Phsyio: Ch 10 Sensory
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:29 PM on 12/6/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
what are sensory receptors?
cells that receive sensory information (aka a stimulus) from the environment
2
New cards
What do sensory receptors do?
Transduce different energy forms
(like pressure, temperature, chemical, light etc)
into graded potentials that initiate action potentials
(like pressure, temperature, chemical, light etc)
into graded potentials that initiate action potentials
3
New cards
what is an action potential?
rapid sequence of changes in the electrical signal across a membrane
4
New cards
Name the 5 classes of sensory receptors
-Mechanoreceptors
-Thermoreceptors
-Photoreceptors
-chemoreceptors
-Nociceptors
-Thermoreceptors
-Photoreceptors
-chemoreceptors
-Nociceptors
5
New cards
what are mechanoreceptors?
receptors that respond to mechanical stimuli
(ex. touch and pressure)
(ex. touch and pressure)
6
New cards
what are Thermoresptors?
respond to cold and warmth
7
New cards
what are Photorecptors?
respond to light
8
New cards
What are Chemoresptors?
receptors that respond to bonding of particular chemicals
(ex. taste)
(ex. taste)
9
New cards
What are Nociceptors?
receptors that respond to painful stimuli
10
New cards
when a sensory stimuli arrives at a sensory receptor cell, the membrane potential of the sensory receptor cell changes by a variable amount
the variable change is called....
the variable change is called....
a Graded potential
11
New cards
what does transduction involve?
opening of ion channels
12
New cards
What does AP (action potential) generate?
It generates depolarization at an initial segment of axon
this reaches a threshold which causes an ion channel to open
this reaches a threshold which causes an ion channel to open
13
New cards
What is adaptation?
a decrease in receptor sensitivity (responsiveness) during maintained stimulation.
14
New cards
What does adaption cause?
it causes a decrease in action potential (AP) frequency in an afferent neuron despite continuous presence of a stimulus
15
New cards
What are the two phase of Adaption.
1.Phasic/fast-adaptaion receptors
2. Tonic/slow-adapting receptors
2. Tonic/slow-adapting receptors
16
New cards
Describe the phasic phase.
They respond quickly before adapting to a constant stimuli
