Vocab - AP PSYCH
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms

Case Study
In-depth examination of an individual or small group over an extended period, often using a variety of data sources such as interviews, observations, and psychological tests.
EX: Studying Phineas Gage to understand brain function after his accident
Confounding Variable
A variable other than the independent variable that could potentially influence the dependent variable, leading to inaccurate interpretations of the results.
EX: In a caffeine-and-test-performance study, students who didn’t sleep well the night before could affect results
Control Group
The group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment or intervention, used for comparison with the experimental group.
EX: A group in a drug trial that takes a sugar pill instead of the medication
Correlation
A statistical measure of the relationship between two variables, indicating how they change together. However, correlation does not imply causation.
EX: As ice cream sales increase, so do drownings (but one doesn’t cause the other)
Correlation Coefficient
A numerical value between -1 and +1 that represents the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
EX: A correlation of +0.85 between hours studied and test scores
Debriefing
The process of providing participants with information about the purpose, procedures, and results of a research study after their participation, especially if deception was used.
EX: After a memory experiment, participants are told the true purpose of the study
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured or observed in an experiment and is expected to change as a result of the manipulation of the independent variable.
EX: The score participants earn on a memory test after studying
Descriptive Statistics
Statistical techniques used to summarize and describe the characteristics or properties of a dataset, such as measures of central tendency and variability.
EX: Calculating the average test score of the class
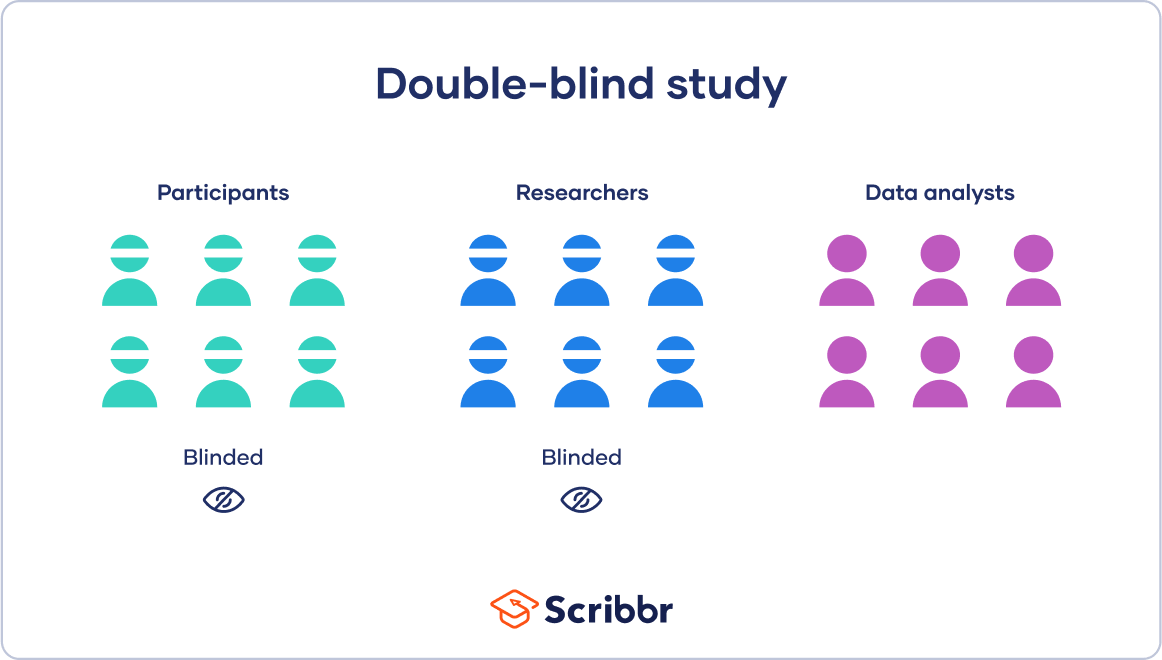
Double-Blind Procedure
An experimental procedure in which both the participants and the researchers involved are unaware of who is assigned to the experimental or control group, reducing bias.
EX: Neither patients nor doctors know who gets the antidepressant or the placebo
Effect Size
A measure of the strength or magnitude of the relationship between variables or the magnitude of a treatment effect, independent of sample size.
EX: Finding that therapy improves depression symptoms by a moderate amount across multiple studies
Experiment
A research method in which one or more variables are manipulated to observe the effect on another variable, while controlling for extraneous factors.
