Lecture 8
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
less
For herbivores, the higher their weight, the ________ they sleep
Carnivores | Herbivores |
|---|---|
Sleep more because they get an energetic kick in their diet faster | Sleep less because they need to eat all the time to maintain their weight |
Carnivores vs. herbivores‘ sleep
Carnivores | Herbivores |
|---|---|
intelligence
There is no obvious correlation between sleep duration and ________
Longest sleepers = koalas
Shortest sleepers = elephants
Which animals are the longest and shortest sleepers?
breathe
sea, land
distance
3 species sleep one hemisphere at a time (unihemispheric sleep):
Dolphins: because they need to remember to ________
Sea otters: sleep 1 hemisphere at a time in the ______ but 2 hemispheres at a time on the ______
Some birds: in long-_________ flights
lower
changes
more
fight
NREM, REM
fragmentation
fever
The host-defense theory of sleep claims that:
Sleep loss = _______ immune defense
Less immune system cells (______ blood cells)
Sleep _______ with disease:
We sleep ______
Maybe to conserve the precious energy required to _______ the disease
Increase in _______ sleep + decrease in ______ sleep
More NREM sleep _________ because we wake up more often
More heat production → _______
1
Some immune markers are affected by even __ day of sleep deprivation
metabolic
less
The conservation of energy theory of sleep claims that:
Sleep has a _______ benefit for the whole body
There is ______ glucose use in NREM sleep
energy
Wake | Sleep |
|---|---|
Waking Effort (WE): | Biological Investment (BI): |
Thermoregulatory Effort (TE): |
The conservation of energy theory of sleep claims that sleep-wake cycles are a schedule of ________ investments:
Wake | Sleep |
|---|---|
calories
temperature
use
Sleep is involved in the conservation of ________. Examples:
Lower body ________ in sleep
Hibernation
Reduced energy ________
Short
________ sleep is associated with:
Risk of diabetes
Obesity
Cravings for carbs
Lower glucose tolerance
more
The glymphatic function theory of sleep claims that the glymphatic system is _______ active in sleep
neurotoxins
In sleep, glial cells eliminate ________ such as amyloid beta
distribution
lipids
waste