(ex. pressure when seated on a chair)
[think... phas=fast]
(ex. pressure when seated on a chair)
[think... phas=fast]
![They respond quickly before adapting to a constant stimuli
(ex. pressure when seated on a chair)
[think... phas=fast]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8ad968e2421b4a7492fa0295b7b4a1cd.jpeg)
17
New cards
Describe the tonic phase
where persistent action potential
or a slow decrease of AP firings.
ex. receptors in a joint or muscle that maintains posture
or a slow decrease of AP firings.
ex. receptors in a joint or muscle that maintains posture
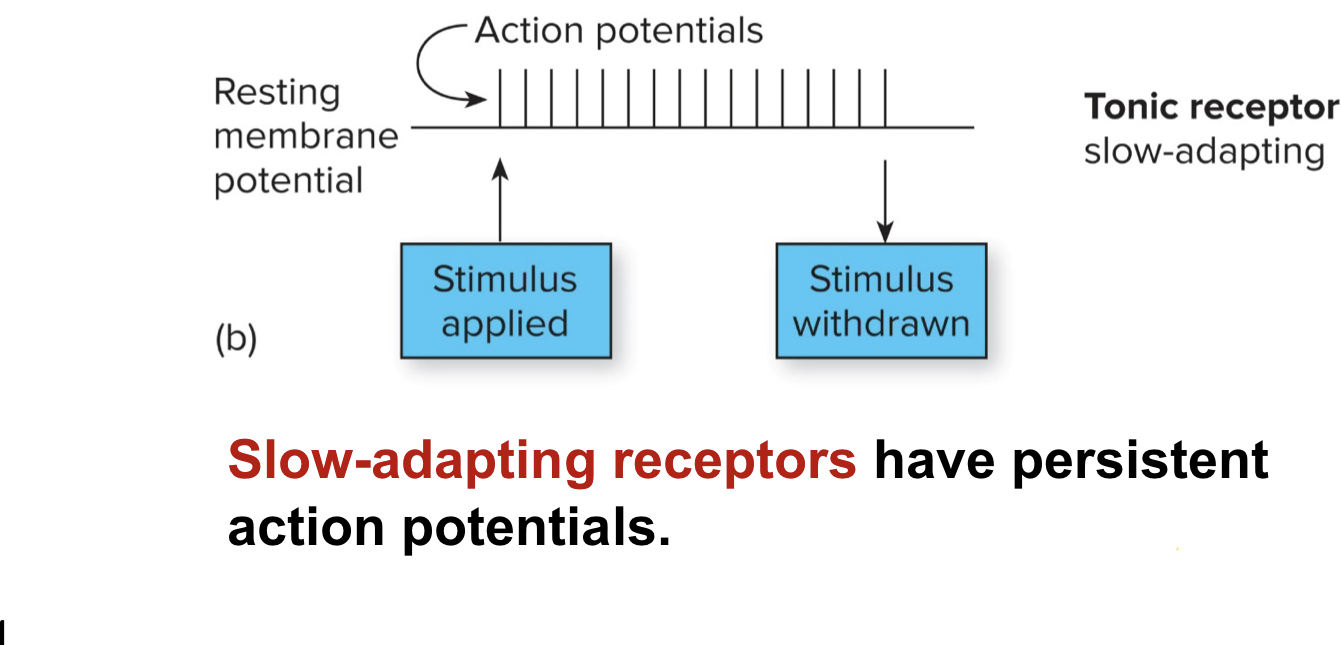
18
New cards
Describe somatic sensation
Touch, Pressure, pain temperature and senses of posture and movement (proprioception)
19
New cards
What are the two types of Chemoreceptors
-Gustation (taste)
-Olfaction (smell)
-Olfaction (smell)
20
New cards
What is the sensory nerve of Gustation connected to?
taste buds! (located in lingual papillae
21
New cards
What are some characteristic of tastebuds?
-comprised of 50-100 specialized epithelial cells called (taste cells)
-various shapes and sizes
-various shapes and sizes
22
New cards
What is the relationship between different tastes and taste cells?
Different types of tastes (salty, sour, sweet, umami, bitter) activate taste cells differently
23
New cards
What ion causes a salty taste
Na+ going through an ion channel
[think NaCl = salt]
[think NaCl = salt]
24
New cards
what ion causes a sour taste?
H+ going through an Ion channel
[Think...H= more acid]
[Think...H= more acid]
25
New cards
how do we recieve sweet and umami flavors?
They bind to membrane receptors
26
New cards
how do we receive bitter flavors?
Quinine bind to membrane receptors
27
New cards
What is olfaction?
sense of smell
28
New cards
What is the stimulant of olfaction?
Odorants
29
New cards
Describe the pathway of olfaction
Odorants bind to proteins which attach to dendrites of the olfactory receptor neurons.
the axons of the olfactory receptors then synapse onto olfactory bulb of the brain.
which then go into the afferent pathway
the axons of the olfactory receptors then synapse onto olfactory bulb of the brain.
which then go into the afferent pathway
30
New cards
What interprets a specific odor?
The unique pattern of the binding of odorants and receptor proteins
31
New cards
where do olfactory receptor cells synapse?
