Ecosystem ecology - nutrient cycling
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms

Nutrient cycling
nutrients assim_____ into pl___ ti____
Passed up trop___ lev____
Detritus deco_____
Soil organic matter - mix of partially and completely deco_____ detritus
Eventually converts nut_____ to inor_____ form (NO3)
Nutrients assimilated into plant tissues
Passed up trophic levels
Detritus decomposed
Soil organic matter – mix of partially and completely decomposed detritus
Eventually converts nutrients to inorganic form (eg. NO3)
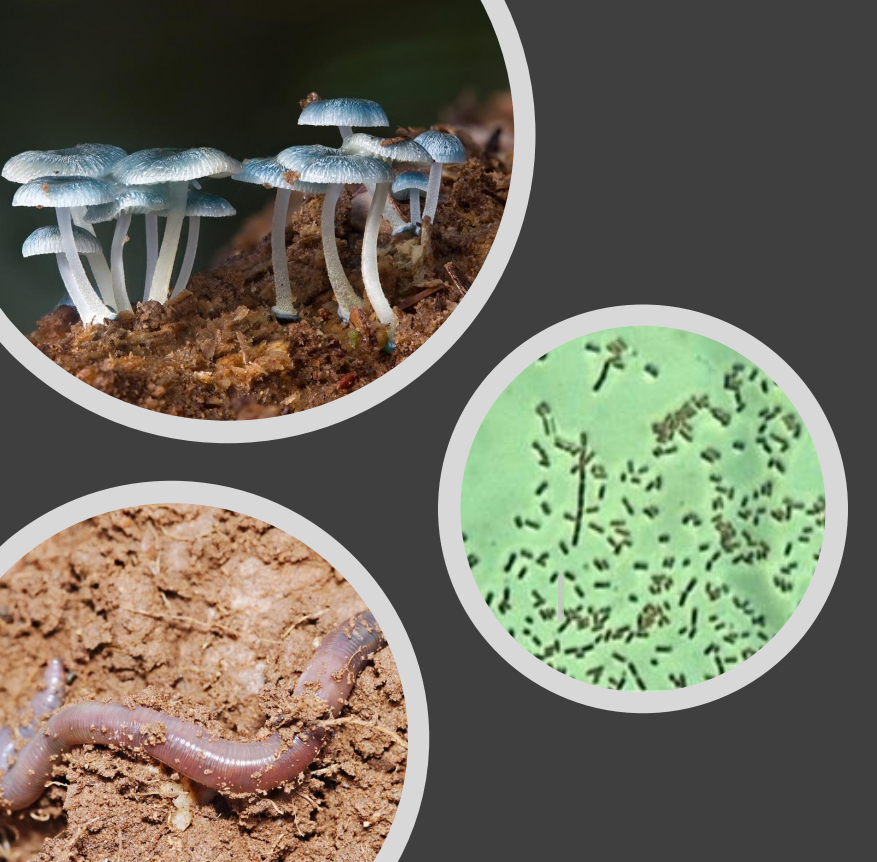

Why does decomposition often limit nutrient cycling in ecosystems?
Abiotic conditions - temp____, ox____, avail_____ & preci______
Type of detritus - lig___ vs cell____e
Abundance and diversity of detri_____s
Abiotic conditions – temperature, oxygen availability & precipitation
• Type of detritus – eg. lignin vs cellulose
• Abundance and diversity of detritivores
The Nitrogen Cycle
Why is N important to biological systems?
Cycling nutrients between li___ and non-li____ components of the eco_______
Cycling nutrients between living and non-living components of the ecosystem
The Nitrogen Cycle
Major nitrogen reservoir?
The atm_____e
the atmosphere

How does N enter biological systems?
