Beef cattle
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are the features of traditional British breeds
Small mature size so low maintenance costs
Early maturing
Hardy to climate and environment
Suited to a forage system
Good suckler cow
What are the features of continental breeds
Large mature size
Late maturing
Higher demands
More carcass
Good terminal sires
What is the average size of a breeding herd
28 cows
What is the scale of the industry
1.6 million breeding cows
0.4 million breeding heifers
2.5 million fattening and slaughter cows
What is included on a cattle passport
ID
Dam
Movements
Death
What should the BCS of a cow be during calving
2.5 for mature cows
3.0 for 1st and 2nd time calvers
What are the essential components of a profitable sucker herd
Low feed cost
Longevity
Tight calving pattern
1x calf every 365 days
Low calf mortality
Solid replacement policy
What is the target for an efficient cow
Rear her calf to >50% of her own bodyweight at weaning
What are the pros of spring calving
Matches grass growth with peak lactation
Calves are weaned in autumn when pasture quality declines
Cows are dry over winter
Better weather for calving
What are the cons of spring calving
Spring weather can be unpredictable
Labour can be high if coinciding with arable work and lambing
What are pros of autumn calving
Calves are older and heavier at spring turnout
Can be sold in summer when prices are higher
Less conflict with spring arable work
Housing may be less crowded
What are cons of autumn calving
High winter feed costs for lactating cows and young calves
Housing space needed during winter
Calving season during poorer weather
What are the nutritional guidelines
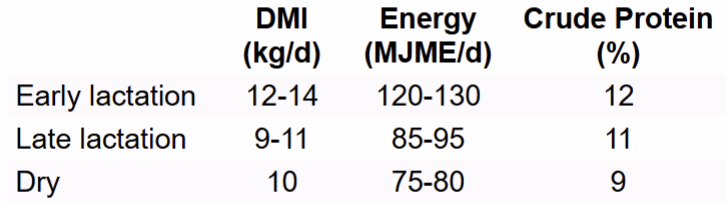
When should calves be weaned
When 6-8 months old
Wean earlier if a cow has a low BCS
Wean later if a cow has a high BCS
How much more energy is required is a cow is out-wintering
15% extra energy requirements
What are the requirements of a cow producing veal
Dairy bred male calves
Fed milk based diet throughout with some had feed and straw
DLWG of 1.2-1.4 kg/day
Slaughtered at 6-7 months old
300 kg live weight at slaughter
150 kg deaf weight at slaughter
What are the welfare standards of calves producing veal
Crates are banned
Must be group housed from 8 weeks old
Diet must meet minimum iron and fibre requirements to prevent anaemia and improve welfare
What are the requirements for a calve producing rose veal
Weaned off milk at 6-12 weeks
Diet includes starchy feeds and straw
Slaughtered at 8-12 months
400 kg LW at slaughter
200 kg DW at slaughter
What is the DLGW of suckler calves
1.2 kg bulls
1.0 kg steers and heifers
What are the rules of selling calves
Illegal under 7 days old
No resale within 28 days
Navel must be healed
What are the rules of transporting calves
Illegal under 10 days old
Illegal under 14 days old if the journey is over 8 hours
Navel must be healed
What is creep feed
Starts minimum of 6-12 weeks prior to weaning
Preserves cows BCS
Primes rumen for post weaning diet
What is the percentage weight gain from dam’s milk
100% in 1st month of life
66% in 3rd month of life
33% in 6th month of life
What are the options after weaning
Intensive - finish between 12 to 14 months
Extensive - finish between 18 to 30 months
Sell as store cattle - sold between 6 to 12 months
Fattening growing cattle - weaned and reared for meat
Finishing cattle - max weight gain a few weeks prior to slaughter
What are barley and silage beef cows
Late maturing breeds
Housed
Target weight of 520 kg
DLWG of 1.2 kg
Feed conversion ratio of 5:1
What are the diet options for barley and silage beef cows
Silage and 3 kg of barley
Ad-lib barley and straw
What is the buller-steer problem
One animal is repeatedly mounted or ridden by others
Causes pain, exhaustion and death
Causes bruising downgrading carcass value
What are clinical problems with barley beef
Carbohydrate overload causing bloat, rumen acidoses and liver abscessation
Hypovitaminosis A
Lameness
Pneumonia
What is feed conservation ratio
How many kg of feed is required for 1 kg of weight gain
How is feed conservation ratio calculated
Total feed to group of cattle / bodyweight gained in group
What is the killing out percentage
(Saleable carcass weight / live weight) x 100
What factors effect killing out percentage
Nutrition - high roughage diet
Gender - steers have heavier skull and skin, heifers have greater fat content
Age - older have greater fat content
Breed