in 2 olfactory bulbs
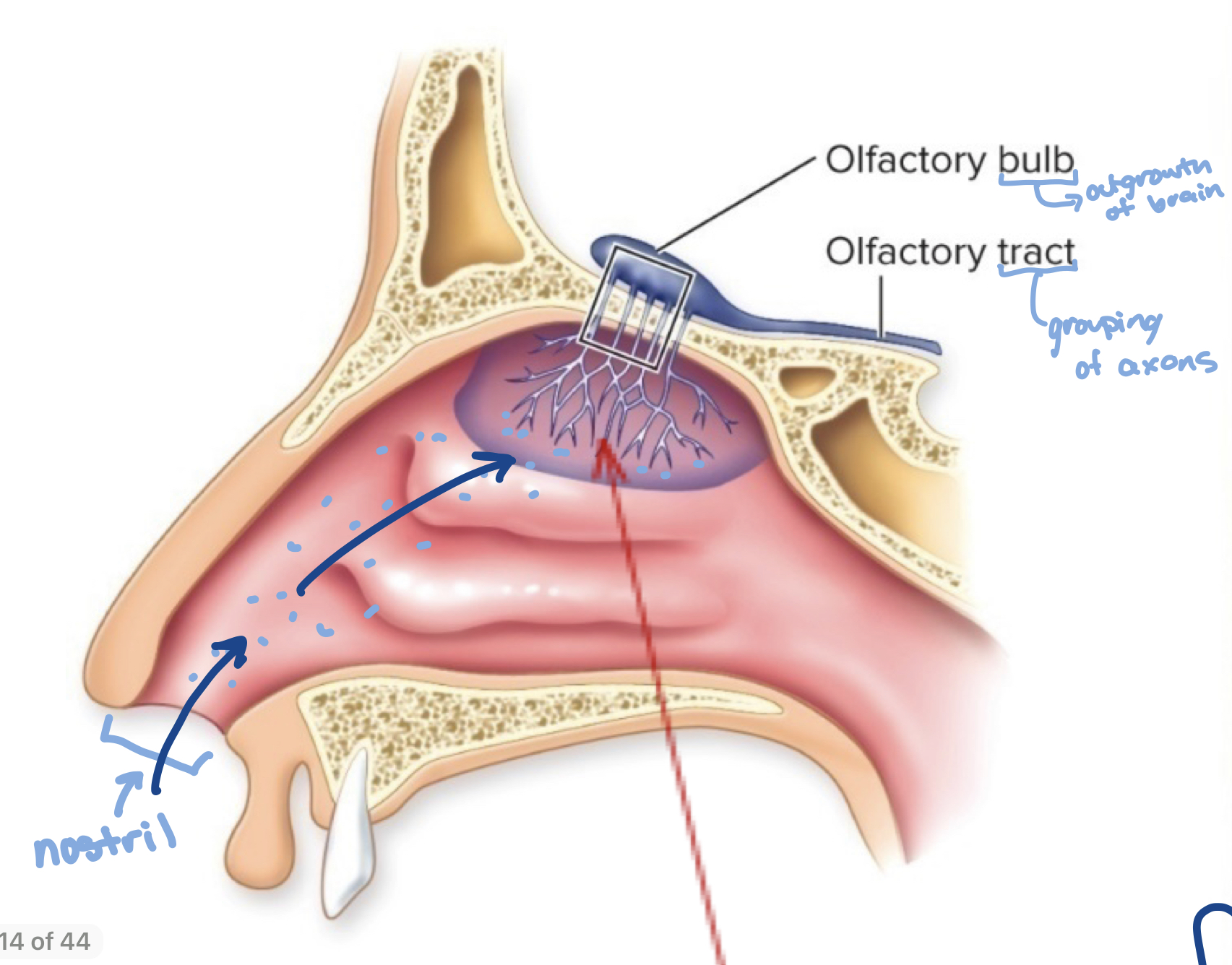
32
New cards
what is the vestibular system?
a structure in the inside of your ear
33
New cards
what is the function of the vestibular system.
to keep track of your head position/movement, spacial orientation and linera acceleration)
(ex. head movement (up/down, side to side, forward/back)
(ex. head movement (up/down, side to side, forward/back)
34
New cards
What are the two vestibular sensors?