Through bac____l nitr____ fixation and denitr_____
Through bacterial nitrogen fixation and denitrification
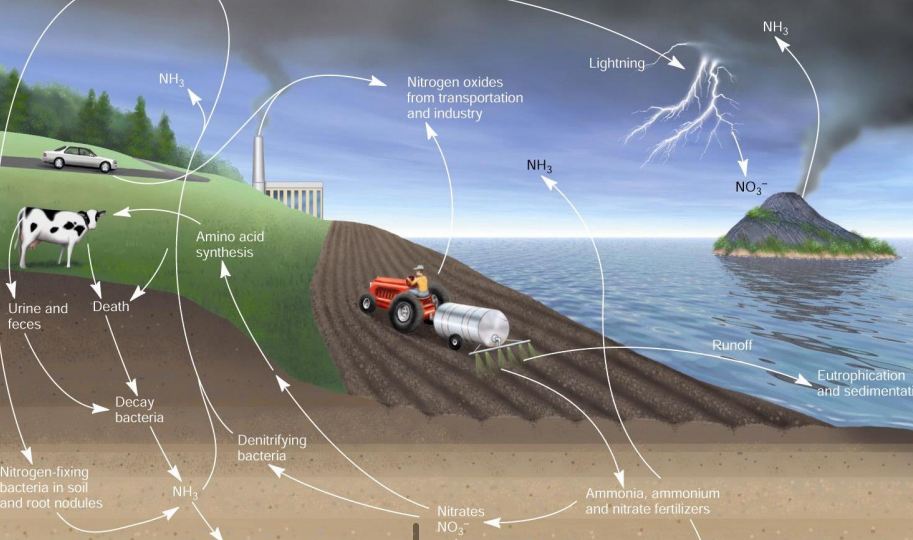
How are humans altering the natural N cycle?‘
synthetic fert_____
Concentrated live_____
R__-o__
Eutro______
synthetic fertilization
Concentrated livestock
Run-off
Eutrophication
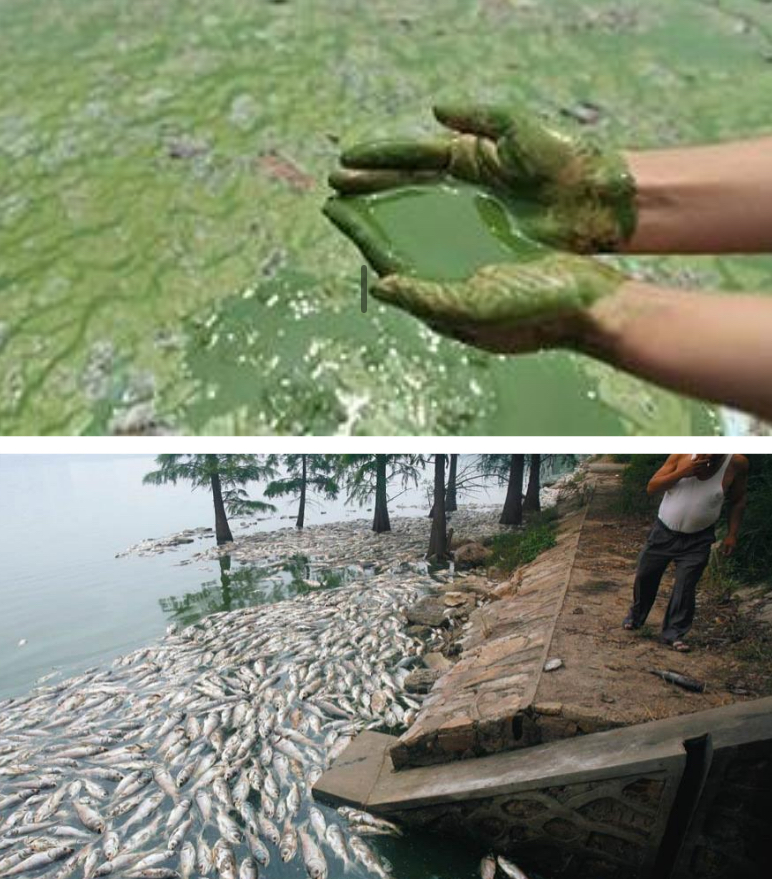

Eutrophication - excessive richness of nu_____ in a la__ or other body of w_____
due to ru_o__ from the la__
Causes a dense growth of al__l life and death of an___ life from lack of ox____
excessive richness of nutrients in a lake or other body of water
• due to runoff from the land
• causes a dense growth of algal life and death of animal life from lack
of oxygen
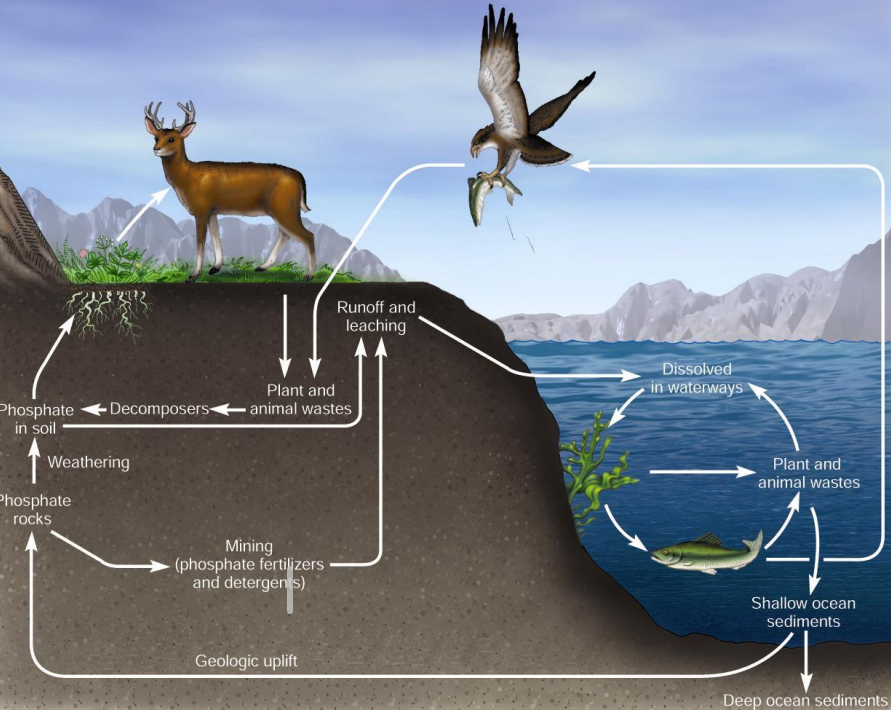
The phosphorus cycle:
Major Reservoirs?
