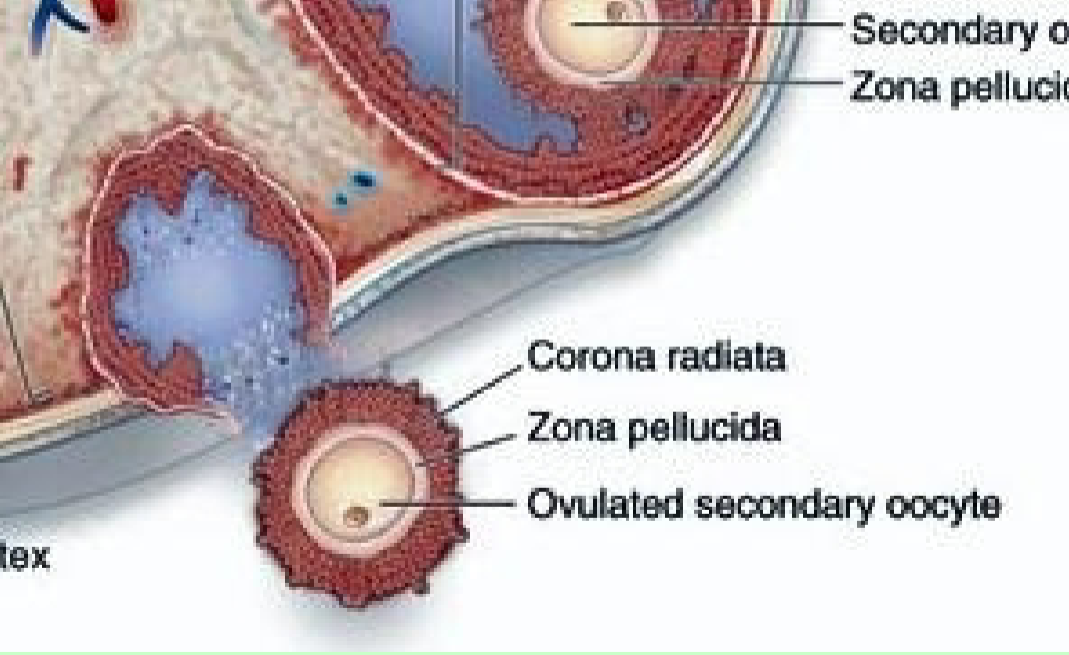
Ovulation…
results from a surge of LH from the anterior pituitary gland
What happens to the secondary oocyte?
fertilized and becomes egg/zygote OR not fertilized and exits body at menstruation
What happens to the vesicular follicle following implantation of blastocyst
becomes corpus luteum
produces Progesterone and Estrogen to maintain endometrium
Continues to produce Progesterone under influence of HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
Placenta eventually produces Progesterone and Estrogen through birth
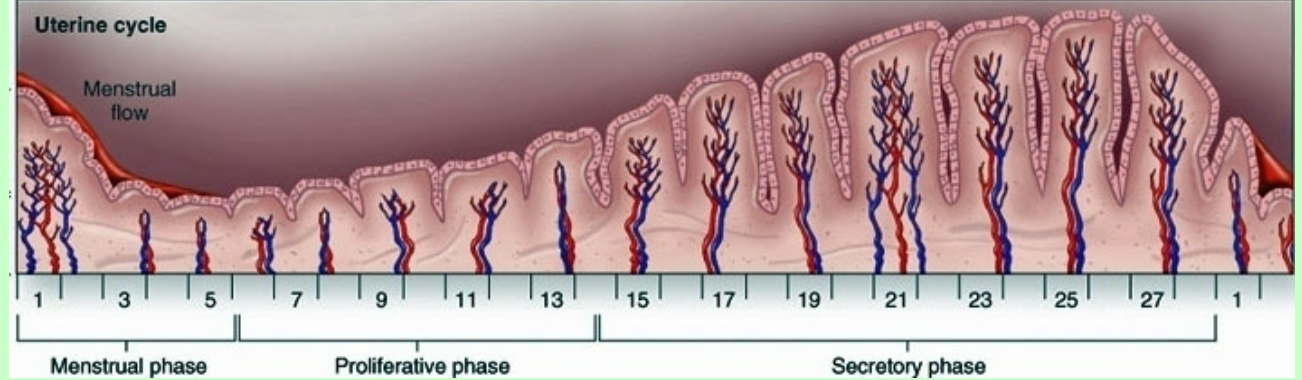
What layers thickens and thins during Uterine cycle?
Endometrium
What actually grows to increase thickness? → uterine glands and blood vessels
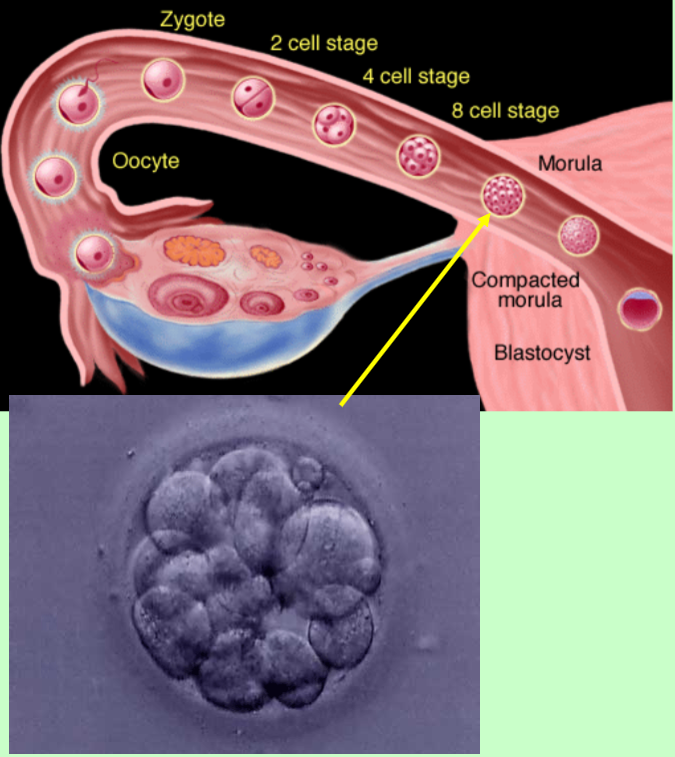
Development in the…
morula