EX: Testing whether chewing gum improves memory retention
Experimental Group
The group in an experiment that is exposed to the treatment or intervention being studied.
EX: The group that actually receives the new teaching method
Experimenter Bias
The influence of the researcher's expectations or beliefs on the outcomes of an experiment, leading to unintentional bias in data collection or interpretation.
EX: A researcher unconsciously smiling more at participants in the “success” group
Falsifiability
The principle that for a hypothesis or theory to be considered scientific, it must be possible to conceive of evidence that would prove it false.
EX: Testing whether a dream theory can be disproven through measurable evidence
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it. It's often referred to as the "I knew it all along" phenomenon.
EX: Saying “I knew it all along” after a football team wins
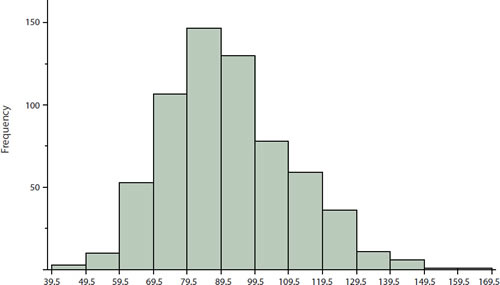
Histogram
A graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data, where the data is divided into intervals (bins) and the height of each bar represents the frequency or count of data points within each interval.
EX: A bar graph showing how many students scored in each grade range on a test

Illusory Correlation
The perception of a relationship between two variables when no such relationship exists, or the perceived relationship is weaker than it appears.
EX: Believing that full moons cause more hospital visits
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated or controlled by the researcher in an experiment to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
EX: The amount of caffeine given to participants in a study
Inferential Statistics
Statistical techniques used to make inferences or predictions about a population based on sample data, including hypothesis testing and estimation.