Ro___(phosphate mineral), bios____(D__, A__, phosp_____s)
Rocks, biosphere (DNA, ATP, phospholipids)
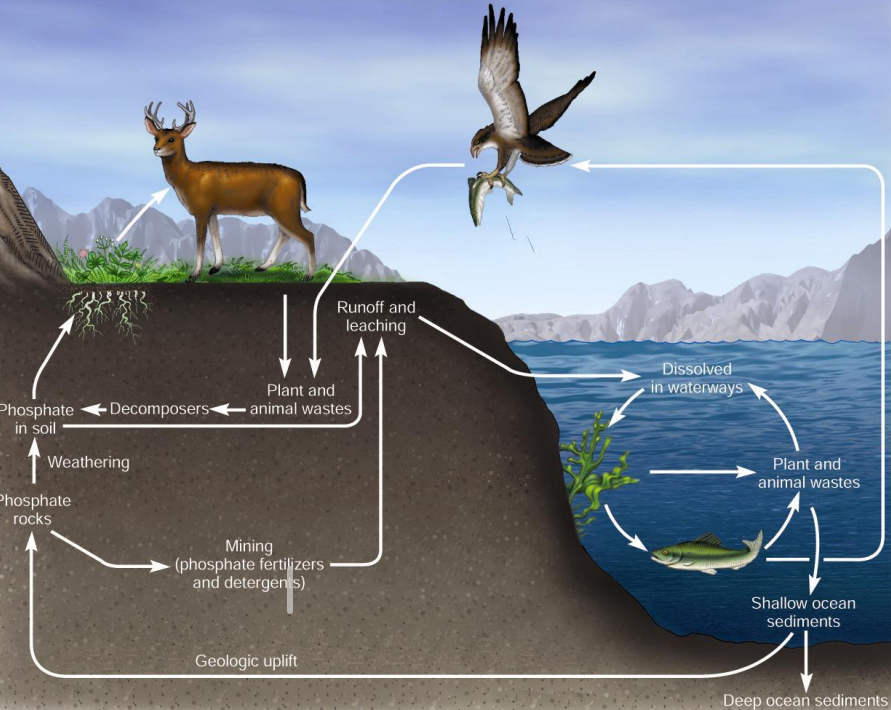
How does P enter the biosphere?
Through weath_____g, ero___, deco_____
weathering, erosion, decomposition
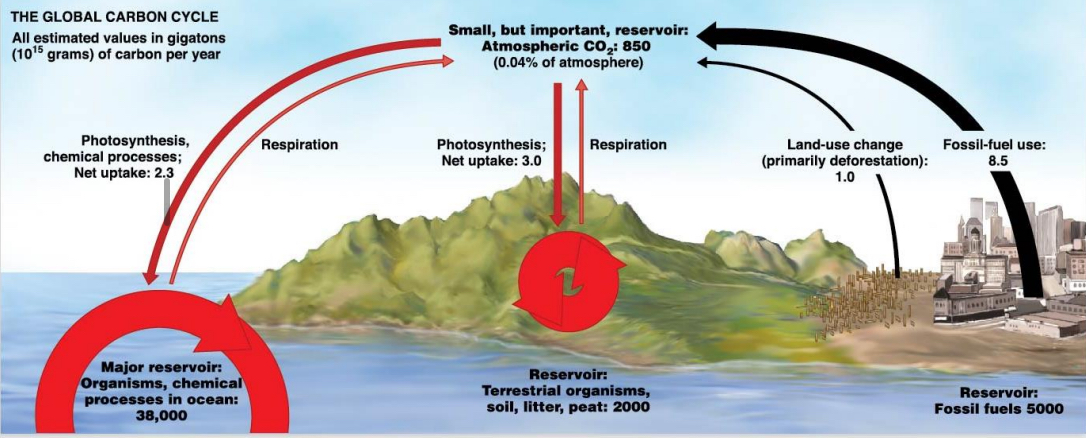
The Carbon Cycle
Major carbon reservoirs?
