Shapes of simple molecules & ions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
bonding pairs + lone (non-bonding) pairs of electrons as charge clouds
repel eachother
pairs of electrons in outer shell of atoms
arrange themselves as far apart as possible to minimise repulsion
lone pair - lone pair repulsion is … than lone pair - lone bond pair repulsion
greater
lone pair - lone bond pair repulsion is … than bond pair - bond pair repulsion
greater
shape of molecules is determined by →
no. of electron pairs around the central atom
each electron pair naturally repels eachother so →
largest bond angle possible exists between covalent bonds
lone pairs around central atom cause
additional repulsive forces, changing the bond angle
for every lone pair, bond angle between covalent bonds is reduced by
2.5 degrees
linear
2 bonding e- pairs
0 lone e pairs
180 degrees bond angle

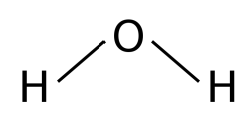
V - shaped
2 bonding e- pairs
2 lone e- pairs
104.5 degrees
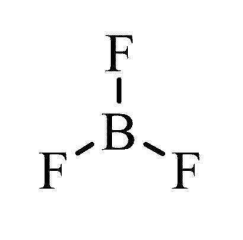
Trigonal Planar
3 bonding e- pairs
0 lone e- pairs
120 degrees
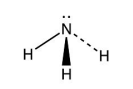
Triangular Pyramid
3 bonding e- pairs
1 lone e- pairs
107 degrees
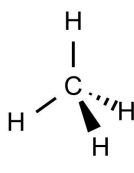
Tetrahedral
4 bonding e- pairs
0 lone e- pairs
109.5 degrees
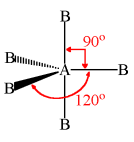
Trigonal Bipyramid
5 bonding e- pairs
0 lone e- pairs
90 + 120 degrees
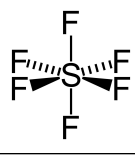
Octahedral
6 bonding e- pairs
0 bonding e- pairs
90 degrees