EX: Using a small sample of voters to predict election results
Informed Consent
The ethical principle requiring that participants in a research study are fully informed about the nature, purpose, risks, and benefits of participation before agreeing to take part.
EX: Participants signing a form agreeing to join a stress study
Meta-Analysis
A statistical technique for combining the findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to determine overall trends or effects.
EX: Combining results from 50 studies about the effects of meditation
Naturalistic Observation
Observation of behavior in its natural context without interference or manipulation by the researcher.
EX: Watching how kids share toys on a playground without interfering
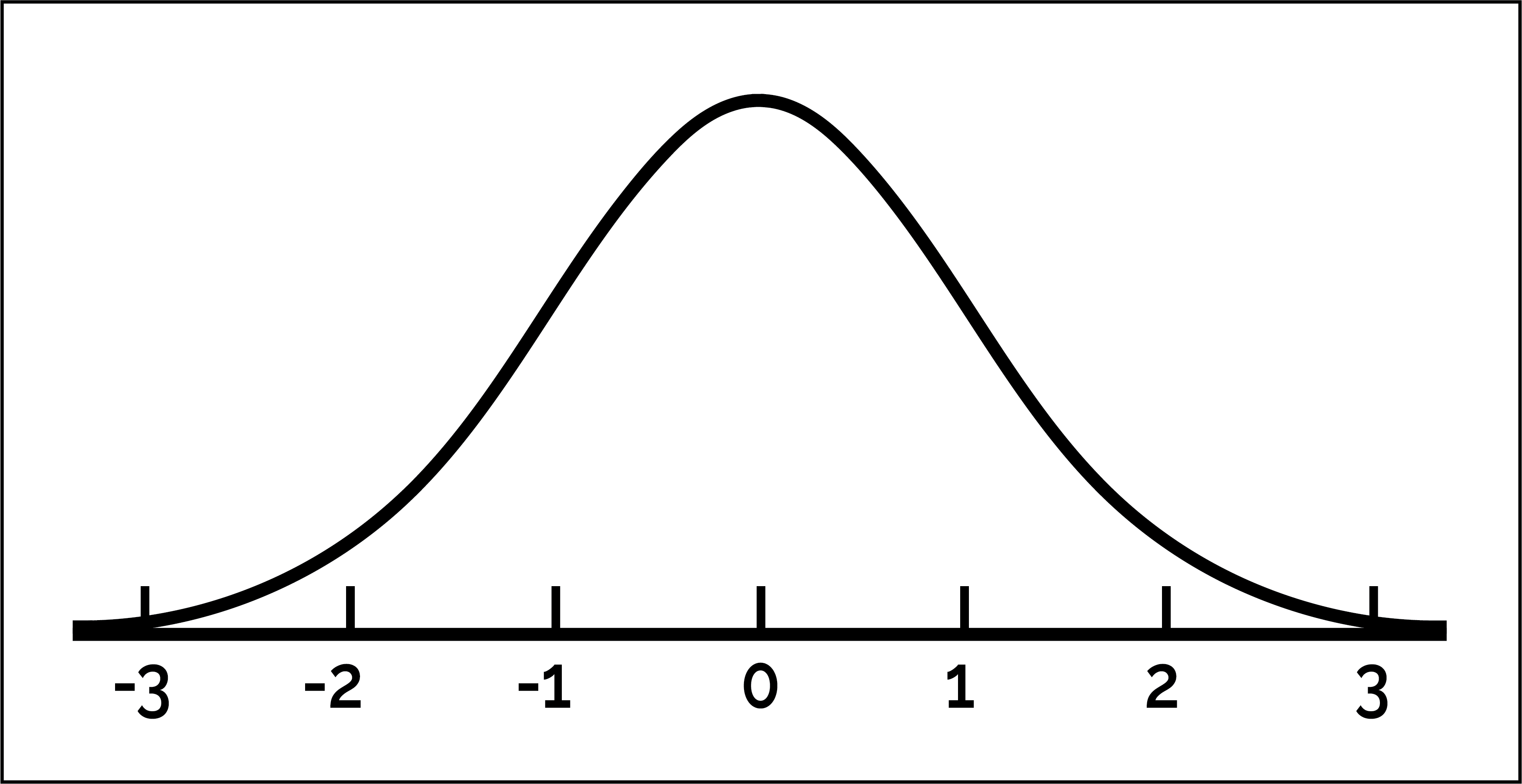
Normal Curve
A symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of scores in a population, with the mean, median, and mode all located at the center.
EX: SAT scores forming a bell curve with most students in the middle range
Operational Definition
Precise descriptions of how variables in a study will be manipulated or measured. They specify the procedures used to define and measure concepts.
EX: defining “aggression” as “number of times a child hits or yells during recess.”

Placebo
An inactive substance or treatment that resembles the experimental treatment, used in research to control for the psychological effects of receiving treatment.
EX: Taking a sugar pill but believing it’s a real headache medication
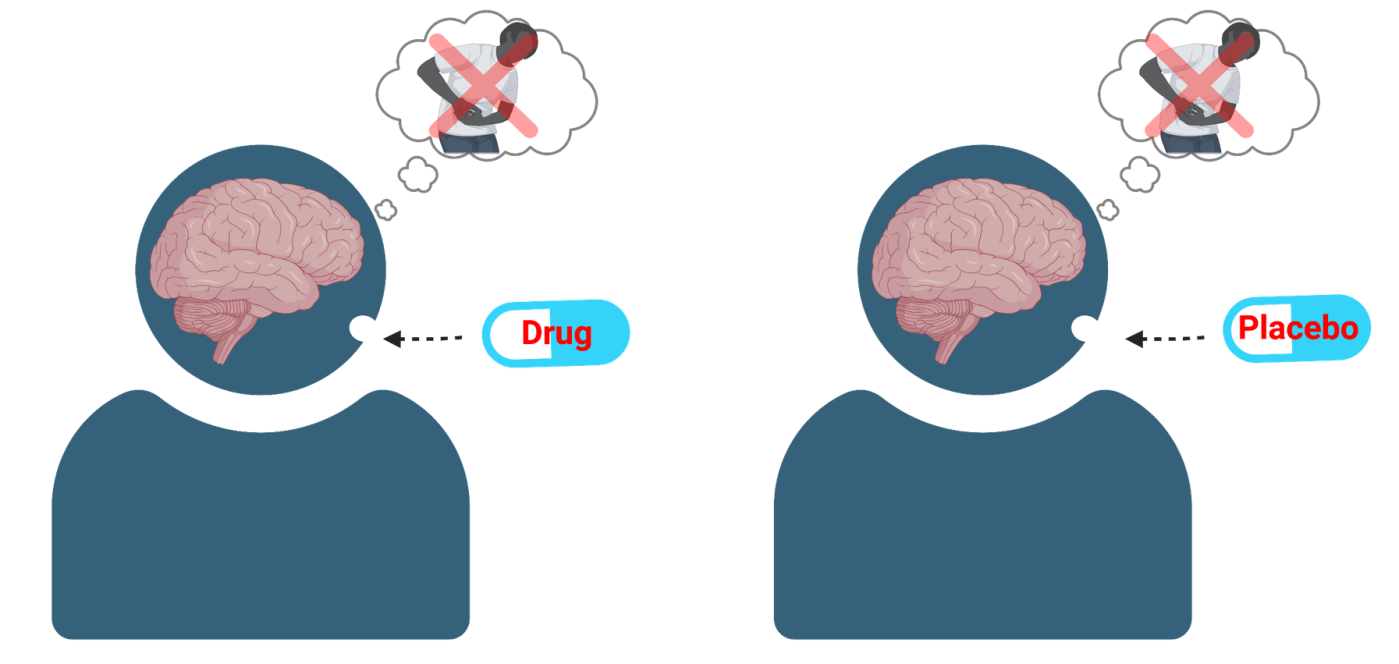
Placebo Effect
The phenomenon where individuals experience a change in their condition or behavior after receiving a placebo, due to their belief in the effectiveness of the treatment.