Bios____, fos___ fu____ (organic) & atm____, and oc___ (inorganic: CO2, H2CO3)
biosphere, fossil fuels, atmosphere, and ocean
How does carbon enter and exit the biosphere?
photo______, resp_____, dec______, comb____
Photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion
How have humans interfered with the global C cycle?
Burning of for____, fuelw____, and organic deb___
Combustion of fos___ fu____ for veh____, elec____, and he__
burning of forests, fuelwood, and organic debris
Combustion of fossil fuels for vehicles, electricity, and heat
How is the carbon cycle related to climate change?
Climate pattern changes
Dri__ and wet___
Melting gla___ and i__ sheets
80% of earths gla___ retreating
Rising s__ le___
Ocean aci______n
Biodiversity l__s
Climate pattern changes
• Drier and wetter
Melting glaciers and ice sheets
• 80%+ of Earth’s glaciers retreating
• Rising sea level
Ocean acidification
Biodiversity loss
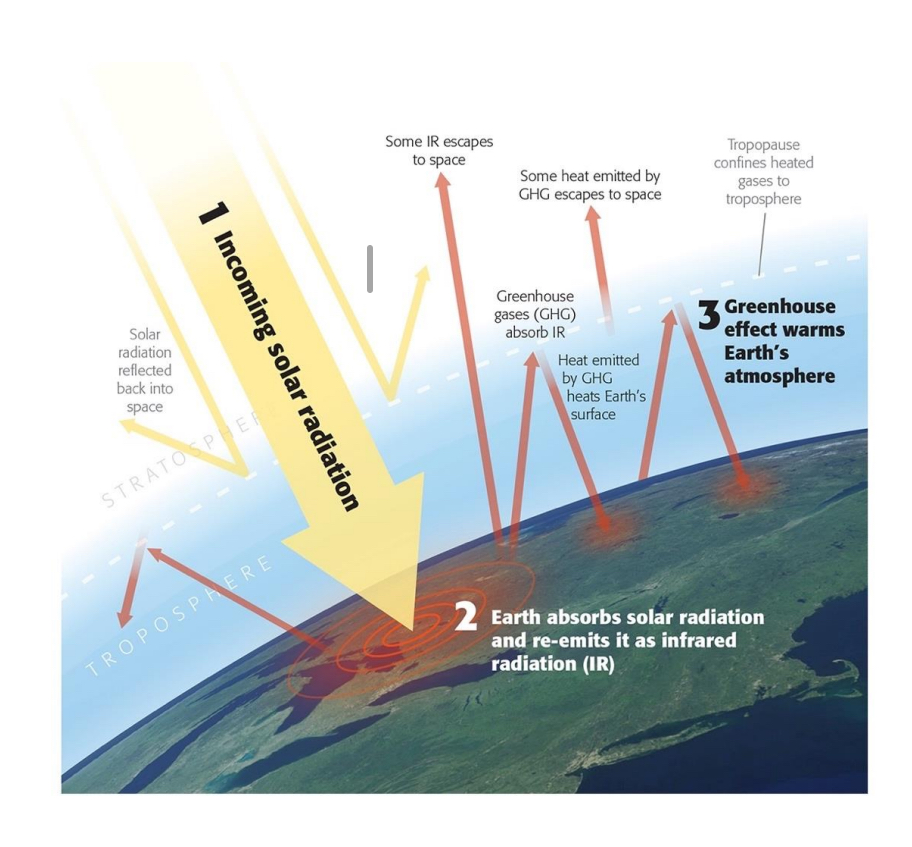
The greenhouse effect
99% of atmosphere = _2 and _2
Gas molecules ab___ he___
W___ va____ (H__)
Ca____ di____ (C_2)
Met_____(C_4)
Nit___s ox___ (N__)
Traps h___ from earth sur___
Exacerbated by defo_______
99% of atmosphere = N2 and O2
Gas molecules absorb heat
• Water vapor (H2O)
• Carbon dioxide (CO2)
• Methane (CH4)
• Nitrous oxide (N2O)
Trap heat from Earth’s surface
Exacerbated by deforestation