Otolith organs (or maculae) and semicircular canal
35
New cards
What do the 2 otolith organs consist of?
the saccule and utricle
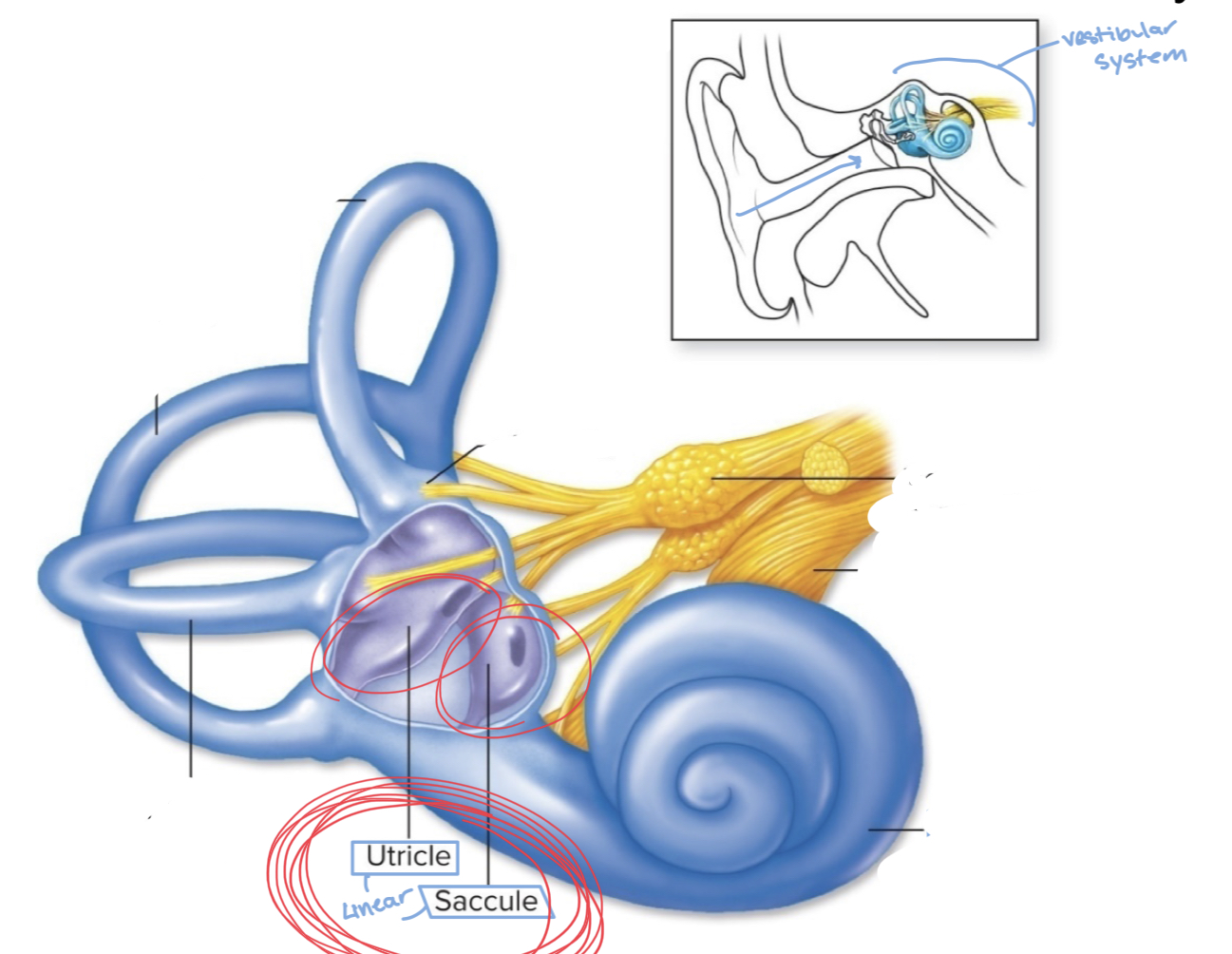
36
New cards
What does the Otolith organs do?