EX: Feeling less pain because you think you took real painkillers
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Measures
Research that focuses on gathering and analyzing non-numerical data, such as observations, interviews, or textual analysis, to understand meanings, experiences, or perspectives VS research that focuses on gathering and analyzing numerical data to understand relationships, patterns, or trends
EX: Interviewing patients about how they feel (qualitative) vs. counting how many panic attacks they have (quantitative)
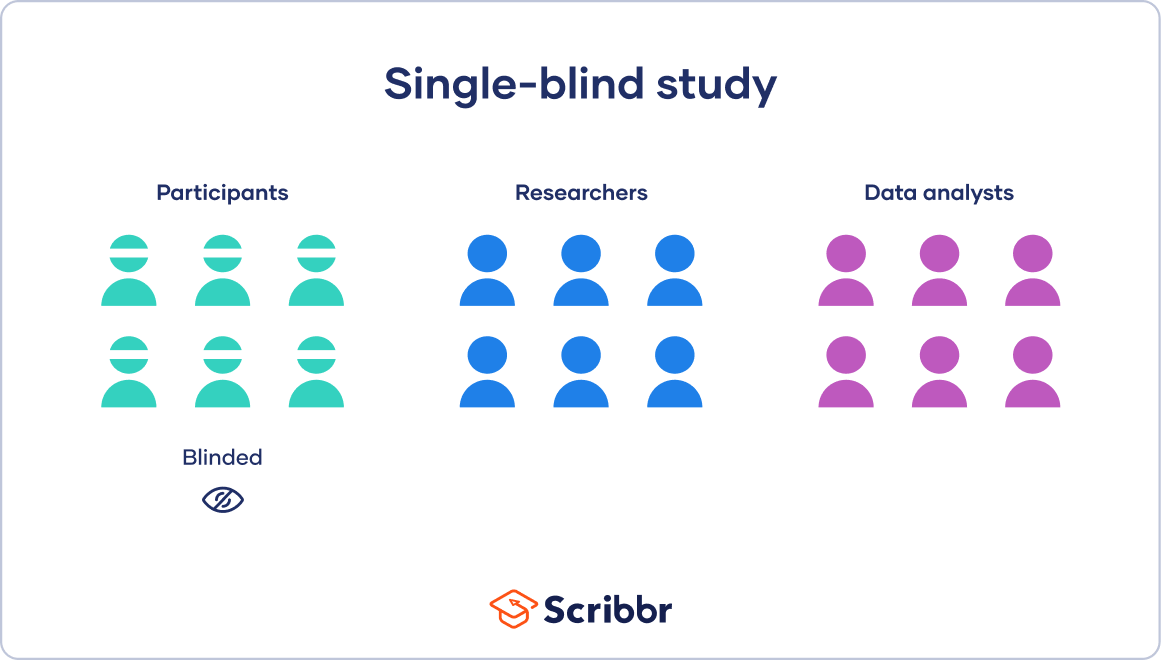
Single-Blind Procedure
An experimental procedure in which either the participants or the researchers involved are unaware of who is assigned to the experimental or control group.