Astrocytes create fluid-conducting channels that facilitate the ________ of important molecules for brain functioning
Influx = ______ and other molecules
Outflow = metabolic ________
synapses
unnecessary
The connectivity/plasticity function theory of sleep claims that:
In wake, we form new ________
In sleep, we remove ________ synapses
learning
wake
sleep, off
NREM, slow, sharp
Synaptic homeostasis hypothesis by Tononi:
New ________ happens primarily by synaptic potentiation
Synaptic potentiation occurs primarily in ______ when the organism interacts with the environment, not in sleep when it is disconnected
Renormalization of synaptic strength happens primarily during _______ when the brain is spontaneously active ______-line, not in wake when a neuron’s inputs are biased by a particular situation
This renormalization and downregulation of synapses happens during _______ sleep and is shown through cortical ______ waves and hippocampal ______ waves
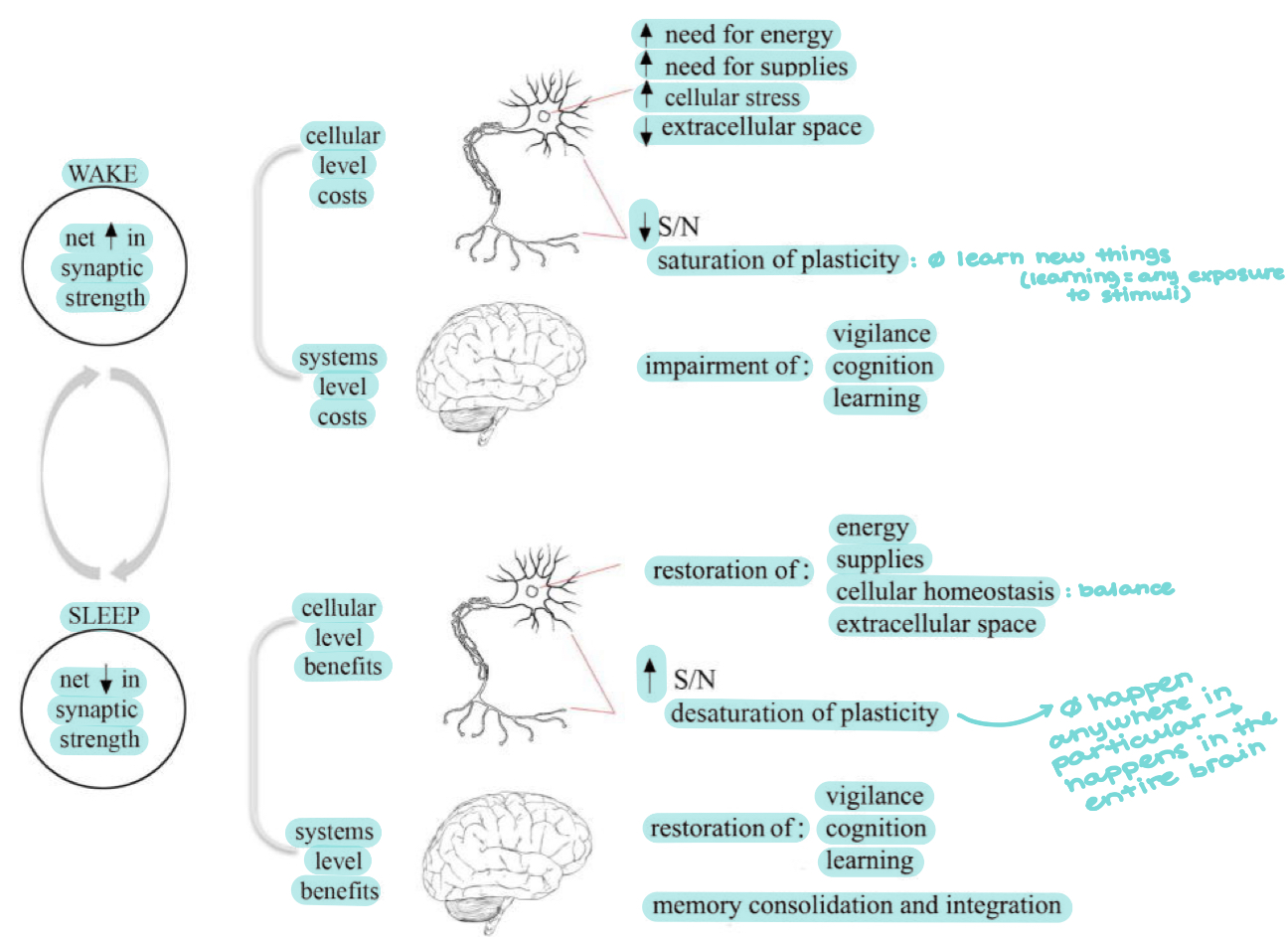
Explain this diagram

current, potentiation
comprehensive, down
In wake = sensory input → _______ sampling + synaptic _______
In sleep = sensory disconnection → _______ sampling + synaptic ________-selection
cognitive
The restoration of performance theory of sleep claims that sleep helps restore __________ functions such as:
Memory
Reflexes
Attention
Mood
Emotional reactivity
Emotion
occipital
A new theory claims that REM sleep internally generate activity that prevents ________ brain areas from being inactive
reorganization
clearance
A new theory claims that there are developmental shifts in sleep function:
Sleep is for neural ________ until 2-3 years of age
Sleep is then for repair and _______
many
Sleep most likely serves _______ functions
neuronal
Sleep appears in any organism with a _______-glial network
Because it comes out of the system but it is not explained by the system itself
Why sleep may be an emergent property?
brain
We don’t know if plants sleep because sleep is defined as a _________ state and they don’t have a brain
animals
Most _______ have some type of quiet sleep
grow
New neurons ________ in the hippocampus even in adulthood
less
Chronic sleep disruption may lead to _______ neurogenesis because it makes it harder to make new memories and encode them