They sense *linear* acceleration
(ex. jumping, bending down)
(ex. jumping, bending down)
37
New cards
Characteristic of maculae (aka otolith organ)
each sensor has a mass of otoliths (tiny stones) on top of a *gelatinous* substance
38
New cards
What do the semicircular canals do?
they sense angular acceleration of the head in a three dimensional space to maintain balance
ex head movement (up/down, side to side, forward/back
ex head movement (up/down, side to side, forward/back
39
New cards
Characteristics of semicircular canals
-each canal has a crista (a sesnroy organ in ampulla)
-each crista has a gelatinous mass (aka cupula) on top which is moved by endolymph movement
-each crista has a gelatinous mass (aka cupula) on top which is moved by endolymph movement
40
New cards
How do otolith organs work?
otoliths (tiny stones) are inside a gelatinous substance that covers hair cells in the utricle and saccule.
[when head moves, the gel moves causing the hair cells to move, which sends signals to brain]
[when head moves, the gel moves causing the hair cells to move, which sends signals to brain]
![otoliths (tiny stones) are inside a gelatinous substance that covers hair cells in the utricle and saccule.
[when head moves, the gel moves causing the hair cells to move, which sends signals to brain]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/34a63b4fff864b4bb0e4692f718737a8.jpeg)
41
New cards
How does the Cupula work?
-the cupula is connected to the semicircular canals of the ear
- when the head moves side to side, the cupula moves/bends which stimulate hair cells that send signals to brain.
- when the head moves side to side, the cupula moves/bends which stimulate hair cells that send signals to brain.
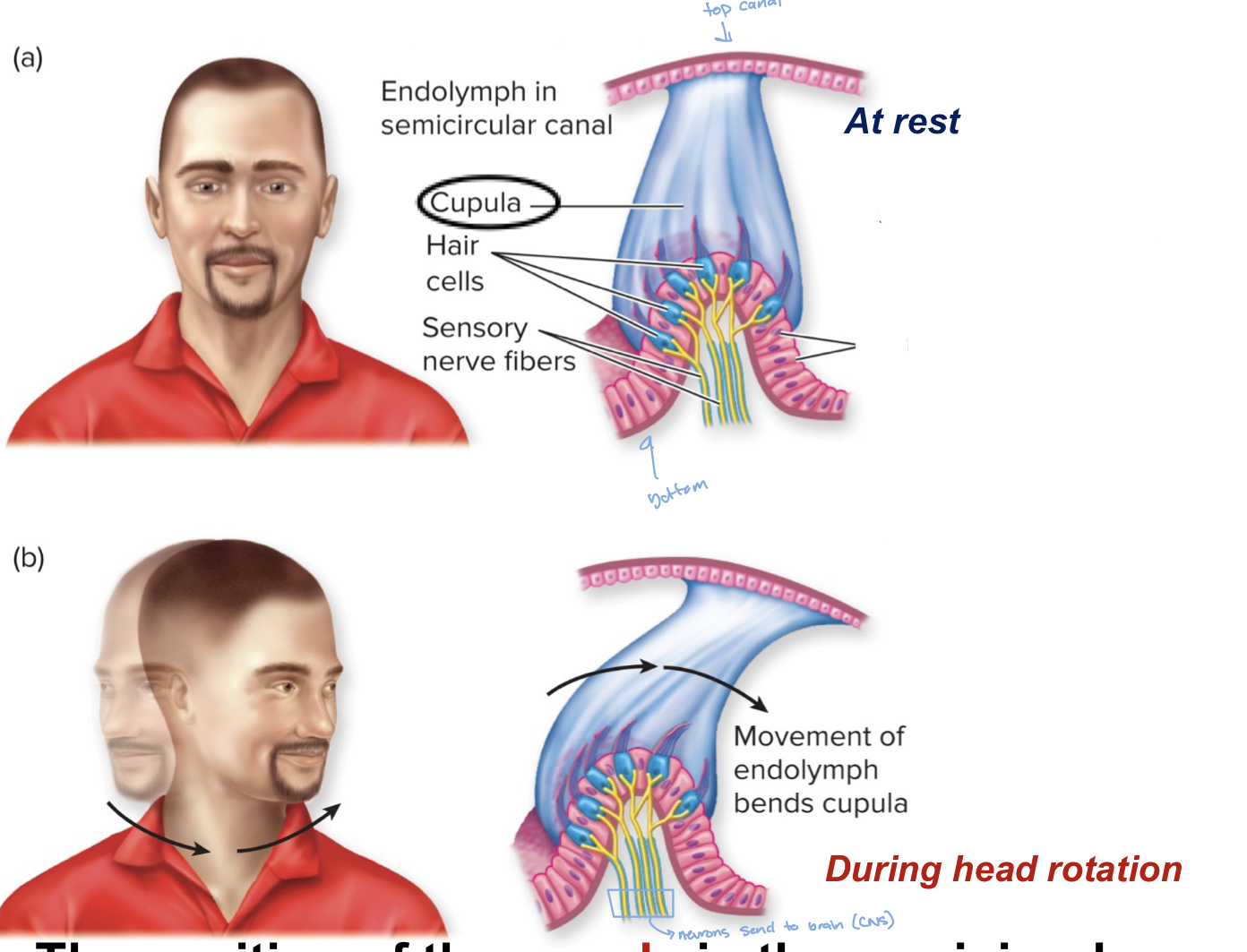
42
New cards
What causes sound?
vibration from gas, liquid or solid molecules
[molecules move, auditory systems move]
[molecules move, auditory systems move]
43
New cards
____ are zones of atmospheric rarefaction.
sound waves
44
New cards
define frequency
the number of cycles per second of the sound wave
45
New cards
what does frequency determine?
frequency determines pitch
[higher freq = higher pitch n vice versa]
[higher freq = higher pitch n vice versa]
46
New cards
define intensity
it is the amplitude of sound waves
47
New cards