EX: Participants don’t know if they got the real drug or the placebo, but the researcher does
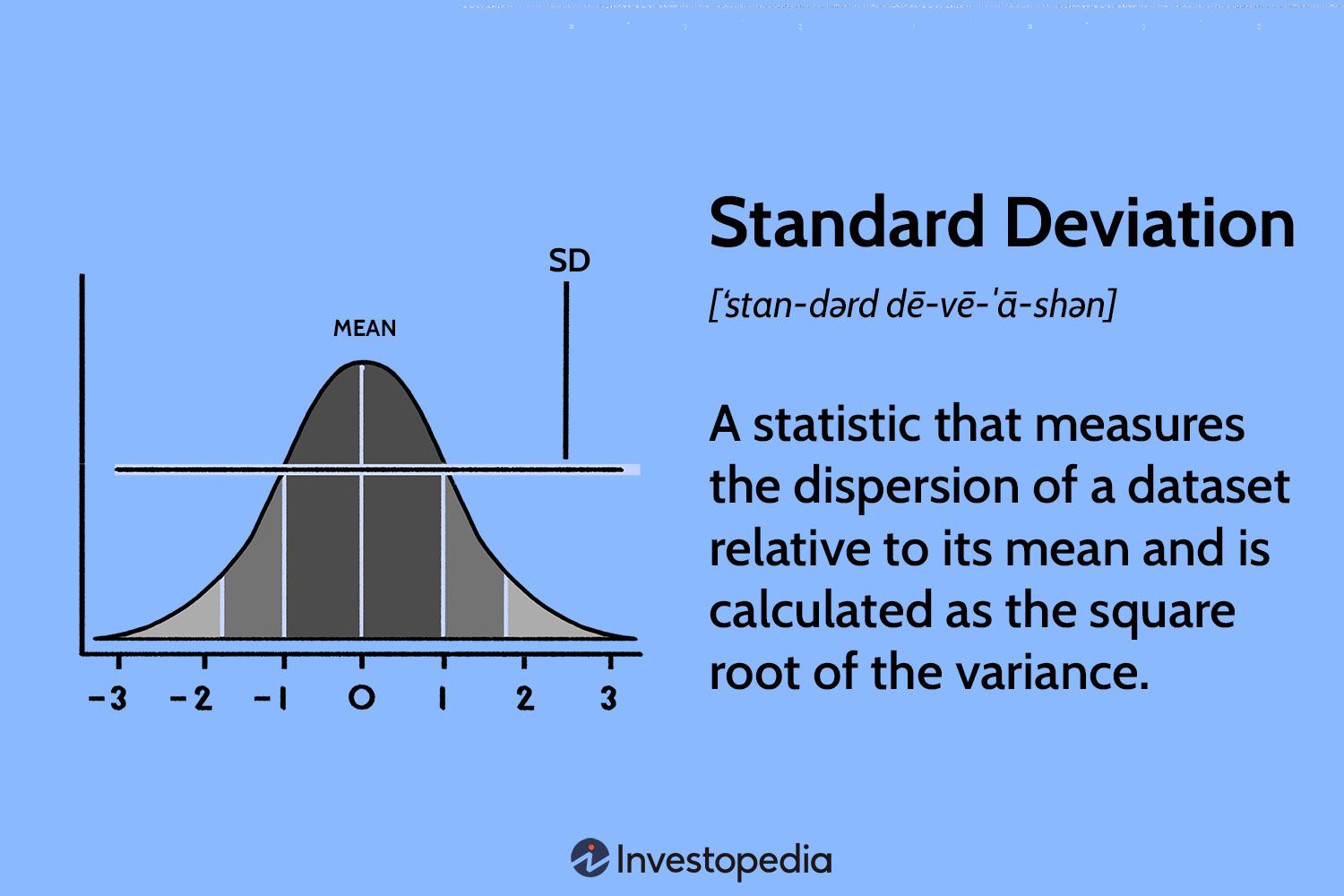
Standard Deviation
A measure of the average distance of each data point from the mean of the dataset, indicating the degree of variability or dispersion in the data.
EX: A class where everyone scores around the same grade has a low standard deviation; a class with a wide range of scores has a high one
Survey
A research method that involves collecting data from a population through the use of questionnaires or interviews to gather information about attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or characteristics.
EX: Polling 500 teens to find out how many hours of sleep they get per night
Frequency Distribution
a table or graph that shows how often different values or categories occur in a dataset
Validity
the degree to which a test, measurement, or research study accurately measures what it intends to measure
Social Desirability Bias
the tendency for individuals to provide answers that are perceived as socially acceptable or desirable, rather than their true beliefs or behaviors