what does intensity determine?
intensity determines loudness
48
New cards
what structures help focus sound waves to the ear drum?
the pinna and external auditory meatus
[aka the external ear, the part you can see]
[aka the external ear, the part you can see]
![the pinna and external auditory meatus
[aka the external ear, the part you can see]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/611f0e0da503420799771e871108afde.jpeg)
49
New cards
what is the scientific word for 'eardrum'
tympanic membrane
50
New cards
Describe the auditory pathway after the tympanic membrane
Tympanic membrane --> ossicles --> oval window --> movement of fluid in cochlea --> vibrations in basilar membrane --> bending of hair cells in Corti
51
New cards
What makes up the organ of Corti?
basilar (bottom) membrane + hair cells + tectorial membrane
52
New cards
what happens in the organ of corti?
auditory transduction occurs in the cochela
53
New cards
What does low frequency cause?
Causes large vibrations in *apical* (at the top) cochlea
[this is a low pitched sound]
[this is a low pitched sound]
54
New cards
What does high frequency cause?
- Causes large vibrations in *basal* (at the bottom) cochlea
[this is a high pitched sound]
[this is a high pitched sound]
55
New cards
what does tonotopic mean?
Arranged by frequency
56
New cards
what is the stimulus in visual system?
light
57
New cards
light has what type of properties?
wave-like properties
[aka travels in waves]
[aka travels in waves]
58
New cards
define wavelength
wavelength is the distance between *two peaks*
(measured in nanometers (nm))
(measured in nanometers (nm))
59
New cards
what does wavelength correspond to?
color
(ex. red = long, blue = short)
^ this is why you notice red colors before you notice blue
(ex. red = long, blue = short)
^ this is why you notice red colors before you notice blue
60
New cards
what is the 'visible spectrum'
what the human eye is able to see and what the brain is able to perceive
61
New cards
what is the range of visible spectrum (in nm) in humans?
appx. 400-700 nm
62
New cards
t/f the wave length is longer, the object will be less bright
FALSE
- if the wavelength is short, the object is less bright
- if the wavelength is short, the object is less bright
63
New cards
what are the three layers of the eye from outermost to innermost?
Fibrous Tunic, Choroid, Retina
64
New cards
What are the two parts of the fibrous tunic?
Sclera and cornea
65
New cards
What is part of the eye is the sclera?
it is within the fibrous tunic and is the whites out our eyes
[this is where the muscles that move our eyes are attached]
[this is where the muscles that move our eyes are attached]
66
New cards
What part of the eye is the cornea?
it is the clear cover of the eye,
this transmits light
this transmits light
67
New cards
Where is the Choroid (second layer of the eye) found?
beneath the sclera
68
New cards
What are the 4 structures of the Choroid?
-pupil
-iris
-uvea
-ciliary muscles
-iris
-uvea
-ciliary muscles
69
New cards
define pupil
anterior opening for light entry into the eye
[the black part of the eye]
[the black part of the eye]
70
New cards
define iris
pigmented muscle around pupil,
it dilates (expands) and constricts (small)
it dilates (expands) and constricts (small)
71
New cards
t/f the eye constricts when there is more light
true
72
New cards
t/f the eye dilates when there is less light
true
73
New cards
define uvea
blood vessels in the eye
[what makes ur eye turn pink]
[what makes ur eye turn pink]
74
New cards
what is the function of the ciliary muscle?
lens accommodation (lenses changes shape to focused on an image)
75
New cards
what are found in the retina?
Photoreceptors
76
New cards
what are human photoreceptors?
rods and cones
77
New cards
Accommodation for near vision means the lens ____
rounds
78
New cards
Accommodation for far vision means the lens ____
flattens
79
New cards
What is the problem with light rays in Hyperopia.
the light focuses behind the retina
[think hyper= adhd = behind in school work]
[think hyper= adhd = behind in school work]
80
New cards
how do you correct hyperopia?
with convex lens to correct farsightedness
81
New cards
What is the problem with light rays in myopia.
light rays focus in front of retina
[ put your hand on your chest to signal 'my', hand is in front]
[ put your hand on your chest to signal 'my', hand is in front]
82
New cards
define accommodation
changing of lens to focus light on the retina
83
New cards
which photoreceptor is most responsive when a person is in a dark environments?
rods
[think... LIGHTning *rods*]
[think... LIGHTning *rods*]
84
New cards
Which photoreceptor is mainly used for color?
(rod or cones?)
(rod or cones?)
cones
[think *C*ones = *C*olor ]
[think *C*ones = *C*olor ]
85
New cards
when you look at a near view object, that means your lens is?
round in order to let less light in
[ciliary muscles are contracted]
[ciliary muscles are contracted]
86
New cards
When you look at something far away, are your ciliary muscles contracted or relaxed?
relaxed
[lens is flat, to let more light come in]
[lens is flat, to let more light come in]
87
New cards
t/f contracted ciliary muscles have lower tension
True
[think opposite for eye muscles, more contracted = less tension]
[think opposite for eye muscles, more contracted = less tension]
88
New cards
t/f relaxed ciliary muscles have lower tension
False
[think opposite for eye muscles, less contracted = more tension]
[think opposite for eye muscles, less contracted = more tension]
89
New cards
Name 3 characteristics of rods
- most sensitive photoreceptors
-black and white vision
-used in dim light
-black and white vision
-used in dim light
90
New cards
Name 2 characteristics of cones
- used for color vision
-used in high resolution vision (fine detail)
-used in high resolution vision (fine detail)
91
New cards
M cone corresponds to what color?
green
[think greeN = M]
[think greeN = M]
92
New cards
S cone corresponds to what color?
Blue
[think... S= Sad (blue) ]
[think... S= Sad (blue) ]
93
New cards
L cone responds to what color?
Red
[think L = love]
[think L = love]